Topic 8- Choosing strategic direction business aqa a level
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is strategy?
an organisation's long-term course of action(designed to deliver a unique customer experience while achieving its goals)
strategy is really important and can influence the competitiveness of a business and determine its success.
Several different types of strategy
what is strategic direction?
the general path a business takes, to meet its mission and to achieve its objectives
involves a business choosing which markets it will operate in and which products it will provide.
Strategic direction is also important because the external env is constantly changing and businesses don't want to suffer from strategic drift.
Also allows businesses to make the best use of their strengths and core competencies
factors influencing a business' strategic direction
-Anticipated returns
-Core competences
-Expected cost
-Ext env
-Stakeholders
What is Ansoff's Matrix?
A marketing planning model that helps a business determine its product and market strategy.
Model asserts that a business can grow depending on whether it is in a new or existing market and depending on whether they are selling an existing or a new product
What are the 4 quadrants of Ansoff's Matrix?
-Market penetration
-Market development
-Product development
-Diversification
Market penetration
Least risky of the strategies
a marketing strategy that tries to increase market share among existing customers through: trying to promote how the product can be used for multiple purposes e.g. corn flakess started to be advertised as not just for breakfast.
Benefits:
-Low risk
-Can maintain/increase market share
-Secure dominance of growth markets
-Drive out competitiors
-Makes use of the business' current resources
-Experience of the market
-may require little investment
Drawbacks:
-Increased risk of becoming complacent
-Growth may be limited
E.g. Coca Cola when the business was starting up
market development
Riskier than market penetration
a marketing strategy that entails attracting new customers to existing products can do this by:
-selling to new geographical markets
-new product dimensions/ packaging
-new distribution channels e.g. ecommerce
-different pricing policies to attract new segments of the market
Benefits:
-Lower investment
-More potential for growth
Drawbacks:
-Risk as the business will be competing against established business
-Risk associated with selling products abroad e.g. the business may not fully understand the tastes of their new customers
e.g. Coca Cola has new entered several different markets (countries) e.g. Greece, Nigeria, Poland etc
product development
Similar risk to market development
When a business introduces new products to an existing market. May require the development of new competencies. This strategy is suitable suitable for a business where the product needs to be differentiated in order to remain competitive.
Benefits:
-Good understanding of market and customers
-May be able to do this by innovate existing products
-Can allow business' to develop a USP and to better meet customer's needs, can lead to increased customer loyalty
Drawbacks:
-Research and development can be very expensive
-Product cannabilisation- the new product the business produces may steal the sales of their current products
Coca Cola have developed products such as Diet Coke and Coca Cola Zero
e.g. Nestle who aimed to sell more specialist/ upmarket coffee
diversification
Riskiest strategy
When a business enters a new market with a new product. Businesses who adopt this strategy need to take into account the risks and benefits and assess whether the benefits outweigh the risks
Benefits:
-Spreads the business' risk by engaging in different markets
-Businesses can utilise and apply their core competence to this new market and new product
Drawbacks:
-Risky because the business has no experience in that market and with the new product
E.g. Coca cola now have several brands such as Dr Pepper, Powerade, Fanta which meet, some of these target new markets such as the sports drink Powerade
e.g. Gregg's vegan sausage roll
what is competitive advantage?
A competitive advantage is an advantage over competitors gained by offering consumers greater value, either by means of lower prices or by providing greater benefits and service that justifies higher prices.
What are Porter's generic strategies for competitive advantage?
Porter developed 4 strategies that he believed help a business gain competitiveness depending on the scope of a business' activities(will they sell to niche or mass markets) and to which extent a business seeks to differentiate its products.
4 quadrants:
-Cost leadership
-Cost focused
-Differentiation leadership
-Differentiation focused
cost leader
Objective is to become the lowest-cost producer in the
industry can acheive this through large scale production and economies of scale.
Strategy seeks competitive advantage in a broad range of market or industry segments.
