Phylum Memorization Invertebrates Diagram | Quizlet
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Ectotherm
outer embryonic germ layer
Endotherm
inner embryonic germ layer
Mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
Coelom
fluid-filled body cavity lined with mesoderm
Protostomes
blastopore becomes mouth
Deuterostomes
blastopore becomes anus
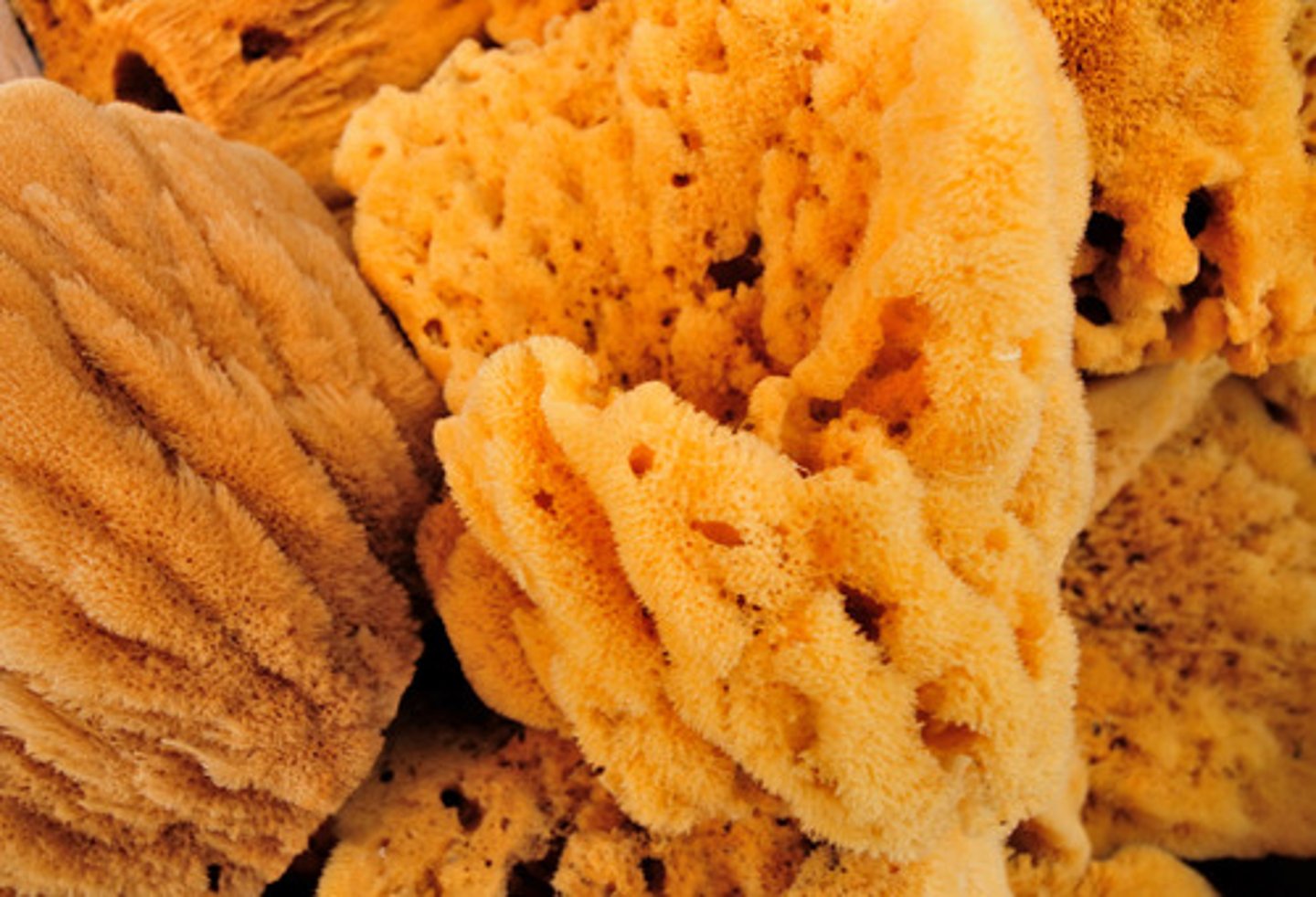
Phylum Porifera Characteristics
no true tissues, no symmetry, acoelomate, pore-bearing, sessile as adults
Describe what sponge reaggregation might tell us about the evolution of the first animals 600 mya...
Animals had cells that used extracellular proteins to glue their cells together cells could join together to reform multicellular organisms after being broken apart.
Choanocytes
cells with flagella that line the insides of sponges, causing current of water that flows through sponges to be able to eat.
Spicules
small, spike shaped particles that make up the skeleton of some sponges
Spongin
Flexible material that make up the skeleton of some sponges.

