Paleo 203 Midterm Condensed
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:03 AM on 12/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
Thrust
The force that generates propulsion.
2
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
The bones that form the limbs and limb girdles. Includes all bones of the shoulders, arms, hips, and legs.
3
New cards
Appendicular locomotion
Motion generated by movement of the limbs. Have flippers or webbed feet to increase thrust and surface area
4
New cards
Flippers
Flatter bones, shorter radius, humerus, ulna, longer and numerous phalanges, covered in smooth flat tissue
5
New cards
Axial skeleton
The bones that form the mid-line of the body. Includes all bones of the skull, spinal column, and ribs.
6
New cards
Axial locomotion
Motion generated by movement of the spinal column. Developers caudal fluke to increase surface area
7
New cards
Caudal fluke
An expanded, soft-tissue fin supported by the last tail vertebrae. Vertical in marine reptiles, horizontal in marine mammals.
8
New cards
Collagen
A structural protein found in connective tissues of animals.
9
New cards
Anguilliform locomotion
A form of axial locomotion in which the entire spinal column undulates, propagating waves of muscle contractions down the entire body. Low efficiency. Animals that use this form of locomotion tend to be long and skinny. Ex. Sea snakes and eels
10
New cards
Thunniform locomotion
A form of axial locomotion in which only the tail undulates. Maximum efficiency. Animals that use this form of locomotion tend to be torpedo-shaped. In high speed predatory fish, not body oscillation, crescent shaped fins and fluke. Ex. Tuna, dolphins
11
New cards
Carangiform locomotion
A form of axial locomotion in which only the back half of the spinal column undulates. Animals that use this form of locomotion tend to be spindle-shaped. ex. Seals, crocs, marine iguanas
12
New cards
Pitch
Up and down motion. One of three planes of motion in a 3D environment.
13
New cards
Roll
Movement where an object turns over on its forward-backward axis. One of three planes of motion in a 3D environment.
14
New cards
Yaw
Left and right motions. One of three planes of motion in a 3D environment.
15
New cards
Dorsal fin
An unpaired fin on the back of an animal which helps to stabilize them against rolling.
16
New cards
Drag
The force that resists the movement of an object through any medium. Increased by both density and viscosity of the medium.
17
New cards
Inertial drag
The force that resists the movement of an object by disturbing the flow of molecules around that object crates a space where the medium fills and pulls body backward. It is based on the density of the medium through which it moves. Needs fusiform body shape, smooth, elongate, decreased surface area, loss of hind limbs and external ears
18
New cards
Fusiform
An oblong morphology that tapers at both ends. Can be described as spindle-shaped or torpedo-shaped.
19
New cards
Viscous drag
The force that resists the movement of an object based on friction generated between the object and the medium it is moving through. Caused by the viscosity of the medium through which it moves. Needs smooth, hairless body
20
New cards
Lactic acid
An organic acid produced in muscles during strenuous activity when there is little oxygen available. Causes muscle fatigue and soreness. In crocs
21
New cards
Nares
Openings in the skull that allow for the passage of air from the nostrils to the windpipe.
22
New cards
Blowhole
Nostrils that have migrated to the top of the head in a marine mammal.
23
New cards
Neutral buoyancy
When an object has the same density as the medium that surrounds it. The object with neither sink nor float.