Products are generally standardised with little differentiation, this makes it very available to a wide range of customers
This strategy requires close cooperation between all the functional areas of a business as the business will want to achieve: high levels of productivity, high capacity utilisation, lean production methods etc
examples: BIC, sell products in a range of markets e.g. stationery and toiletries and they sell their products at low prices
other examples: Aldi/Lidl
benefits and drawbacks of cost leader
-can achieve high profit margins as cost per unit is low and they are targeting a whole industry/ several segments
-this strategy is not achievable for all businesses
Cost Differentiation
aim is to seek a lower-cost advantage in just one or a small number of market segments.
Product will be basic and possibly similar to the higher-priced and featured market leader.
benefits: Can understand the target audiences needs and wants well
Drawbacks: Limited profits, market may disappear if it is very niche
e.g. Pure Gym
differentiation leadership
When a business targets much larger markets and aims to achieve competitive advantage through differentiation across the whole of an industry.
To achieve this strategy, businesses need to select one or more criteria used by buyers in the market then position themselves in accord with this. Businesses need to emphasise the value of their products and why it is better than others which may be cheaper
Businesses will charge a premium price for their product
Products can be differentiated by:
-having superior quality e.g. feature wise, benefits wise, durability wise etc
-branding
-industry wide distribution across all major channels
-consistent promotional support
examples: Nike, Apple
differentation focused
Business aims to differentiate within just one or a small number of target market segments.
Opportunities for this strategy exist when customer's have special needs which aren't being met by competitors
Businesses can charge high prices because they are meeting this need.
benefit: customers are willing to pay a high price, can allow businesses to generate a reasonable amount of profit.
drawbacks: products may income elastic, if there are economic changes, the business may perform badly
e.g. Ferrari, Tesla
benefits and drawbacks of differentiation leadership
-able to generate high levels of profit as businesses charge high prices and they are targeting several markets/ a whole industry