Porifera examples
sponges

Phylum Cnidaria Characteristics
ectotherm and endotherm, radial symmetry, acoelomate, tentacles with nematocysts
Cnidocytes
cells containing nematocysts
nematocysts
Small capsules that contain a toxin which is injected into prey or predators
Hydra
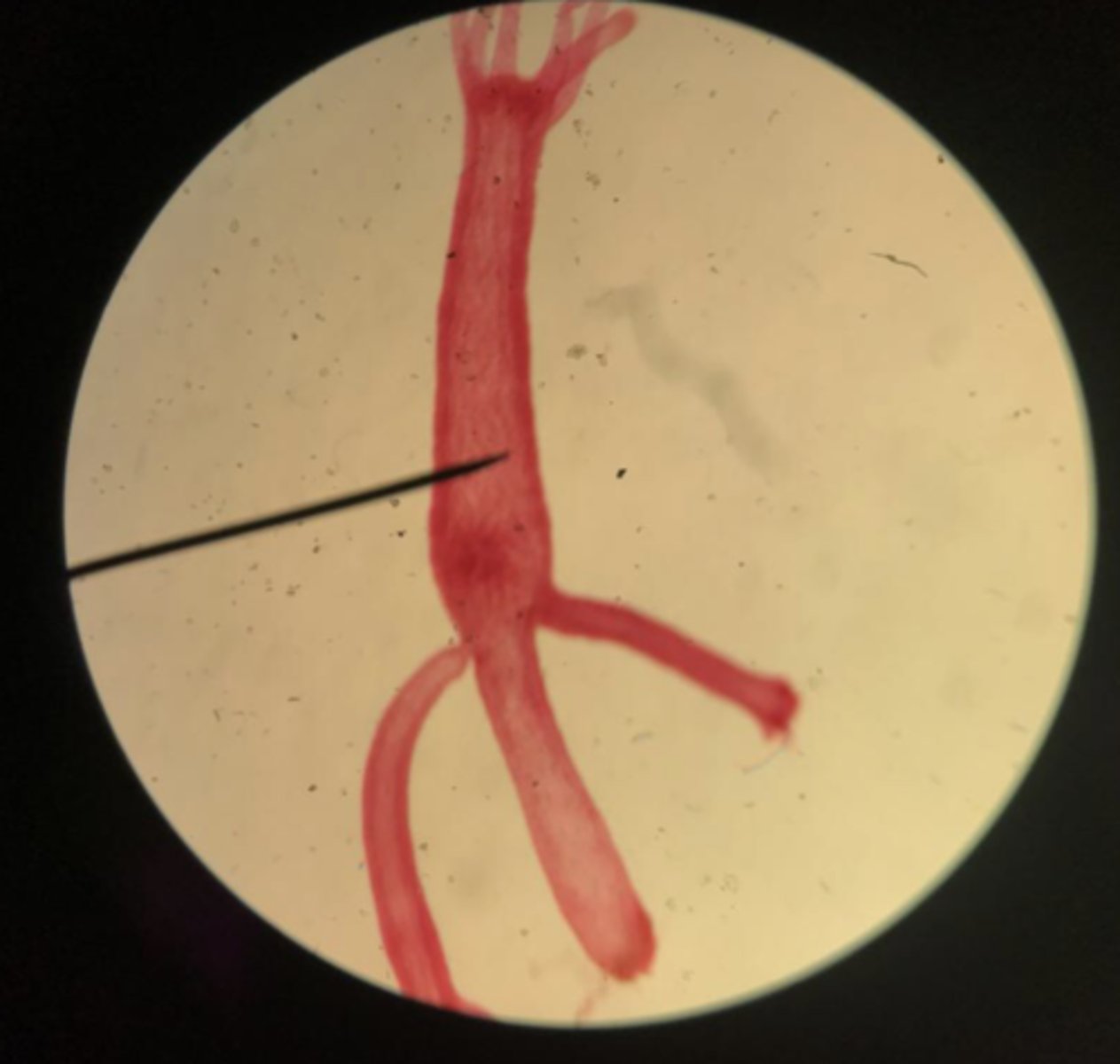
How do hydra capture prey?
- paralyzing/ killing organism using nematocyst
- prey brought to the mouth by tentacle
Cnidaria examples
Jellyfish, hydra, sea anemone, coral

Polyp form