24
New cards
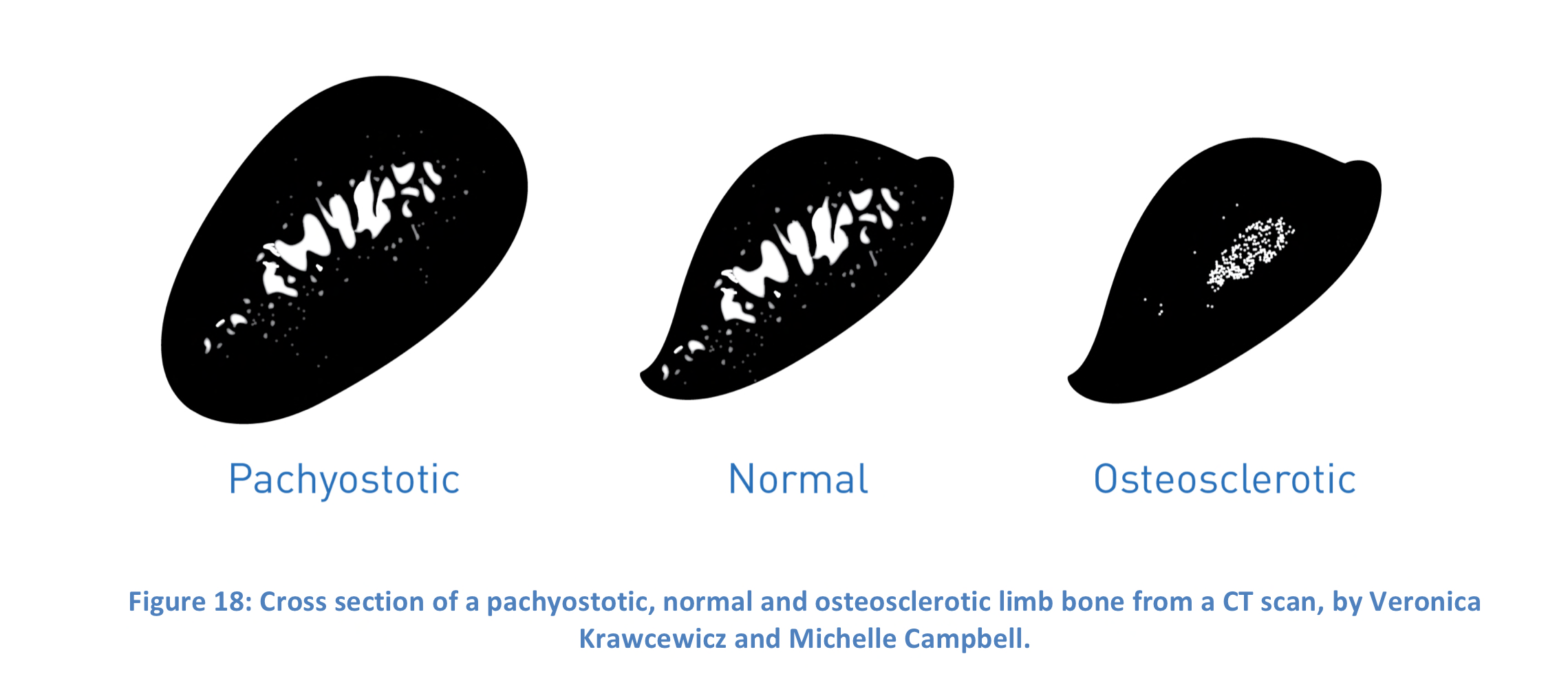
Pachyostosis
A condition in which bones become denser and larger due to increased growth of the denser outer layers of the bones. In manatees, penguins, early whale relatives
25
New cards
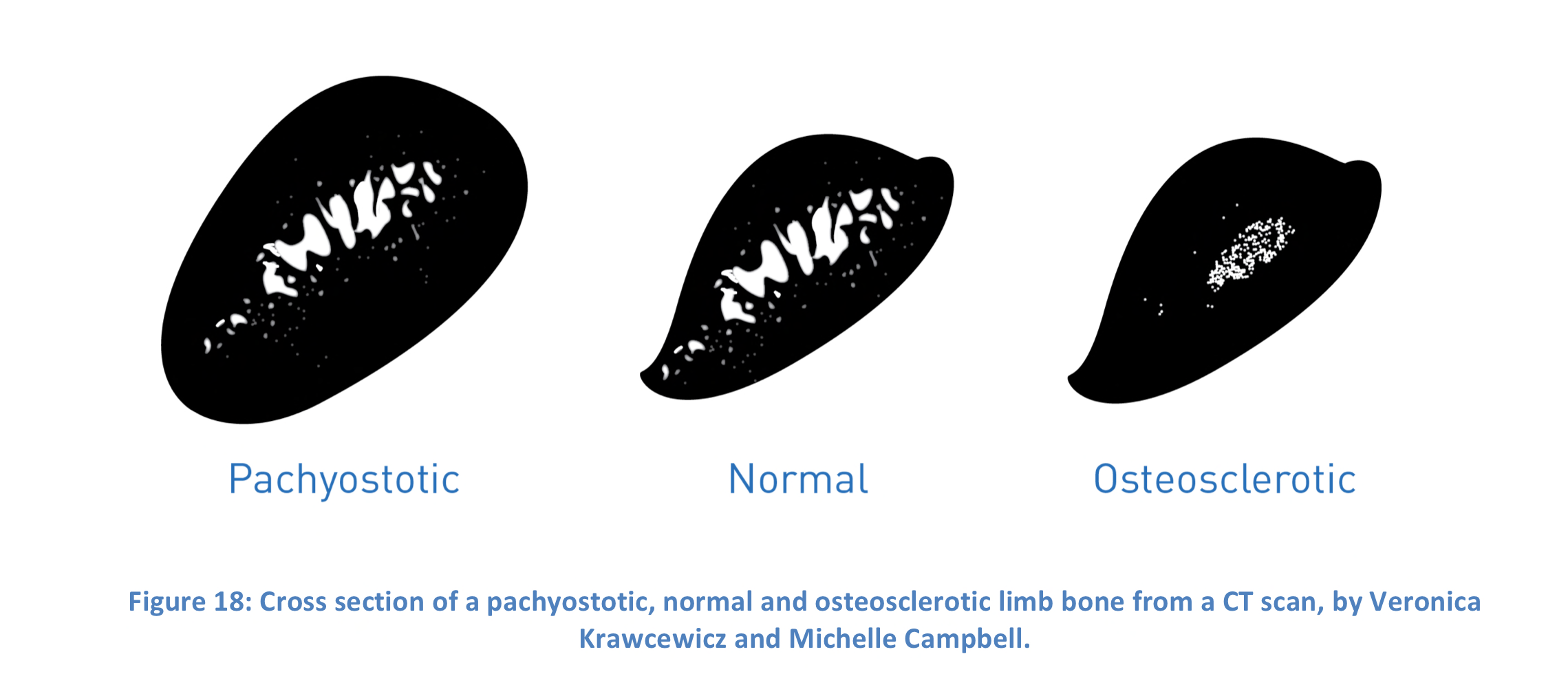
Osteosclerosis
A condition in which bones become denser, but not larger, due to increased mineralization usually in the spongy inner regions of the bones. In walrus and turtles
26
New cards
Salt gland
A special gland that concentrates salt from the blood so that it can be expelled from the body. On crocs tongue, under sea snake tongue, above sea turtle and bird eyes, connected to nostrils in marine iguanas (expel by sneeze)
27
New cards
Metabolism
The sum total of all chemical processes that occur within an organism in order to maintain life. Hard to maintain in water because water is a good heat conductor
28
New cards
Underhairs
The shorter, finer hairs close to the skin of a mammal. Function primarily as insulation. Traps heat near skin
29
New cards
Guard hairs
The outer layer of longer, coarser hairs on a mammal. Functions primarily as protection. Keeps water away from underhairs. Layer like shingles
30
New cards
Tapetum lucidum
A lining on the back of the eyes that reflects incoming light through the retina a second time, increasing the effectiveness of the eye in low light conditions. Seals, crocs, cats
31
New cards
Water properties related to sight
1. Density changes how light bends - bends less in water
2. Light doesn’t travel as far and diffracts
3. Only some spectrum of light is seen in greater depths - blue and green penetrate deeper, total darkness at 200m
32
New cards
Bone conduction
The transmission of sound waves from the surrounding environment to the inner ear through the skull bones. Uses vibrations, less distortion, secondarily aquatic adaptation
33
New cards
Hearing in water
Easier to hear in water, travel 5x faster
34
New cards
Echolocation
A type of sonar used by some animals to detect objects. The animal emits high-pitched sounds which bounce off of surrounding objects and back to the animal's ears, revealing the location of the objects.
35
New cards
Paleoecology
(see ecology) The ecology of extinct organisms.
36
New cards

Marine Reptile clades
Ichthyoperygians, sauropterygians, mosasauroids
37
New cards
When first tetrapods colonized
During Devonian
38
New cards
Anapsid
Having no temporal fenestrae in the skull.
39
New cards
Synapsdid
Having one pair of temporal fenestrae in the skull.
