Biochemistry: Enzymes, Catalysts, and Chemical Reactions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
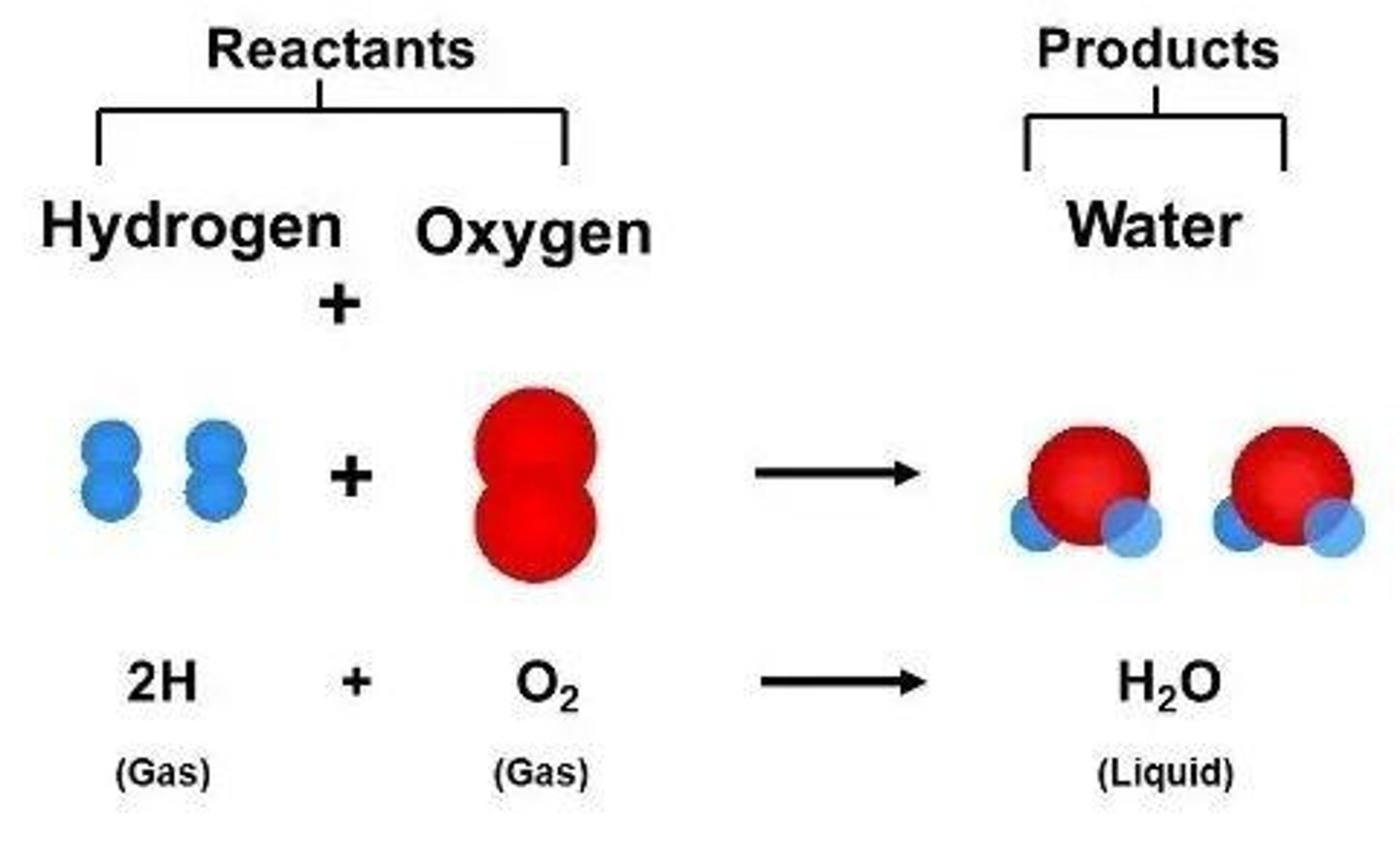
What are reactants in a chemical reaction?