sessile, tubular body with mouth at top surrounded with tentacles (corals and sea anemones)
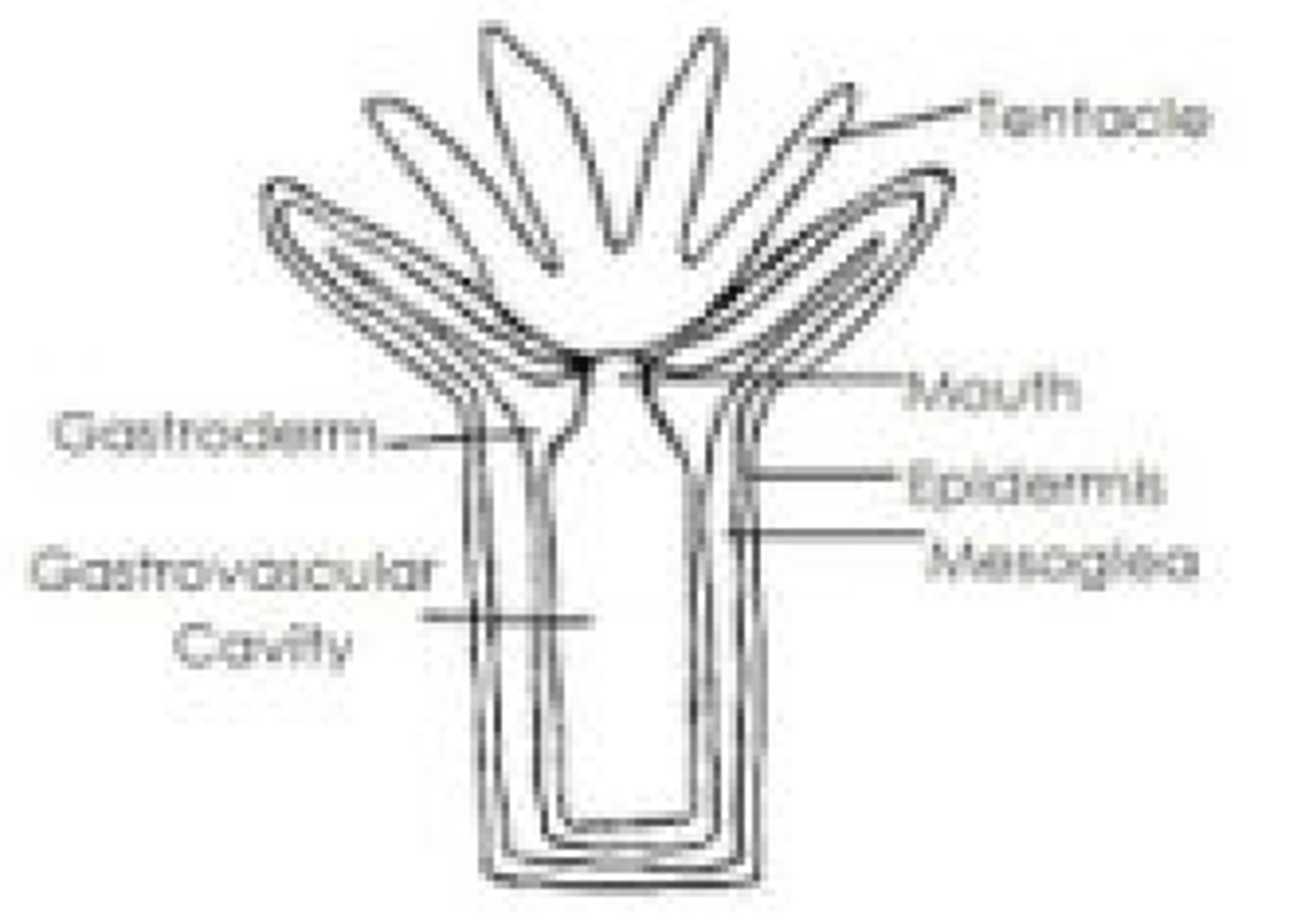
Medusa form
floating or free-swimming, umbrella shaped body, mouth on concave side, tentacle extend from rim (jellyfish)
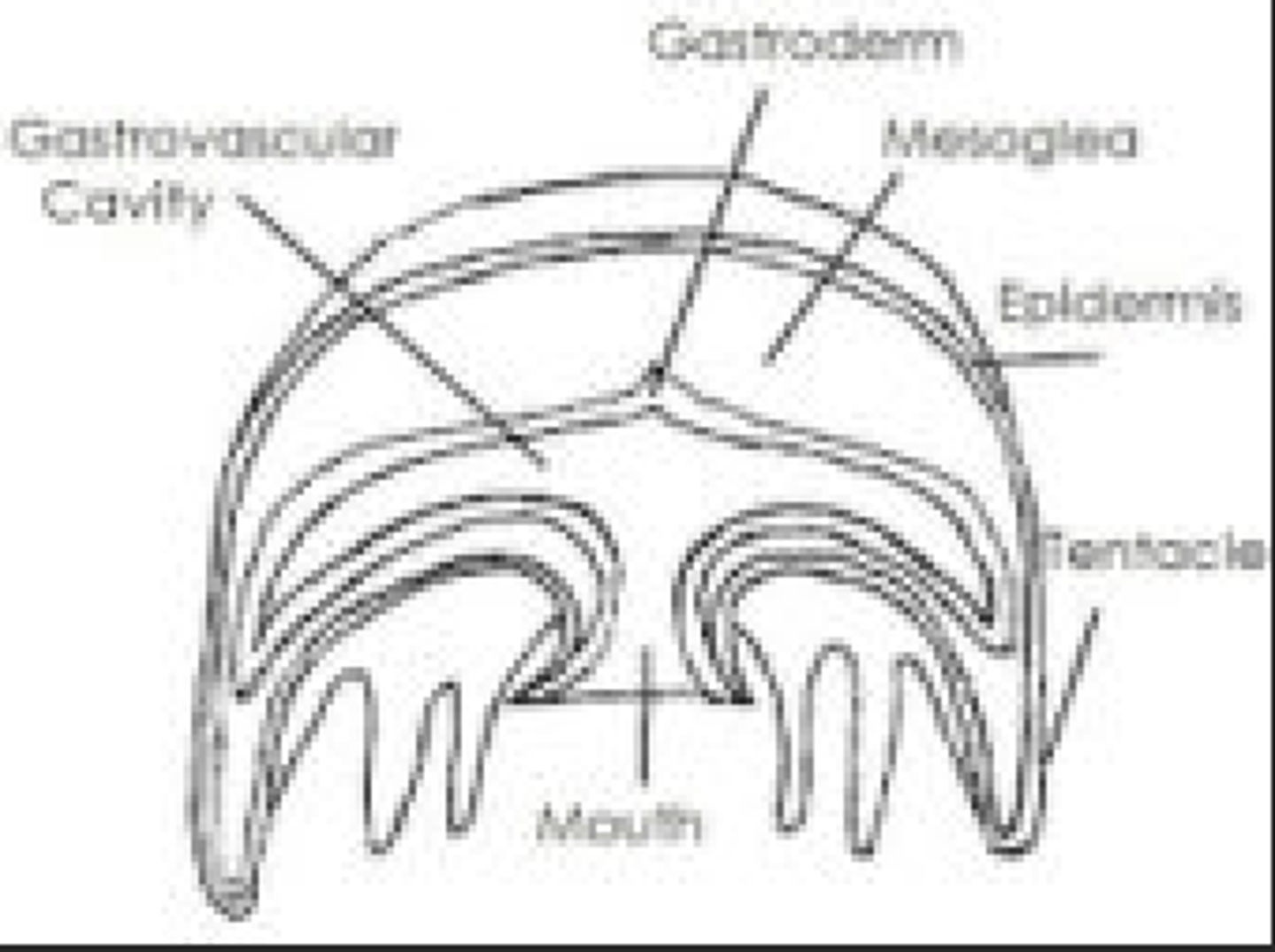
Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics
have all 3 tissue layers, bilateral symmetry, acoelomate, protostomes, cephalization, flat worms
Planaria
Platyhelminthes
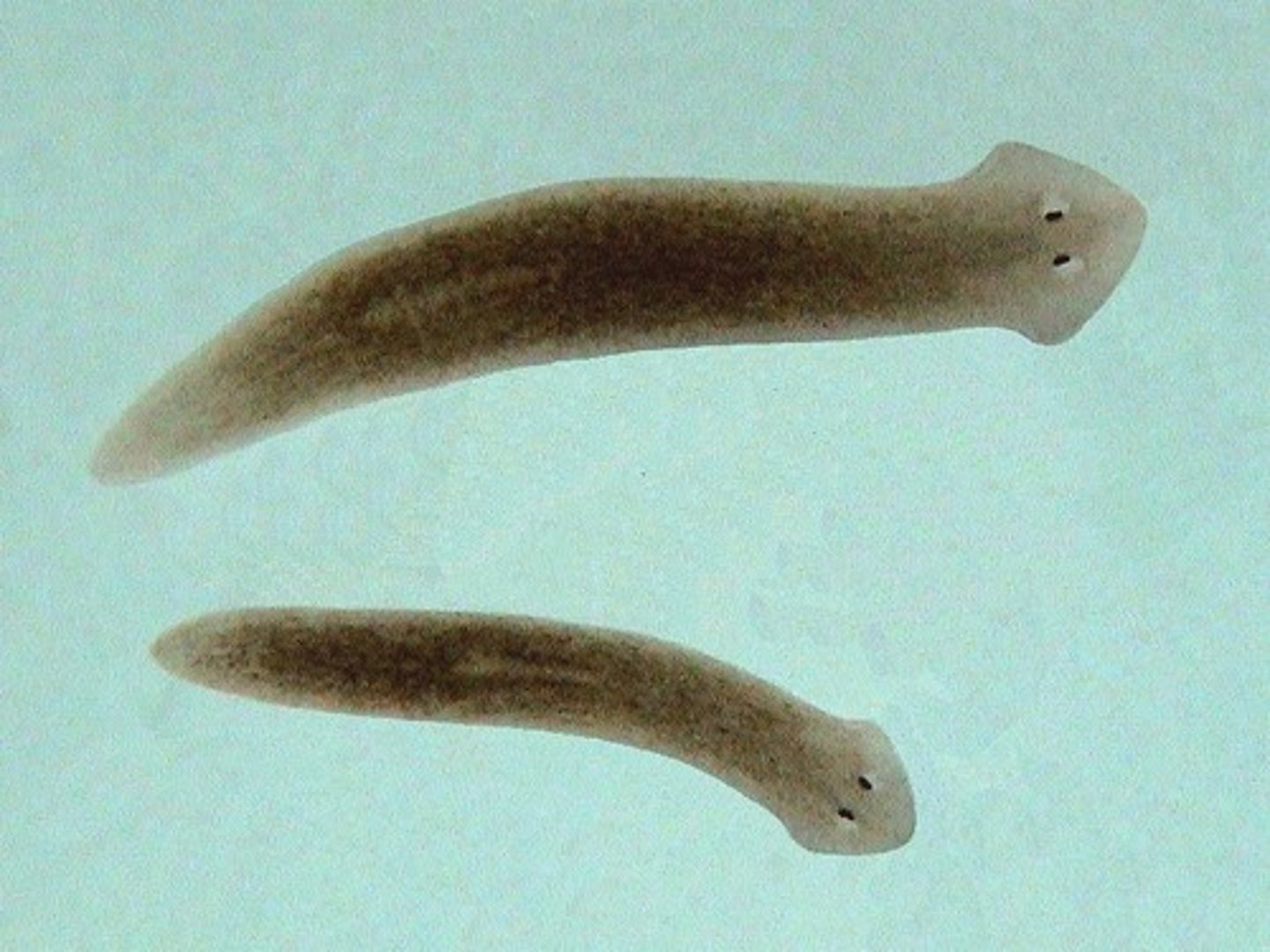

What is an advantage to the cephalization exhibited in planaria?