40
New cards
Diapsid
Having two pairs of temporal fenestrae in the skull: the laterotemporal and supratemporal fenestrae.
41
New cards
2 diapsida lineages
Archosauromorpha, Lepidosauromorpha
42
New cards
Synapsida (informally, synapsids)
With the Sauropsida, is one of the two major divisions of amniotes. This group have only one temporal fenestra. Mammals are the modern representatives of this group.
43
New cards
Sauropsida (informally, sauropsids)
With the Synapsida, is one of the two major divisions of amniotes. This group has two temporal fenestrae. Crocodiles, lizards and birds, Parareptiles and diapsida
44
New cards
Parareptilia (informally, parareptiles)
With the Diapsida, is one of two major divisions within the Sauropsida. Has the anapsid skull condition.
45
New cards
Diapsida (informally, diapsids)
With the Parareptilia, is one of two major divisions within the Sauropsida. Has the diapsid skull condition.
46
New cards
Laterotemporal fenestra
The lower of two temporal fenestrae in the diapsid skull condition, found below and/or behind the eye.
47
New cards
Supratemporal fenestra
The upper of two temporal fenestrae in the diapsid skull condition, found above and/or behind the eye.
48
New cards
Archosauromorpha (informally, archosaurs)
Ruling reptiles. With the Lepidosauromorpha, is one of two major divisions of the Diapsida. Have an additional fenestra in front of the eye and on the jaw. Members include birds, crocodiles, dinosaurs and pterosaurs.
49
New cards
Lepidosauromorpha (informally, lepidosaurs)
Scaly Reptiles. With the Archosauromorpha, is one of two major divisions of the Diapsida. Members include lizards and snakes. No extra temporal openings
50
New cards
Water density
Results in resistance when swimming, push against this to produce thrust
51
New cards
Ichthyopterygia (informally, ichthyopterygians)
A group of aquatic diapsids best known for their most derived members- the ichthyosaurs, eurryapsids
52
New cards
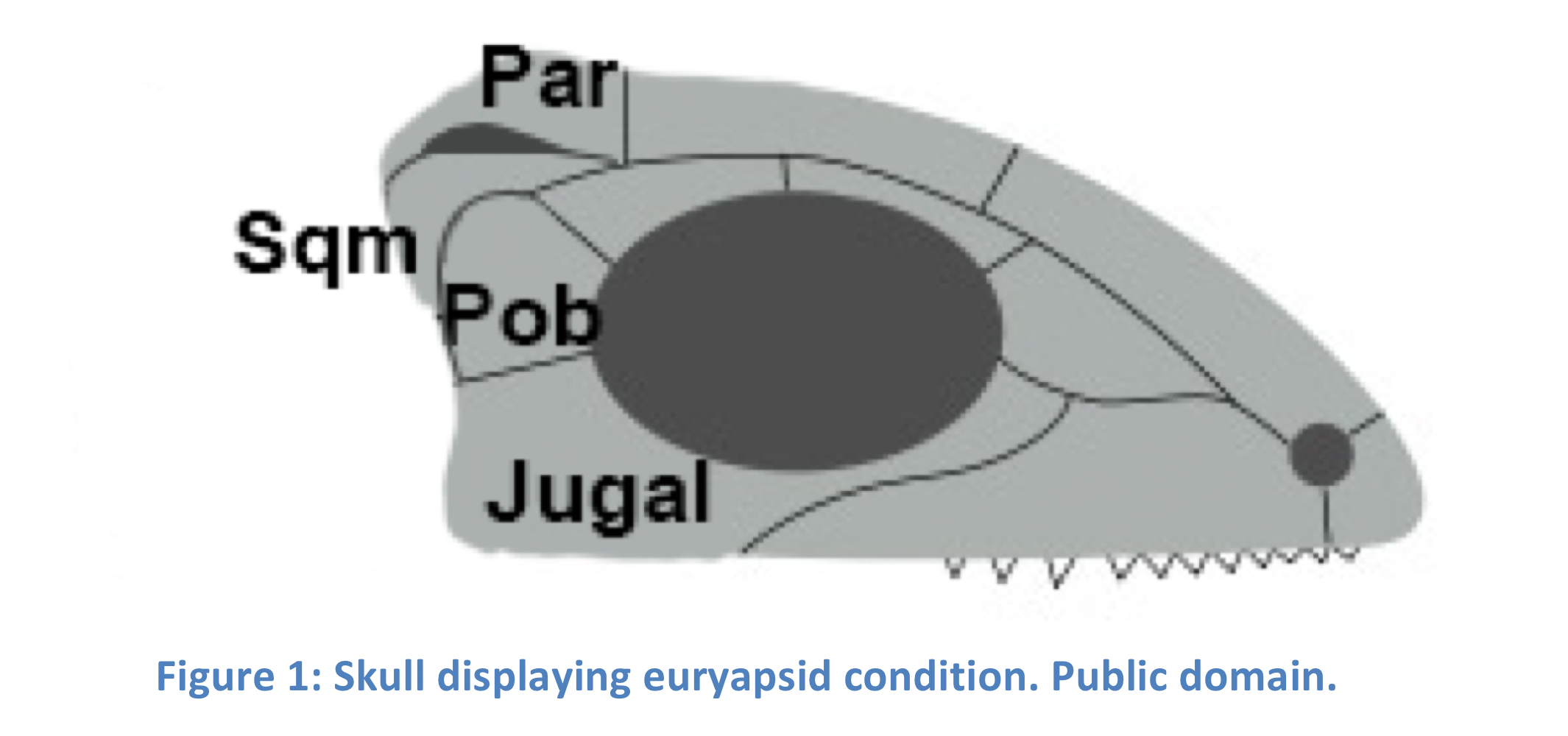
Euryapsid
A skull condition with one temporal opening, derived from the diapsid condition. Developed in ichthyopterygians when the lower temporal fenestra disappeared due to reduction of the back part of the skull.
