Princeton Review AP Environmental Science Chapter 8
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
energy
the capacity to do work
potential energy
energy at rest; stored energy
kinetic energy
energy in motion
radiant energy
energy carried by light; the only form of energy that can travel through empty space (sunlight)
convection
the transfer of heat by the movement of a heated matter
conduction
the transfer of energy through matter from particle to particle
net energy yield
refers to the comparison between the energy cost of extraction, processing, and transportation, and the amount of useful energy derived from the fuel
energy units
joules (J), calories (cal), British thermal units (Btu), and kilowatt-hours (kWh)- a measure of watts x time
power units
watts (W) and horsepower (hp)
power
the rate at which work is done
First Law of Thermodynamics
says that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be transferred and transformed (ex. photosynthesis)
Second Law of Thermodynamics
says that the entropy (disorder) of the universe is increasing; in most energy transformations, a significant fraction of energy is lost to the universe as heat (ex. food chains)
fossil fuels
coal, oil, natural gas; 65% of world's electricity
nuclear energy
20% of world's electricity
renewable energy sources
15% of world's electricity
oil, coal, and natural gas
the order in which the fossil fuels are most useful- most used to least used
seams
long, continuous deposits (referring to coal)
exploratory wells
used to drill and sample a particular area for fossil fuel deposits, can provide estimate the proven reserve
proven reserve
an estimate of the amount of fuel that can be obtained from an area
crude oil
oil pumped fresh from a reserve
gusher
an oil well that produces a large amount of oil that can easily be pumped to the surface due to the reserve's high pressure
pressure extraction
a method of extracting oil in which people use mud, CO2 and saltwater to push out the oil from the reserve; this is used when oil is harder to extract
shale oil
