QC Topics (weeks 2 and 3)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:49 PM on 10/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Msbuild
Microsoft build platform for builing appications
2
New cards
Common Language Infrastructure
a Microsoft specification for running high-level language program applications in different computer systems without changing the application code. CLI is based on the Microsoft .NET concept that some high-level language programs require modifications due to system hardware and processing constraints
3
New cards
Automatic Memory Management
Automated system for allocating and deallocating memory. C# specifically has a garbage collector That handles is automatic memory management
4
New cards
NuGet and Package References
a NuGet package is a single ZIP file with the .nupkg extension that contains compiled code (DLLs), other files related to that code, and a descriptive manifest that includes information like the package's version number. Developers with code to share create packages and publish them to a public or private host. Package consumers obtain those packages from suitable hosts, add them to their projects, and then call a package's functionality in their project code. NuGet itself then handles all of the intermediate details.
5
New cards
xUnit
xUnit is a free, open source Unit testing framework for .Net
6
New cards
Theory tests with inline data
The Theory attribute in XUnit specifies that a test method can have inputs, and that the method needs to be tested for many different combinations of inputs.
Test methods marked with the [Theory] attribute can have input parameters, and have values passed to them by using the [InlineData] attribute. In this way, a single test method can support many tests, and developers save significant time writing tests by using these attributes.
Test methods marked with the [Theory] attribute can have input parameters, and have values passed to them by using the [InlineData] attribute. In this way, a single test method can support many tests, and developers save significant time writing tests by using these attributes.
7
New cards
AAA (Unit testing)
Arrange, Act, Assert:
The Arrange section of a unit test method initializes objects and sets the value of the data that is passed to the method being tested.
The Act section invokes the method being tested with the arranged parameters.
The Assert section verifies that the action of the method being tested behaves as expected. For .NET, methods in the Assert class are often used for verification.
The Arrange section of a unit test method initializes objects and sets the value of the data that is passed to the method being tested.
The Act section invokes the method being tested with the arranged parameters.
The Assert section verifies that the action of the method being tested behaves as expected. For .NET, methods in the Assert class are often used for verification.
8
New cards
List
A generic collection type in C# used to store a set of data of the same type
9
New cards
foreach
A feature usable by classes that inherit from IEnnumerable that allow for the iteration through all data stored by the class
10
New cards
Linked List
consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list
11
New cards
Queue
A collection of data the has FIFO Access. This can be thought of as a line at the bank where the first person in gets, served the last person in line is served last.
12
New cards
Stack
A collection of data that has FILO access. This can be thought of as a stack of papers, only the last element added
13
New cards
Hashset
An unordered data structure used for holding unique elements
14
New cards
Dictionary
An unordered data structure for storeing key value pairs
15
New cards
Unmanaged Resources
Resources that need to be disposed or closed after use
16
New cards
IDisposable
An interface needed to use a using statement, on garbage collection the dispose method will be called so that any resources will be released
17
New cards
using statments
A new feature in C# used to automatically release resources when it is finished. It need to implements the IDisposable interface
18
New cards
Serialization
The object is serialized to a stream that carries the data. From that stream, the object can be stored in a database, a file, or memory.
19
New cards
persistence
Data a program uses can still exist for the next runtime of the program.
20
New cards
Logging
the process of recording events in software as they happen in real-time, along with other information such as the infrastructure details, time taken to execute, etc. Logging is an essential part of any software application. Having logs is crucial, especially when things go wrong. Logs help you understand the failures or performance bottlenecks and fix the problems.
21
New cards
Inheritance
Inheritance is all about inheriting the common state and behavior of parent class (super class) by its derived class (sub class or child class). A sub class can inherit all non-private members from super class, by default.
22
New cards
Upcasting
conversion from a derived (child) class to a base (parent) class; in other words, going up the family tree.
23
New cards
Downcasting
going from a base class to a derived class; in other words down the family tree.
