ch.12 pt3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Most women are born with 2 ovaries; however, can have both removed and still become pregnant.
• Embryo is implanted in uterus
true
Ovaries are within the______; symptoms present as nonspecific pain locations
peritoneal cavity
where are the ovaries located
LRQ and LLQ
fallopian tubes
• Projections of the uterus (bilaterally)
• Egg travels from ovary to uterus via fallopian tubes
ovarian cysts
80% resolve without intervention
Ectopic Pregnancy
1%-2% of all pregnancies in the U.S
signs/symptoms of ovarian cyst and ectopic pregnancy
• Abdominal pain
• Vaginal bleeding
• Nausea and/or vomiting
• Abdominal tenderness
• Amenorrhea is common with both conditions
• Absence of a menstrual cycle
testicles
Paired organ that is external to the body
scrotum
A bifurcated sack that houses each testis and epididymis,as well as the spermatic cords
• The cord is a group of vesicles, artery, nerve, and duct
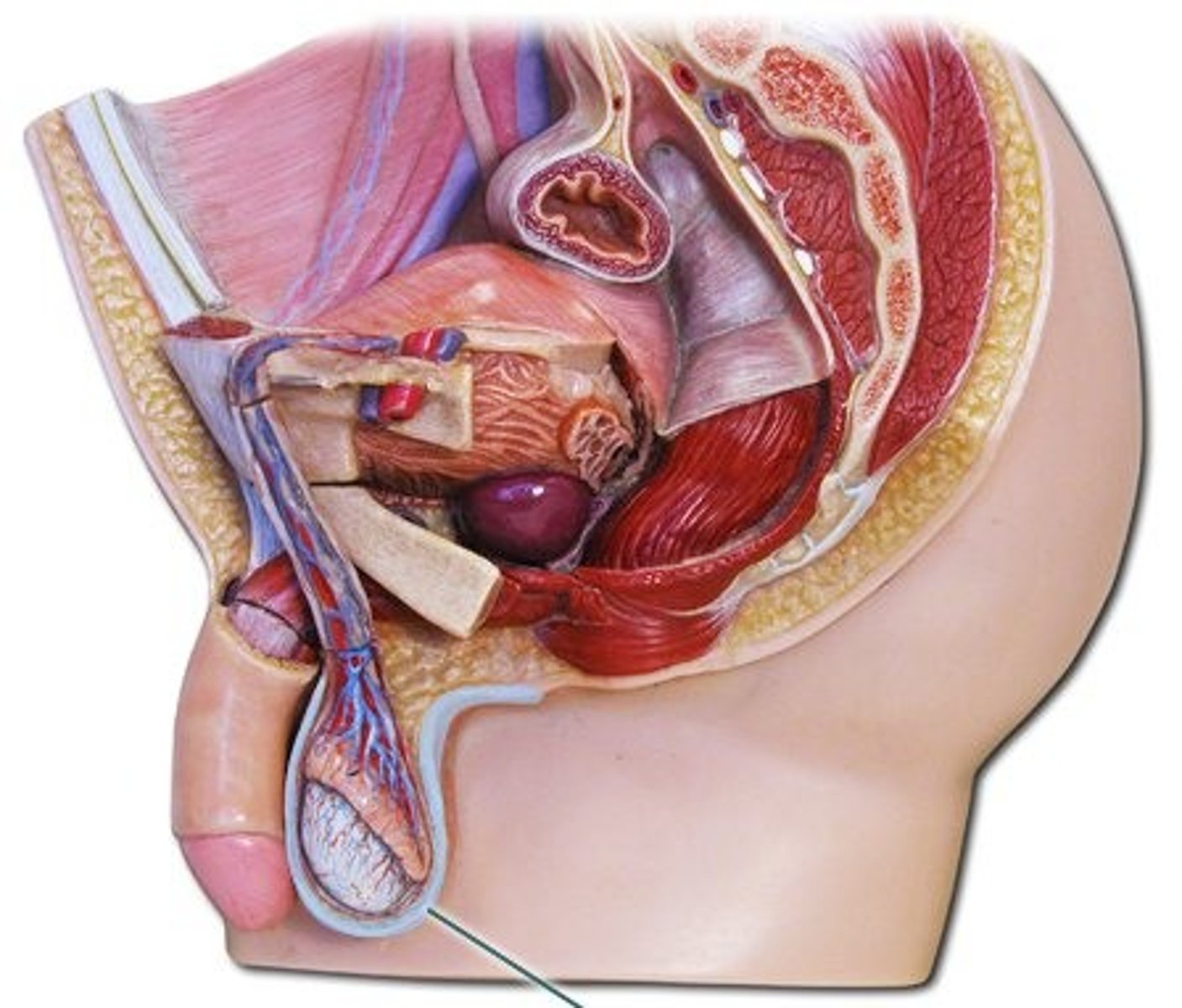
Sperm needs to be maintained at about 2-3°F cooler than the body
true
Dartos and cremaster muscles contract to bring scrotum closer to the body in colder weather and relax in the warmer conditions.
true
More testicular injuries occur in ______ weather than in colder weather,because they are less protected
warmer
testicle contusion
Blood accumulating within the testis or between the testis and the scrotum
testicular torsion
Causes infarct due to the spermatic cord twisting to a point where nutrients no longer reach the individual testis
Acute trauma to male genitals symptoms
• Nausea, vomiting, hyperventilation, pale skin•
Often not able to effectively communicate pain symptoms immediately after injury
Signs of testicular contusions
•Swollen testicle, sometimes to the point where scrotum appears stretched to capacity
Signs of testicular torsion
Higher testicle than typical for the patient, or a transverse-lying of the affected testis
testiucular contusion or torsion conditions should be referred immediately to a
urologist
Testicular detorsion that occurs within 6 hours of injury has the highest testicle salvage rate.
true
trauma to abdominal organs
Observe, auscultate, palpate, percuss
Patient should be supine or hook lying for exam
Blunt abdominal trauma as a common lead cause of mortality and morbidly
true
Observing the abdomen
Rigidity, bruising, scrapes; signs of internal or external bleeding
Auscultate the abdomen
Listen with stethoscope for normal or abnormal GI sounds
palpate the abdomen
• Size and quality of superficial organs (pain), fluid, or gas
• If no pain, palpate each quadrant deeper
Percuss the abdomen
Listen for quality of sound
History Questions for Evaluating a Blow to the Abdomen
What happened? (Obtain MOI.)
• Have you been ill recently?
• Have you seen the physician recently?
• Have you recently been diagnosed with a sore throat mormononucleosis?
• Have you been very tired lately?
History Questions for aSuspected Gastrointestinal Illness
• When did you begin to feel unwell?
• Where exactly is your pain? Has it moved?
• When was the last time you ate, and what did you eat?• Do you have food allergies or reactions? If so, to what?
• Do you have any chronic gastrointestinal conditions (e.g.,GERD, gastritis, Crohn's disease, celiac disease)?•
When was your last normal bowel movement?(continued)