Chapter 7
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Fiber-reinforced
Composite in which the one material forms the outer matrix and transfers any loads applied to the stronger, more brittle fibers (e.g. kevlar-epoxy)
Particulate
Composite that contains large numbers of coarse particles to reinforce the matrix (e.g. concrete)
Laminar
composite that is made by alternating the layering of different materials affixed together with an adhesive (e.g. plywood)
Hybrid
composite made of other composite materials (e.g. rebar-reinforced concrete)
Fibers
withstands tensile loads in the direction of alignment; thinner and longer is better
Aligned fibers
handle loads in the longitudinal direction but contribute nothing to handling transverse loads
Transverse fibers
perpendicular to composites and handle loads in transverse direction
Matrix
surrounds and orients the fiber. Protects fibers from environment and transfers load
Aspect ratio
is the ratio of fiber length to diameter
(l/d). Large aspect ratios result in stronger composites, but they are more difficult to orient and are often limited by the size of the composite itself
critical length (lc)
above which the fiber behaves roughly as if it were infinitely long lc = sfd/2ti
isostrain condition
If the quality of bonding between the fiber and matrix is sufficient, they elongate at the same rate under stress and experience the same strain
Fiber Pull-out
When the bonding is less strong, the bonds between the fiber and matrix break
isostress condition
When the load is applied in the transverse direction, the fibers provide essentially no reinforcing benefit to the matrix. All the stresses experienced by the fibers and matrix are the same
Uniaxial
Fibers aligned along a single axis in almost perfect alignment. Composite is much stronger in the longitudinal direction than
the transverse
Chopped
The random orientation of small chopped fibers provides essentially isotropic properties in all directions. Because the fibers are smaller and only a fraction are oriented in any specific direction they are much less strong than
uniaxial composites
Resin formulation
Bits of chopped fiber and poured or blown into the matrix material (often already in the desired mould) Curing agents, accelerators, diluents, fillers, and pigments are added as well. The matrix material hardens into the shape of the mold
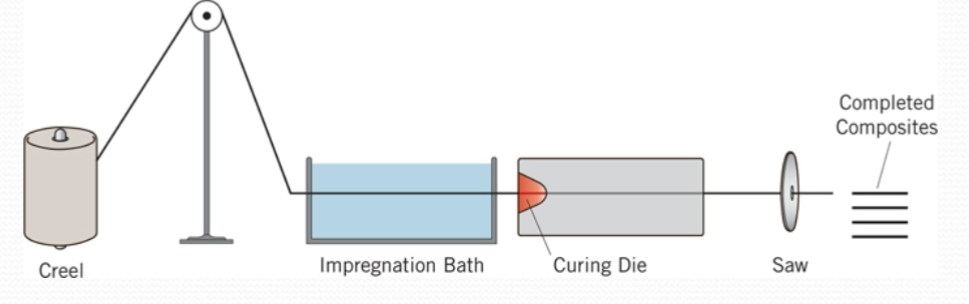
Pultrusion
Large numbers of single strands are wound in
parallel to form a roving. Many rovings are connected into a device called a creel that lets fibers to be pulled together. Fibers are coated with matrix material and are cured in a heated die then cut into shape
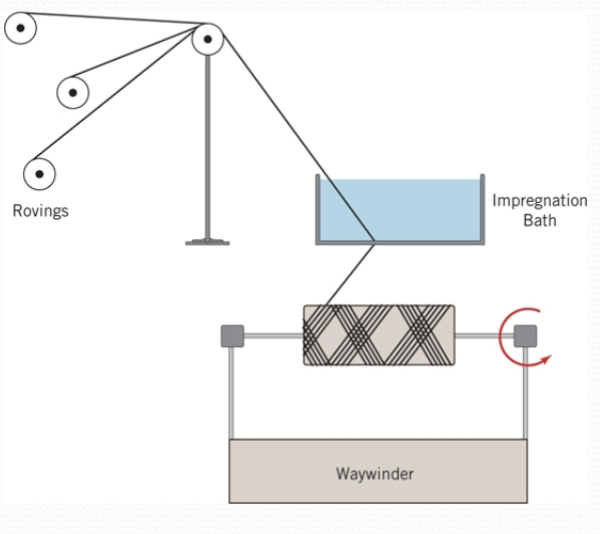
Wet filament winding
Continuous fibers from rovings are pulled through a resin impregnation bath then wound
into the desired shape. When enough wet filaments are wound around the part, it is
taken to a curing oven to complete a composite of the desired shape
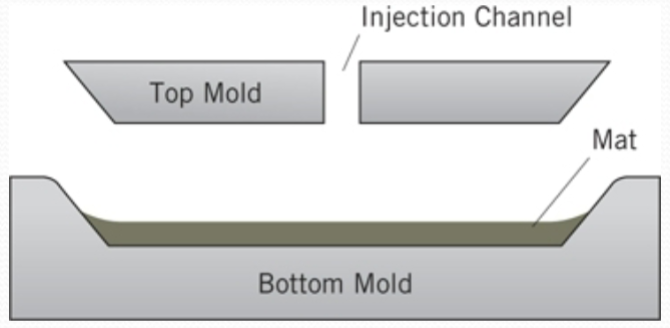
Resin Transfer Molding
Woven fiber mats are placed into a space between the top and bottom mold. Resin is injected through the top cavity under sufficient
pressure to ensure that it penetrates and surrounds the mat. The molds are cured using heat and pressure to create a composite part in the shape of the mold
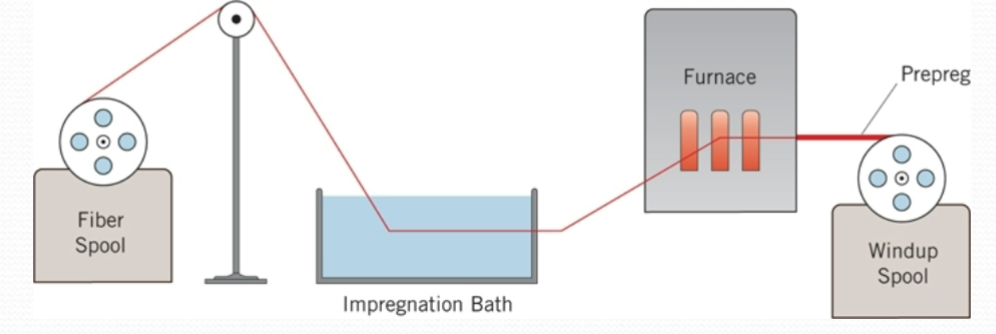
Prepregging