Better sensory perception and coordination
How to planaria feed?
The pharynx extends from their body, which takes up food from the environment.
tapeworm
Platyhelminthes
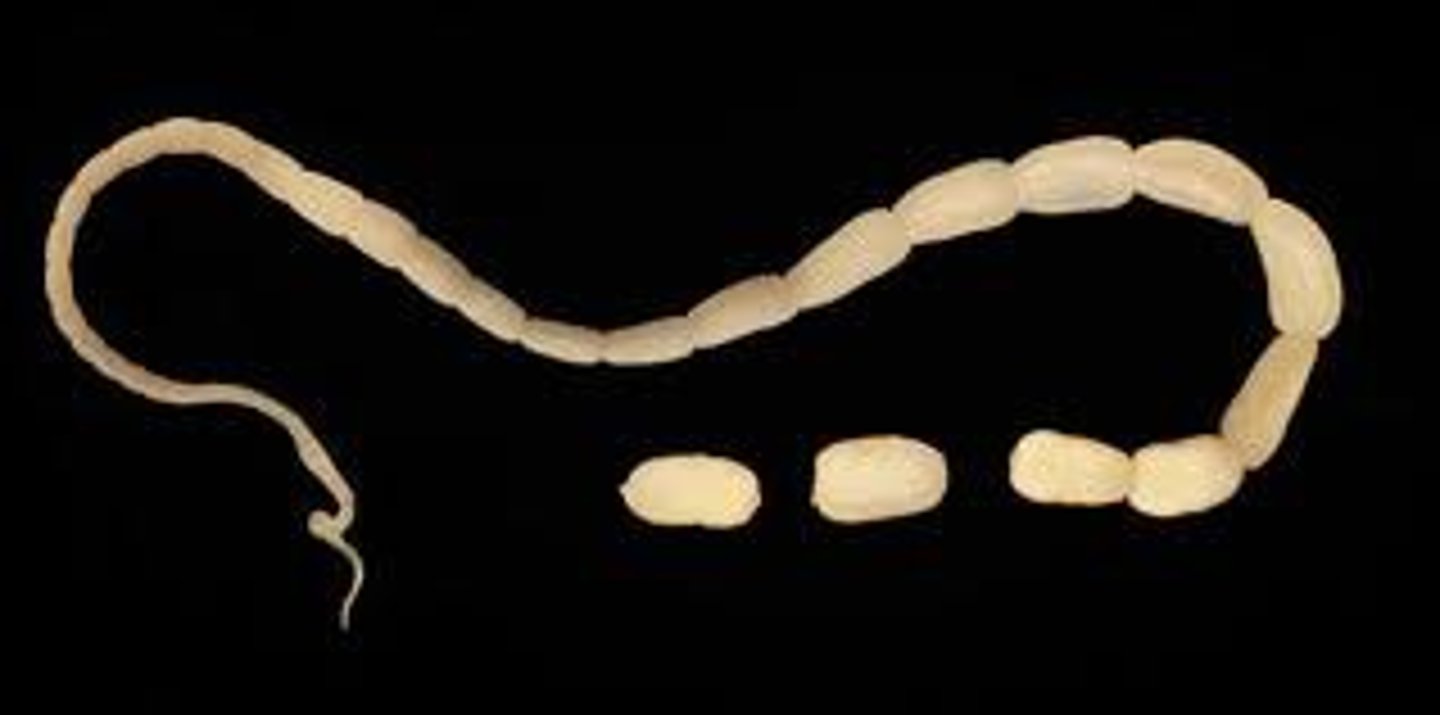
Which of the two Platyhelminthes examples is a parasite?