53
New cards
Gastralia
A series of long slender bones found in the ventral region of the body that provide support and protection to the abdomen and can serve as muscle attachment sites. Also known as "belly-ribs".
54
New cards
Articulate
When bones fit together and form a joint or suture.
55
New cards
Amphicoelous
A type of vertebral shape where both articulating surfaces are concave.
56
New cards
Plicidentine
A type of tooth tissue in ichthyopterygians where the inner tooth tissues have a distinct folded pattern.
57
New cards
Centrum
The solid central part of a vertebra, to which the processes and spines are attached.
58
New cards
Ichthyopterygian Locomotion
Axial, with reduced articulation in spine and pelvic girdle, fully aquatic, pelvic bones float in layers of muscles in the wall of the abdomen, decreased amount of joints between hind legs, shorter less flexible centra, plate like vertebrae, neural spines less attached
59
New cards
Fluted
Grooved. With the appearance of having columns.
60
New cards
Neural spines
Arched vertebral processes that protect the spinal cord and provide sites for muscle attachment. Become simplifies in ichthypoterygians
61
New cards
Sclerotic ring
A ring of bone inside the eyes that helped to support and focus the eyeball.
62
New cards
Ram feeding
A type of underwater feeding strategy where the predator moves through the water with its mouth open, engulfing the prey and the water surrounding it. Also known as filter feeding. Water inhaled flows out the gills and strained with gill rakers
63
New cards
Lunge feeding
A type of ram feeding where a predator takes in a large mouthful of prey and water, and then pushes the water out through a filter such as baleen, leaving the prey in trapped in the mouth.
64
New cards
Baleen
A fibrous material that has replaced the teeth of some whales. Used a filter during lunge feeding.
65
New cards
Manipulation
A feeding strategy where teeth are the instruments used to capture prey. Used for prey on the seafloor of big bites of large open water prey
66
New cards
Feeding guilds
Groups of species, not necessarily closely related, that use similar resources in their environments.
