psych exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:24 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
what are some severe medical problems from bulimia nervosa
erosion of dental enamel, electrolyte imbalance, kidney failure, cardiac arrhythmia, seizures, intestinal problems, permanent colon damage
2
New cards
Stice's Dual-Pathway model of bulimic pathology
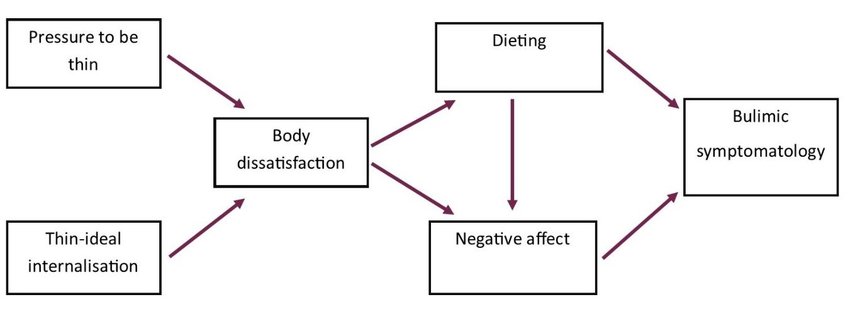
3
New cards
cultural differences used to serve as protective factors
equivalent rates across ethnic groups in US, LGBTQ+ higher rates of ED, food insecurity higher rates of bingeing
4
New cards
who is Emil Kraepelin
coined the term dementia praecox, focused on subtypes of schizophrenia, recognized it as a disease of the brain, recognized that several distinct symptoms appeared to be part of a broader syndrome, differentiated "dementia praecox" from manic-depressive illness
5
New cards
who is Eugen Bleuler
introduced the term schizophrenia, "splitting of the mind"; inability to keep a consistent train of thought, described "positive" and "negative" symptoms (negative symptoms cause more distress)
6
New cards
delusions
distortion in thought content, erroneous beliefs that usually involve a misinterpretation of perception or experiences.
7
New cards
what is persecutory delusions
most common; "the FBI is after me"
8
New cards
what is referential delusions
"when madonna waved to the audience, she was really singing to me"
9
New cards
what is erotomaniac delusions
"madonna is in love with me"
10
New cards
what is somatic delusions
my liver is dead and rotting inside me
11
New cards
what is nihilistic delsuions
the world is ending
12
New cards
what is grandiose delusions
I am president of the entire world
13
New cards
what are "bizarre" delusions
thought insertion, thought withdrawal, outside forces are controlling one's body or actions
14
New cards
what are hallucinations
experience of sensory events without environmental input; can experience in any sensory mode
15
New cards
what is the most common type of hallucination
auditory, usually in the form of "voices" familiar or not, that are heard as being distinct from own thoughts
16
New cards
what are the finding from imaging studies for hallucinations
subtle structural damage in parts of brain associated with auditory processing, thinner cortex
17
New cards
what does fMRI show
activation of auditory regions during auditory hallucinations
18
New cards
what are the disorganized symptoms of schizophrenia
include severe and excess disruptions; speech, behavior and emotion
19
New cards
schizophreniform disorder
schizophrenic symptoms for a few months (less than 6; more than 1); impaired functioning not required; some never progress on to schizophrenia but more do (or schizoaffective disorder)
20
New cards
schizoaffective disorder
symptoms of schizophrenia and mood disorder (unlike a mood disorder with psychotic features); prognosis is similar for people with schizophrenia; such persons do not tend to get better on their own
21
New cards
what is bipolar type schizoaffective disorder
if mania is part of the presentation
22
New cards
what is a depressive type schizoaffective disorder
if only major depressive episodes are part of the presentation
23
New cards
what is delusional disorder
presence of one or more delusions that persist for 1 month or more; lack other positive or negative symptoms; rare (0.2%), better prognosis than schizophrenia
24
New cards
what are the types of delusional disorder
erotomaniac ( someone else is in love with person), grandiose, jealous (spouse or partner is unfaithful), persecutory, somatic (involved bodily functions or sensations), bizarre content ( clearly implausible, not understandable)
25
New cards
brief psychotic disorder
one ore more positive symptoms of schizophrenia (delusions, hallucinations, disorganized behavior/speech, lasts at least 1 day but not longer than 1 month), not due to substance use, usually precipitated by extreme stress or trauma, tends to remit on its own
26
New cards
schizotypal personality disorder
may reflect a less severe form of schizophrenia
27
New cards
process vs reactive distinction
process - insidious onset, biologically based, negative symptoms, poor prognosis
reactive - acute onset (extreme stress), notable behavioral activity, best prognosis
reactive - acute onset (extreme stress), notable behavioral activity, best prognosis
28
New cards