24
New cards
overriding
overriding is a feature that allows a subclass or child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its super-classes or parent classes
25
New cards
Abstract class
is the process of hiding the internal details and showing only the functionality. An abstract class is the way abstraction is achieved in C# using the "abstract" prefix
26
New cards
Constructors
A specialized method used to construct a new object from a class
27
New cards
Dependency Injection
A dependency is an object that another object depends on. Dependency Injection (or inversion) is basically providing the things that an object needs, instead of having to construct the objects themselves.
28
New cards
Structs
is a value type that can encapsulate data and related functionality
29
New cards
Enums
is a value type defined by a set of named constants of the underlying integral numeric type
30
New cards
Boxing
Boxing is the process of converting a value type to the type object or to any interface type implemented by this value type.
31
New cards
Unboxing
Unboxing extracts the value type from the object
32
New cards
Generics
Generics introduces the concept of type parameters to .NET, which make it possible to design classes and methods that defer the specification of one or more types until the class or method is declared and instantiated by client code.
33
New cards
User defined Exceptions
.NET provides a hierarchy of exception classes ultimately derived from the Exception base class. However, if none of the predefined exceptions meet your needs, you can create your own exception classes by deriving from the Exception class.
34
New cards
Extension methods
Extension methods enable you to "add" methods to existing types without creating a new derived type, recompiling, or otherwise modifying the original type. Extension methods are static methods, but they're called as if they were instance methods on the extended ty
35
New cards
Delegates
A delegate is a type that represents references to methods with a particular parameter list and return type. When you instantiate a delegate, you can associate its instance with any method with a compatible signature and return type. You can invoke (or call) the method through the delegate instance.
Delegates are used to pass methods as arguments to other methods. Event handlers are nothing more than methods that are invoked through delegates. You create a custom method, and a class such as a windows control can call your method when a certain event occurs.
Delegates are used to pass methods as arguments to other methods. Event handlers are nothing more than methods that are invoked through delegates. You create a custom method, and a class such as a windows control can call your method when a certain event occurs.
36
New cards
Lamda Expressions
You use a lambda expression to create an anonymous function. Use the lambda declaration operator => to separate the lambda's parameter list from its body.
37
New cards
Linq
Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) is the name for a set of technologies based on the integration of query capabilities directly into the C# language.
38
New cards
Pattern Matching
Pattern matching is a technique where you test an expression to determine if it has certain characteristics.
39
New cards
out parameters
The out keyword causes arguments to be passed by reference. It makes the formal parameter an alias for the argument, which must be a variable. In other words, any operation on the parameter is made on the argument. It is like the ref keyword, except that ref requires that the variable be initialized before it is passed
40
New cards
nullable reference types
The specific operators used to allow null values in C#
41
New cards
Four principles of OOP
A PIE, Abstraction, Polymorphism, Inheritance, and Encapsalation
42
New cards
SOLID
Single responsibility, Open-closed, Liskov substitution, Interface segregation, and Dependency inversion
43
New cards
Seperation of concerns
The principle is simple: don’t write your program as one solid block, instead, break up the code into chunks that are finalized tiny pieces of the system each able to complete a simple distinct job.
44
New cards
Singleton pattern
A Singleton is a design pattern which allows the creation of an object in memory only once in an application and can be shared across multiple classes. It can be useful for services in an application, or other resources like a connection or thread pool.
45
New cards
Factory Method Pattern
One definition reads as, “Define an interface for creating an object, but let the subclasses decide which class to instantiate. The Factory method lets a class defer instantiation it uses to subclasses”.