Substances that undergo a change during the reaction.
What are products in a chemical reaction?
Substances that are formed as a result of the reaction.
What is bond energy?
The amount of energy needed to break a bond between two atoms.
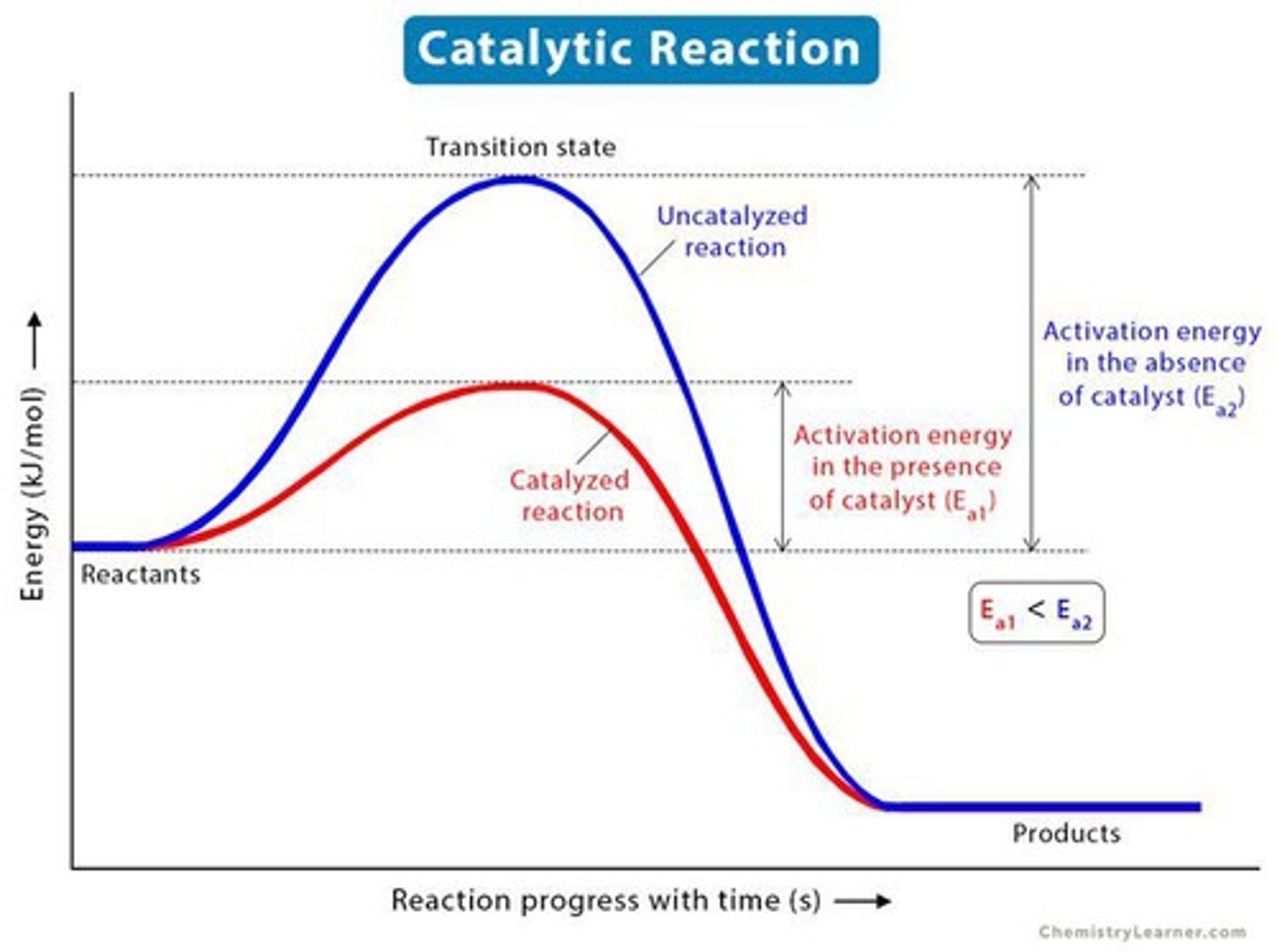
What is a catalyst?
