B4.2 Ecological Niches
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Niche
Ecological niche: The role a species plays in its ecosystem
What niche an organism can fill depends on:
How it obtains food (specialisation reduces competition)
Zones of tolerance (range determines habitat)
How it interacts with other species In the ecosystem
Fundamental vs Realised niche
Fundamental niche: Potential niche species could occupy with no competition
Realised niche: Actual niche a species occupies in presence of its competitors - range of tolerance is occupied by competitors
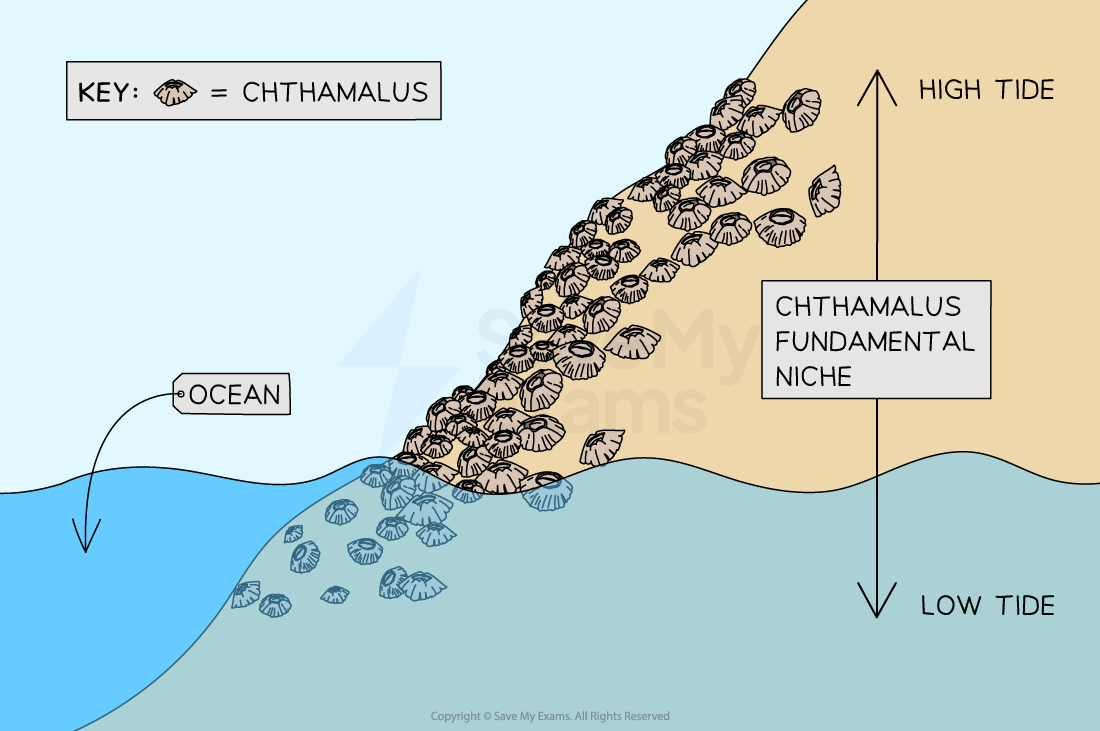
E.g. Chthamalus barnacles
Fundamental: low tide + high tide
Realised: Only high tide due to competition with Semibalanus barnacles.
Competitive exclusion
When fundamental niches of 2 species overlap causes competition
Which can lead to one species outcompeting the other, resulting in the exclusion of the less competitive species from that niche.
