Radioactivity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Half-life
the time that it takes for half of the radioactive atoms to become stable
Fission
the splitting a nucleus into smaller fragments, with release of large amount of energy
Fusion
the combining nuclei to produce a nucleus of greater mass
Nuclear Reactor
the device used to initiate and control a self-sustained nuclear chain reaction
Calorimeter
the apparatus for measuring heat from a chemical reaction
Thermochemical Reaction
the chemical equation that includes the enthalpy change, ΔH
Specific Heat
the amount of heat needed to raise 1 g of substance 1 oC
Joule
the SI unit of energy
Beta decay
a radioactive process where an unstable nucleus emits a beta particle (high speed electron) and the atom changes from one element to another
Heat
the flow of energy from an object of higher temperature to one of lower temperature
Endothermic
2 AlCl3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g) -- > 2 Al (s) + 6 HCl (aq) ΔH = 1049 kJ
Exothermic
the beaker gets hot
Exothermic
CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) -- > CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) + 890 kJ
Endothermic
absorbs heat
Endothermic
reactants below, products high
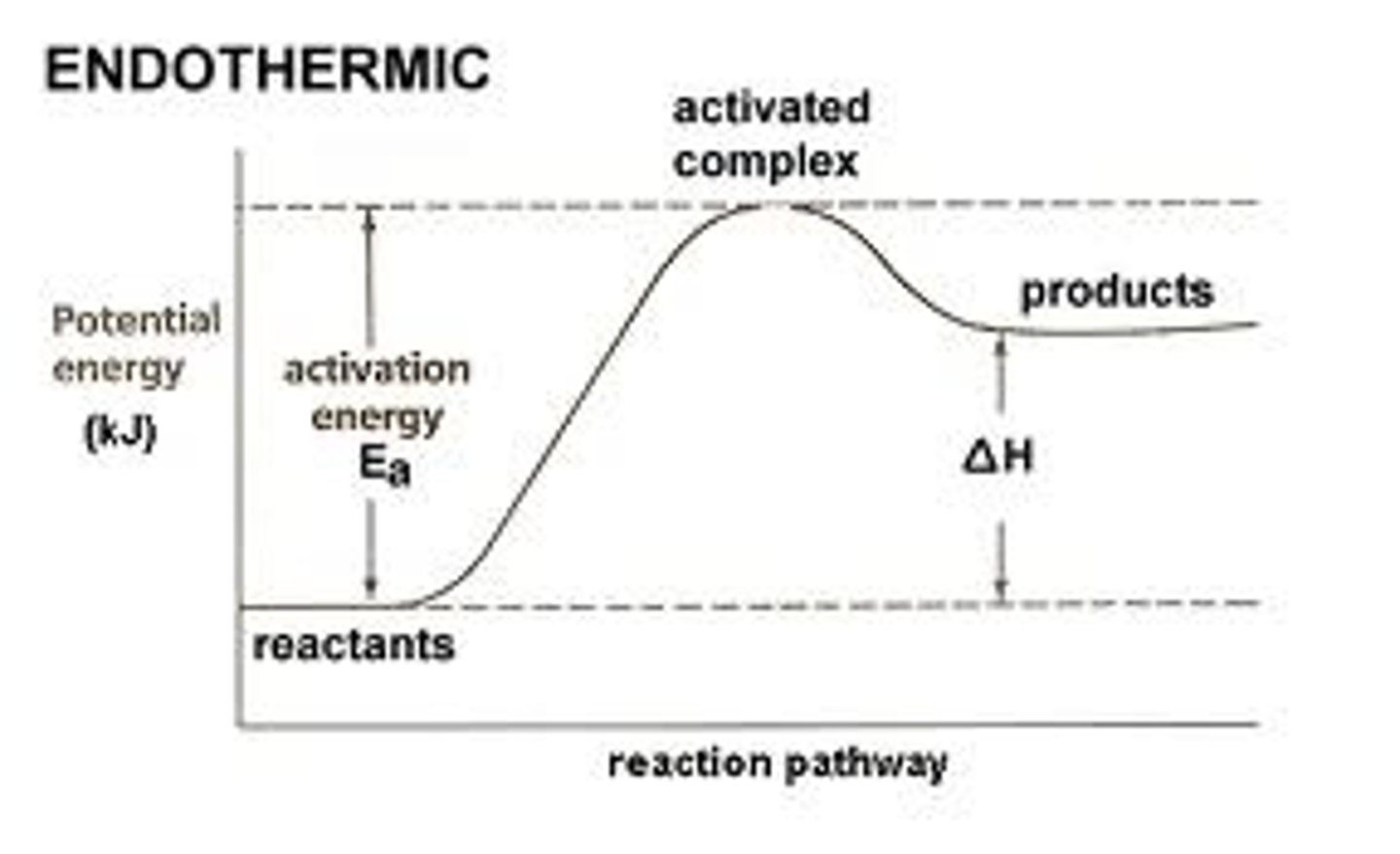
Endothermic
Photosynthesis
True
Heat flows from warmer object to cooler one
True
Radioactivity is greatly affected by temperature, pressure and catakysts