A chemical that speeds up a reaction without being consumed or changed.
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
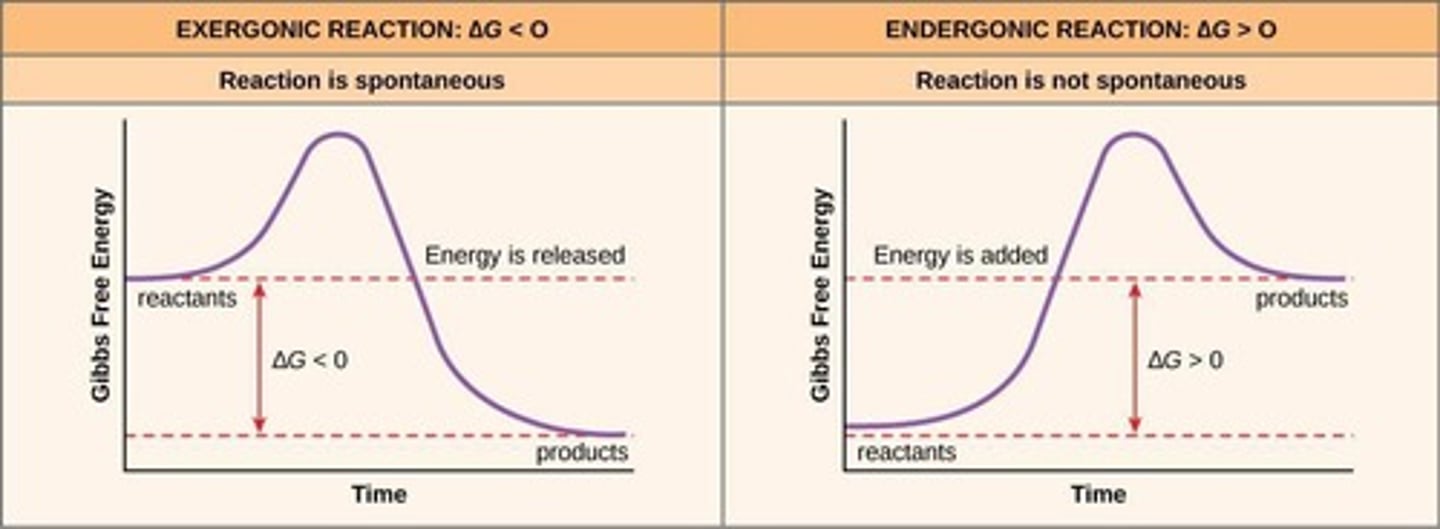
What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions release energy, while endothermic reactions absorb energy.