Only if the non competing species is outcompeted in all parts of its fundamental niche
Weaker species is eliminated
E.g. 2 species of protozoans
Paramecium aurelia + Paramecium caudatum
aurelia survived and outcompeted caudatum
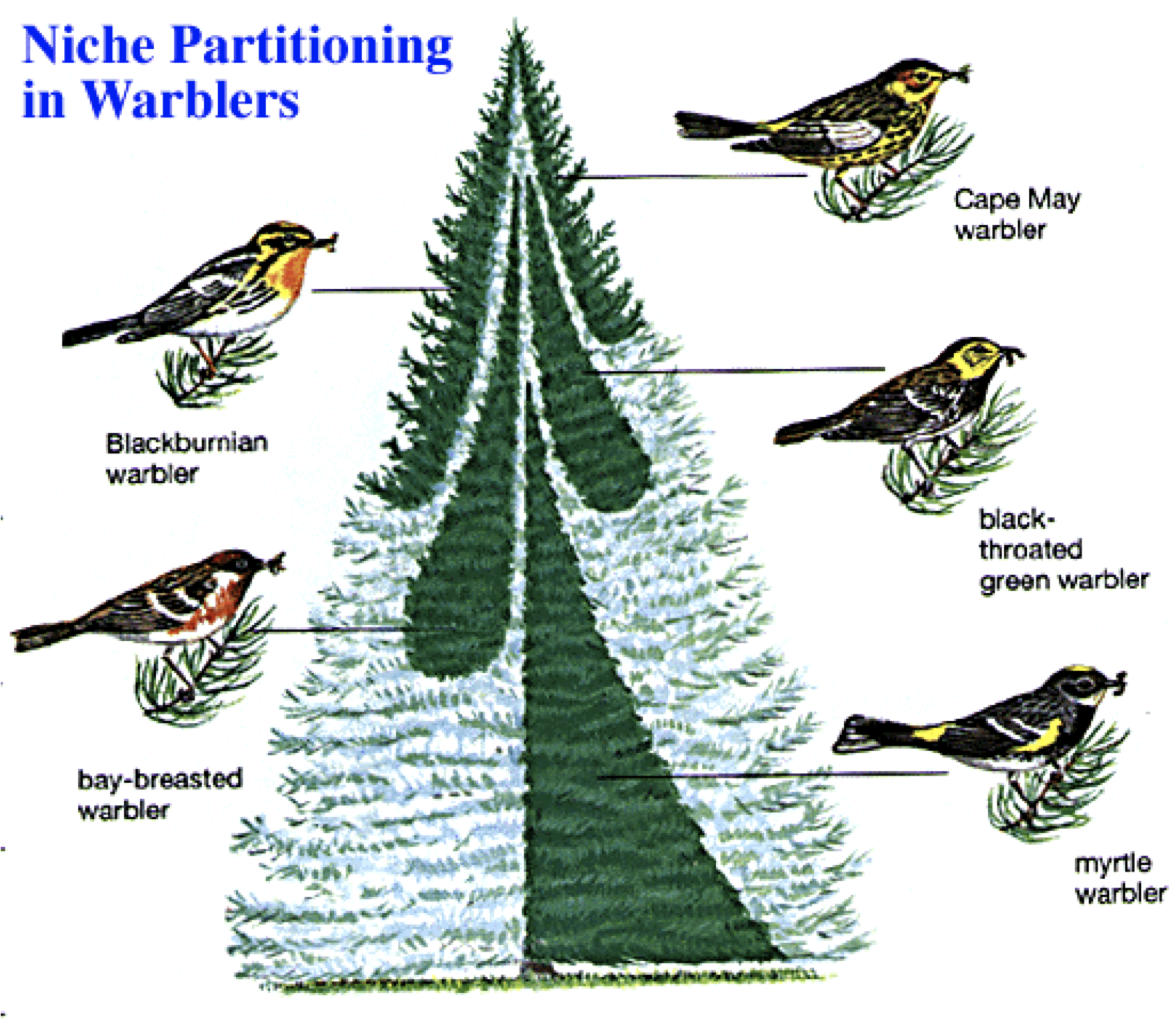
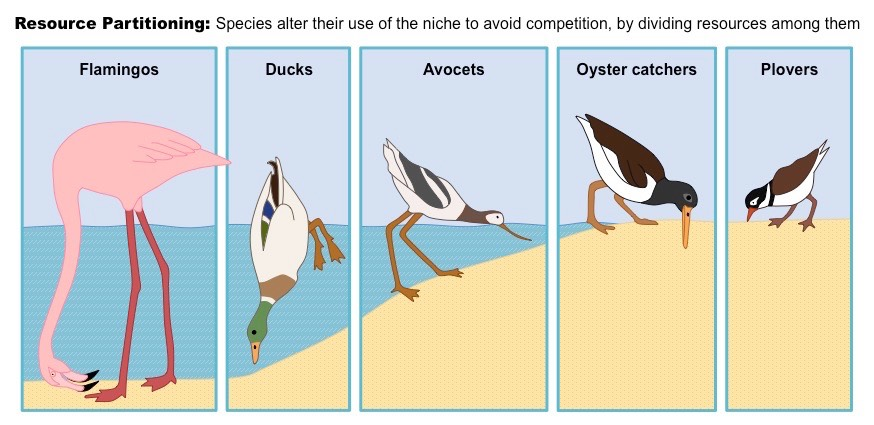
Niche partitioning
The process by which competing species in fundamental niche coexist
By utilising different resources or habitats to reduce competition
Allowing them to occupy the same area without directly competing for the same resources
Both become restricted to just part of fundamental niche
E.g. Warbler birds inhabiting particular part of same tree
E.g. Shore birds that share area on shore
Obligate Anaerobes, facultative anaerobes, + obligate anaerobes
Anaerobes survive in environments with no air/oxygen - eutrophication, polluted lake/soil
Aerobes require oxygen to survive and thrive in oxygen-rich environments, such as the atmosphere.