oil reserves found in rock
tar sands
mixture of clay, sand, water and bitumen; bitumen can be extracted and refined into oil- dirtiest of all oils extracted and can have detrimental environmental impacts along with a high energy input
anthracite
purest coal; almost pure carbon
bituminous
second purest coal
subbituminous
third purest form of coal
lignite
least pure coal
underground mining
involves sinking shafts to reach underground deposits; networks of tunnels are dug or blasted, and humans enter these tunnels to manually retrieve the coal
subsidence
the gradual caving in or sinking of an area of land
strip mining
involves the removal of the Earth's surface, all the way down to the level of the coal seam (overburden removed and thrown back when coal is extracted fully)
overburden
layer of soil and rock overlying a mineral deposit; surface mining removes this layer
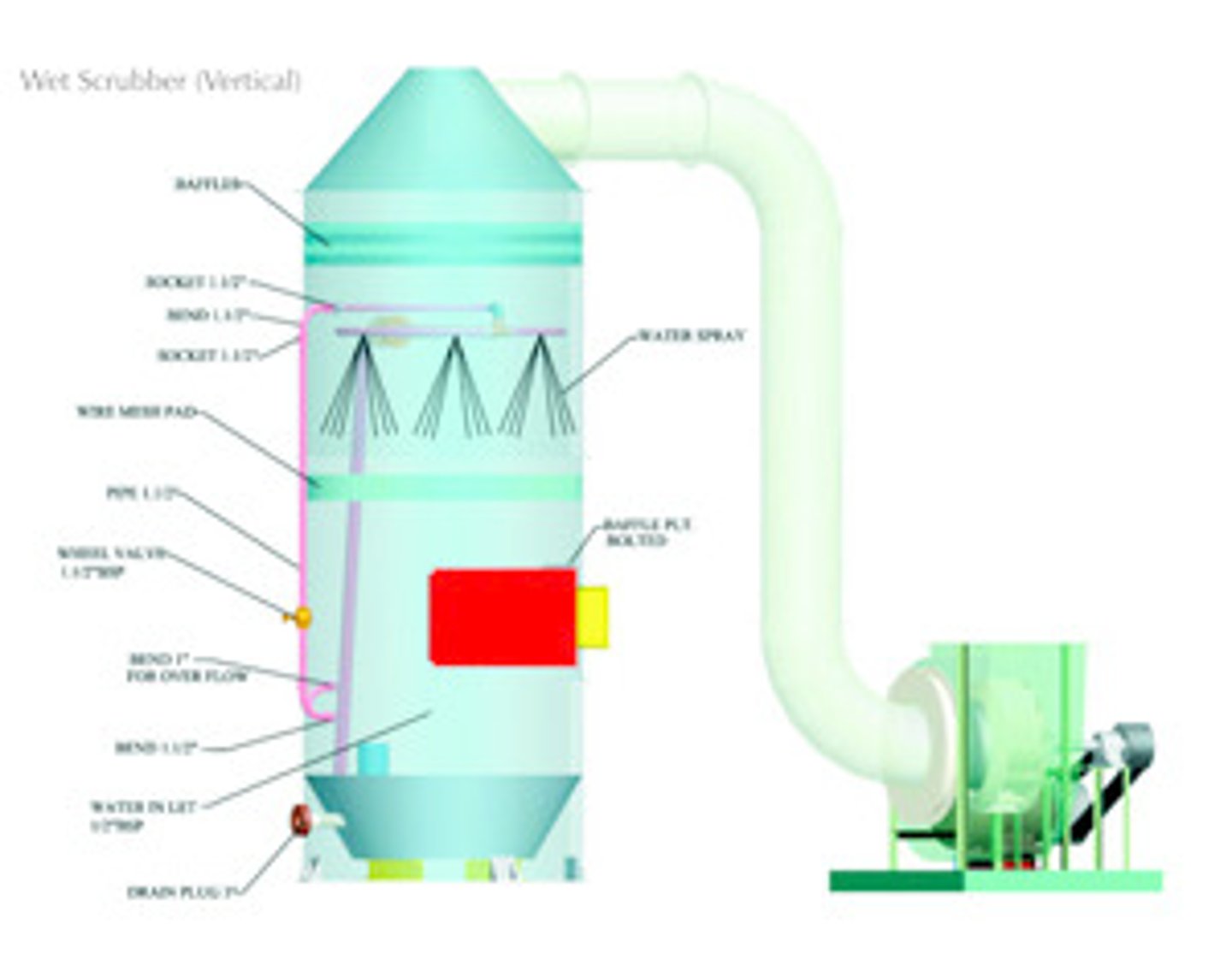
scrubbers
devices containing alkaline substances that precipitate out much of the sulfur dioxide from industrial plants
fly ash
the residue collected from the chimney or exhaust pipe of a furnace; byproduct of burning coal

boiler residue
a waste product produced by the burning of coal
combustion
the process of burning something
wet scrubbing
a process used to remove pollutants from flue gases, in which a fine mist of water is used to transform sulfur oxides (SOx) from an air pollution issue to either a water pollution issue or to a commercial product: sulfuric acid
electrostatic filters
use an electric charge to attract dust particles to metal surfaces where they can be gathered and disposed of as solid waste
acid mine drainage
highly acidic water which flows to surrounding areas, caused by abandoned metal and coal mines
Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS)
provides emission limits for mercury, particulate matter, hydrogen chloride, and hydrogen fluoride for approximately 600 coal and oil power plants
liquefied natural gas (LNG)
natural gas converted to liquid form by cooling it at a very low temperature
Hubbert peak (peak oil)