46
New cards
Test-Driven Development
The TDD process consists of writing unit tests first, before the implemented application code has been written. Then, the implemented application code can be written to make the test pass and the process can be completed for each piece of functionality required
47
New cards
Azure
Microsoft's cloud platform
48
New cards
RDBMS (definition)
The software used to store, manage, query, and retrieve data stored in a relational database is called a relational database management system
49
New cards
Normalization
database design technique that reduces data redundancy
50
New cards
First normal Form
Unique Key, Atomic Values
51
New cards
Second Normal Form
1NF + No Partial Dependency
52
New cards
Third Normal Form
2NF + No Transitive Dependency between non-key columns
53
New cards
DML Keywords
Select, insert, update, delete
54
New cards
DML Aggregation
Count, Sum, Min, Max, Avg
55
New cards
DML Join Operations
Inner, Full Outer, Left Outer, Right Outer using the ON keyword
56
New cards
DML Subquery
A query within the FROM or WHERE clauses of an SQL select
57
New cards
DDL Keywords
Create, Alter, Drop, Truncate
58
New cards
DDL Columns
Data Type, Null, Not Null
59
New cards
DDL Constraints
Primary key, Foreign key, Unique, Check
60
New cards
DDL Cascading
Similar to trigger, works after deletes
61
New cards
DDL Indexes
Used for searching, Primary key automatically creates an index, non PK indecies do not need to be unique
62
New cards
ERD
Entity realationship diagram
63
New cards
DDL Functions
Can return a scaler or a table
64
New cards
DDL Procedures
A stored procedure contatins a set of queiers that can be called together
65
New cards
DDL Triggers
A trigger is used after, before, or instead of an SQL event.
66
New cards
Transaction - Isolation Levels
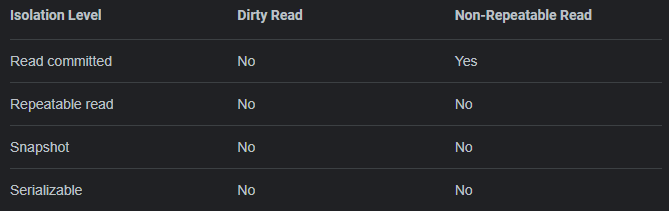
67
New cards
ADO.NET
ADO.NET is a large set of .NET classes that enable us to retrieve and manipulate data, and update data sources, in very many ways.
68
New cards
Connection String
A connection string contains initialization information that is passed as a parameter from a data provider to a data source. The data provider receives the connection string as the value of the DbConnection.ConnectionString property. The provider parses the connection string and ensures that the syntax is correct and that the keywords are supported. Then the DbConnection.Open() method passes the parsed connection parameters to the data source. The data source performs further validation and establishes a connection.
69
New cards
Connection (ADO.NET)
The object used to store information about a connection and establish it
70
New cards
Command (ADO.NET)
This object used to create a SQL query in C# using a connection
71
New cards
ExecuteNonQuery (ADO.NET)
This command function is used to execute a command if no info is needed from the query
72
New cards
DataReader (ADO.NET)
The object is created when ExecuteReader is called so that the returned rows can be used
73
New cards
Disconnected Architecture
Disconnected architecture refers to the mode of architecture in Ado.net where the connectivity between the database and application is not maintained for the full time.
74
New cards
SQL Injection and Parameters
A SQL injection attack consists of insertion or “injection” of a SQL query via the input data from the client to the application.
75
New cards
Repository Pattern
we can say that a Repository Design Pattern acts as a middleman or middle layer between the rest of the application and the data access logic. That means a repository pattern isolates all the data access code from the rest of the application
76
New cards
Unit of Work Pattern
The Unit of Work pattern is used to group one or more operations, usually database CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations, into a single transaction or “unit of work” so that all operations either pass or fail as one uni
77
New cards
Manual Testing
Manual testing is done in person, by clicking through the application or interacting with the software and APIs with the appropriate tooling. This is very expensive since it requires someone to setup an environment and execute the tests themselves, and it can be prone to human error as the tester might make typos or omit steps in the test script.
78
New cards
Automatic Testing
are performed by a machine that executes a test script that was written in advance. These tests can vary in complexity, from checking a single method in a class to making sure that performing a sequence of complex actions in the UI leads to the same results. It's much more robust and reliable than manual tests – but the quality of your automated tests depends on how well your test scripts have been written.
79
New cards
Unit tests
Unit tests are very low level and close to the source of an application. They consist in testing individual methods and functions of the classes, components, or modules used by your software
80
New cards
Integration Tests
Integration tests verify that different modules or services used by your application work well together. For example, it can be testing the interaction with the database or making sure that microservices work together as expected. These types of tests are more expensive to run as they require multiple parts of the application to be up and running.