-may face high costs because of promotion and production
what does it mean to be stuck in the middle?
-means that the business' strategy doesn't belong to a distinct quadrant of Porter's generic strategies
-this according to Porter is a very bad place to be as it can eventually lead to business failure
-Take BHS, they competed neither on price or differentiation Customers of BHS could either get lower prices elsewhere, or better perceived value from the alternative department store brands.
What is Bowman's Clock?
A model that explores the options for strategic positioning based on the value of a product in relation to its price. There are 8 positions: low price/low added value, low price, hybrid, differentiation, focused differentiation, high profit margins, monopoly pricing, loss of market share.
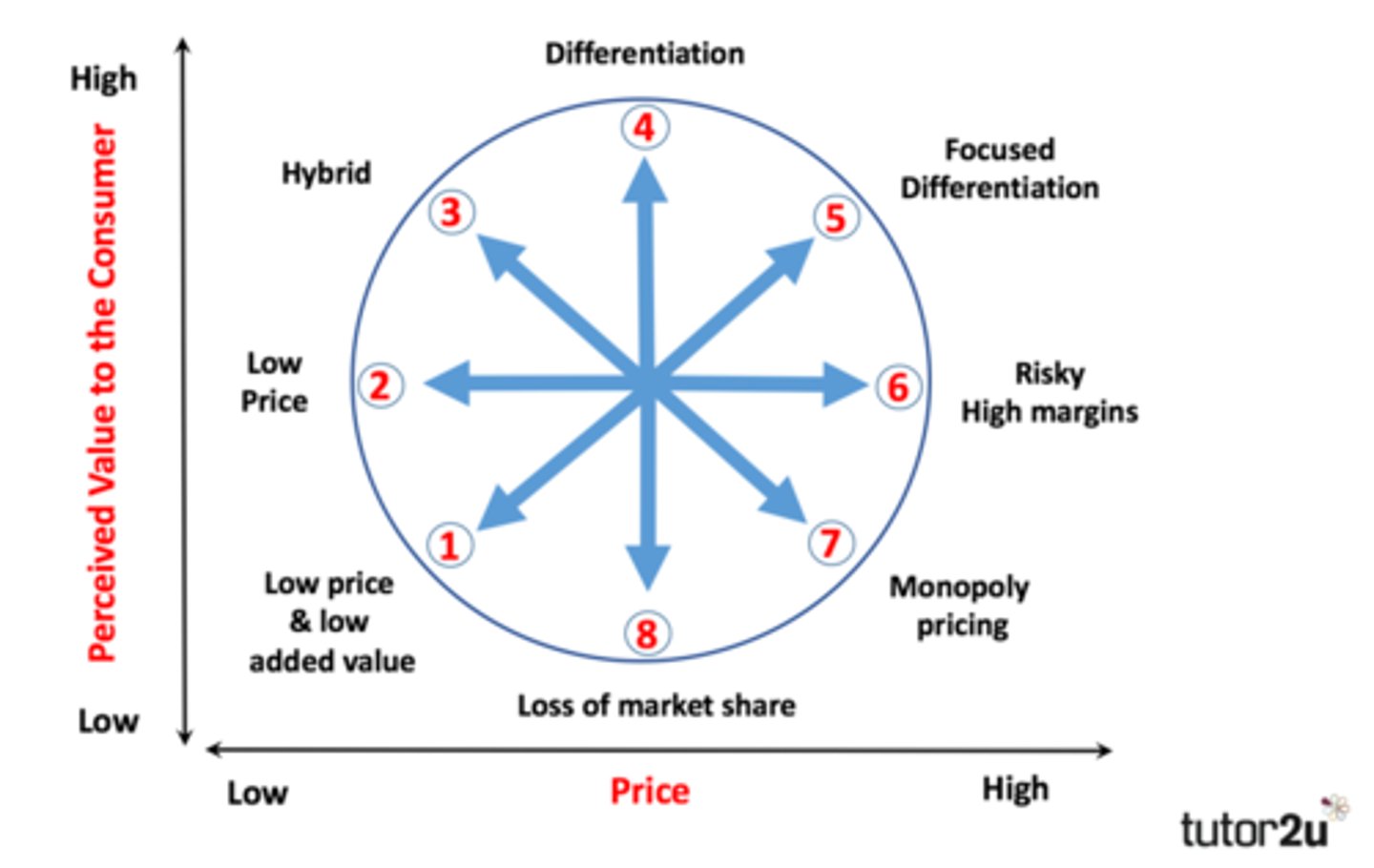
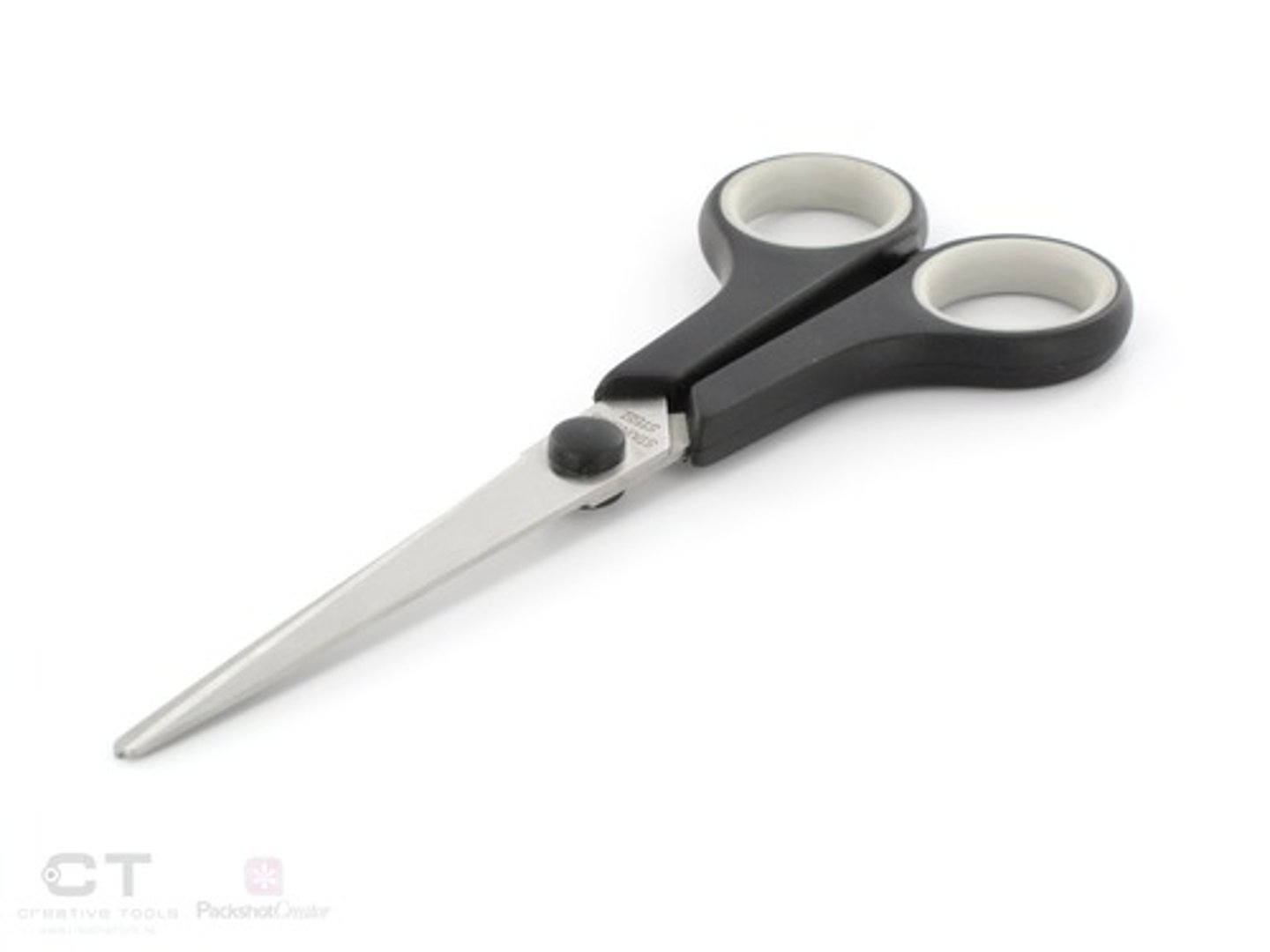
low price/ low added value
budget/ no frills product. This position may be unsustainable.
Examples include scissors- people do not really care about scissors, they just need them to function

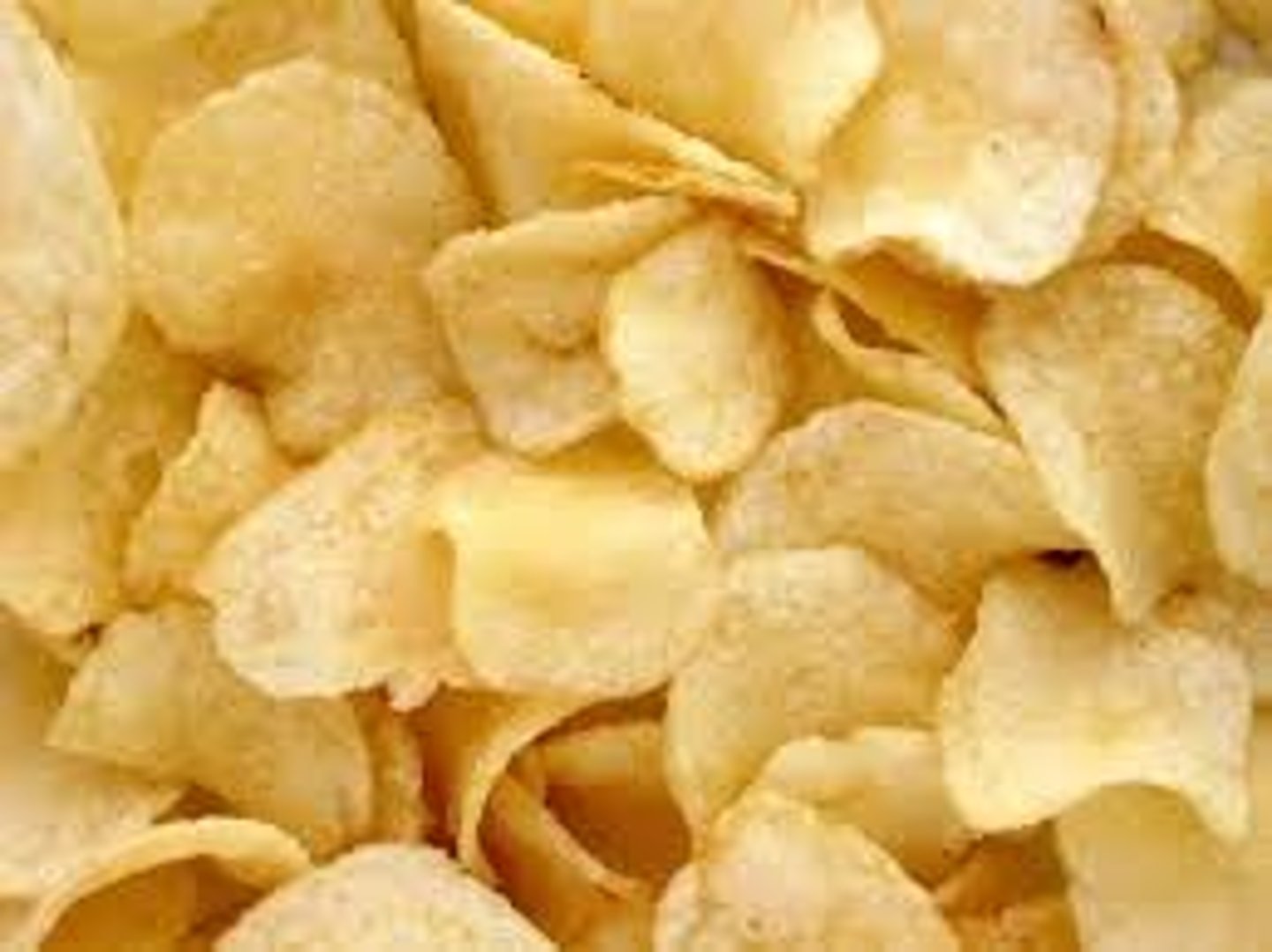
low price
Higher perceived value
Businesses looking to be low cost leaders may adopt this strategy