tapeworms
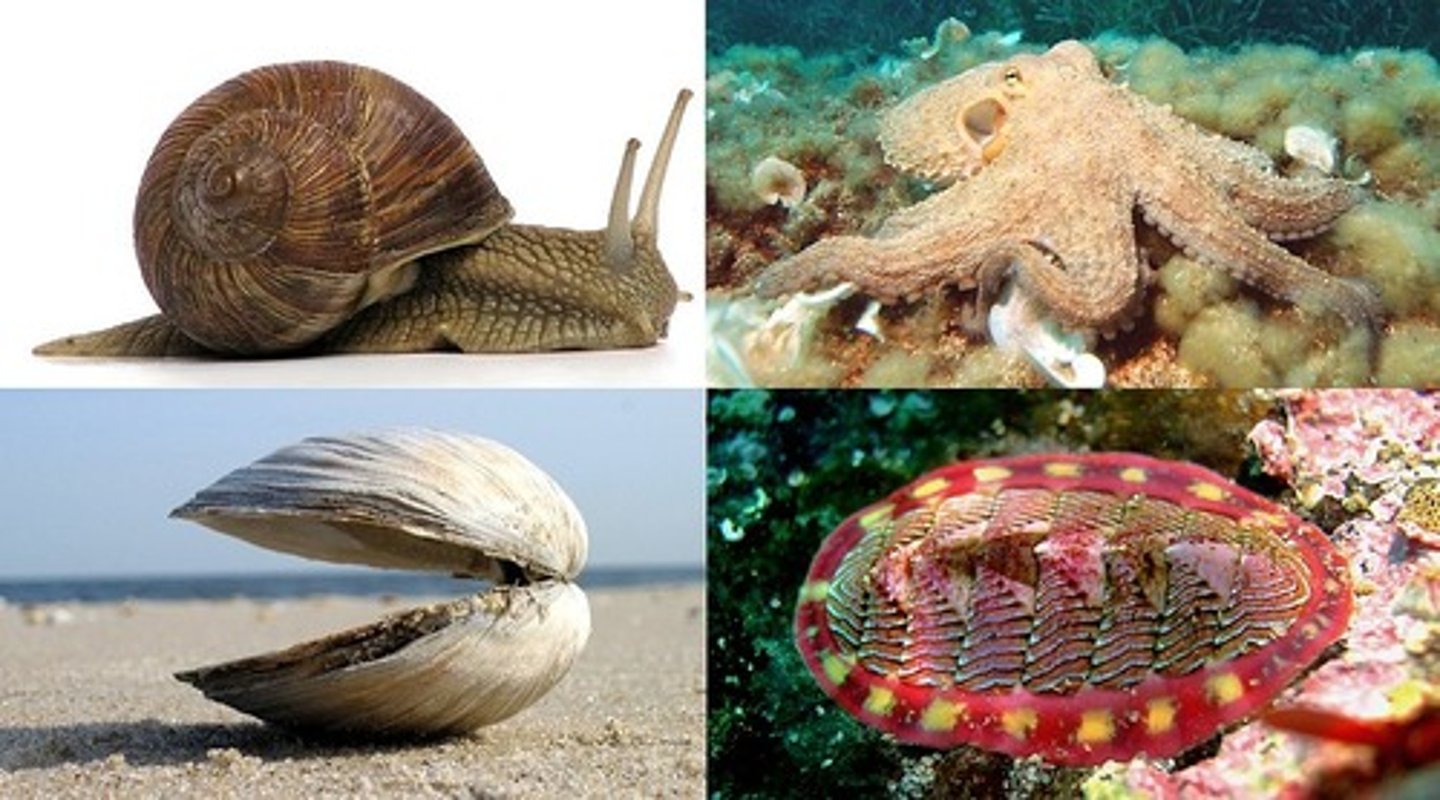
Phylum Mollusca Characteristics
3 tissue layers, bilateral symmetry, coelomate, protostomes, mantle and muscular foot
Mantle
body is covered in part by a thin flesh layer
Muscular Foot
muscle tissue specialized for movement
Radula (sometimes called a beak)
An organ covered with teeth that mollusks use to scrape food into their mouths
Mollusca Examples
snails, slugs, clams, squids, and octopi

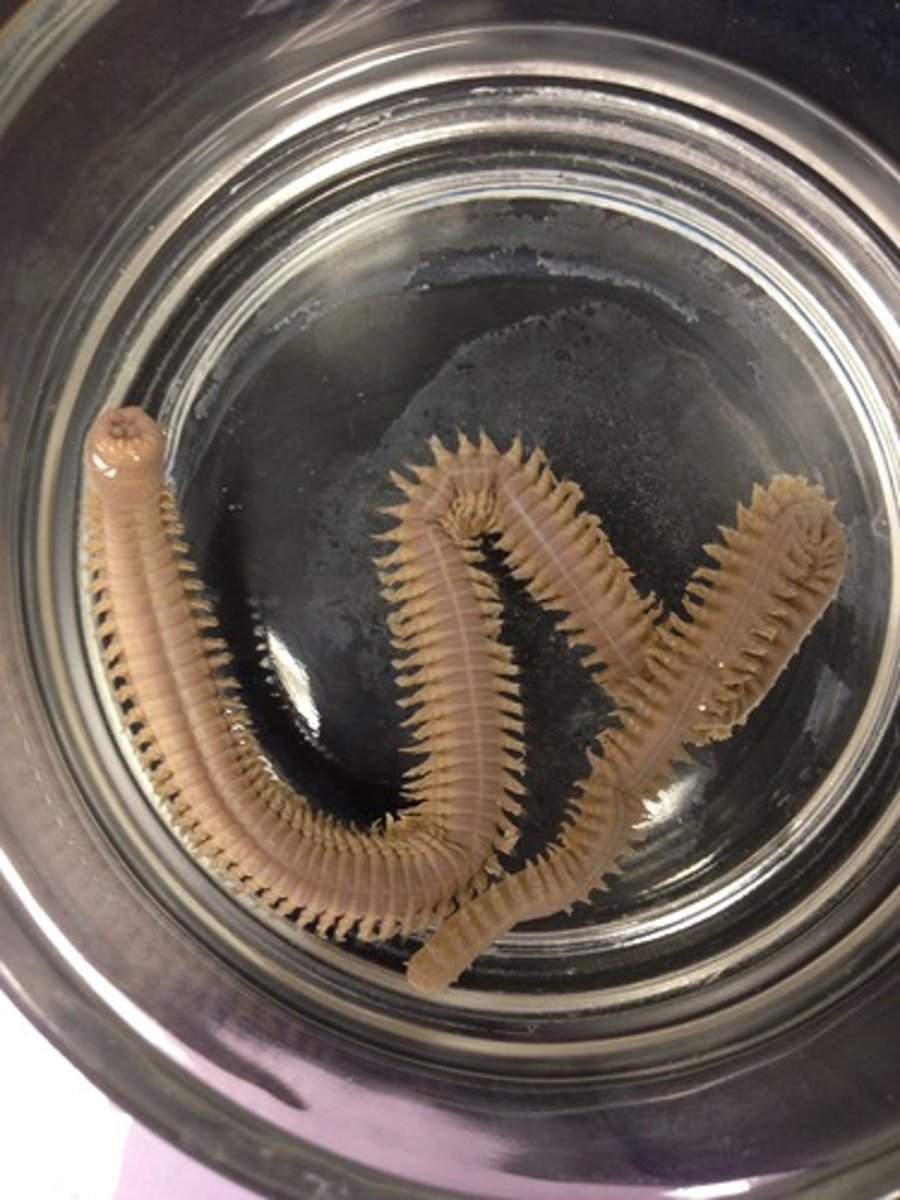
Phylum Annelida Characteristics
3 tissue layers, bilateral symmetry, coelomate, protostomes, and segmented
Paired Setae
characteristic of Annelids, bristles that serve as anchoring points for movement
Annelids have ___ and ___ muscles.
longitudinal, circular
How do annelids make use of their coelom for body support and movement?