67
New cards
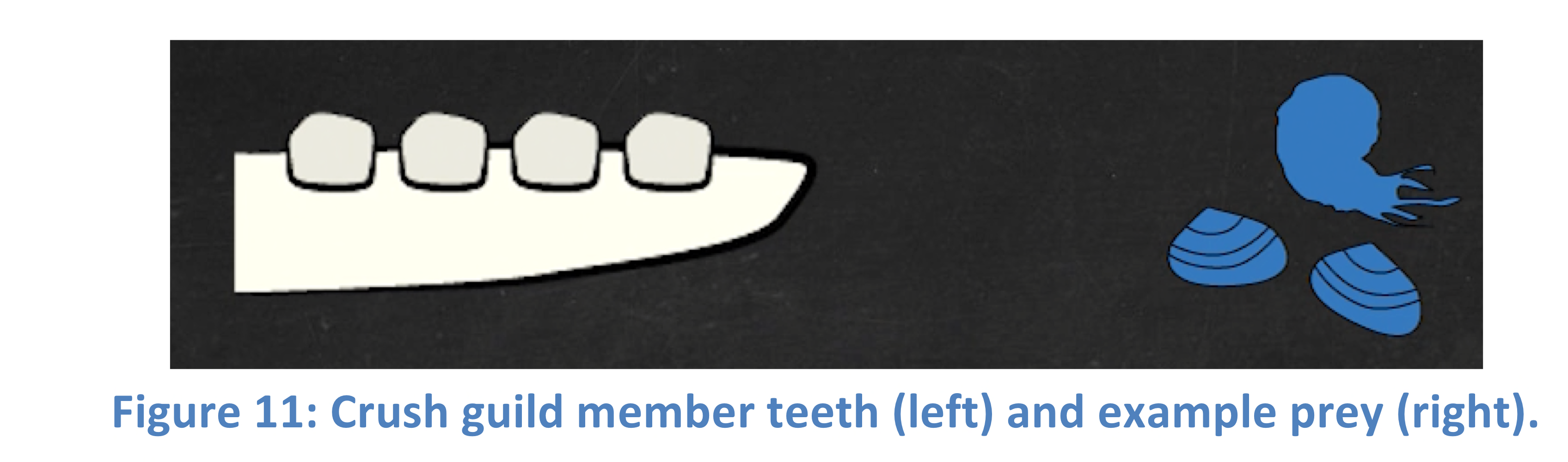
Crush guild
An aquatic feeding guild whose members possess robust teeth for crushing hard-shelled prey such as molluscs.
68
New cards

Smash guild
An aquatic feeding guild whose members possess small teeth with rounded points for eating soft-prey such as squid.
69
New cards
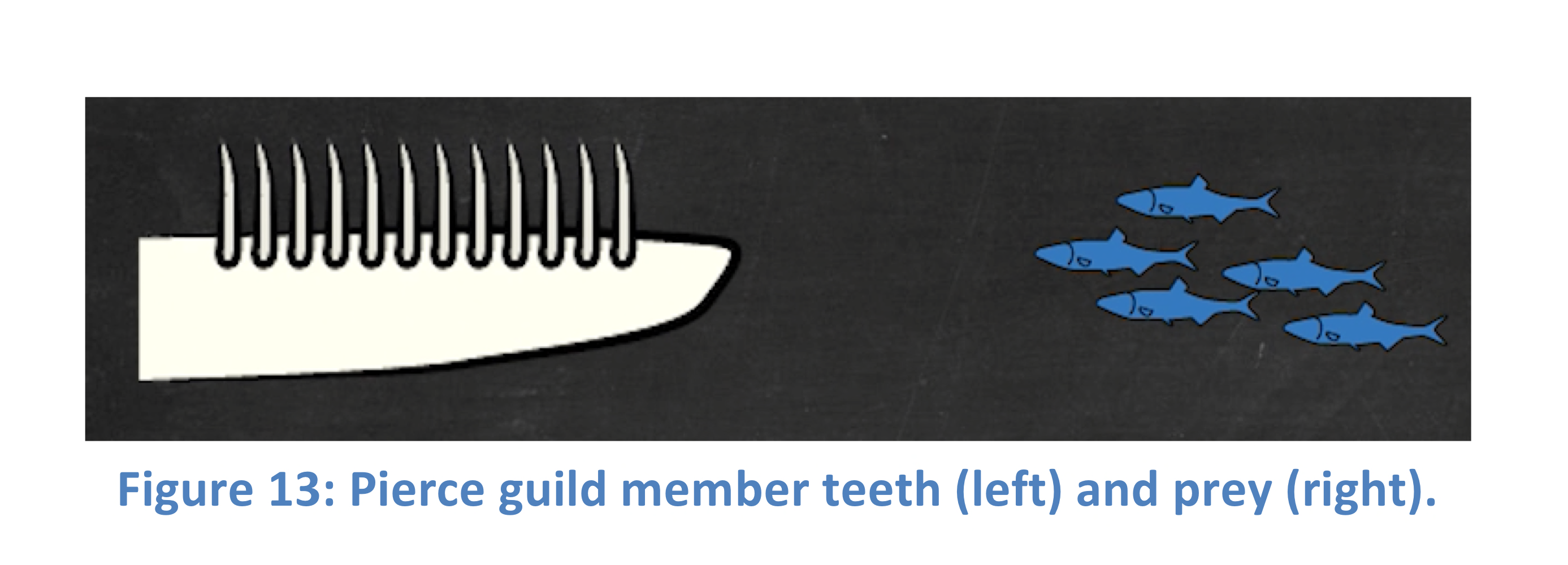
Pierce guild
An aquatic feeding guild whose members possess long, pointed teeth for trapping and piercing small, slippery prey such as small fish.