Profit margins on each product are low but the high volume of output can still generate high overall profits
example; crisps

hybrid
Inolves some element of low price but also some differentiation.
Aims to persuade consumers that there is good added value through the combination of a reasonable price and acceptable product differentiation.
example; mcdonald's

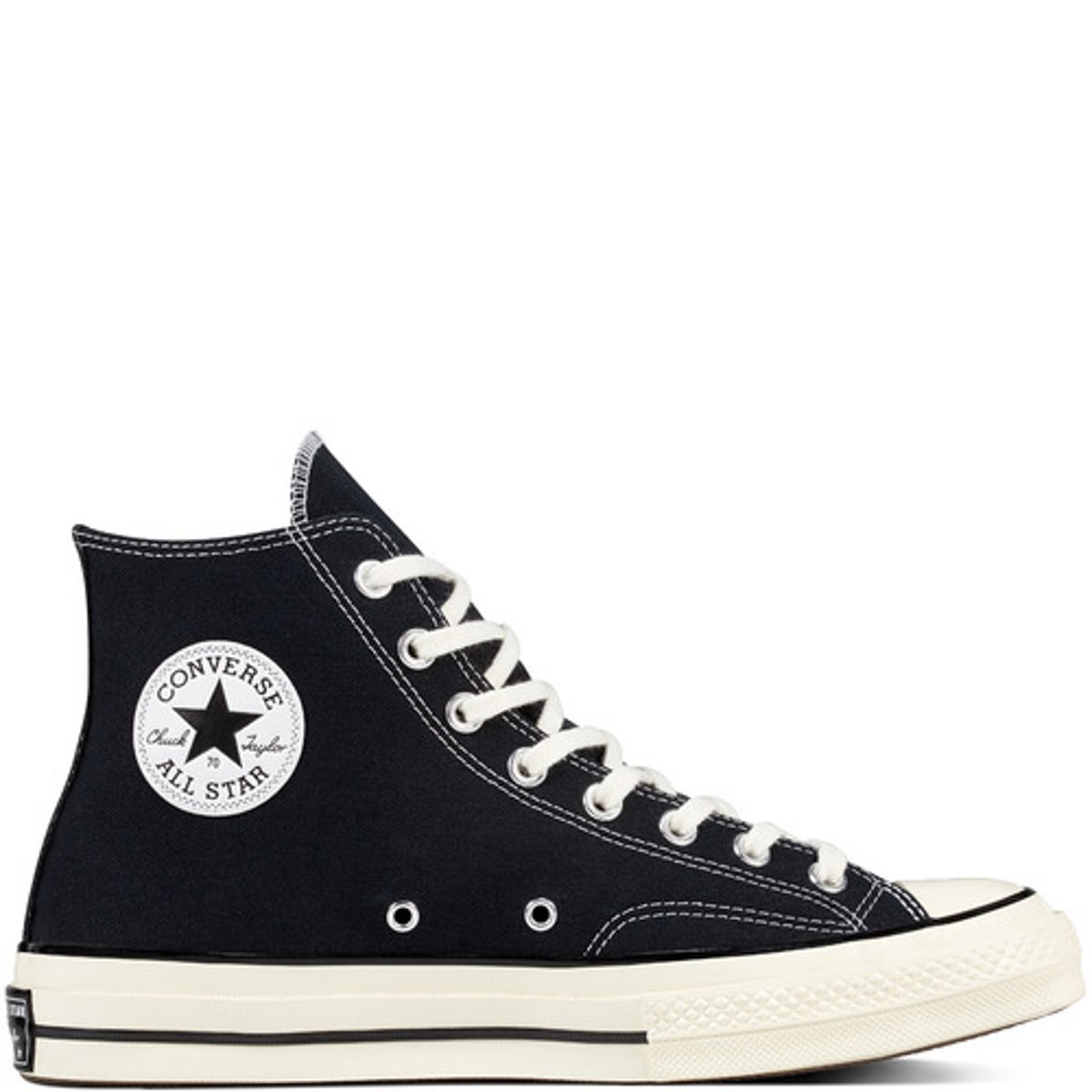
differentiation
aims to offer customers the highest level of perceived added value, yet the pricing is not too high
effective branding plays a large part in influencing the perceived added value of these products
example; converse

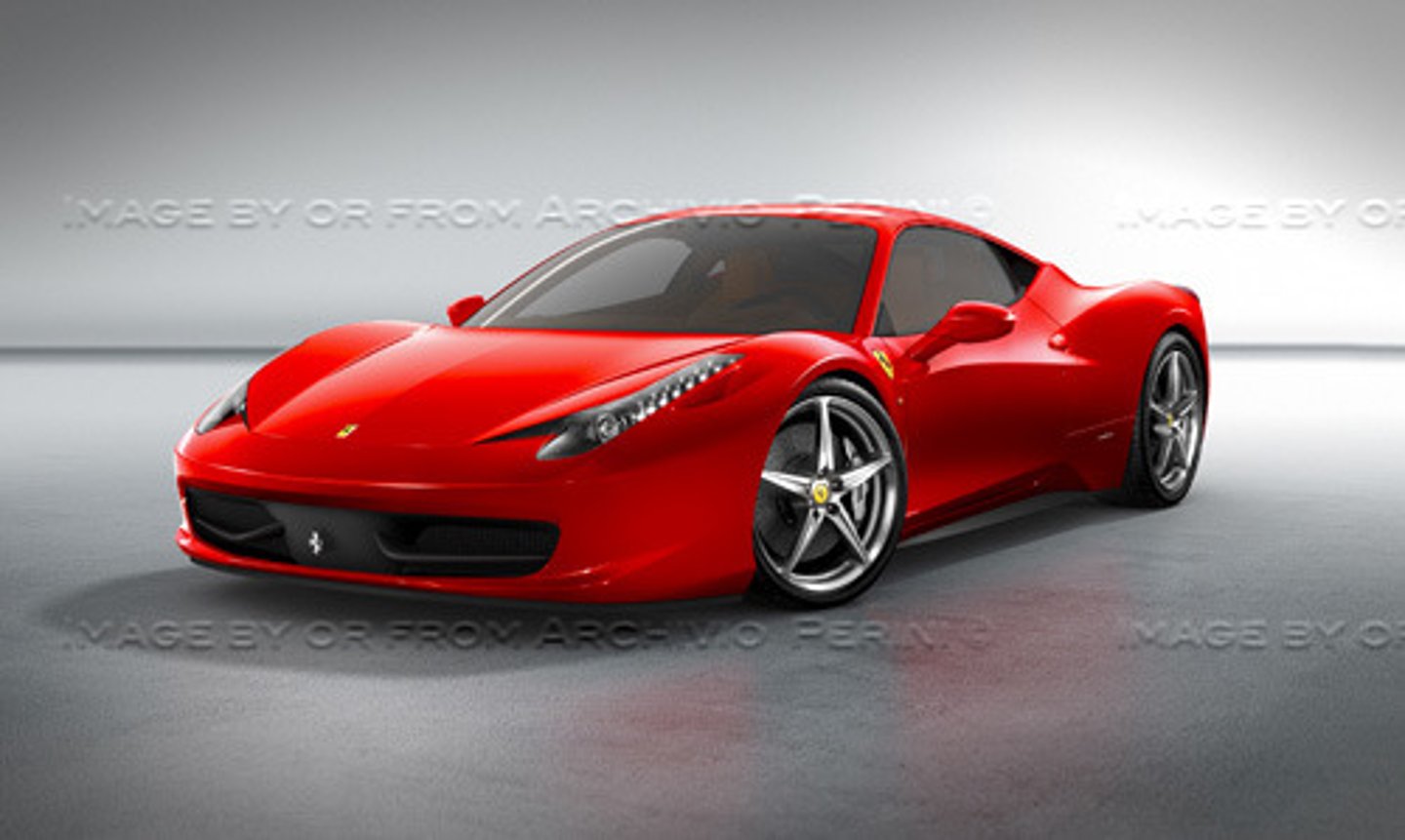
focused differentiation
aims to position a product at the highest levels where customers buy the product because of the high perceived value.
effective branding plays a large part in influencing the perceived added value of these products
-luxury brands use this strategy
-can generate very high profit margins
example; Ferrari

risky high margins
high prices without offering any extra perceived value. customers may look into a lower cost and same value alternative
ST strategy, consumers can find a product with better added value or that is a lower price