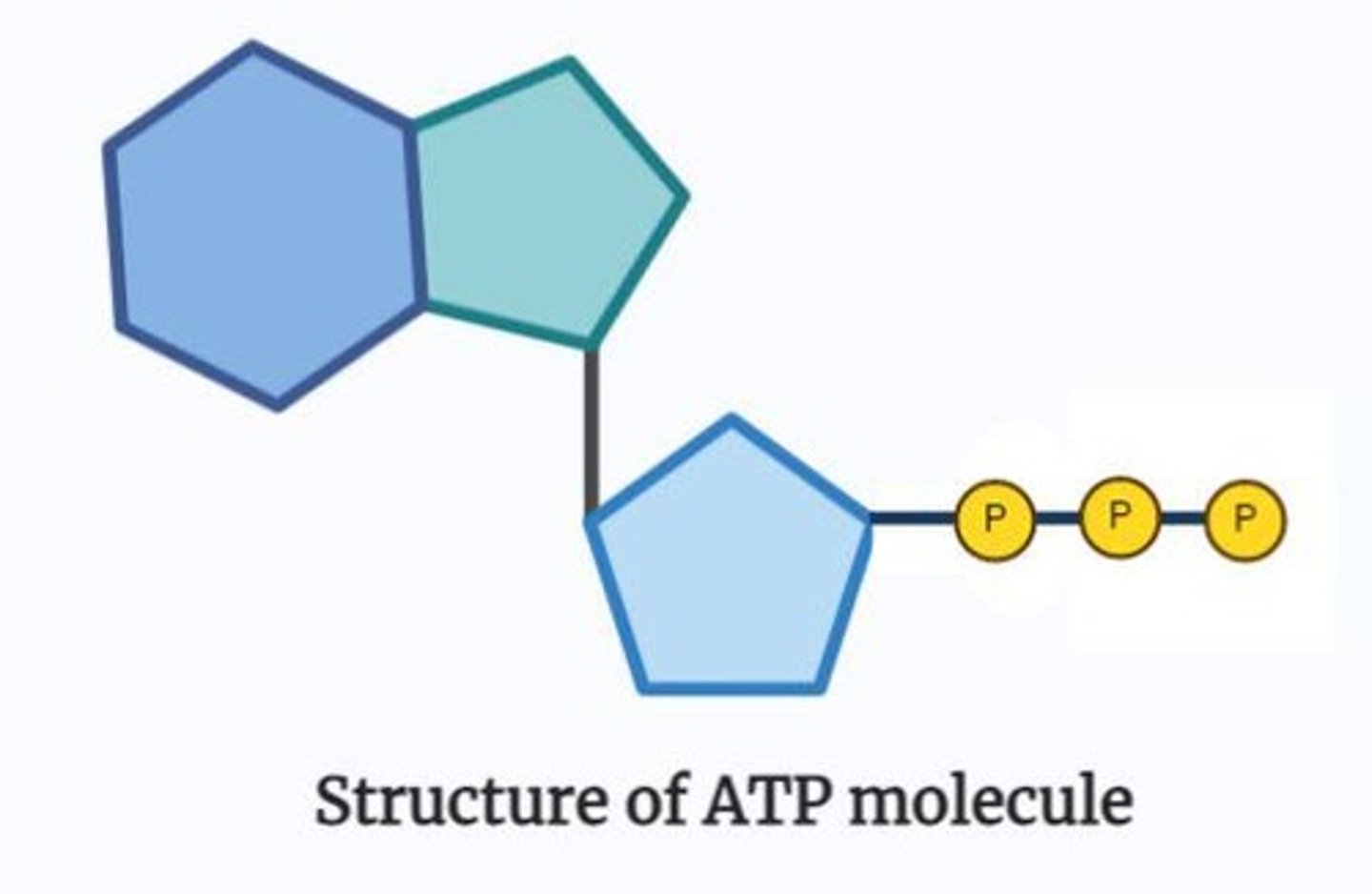
What does ATP stand for and its role?
Adenosine triphosphate; it serves as a source of energy in cells.
What are enzymes?
Proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions in living organisms.
What is the function of enzymes?
To speed up chemical reactions, break things apart, and put things together.
What is a substrate?
The reactants that bind to an enzyme during a reaction.
What is an enzyme-substrate complex?
A temporary molecule formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme.