Their coelom serves as a hydrostatic skeleton that muscles can pull against
Annelida Examples
earthworms, leeches

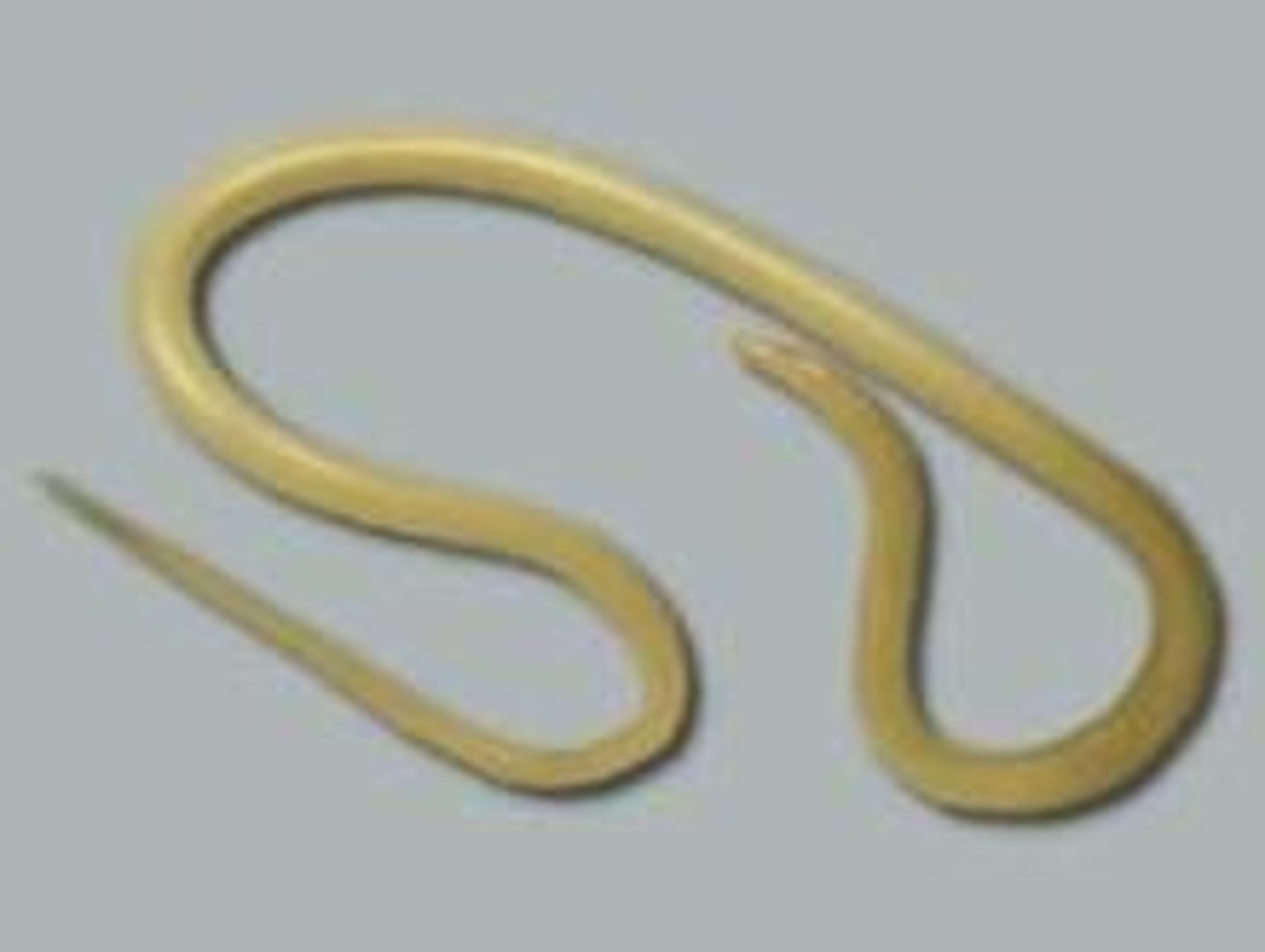
Phylum Nematoda Characteristics
3 tissue layers, bilateral symmetry, pseudocoelomate, protostomes, round-bodied worms with tapered ends