Organisms can be placed into 3 categories
Facultative anaerobes - can survive in either oxic (aerobic) or anoxic (anaerobic) environments
E.g. E. coli, yeast
Obligate aerobes - must have oxygen = all animals + plants
E.g. humans, most animals
Obligate anaerobes - cannot survive in oxygen
E.g. Clostridium species
Autotrophic nutrition
Photosynthesis is the mode of nutrition in plants, algae + several groups of photosynthetic prokaryotes
Produce own organic compounds from inorganic (self-feeding) - through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Plants, algae, some bacteria
Organisms such as plants and some bacteria that convert sunlight or chemical energy into food, forming the base of the food chain
Photosynthetic prokaryotes (Cyanobacteria) even tho there aren’t any organelles the whole thing is like a chloroplast
Adaptations of plants for harvesting light
Lianas (type of plant): Climbs to the top by using other plants - top has more light
Epiphytes: Germinate high up (not rooted in soil), grow on other plants, gaining access to sunlight without harming their host, get nutrients and water from air/moisture/host branch
not parasites but need a host plant
Strangler epiphytes: Start same as epiphytes BUT grow long roots down, gradually enveloping it and competing for light, eventually outcompete the host--killing it.
Shade tolerant shrubs/herbs: These plants can thrive in low-light conditions, adapting their leaf structure and photosynthetic efficiency to maximize light capture in shaded environments.
Trees grow very tall so no competition of light - Yellow Meranti
Heterotrophic nutrition
Obtain organic compounds from other compounds (feed on others)
All animals + All fungi
Includes:
Holozoic - whole pieces of food eaten + digested internally (ingest food, digest (chemical breakdown into smaller molecules, absorption (of some of smaller molecules) assimilate (incorporate into new material), egestion (leave as waste))
Amoeba, Humans
Saprotrophic - type of decomposer that digests matter externally (don’t ingest, release enzymes onto food to digest and absorb the digested food)
Fungi + bacteria
Detrivitores: digest matter internally - holozoic nutrition
Mixotrophic nutrition
Organisms can obtain energy and nutrients through both autotrophic and heterotrophic means, such as some protists and plants.
This allows them to adapt to varying environmental conditions.
E.g. Euglena is a freshwater example - facultative mixotroph
Obligate mixotroph: must use both methods
Facultative mixotrophs: can use one method or other depending on what is available in the environment
Diversity of nutrition in archaea
Archaea: one of three domains of life
Archaea are very diverse with many methods of nutrition
Main methods
Phototrophic: absorption of light energy
Chemoautotrophic: oxidation of inorganic chemical substances to obtain energy (Fe2+—>Fe3+)
Heterotrophic: Obtain organic compounds from other compounds (feed on others)
Adaptations of herbivores for feeding on plants and of plants for resisting herbivore
Herbivore: Organisms that primarily consume plants or plant-based materials for energy and nutrients, playing a key role in the food chain.
Adaptations of herbivores: Leaf eating insects - E.g. Aphid Insect
Chewing mouth part (mandibles)
Piercing mouth part (Stylets) used to suck up sap from phloem
Adaptations of plants for resisting herbivore (being eaten by herbivores)
Spines/spikes
Stinging parts
Toxins (poisoners or just stingers)
Some herbivores have adaptations for overcoming these adaptations ^^^
Some aphids produce saliva that acts like a barrier + protects it from plant toxin
Omnivores
Organisms that consume both plants and animals for energy and nutrients, contributing to various trophic levels in ecosystems.
Carnivores
Organisms that primarily consume other animals for energy and nutrients, often serving as predators in the food chain.
Adaptations of predators for finding, catching and killing prey and of prey animals for resisting predation
Predators: Organisms that hunt and kill other animals for food, playing a crucial role in controlling prey populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
Not all carnivores are predators - vultures do not kill
Adaptations of predators for catching prey
Physical: Stealth + speed, eagle spot prey from 3km away, Owl hears everything even tiny movements by mouth, teeth/claws in lion
Chemical: Cone snail injects venom
Behavioural: Dolphins hunt in packs
Adaptations to resist predation - some adaptations develop more quickly than others (behavioural is fastest - chemical is slowest)
Chemical: Monarch butterflies produce toxin that kills predator, skunk spray is a pungent liquid from anal glands
Physical: Walking stick bug camouflage
Behaviour: mackerel fish school together and seem larger to avoid predation
Prey
Organisms that are hunted and consumed by predators, playing a vital role in food webs and ecosystem dynamics.
Relationship between dentition (teeth) + diet of omnivorous + herbivorous members of family hominidae
For extinct species we can figure out what they were by: By examining their fossilised teeth and jaw structures, scientists can infer dietary habits and classify them as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores.
Hominidae: family that includes humans, orangutans, chimpanzees, + gorillas
Shape of teeth = indicators of what they eat
Carnivore: sharp teeth adapted for tearing flesh - sharp canine incisors
Herbivore: flat teeth designed for grinding plants
Omnivore: a combination of sharp and flat teeth for consuming both plants and animals.