Fibers are passed through an impregnation bath that coats them with small quantities of resin. They are then passed through a furnace and heated slightly to ensure that the resin sticks to the fiber. The resulting coated fibers can be used later to form composites
Specific strength
tensile strength divided by density
Tradeoffs
Ceramic fibers tend to be strong and stiff, but dense. Glass fibers offer chemical resistance and blend of properties but are easily broken during processing. Metals are strong but are also heavy. High performance polymers are strong and light, but have trouble withstanding compressive forces
Polyester Resins
most common and economical resin
Isophthalic Polyester Resins
used when water resistance is needed
Epoxy Resins
more expensive but provide improved
mechanical properties and exceptional environmental resistance
Vinyl Ester Resins
compromise between the economic advantages of polyester and the properties of epoxy
Phenolic Resins
Poor mechanical properties but excellent fire resistance
Polyimide Resins
expensive and used only for high-end applications such as missiles and military aircraft
Metal Matrix Composites
High strength. Excellent environmental resistance. Greater thermal conductivity and abrasion resistance
Ceramic Matrix Composites
Increased fracture toughness. Ability to withstand extremely high temperatures. Corrosion resistance
Particulate Composites
Contain a large number of randomly oriented particles called aggregate that help the composite withstand compressive loads. Tend to be isotropic and are free from orientation issues. Include the most important commercial composite (e.g. concrete is mix of gravel and Portland Cement)
Hydration Catalysts
alter the rate of hydration in the Portland Cement. Accelerators speed up the reactions, while retarders slow them down
Air-Entrainers
cause tiny air bubbles to form and distribute throughout the concrete to withstand the freeze-thaw expansion cycles without failing
Plasticizers
reduce the viscosity of the cement paste, making it easier to flow the concrete mixture into its final form
Modulus of Rupture
The maximum tensile strength at the bottom of the test beam
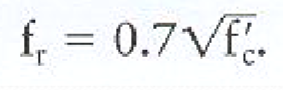
Rebar
Steel-deformed reinforcing bars that add strength to concrete. The result is a hybrid composite with the concrete serving as the matrix and the rebar handling tensile loads
Asphalt
blend of a mineral aggregate in an asphalt binder. Costs much less than concrete, but lasts only half as long
Hot-Mix Asphalt Concrete (HMAC) Process
uses asphalt softened at 160°C before mixing the aggregate then the road is compacted at 140°C. Significant amount of organic vapors are released
Warm-Mix Asphalt Concrete (WAM) Process
uses zeolites to reduce the softening temperature by as much as 25°C, resulting in reduced emissions and lower costs
Cold-Mix Asphalt Process
adds water and surfactant molecules to the asphalt before mixing it with the aggregate.
When the water evaporates, the properties are similar to asphalt produced by the HMAC process. Used for patches
Plywood
layers of wood veneers bonded together
by adhesives. More resistant to shrinking and warping than regular wood because of crossbanding
Sandwich composites
Used to increase strength with little weight. the honeycomb can be made of cardboard, but high-performance polymers are used for higher-end applications