C. elegans (most commonly used nemotode speciman)
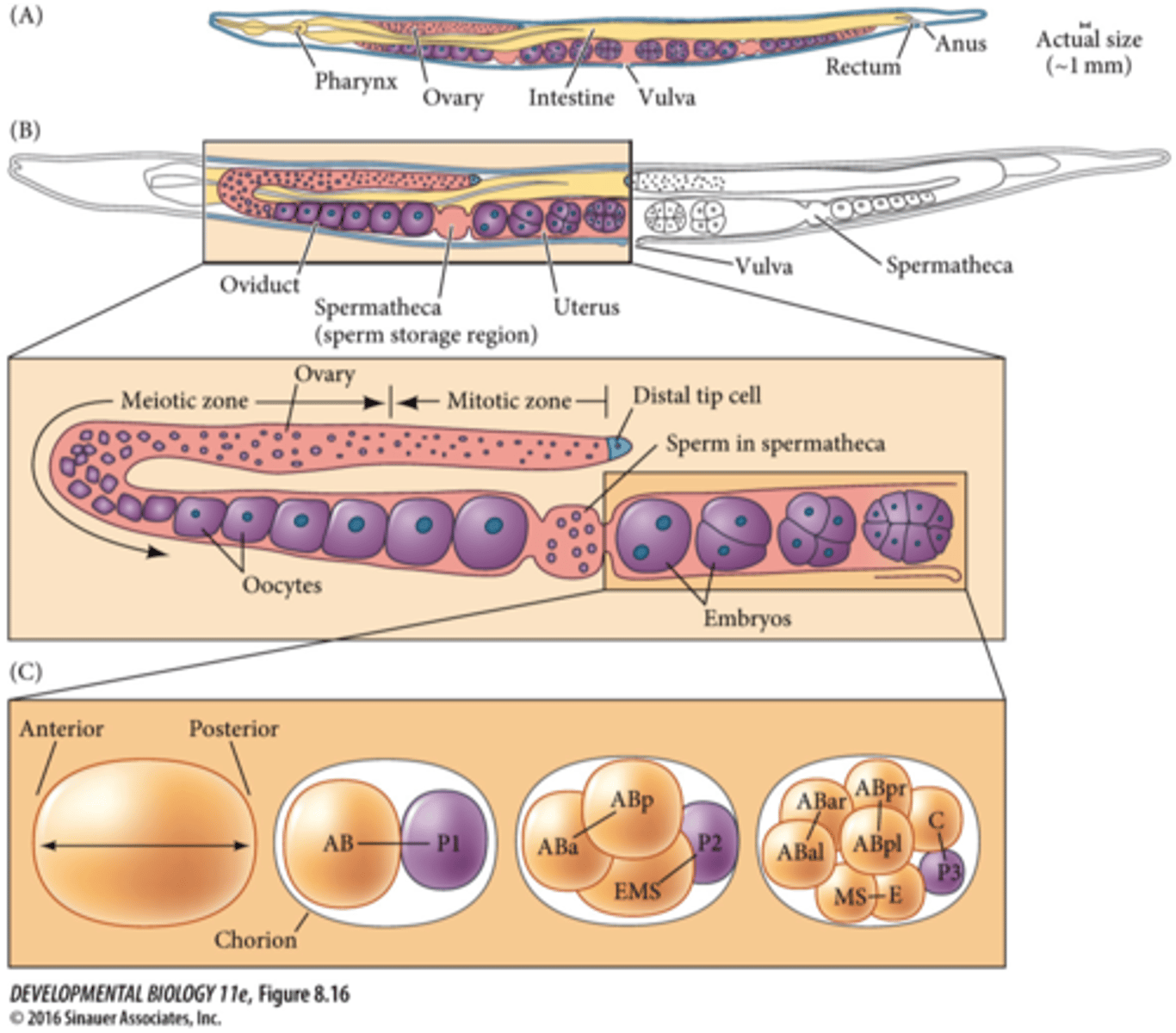
Ascaris
roundworm parasite

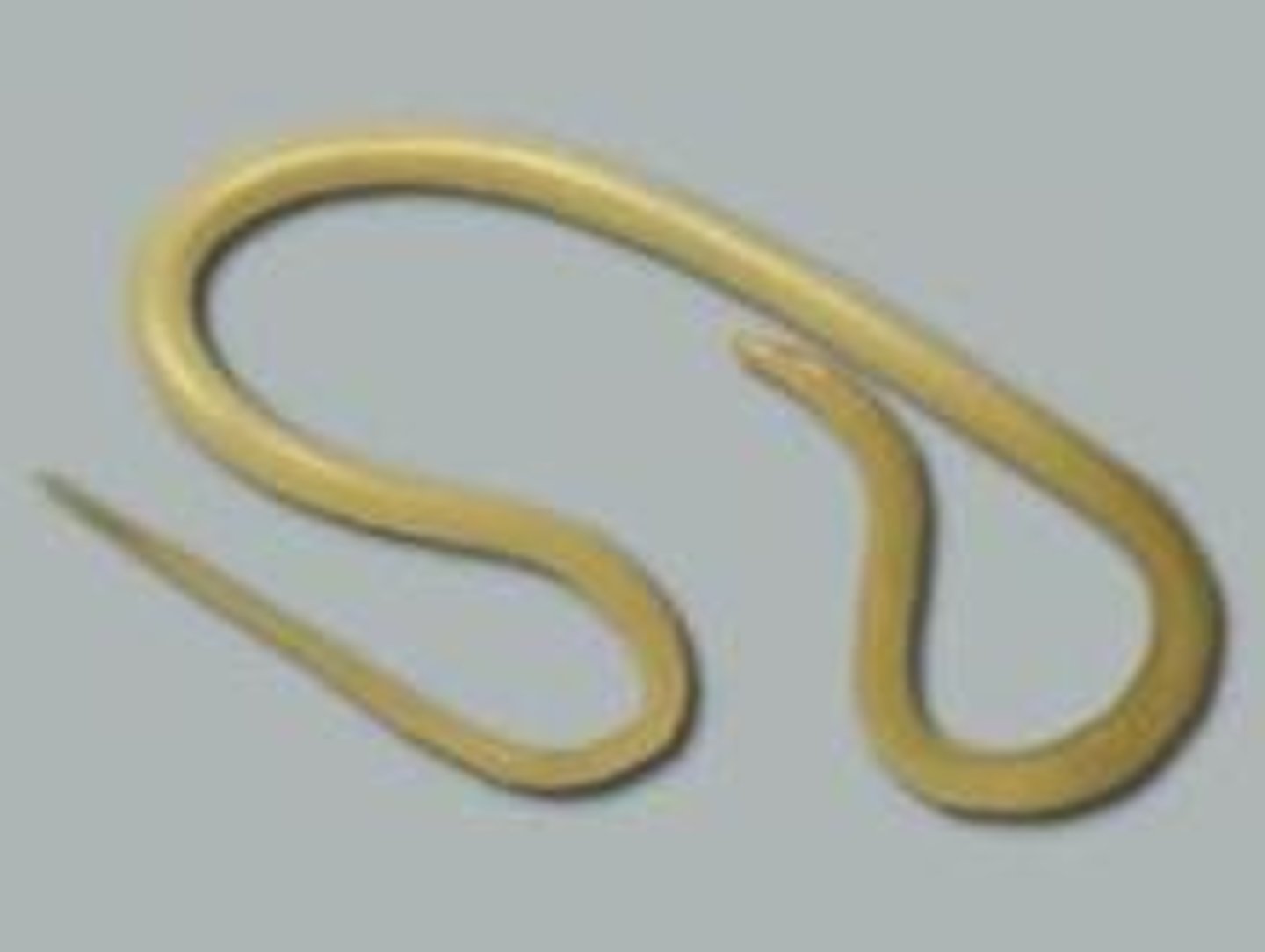
Pseudocoelomate
An animal whose body cavity is not completely lined by mesoderm
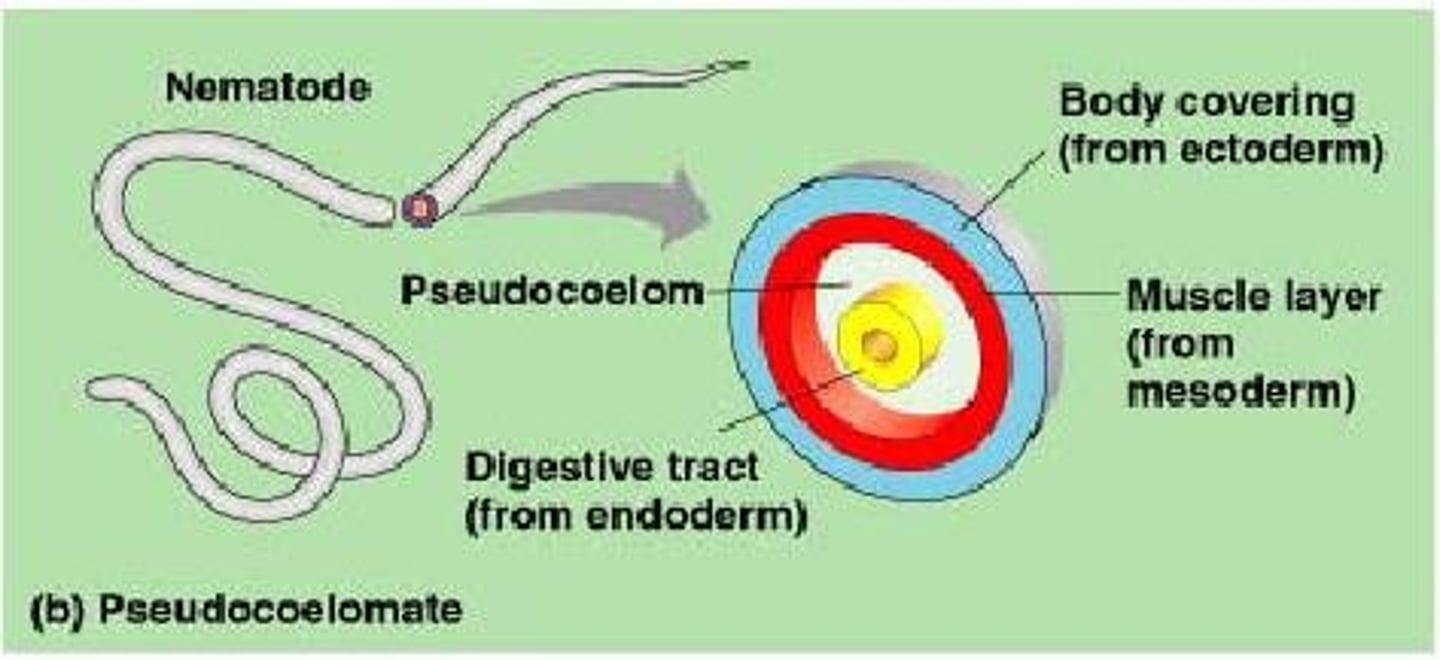
Why do nematodes move differently than annelids?