good vs poor premorbid functioning in schizophrenia
focus on functioning prior to developing schizophrenia, no longer widely used
29
New cards
type 1 vs type 2 distinction
Type 1 - positive symptoms, good response to medication, optimistic prognosis, and absence of intellectual impairment
type 2 - negative symptoms, poor response to medication, pessimistic prognosis, and intellectual impairments
type 2 - negative symptoms, poor response to medication, pessimistic prognosis, and intellectual impairments
30
New cards
paranoid subtype of schizophrenia
presence of prominent hallucinations and delusions (usually persecution or grandeur) but have relatively intact cognitive skills and affect; organized around coherent theme; do not show disorganized behavior, later onset, the best prognosis of all types of schizophrenia
31
New cards
disorganized subtype of schizophrenia
marked disruption in speech and behavior (flat or inappropriate affect, hallucination and delusions, if present, tend to be fragmented, develops early, tends to be chronic, associated with a continuous course without remissions)
32
New cards
catatonic subtype of schizophrenia
show unusual motor response and off mannerisms (immobility, excessive motor activity, motor negativism, waxy flexibility), tends to be severe and quite rare
33
New cards
what is echolalia
mimic or repeat words
34
New cards
what is echopraxia
mimic movements
35
New cards
undifferentiated subtype of schizophrenia
wastebasket category, major symptoms of schizophrenia, fail to meet criteria for another type
36
New cards
residual subtype of schizophrenia
past diagnosis of schizophrenia, absence of prominent delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and behaviors, continue to display less extreme residual symptoms
37
New cards
family studies for schizophrenia
inherit a tendency for schizophrenia, do not inherit specific forms of schizophrenia (different subtypes and different forms of psychotic disorders), risk increases with genetic relatedness
38
New cards
twin studies for schizophrenia
monozygotic twins - risk for schizophrenia is 48%
fraternal twins - risks drops to 17%
both parents schizophrenia - 46%
on schizophrenic parent - 16%
fraternal twins - risks drops to 17%
both parents schizophrenia - 46%
on schizophrenic parent - 16%
39
New cards
adoption schizophrenia studies
risk for schizophrenia remains high in cases where a biological parent has schizophrenia, appears to be significant overlap in the genes that contribute to schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorders and manic syndromes
40
New cards
summary of genetic research for schizophrenia
risk of schizophrenia increases with genetic relatedness, risk transmitted independently of diagnosis, strong genetic component does not explain everything, can be a 'carrier" of schizophrenia genes but does not display disorder
41
New cards
structural abnormalities in the brain
brain dysfunction appears before onset of schizophrenia
42
New cards
children and structural and functional abnormalities in the brain with schizophrenia
lower intelligence and achievement scores than healthy siblings as children, abnormalities in social behavior, less socially responsive, show less positive emotion, poorer social adjustment, delays and abnormalities in motor development
43
New cards
adolescents and structural and functional abnormalities in the brain with schizophrenia
subclinical signs of psychosis (unusual ideas and sensory experiences; eccentric behavior - signs of schizotypal personality disorder)
44
New cards
tardive dyskinesia
involuntary movements of the tongue, face, mouth and jaw (tongue sticking out, chewing motions), irreversible
45
New cards
agranulocytosis
severe reduction in white blood cells - caused by Clozaril
46
New cards
cognition for general criteria for all personality disorders
ways of perceiving and interpreting self, other people and events
47
New cards
affectivity for general criteria for all personality disorders
range, intensity, lability, and appropriateness of emotional response
48
New cards
general criteria for all personality disorders
cognition, affectivity, interpersonal functioning, impulse control
49
New cards
which personality disorders did they try to get rid of
paranoid PD, schizoid PD, histrionic PD, dependent PD
50
New cards
paranoid PD
a pattern of distrust and suspiciousness such that others motives are interpreted as malevolent