an influential theory that concerns the long-term rate of conventional oil (and other fossil fuel) extraction and depletion. It predicts that future world oil production will soon reach a peak and then rapidly decline
fission
a nuclear reaction in which a massive nucleus splits into smaller nuclei with the simultaneous release of energy
breeder reactors
reactors that generate new fissionable material faster than they consume such material
nuclear fusion
a nuclear reaction in which atomic nuclei of low atomic number fuse to form a heavier nucleus with the release of energy
half-life
the time is takes for half of a radioactive sample to degrade
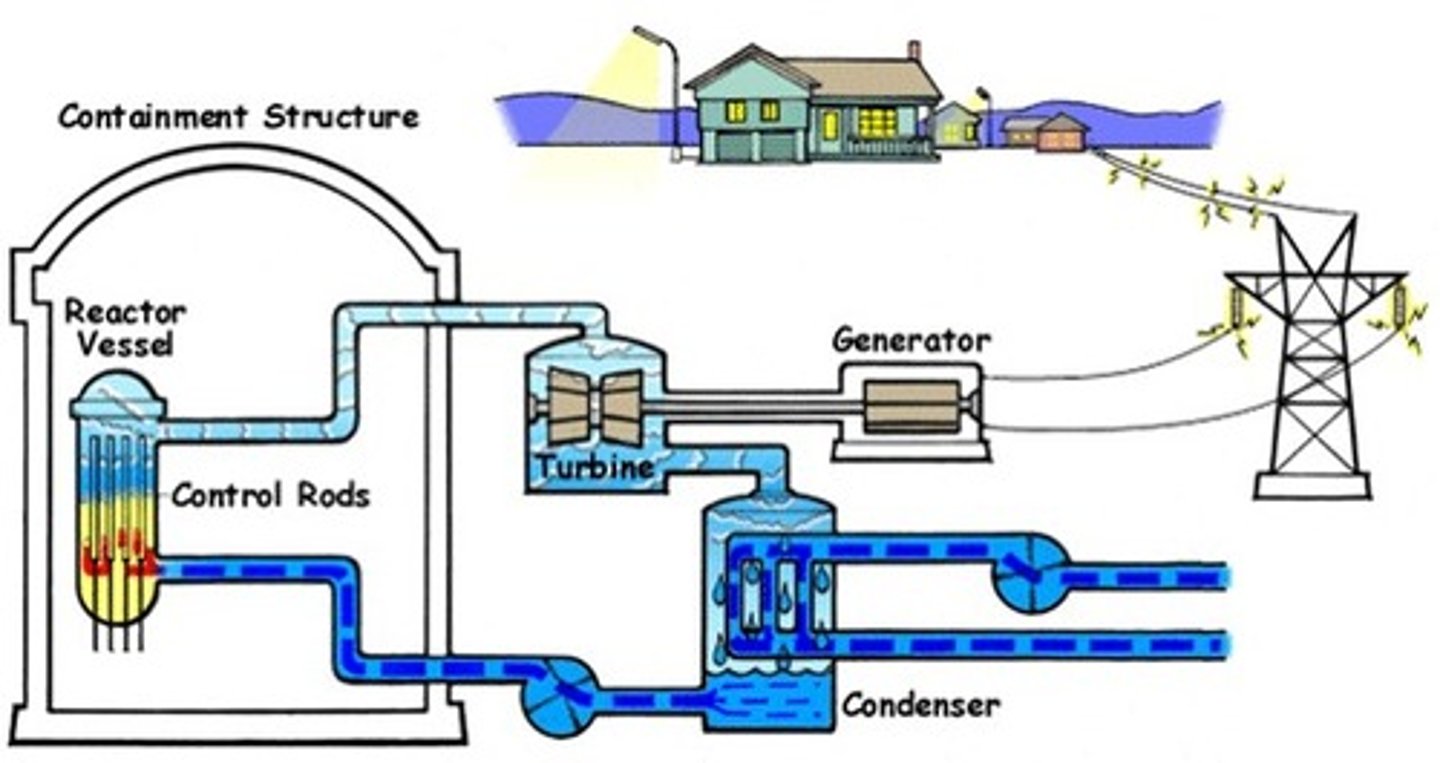
boiling water reactors
reactors that use the heat of the reactor core to boil water into steam, which is piped directly to the turbines; steam spins turbines- generates electricity; water is cooled back into a liquid and pumped back to the core to be turned into steam again (2 water circulation systems)
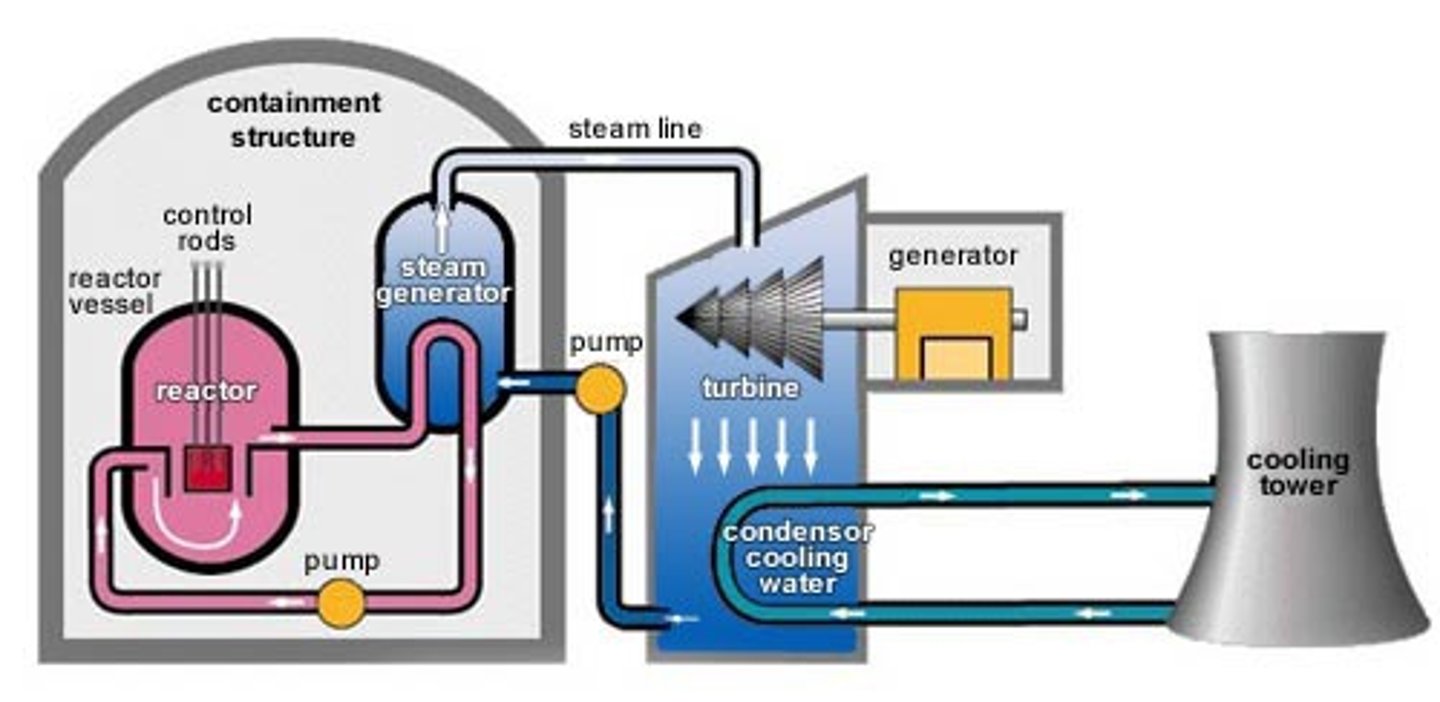
pressurized water reactors
reactors that produce electricity by generating steam but contain 3 water circulation systems: heat produced from reactor core is used to heat the first water supply, which is kept under high pressure to prevent it from boiling; it is then passed through the reactor heat exchange, where heat from the first water supply is transferred to the second water supply, which is not kept under high pressure, so that it can form steam to spin the turbines; third water supply cools the steam from the turbines to regenerate the second water supply
meltdown
a dangerous condition in which fuel rods inside a nuclear reactor melt
thermal pollution
a temperature increase in a body of water that is caused by human activity and that has a harmful effect on water quality and on the ability of that body of water to support life
charcoal
wood that has been baked to remove water and impurities
gasohol
a gasoline extender made from a mixture of 90% gasoline and 10% ethanol; reduces some emissions of pollutants, but carbon is a byproduct, and the fuel efficiency is lower