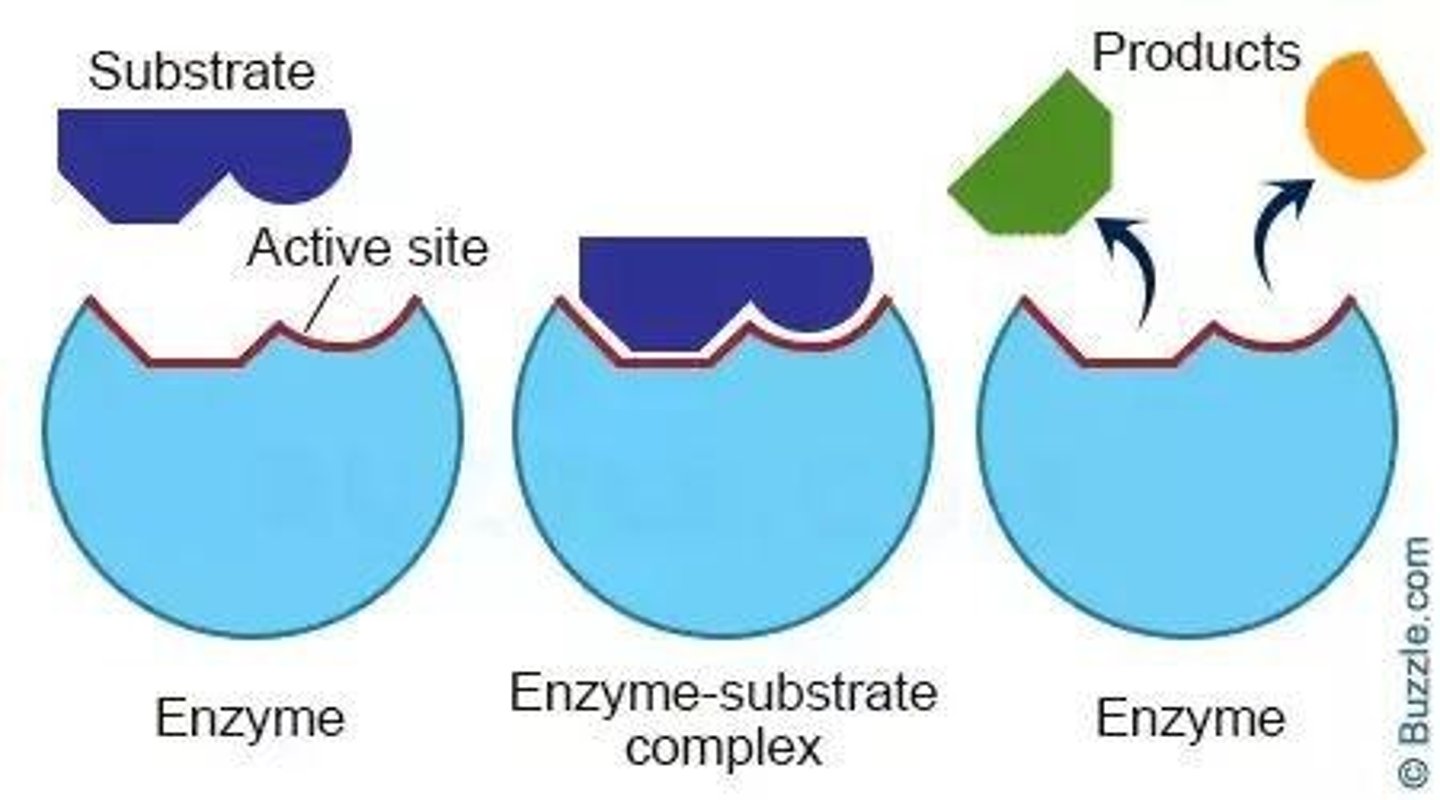
What is the lock-and-key model in enzyme activity?
The model that describes how specific substrates fit into their corresponding enzymes.
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Temperature, pH, and concentration.