51
New cards
schizoid PD
a pattern of detachment from social relationships , and a restricted range of emotional expression
52
New cards
schizotypal PD
a pattern of acute discomfort in close relationships, cognitive or perceptual distortions, and eccentricities of behavior
53
New cards
what is another name for Cluster A of PD
the weird w
54
New cards
what PD are in cluster A
paranoid, schizoid and schizotypal
55
New cards
what is another name for cluster B
the wild
56
New cards
what PD are in cluster B
antisocial, borderline, histrionic, narcissistic
57
New cards
antisocial PD
a pattern of disregard for, and violation of the rights of others
58
New cards
borderline PD
a pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and affects and marked impulsivity
59
New cards
histrionic PD
a pattern of excessive emotionality and attention seeking
60
New cards
narcissistic PD
a pattern of grandiosity, need for admiration, and lack of empathy
61
New cards
what is another name for cluster C
the worried
62
New cards
what PD are in cluster C
avoidant, dependent , and OCPD
63
New cards
avoidant PD
a pattern of social inhibition, feelings of inadequacy, and hypersensitive to negative evaluation
64
New cards
dependent PD
a pattern of submissive and clinging behavior related to the excessive need to be taken care of
65
New cards
OCPD
a pattern of preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism and control
66
New cards
dimensional versus categorical
using a general model of personality is very clearly a dimensional approach - no attempt to delineate normal from "disordered"
67
New cards
comorbidity of PD
# of PD diagnoses patients typically receive varies: 2.4 and 4.6
68
New cards
narcissism and antisocial _____ be comorbid given the string shared component of antagonism
SHOULD
69
New cards
gender differences of PD
gender differences in prevalence rates of PDs should be consistent with gender differences in general personality functioning (men lower in agreeableness: antisocial narcissistic; women higher in neuroticism: borderline, dependent)
70
New cards
coverage of PD
most common PD diagnosis in clinical practice- personality disorder not other specified
71
New cards
identity self impairment
experience oneself as unique, with clear boundaries between self and others; stability of self-esteem and accuracy of self-appraisal; capacity/ability to regulate emotional experience
72
New cards
self-direction self impairment
pursuit of coherent and meaningful short and long term goals; use of constructive and prosocial internal standards of behaviors, ability to self-reflect
73
New cards
empathy interpersonal impairment
comprehension and appreciation of others experiences and motivations; tolerance of different perspectives, understanding the effects of one's own behavior on others
74
New cards
intimacy interpersonal impairment
depth and duration of connection with others, desire and capacity for closeness, mutuality or regard reflected in interpersonal behavior
75
New cards
antisocial PD impairment
geocentricism, goal setting based on personal gratification; lack of concern for others; exploit, deceive, dominant, coerce others
76
New cards
traits of antisocial PD
manipulativeness, callousness, deceitfulness, hostility, risk taking, impulsivity, irresponsibility (6 or 7)
77
New cards
overview and clinical features of paranoid PD
pervasive and unjustified mistrust and suspicion
78
New cards
what are the causes of paranoid PD
biological and psychological contribution are unclear, early learning that the world is a dangerous place, evidence unclear whether it is a variant of psychotic disorder; research suggests "maybe"
79
New cards
treatment options for paranoid PD
few seek professional help on their own, treatment focuses on development of trust, cognitive therapy to counter negativistic thinking, lack good outcome studies
80
New cards
overview and clinical features of schizoid PD
pervasive pattern of detachment from social relationships (not interested in close relationship, little interest in sexual experiences, no close friends, indifferent to praise or criticism), very limited range of emotions in interpersonal situations (takes pleasure in few things, flattened affectivity - appear cold, detached)
81
New cards
causes of schizoid PD
etiology is unclear, preference for social isolation resembles autism, an extreme variant of shyness/introversion?