biodiesel
a diesel substitute produced by extracting and chemically altering oil from plants (ex. soybean oil)
fish ladders
a stair-like structure that allows migrating fish to get around a dam
passive solar energy collection
the use of building materials, building placement, and design to passively collect solar energy, such as through windows, that can be used to keep a building warm or cool
active solar energy collection
the use of devices, such as solar panels, that collect, focus, transport, or store solar energy
photovoltaic cells (PV cells)
direct collectors of solar energy, which produce electricity that is later stored in batteries by energizing electrons when sunlight strikes the panels, thus enabling them to flow freely, producing an electric current
wind turbine
a turbine that converts wind energy into electricity
nacelle
the base of the windmill
wind farms
large arrays of wind turbines
geothermal energy
energy that is produced by harnessing the Earth's internal heat due to radioactive decay of elements under the Earth's crust
electrolysis
a process by which hydrogen atoms are stripped from water, leaving the oxygen atom; used for function of hydrogen cells as energy source
co-generation
an energy source in which the waste heat from electricity generation is used in another industrial or residential process, thereby increasing the efficiency of the use of that fuel
energy conservation
the practice of reducing our use of fossil fuels and reducing the impact we have on the environment as we produce and use energy
biofuel
liquid fuel created from processed or refined biomass
Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE)
standards that set mile-per-gallon standards for a fleet of cars; the goal is to reduce energy consumption by increasing the fuel economy of cars and light trucks
cost-benefit analysis
a study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public good
ocean tides
caused by differencees in the gravitational pull of the moon on opposite sides of the earth