This is an uncomptetitive position as price is greater than perceived value
monopoly pricing
a monopoly is when there is only one business offering the product/service. This means that they can set very high prices as there are no/little alternatives
examples; McAfee Anti-Virus protection
This is an uncomptetitive position as price is greater than perceived value
loss of market share
Standard price for a product with low perceived value. customers will look for alternatives e.g. Phone companies
This is an uncomptetitive position as price is greater than perceived value
what are the two types of competitive adv?
-Comparative advantage-cost advantage- a business's ability to produce a good or service at a lower cost than its competitors.
-Differential advantage- arises from a business's ability to differentiate goods and services from its competitors in a way that enables them to be seen as superior to the competition.
determinants of competitive adv
-Investment in new equipment & technology
-Effective human resource
-Improving quality
-Efficient operational procedures
-Innovation through investment in research & development
-Enterprise- taking on activities with financial risks in the hope of making a profit
difficulties of maintaining a competitive advantage
-high costs involved when investing in new equipment and technology
-may be difficult to hold onto effective staff
-high costs of R+D and can't guarantee returns
-high costs of maintaining quality
-risk with enterprise
what is the value of strategic direction?
-as the ext env is always changing, strategic positions allow a business to respond to this change, responding to this change can allow business' to survive/ remain successful e.g. the strategy of cost leader adopted by Aldi/ Lidl has influenced the strategy of other supermarkets e.g. Tesco who now compete with them on price.
-Strategic positioning therfore also allows businesses to maximise their profitability as they are responding to the market conditions and it can allow them to avoid direct competition if they position themselves differently to competitors
how can sustainable competitive adv be achieved?
Through:
-Architecture-refers to the relationship within the business with different stakeholders
-Innovation-allows a business to produce unique products/ a unique process
-Reputation- building a good repetition over years with consumers allows businesses to have a USP and to be chosen by consumers over competitors, giving them a USP.