82
New cards
treatment options for schizoid PD
few seek professional help on their own, focuses on the value of interpersonal relationships, building empathy and social skills, lack good outcome studies
83
New cards
overview and clinical features of schizotypal PD
odd and unusual behavior, appearance and cognition, most are socially isolated, highly suspicious, magical thinking, ideas of reference and illusions, unusual perceptual experiences, many meet criteria for major depression
84
New cards
causes of schizotypal PD
a phenotype of a schizophrenia genotype? diagnosis came about a result of research on family members of schizophrenics; higher rates of schizotypal PD in family members of schizophrenic
85
New cards
treatment options for schizotypal PD
main focus is on developing social skill, treatment also addresses comorbid depression, medical treatment similar to schizophrenia - use of antipsychotics, treatment prognosis is generally poor
86
New cards
overview and clinical features of antisocial PD
noncompliance with social norms, violate rights of others, irresponsible, impulsive and deceitful, lack empathy and remorse, lack concern for safety of self or others, must be evidence of conduct disorder before age 15
87
New cards
symptoms of borderline PD
frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment, a pattern of unstable and intense interpersonal relationships characterized by alternating between extremes of idealization and devaluation, identity disturbance, impulsivity in a least 2 areas that are potentially self-damaging, recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures, or threats or self-mutilating behavior, affective instability due to marked reactivity of mood, chronic feelings of emptiness, inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger, transient, stress-related paranoid ideation or severe dissociative symptoms
88
New cards
causes of borderline PD
runs in families, early trauma and abuse seem to play some role, major theory is biosocial
89
New cards
what is biosocial theory
emotionally vulnerable individual (excessive reaction to stress, long recovery rate following stressor), invalidating environment (broadly conceived, being told feelings aren't ok or reasonable, being told perceptions are wrong; physical or sexual abuse - invalidates one's autonomy, sense of boundaries, privacy)
90
New cards
overview and clinical features of histrionic PD
overly dramatic, sensational, and sexually proactive, impulsive and need to be the center of attention, thinking and emotions are perceived as shallow, common diagnosis in females
91
New cards
causes of histrionic PD
etiology is largely unknown, sex-typed variant of anti-social personality?
92
New cards
treatment options of histrionic PD
focus on attention seeking/ long-term consequences, address problematic interpersonal behaviors, little evidence that treatment is effective
93
New cards
overview and clinical features of narcissistic
exaggerated/unreasonable sense of self-importance, preoccupation with receiving attention, lack sensitivity and compassion for other people, sensitive to criticism, envious and arrogant, mainly causes social impairment
94
New cards
causes of narcissistic PD
link with early failure to learn empathy as a child because of parents failure to effectively "mirror" a child, parents are spiteful and cold but find 1 talent or quality in the child to reward, child over-valued - parents provide non-contingent praise, attention and tribute to the child, appears that over OR under evaluation can cause it r
95
New cards
treatment options for narcissistic PD
focuses on grandiosity, lack empathy, little evidence that treatment is effective
96
New cards
overview and clinical features of avoidant PD
extreme sensitivity to the opinions of others, highly avoidant of most interpersonal relationships, interpersonally anxious and fearful of rejection, "Look like" schizoid individuals
97
New cards
causes of avoidant PD
numerous factors have been proposed, difficult temperament and early rejection, recall feeling isolated and rejected in childhood, extreme variant of introversion
98
New cards
treatment options for avoidant PD
several well-controlled treatment outcome studies exist, treatment is similar to that used for social phobia, treatment targets include social skills and anxiety-reduction
99
New cards
overview and clinical features of dependent PD
reliance on others to make major and minor life decisions, unreasonable fear of abandonment, clingy and submissive in interpersonal relationships, focused on maintenance of supportive/nurturing relationships
100
New cards
causes of dependent PD
largely unclear (may be due to feelings of incompetence and low self-efficacy), linked to early disruptions in learning independence, early disruption of important attachment relationships, temperamental differences in negative emotionality