17. Lower respiratory tract diseases: Chronic bronchitis, Feline asthma.
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is chronic bronchitis?
Long-term inflammation of bronchial airways, involving a cough lasting more than 2 months
Which animals are mostly affected by chronic bronchitis?
Middle-aged/old, small, obese dog breeds
What are some potential causes of chronic bronchitis?
Unknown, but may include chronic inflammation of mucous membranes, immunological stimulation, congenital IgA deficiency, decreased ciliary clearance, smoke inhalation, and exposure to chemical fumes
What can worsen the cough associated with chronic bronchitis?
Sudden changes in weather or other environmental stresses
What is the pathogenesis of chronic bronchitis?
Neutrophil infiltration leading to protease and toxic oxidant release, damaging mucous membranes and causing chronic cycles of inflammation, hypertrophy and hyperplasia of mucous glands and cells, mucus overproduction, and airway obstruction
What are some clinical signs of chronic bronchitis?
Chronic coughing for 2 months (dry/wet/sharp), abdominal pressure when coughing, exercise intolerance, tachypnoea, crackles, harsh, noisy sounds, and prolonged expiration
How is chronic bronchitis diagnosed?
History, clinical signs, haematology, biochemistry, biopsy, swab, culture, parasitology, and X-rays
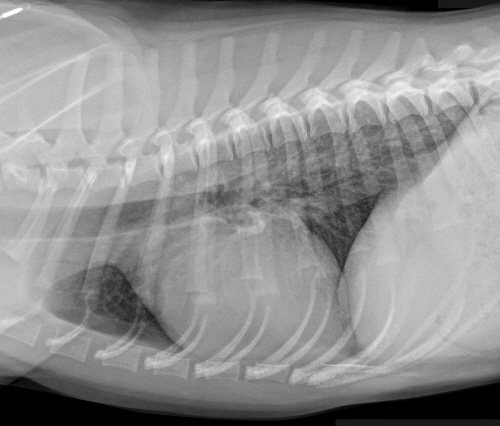
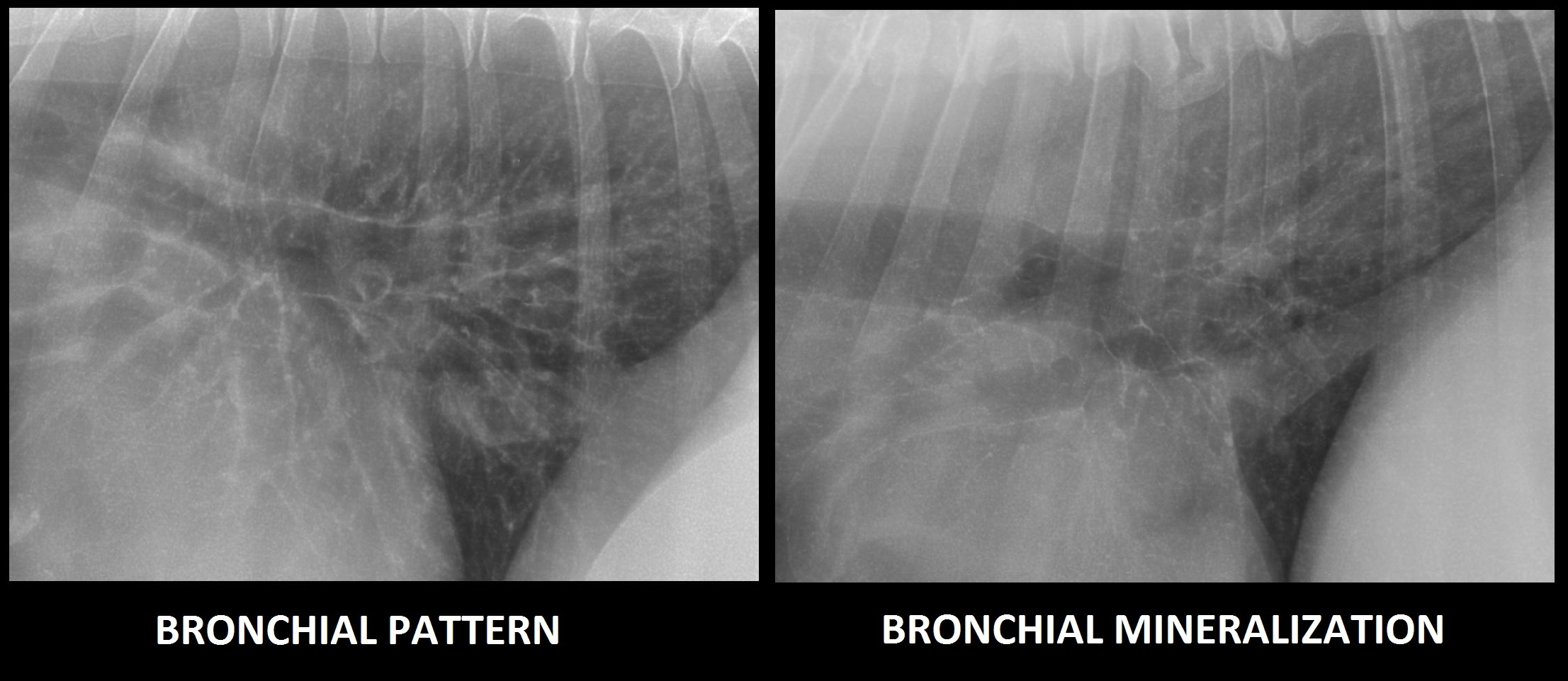
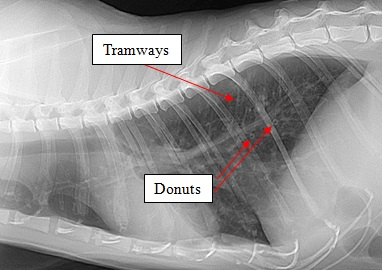
What are characteristic X-ray findings in chronic bronchitis?
Mucus in airways outlining the shape of airways in patterns that look like parallel lines (tram lines) or circles (doughnuts)
What are some treatments for chronic bronchitis?
Corticosteroids
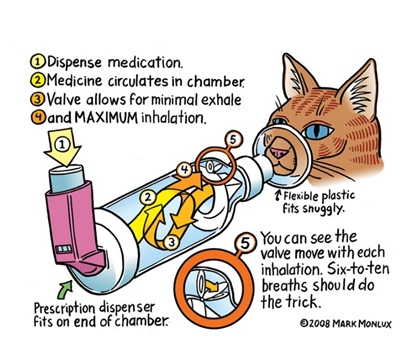
Nebulisation/inhaler
Bronchodilators (aminophylline)
Long-term antibiotics
Antitussives (dextromethorphan)