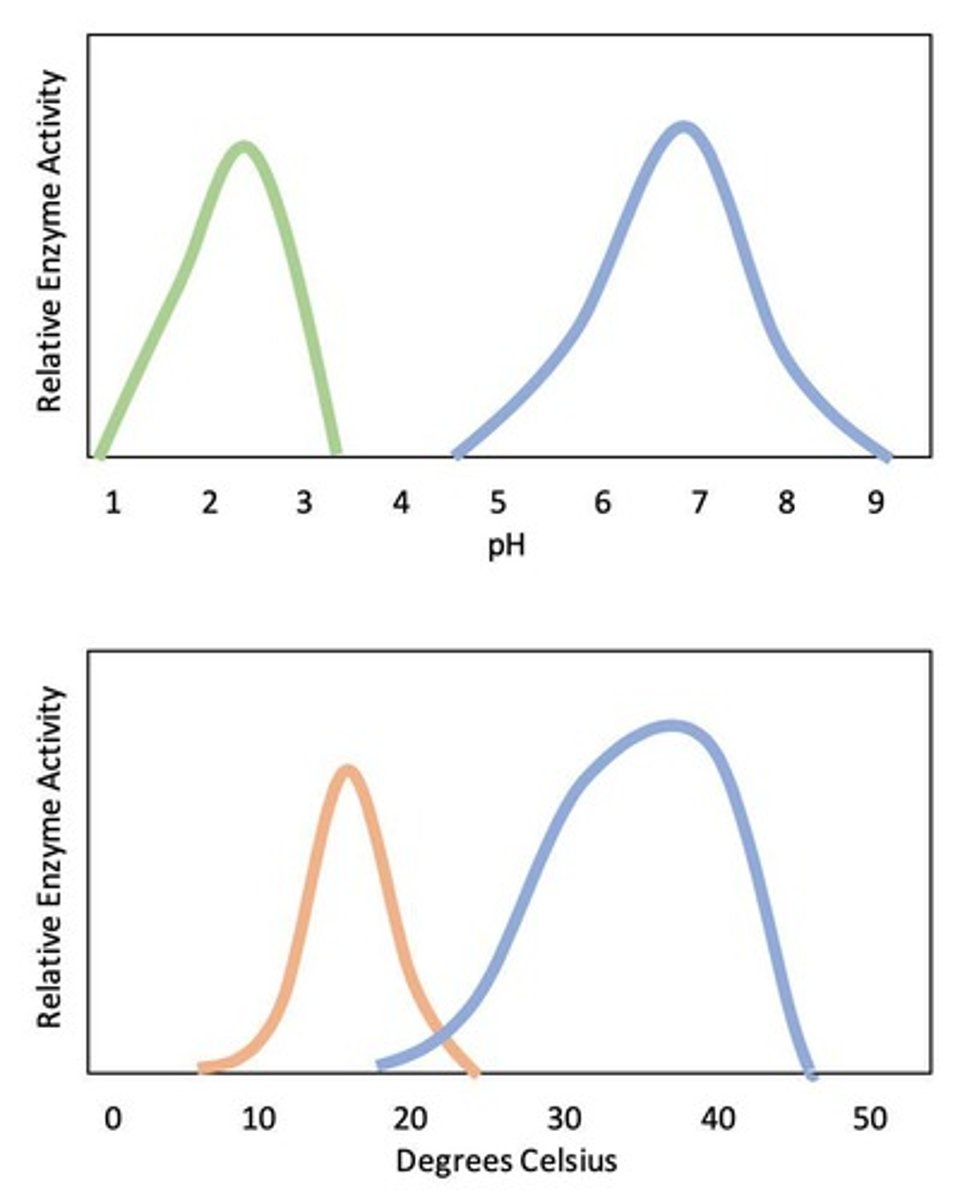
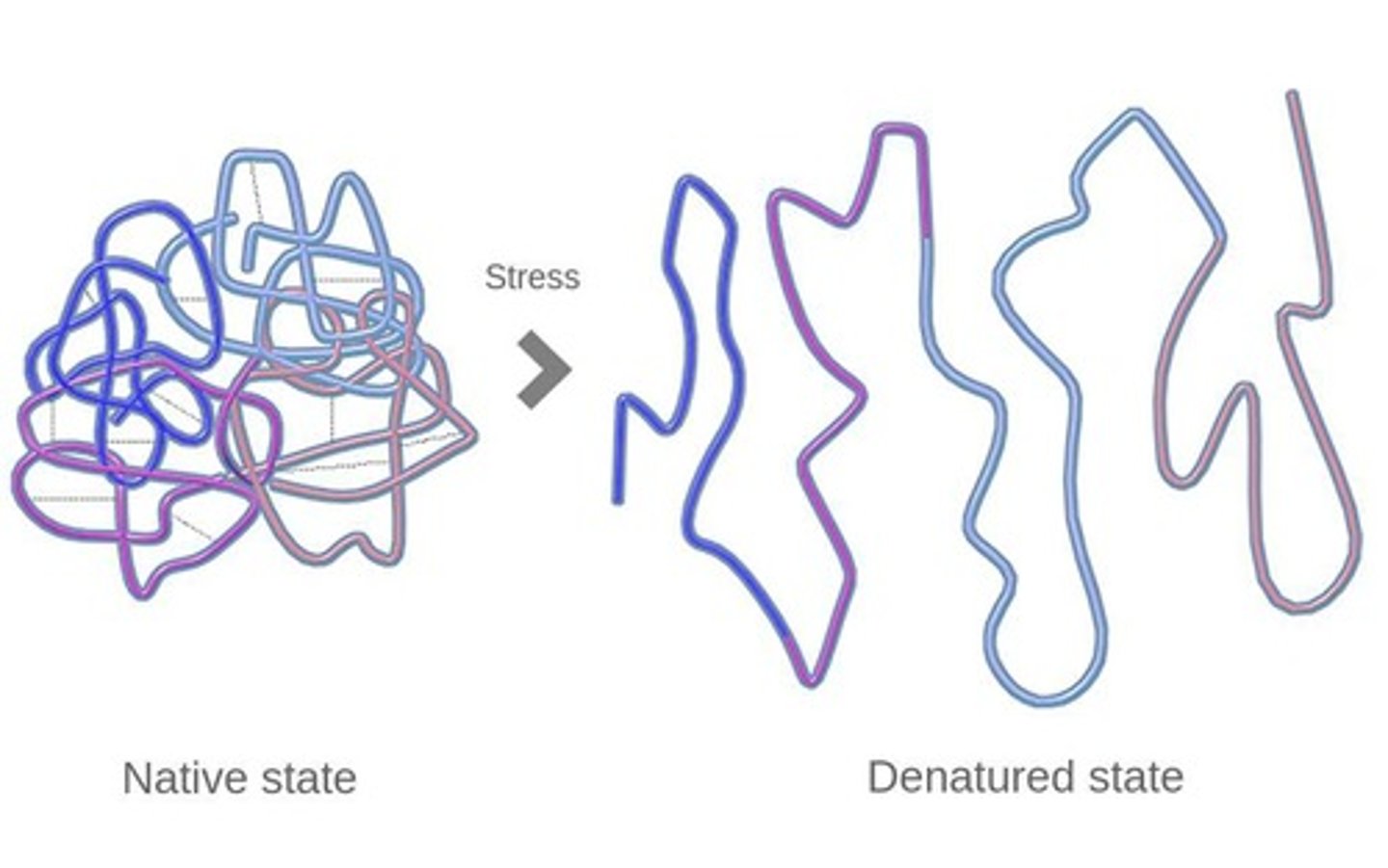
What happens to enzymes outside their optimal conditions?
They can become denatured, losing their shape and function.
What is competitive inhibition?
When an inhibitor binds directly to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding.