they only have longitudinal muscles, so they move in an S-shape
Nematoda examples
roundworms, hookworms

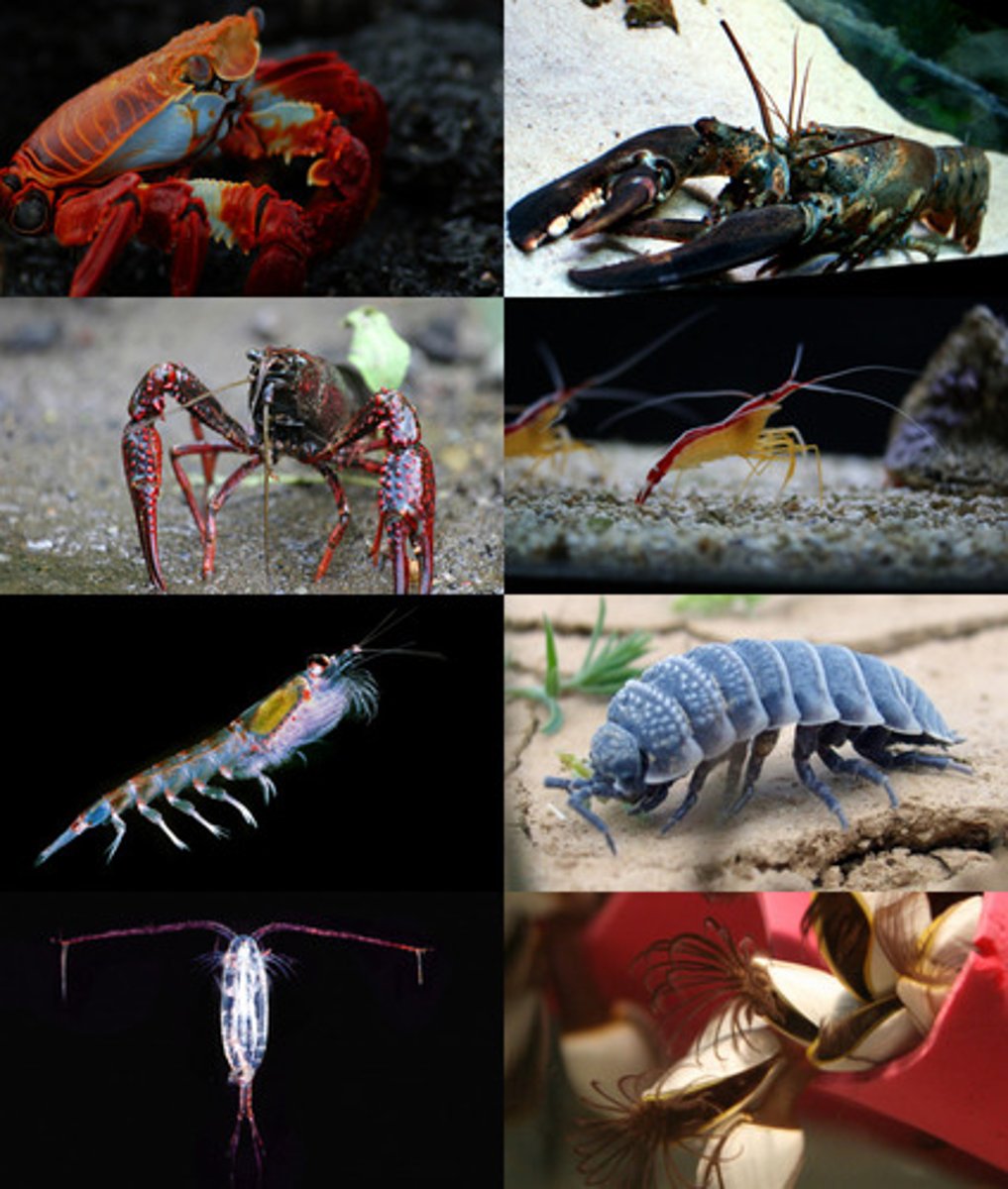
Phylum Arthropoda Characteristics
3 tissue layers, bilateral symmetry, coelomate, protostomes, jointed appendages, chitinous exoskeleton
exoskeleton
A body covering, typically made of chitin, that provides support and protection
Jointed appendages
Arms, legs and antennae that have joints
How many legs do spiders and scorpions have?
8
How many legs do insects have?
6
How many body segments do spiders and scorpions have?
2
How many body segments do insects have?
3
Arthropoda examples
insects, crustaceans, arachnids (spiders and scorpions)

Phylum Echinodermata Characteristics
3 tissue layers, bilateral and secondary pentaradial symmetry, coelomate, deuterostome, spiny skin with exoskeleton, water vascular system, shell
Why is radial symmetry in echinoderms considered secondary?
They exhibit bilateral symmetry as larvae and exhibit pentaradial symmetry as adults
Tube feet
Extensions of an echinoderm's water vascular system used for movement, respiration, and feeding
Test
the shell, or hardened covering, of some invertebrates
Echinodermata examples
sea stars, sea urchins, sand dollars

TERM
vertebrates
DEFINITION
having a notochord
TERM
sponges
DEFINITION
have no true tissues