81
New cards
Functional Tests
Functional tests focus on the business requirements of an application. They only verify the output of an action and do not check the intermediate states of the system when performing that action.
There is sometimes a confusion between integration tests and functional tests as they both require multiple components to interact with each other. The difference is that an integration test may simply verify that you can query the database while a functional test would expect to get a specific value from the database as defined by the product requirements.
There is sometimes a confusion between integration tests and functional tests as they both require multiple components to interact with each other. The difference is that an integration test may simply verify that you can query the database while a functional test would expect to get a specific value from the database as defined by the product requirements.
82
New cards
End-To-End Tests
End-to-end testing replicates a user behavior with the software in a complete application environment. It verifies that various user flows work as expected and can be as simple as loading a web page or logging in or much more complex scenarios verifying email notifications, online payments, etc...
83
New cards
Acceptance testing
Acceptance tests are formal tests that verify if a system satisfies business requirements. They require the entire application to be running while testing and focus on replicating user behaviors. But they can also go further and measure the performance of the system and reject changes if certain goals are not met.
84
New cards
performance testing
Performance tests evaluate how a system performs under a particular workload. These tests help to measure the reliability, speed, scalability, and responsiveness of an application.
85
New cards
Smoke testing
Smoke tests are basic tests that check the basic functionality of an application. They are meant to be quick to execute, and their goal is to give you the assurance that the major features of your system are working as expected.
86
New cards
File.Exists
A predicate that returns true if and only if a file exists at the given path
87
New cards
File.Create
Create a file (returns a file object that needs to be closed before anything else if done)
88
New cards
File.Delete
Delete a file
89
New cards
File.ReadAllLines
Reads a complete file into an array of strings
90
New cards
File.ReadAllText
Reads a complete file into a single string
91
New cards
Single inheritance
There is one Parent class and one Child class. One child class extends one parent class
92
New cards
Multi-level inheritance
In multilevel inheritance, there will be inheritance between more than three classes in such a way that a child class will act as parent class for another child class.
93
New cards
Hierarchical inheritance
In hierarchical inheritance, there is one super class and more than one sub classes extend the super class.
94
New cards
Multiple inheritance
In multiple inheritance, a class can inherit the behavior from more than one parent classes as well.
95
New cards
Partial Class
The partial keyword is used to split the definition of a class or struct or interface across multiple source files.
96
New cards
Sealed class
A sealed class is that a class that cannot be used as a base class. In other words, it cannot be derived from; it is at the end of the derivation chain
97
New cards
Single responsibility principle
“a class should have one, and only one, reason to change.” Following this principle means that each class only does one thing and every class or module only has responsibility for one part of the software’s functionality. More simply, each class should solve only one problem.
98
New cards
Open-closed priciple
well-tested classes will need to be modified when something needs to be added. Yet, changing classes can lead to problems or bugs. Instead of changing the class, you simply want to extend it. With that goal in mind, Martin summarizes this principle, “You should be able to extend a class’s behavior without modifying it.”
99
New cards
Liskov substitution principle
the Liskov Substitution Principle is perhaps the most difficult one to understand. Broadly, this principle simply requires that every derived class should be substitutable for its parent class. The principle is named for Barbara Liskov, who introduced this concept of behavioral subtyping in 1987. Liskov herself explains the principle by saying:
"What is wanted here is something like the following substitution property: if for each object O1 of type S there is an object O2 of type T such that for all programs P defined in terms of T, the behavior of P is unchanged when O1 is substituted for O2 then S is a subtype of T."
"What is wanted here is something like the following substitution property: if for each object O1 of type S there is an object O2 of type T such that for all programs P defined in terms of T, the behavior of P is unchanged when O1 is substituted for O2 then S is a subtype of T."
100
New cards
Interface segregation principle
it’s better to have a lot of smaller interfaces than a few bigger ones. Martin explains this principle by advising, “Make fine grained interfaces that are client-specific. Clients should not be forced to implement interfaces they do not use.”