Mucolytics (calcium iodide, potassium iodide)
Weight loss
owner smoking cessation/avoidance of collars
What is feline bronchial asthma (allergic bronchitis)?
Inflammation of lower airways without an obvious identifiable cause, associated with airway hyperresponsiveness, airflow obstruction, airway remodelling, and eosinophilic airway inflammation
Which cats are most often affected by feline bronchial asthma?
Young cats, especially Siamese and Himalayan breeds
What is the most likely cause of feline bronchial asthma?
Allergy to inhaled substances (pollen, house dust mites)
What is the pathogenesis of feline bronchial asthma?
Allergens→ histamine release, mast cell activation, and eosinophilic secretions → inflammation, mucous membrane oedema, mucus overproduction, epithelial necrosis, and bronchoconstriction
What are some clinical signs of feline bronchial asthma?
Cough (lay on floor with neck extended), respiratory distress, cyanosis, noisy breathing (wheezing), and open-mouth breathing

Why is feline bronchial asthma often misdiagnosed?
Vomiting
How is feline bronchial asthma diagnosed?
History, physical examination
Laboratory examination (biopsy, swabs, haematology showing eosinophilia, neutropenia, monocytosis)
Bronchoalveolar lavage (eosinophilia)
Bronchoscopy
X-ray (air trapping, over-inflation)
What are some differential diagnoses for feline bronchial asthma?
Heart and lung diseases
What are some treatments for feline bronchial asthma?
Oxygen, corticosteroids, bronchodilators, mucolytics, and broad-spectrum antibiotics
Is feline bronchial asthma curable?
No, the bronchial changes are considered irreversible
What is a typical type of body position for cats coughing?
Cats lie on the floor with elongated neck and cough
Which method can be used to diagnose chronic bronchitis in dogs, but not cats?
Endoscopy and biopsy
What type of reaction leads to feline asthma?
Histamine response