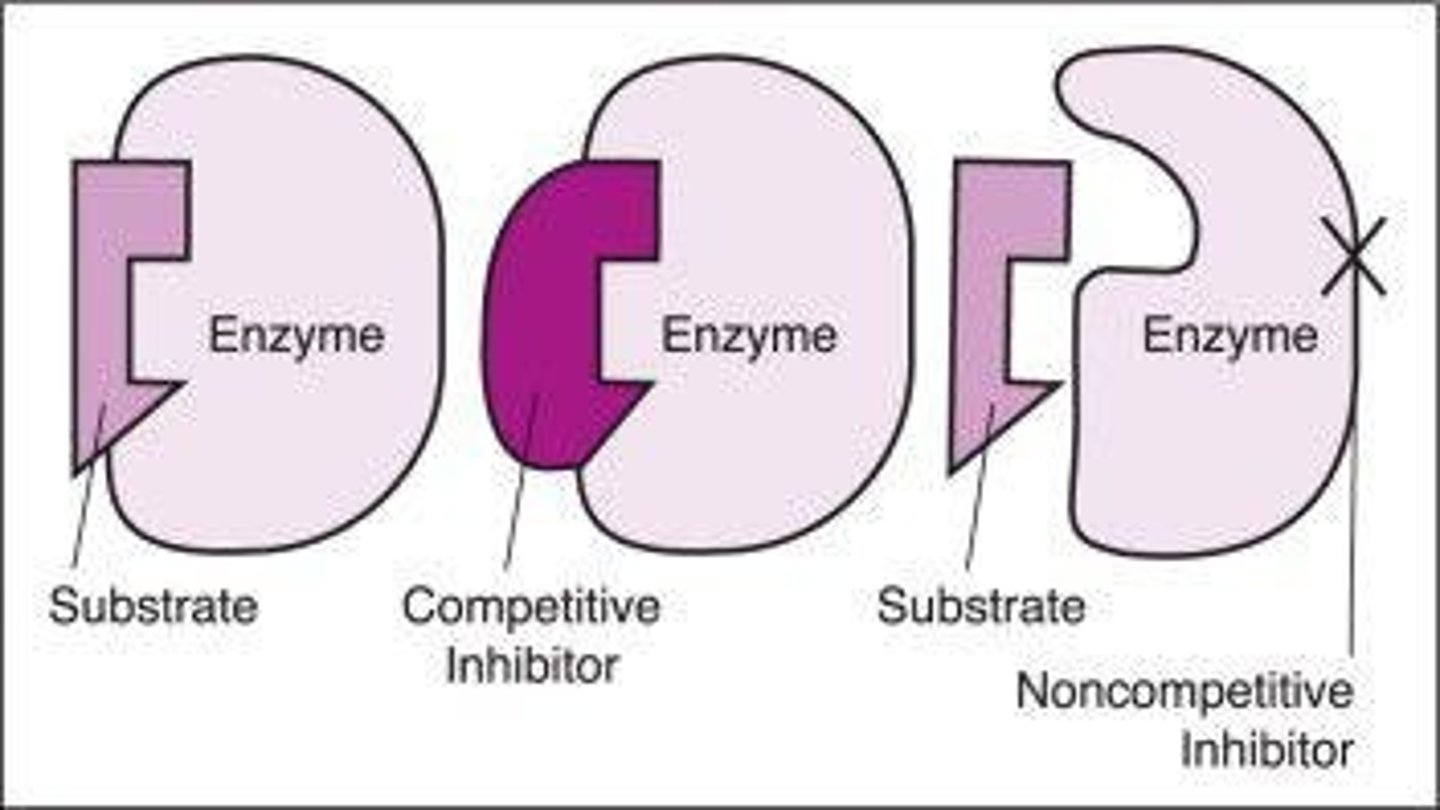
What is non-competitive inhibition?
When an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site.
Give an example of a competitive inhibitor.
Cyanide, which blocks ATP production in cellular respiration.
Give an example of a non-competitive inhibitor.
Penicillin, which prevents the formation of cross-links in bacterial cell walls.