70
New cards

Cut guild
An aquatic feeding guild whose members possess pointed teeth with cutting edges for tearing apart large prey. In apex predators
71
New cards
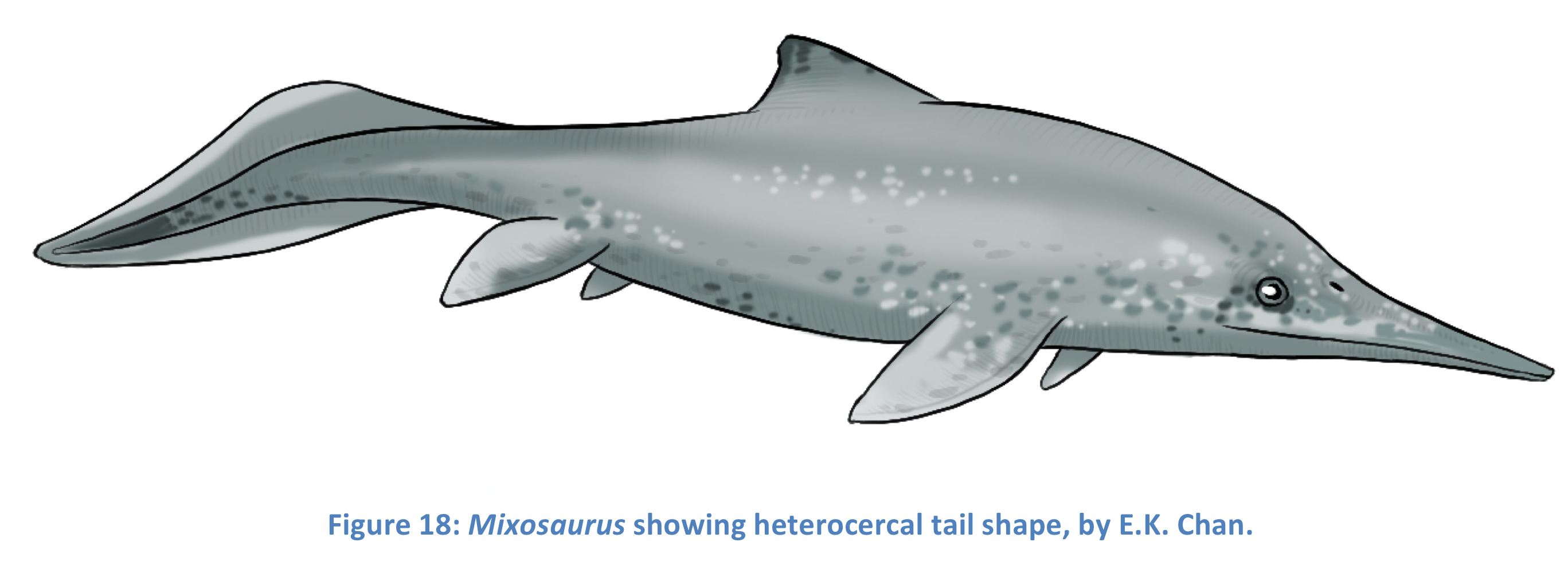
Heterocercal
A tail shape where one lobe is longer than the other. In basal ichysosaurs, had cartilaginous blade to support short top lobe, downward tail bend. Ex. Mixosaurus
72
New cards
Homocercal
A tail shape where both lobes are approximately the same length. 2nd derived tails in ichyosaurs. Ex. Platypterygians
73
New cards
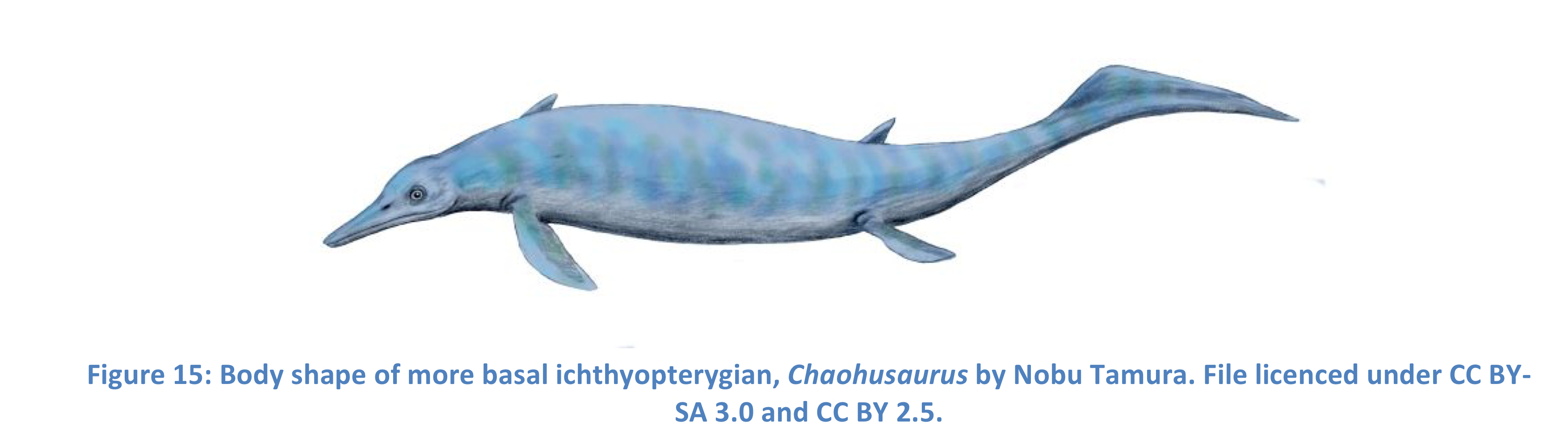
Basal Ichthyopterygian Locomotion
Long serpentine bodies, not for high speeds, long distance predators ambushed prey, good at quick turns ex. Utatsussaurs, chaohussaurs
74
New cards

Derived Ichthyopterygian Locomotion
Chased and manipulated prey, streamlined tuna-like bodies, short torso, crescent shaped tail fluke, high energy cruising, pursuit predators. Ex. Stenopterygians
75
New cards
Hyperphalangy
The condition where the digits of an organism have more phalanges than seen in the ancestral state.
76
New cards
Hyperdactyly
The condition where an organism has more digits (fingers or toes) than seen in the ancestral state.
77
New cards
Avascular necrosis
The death of bone tissue caused by a lack of blood supply leading to tiny breaks in the bones, and areas of collapse. In diving animals, can be caused by a rapid ascent, when dissolved gases in the blood form bubbles that block blood vessels.
78
New cards
The Bends
A condition in diving animals where rapid ascent can lead to blood supply being cut off. Also known as decompression sickness. See avascular necrosis.
79
New cards
Photoreceptors
The structures or cells, such as those that line the back of the eyeball, that respond to light.
80
New cards
Aperture
The space through which light passes in an optical instrument such as the eye. Bigger one means more likely to have depression sickness, biggest in ophthalmosaurus
81
New cards
Endothermy
Generation ad regulation of body heat using the body's metabolism. This property is also known as being warm-blooded.
82
New cards
Ectothermy
Regulation of body heat using external sources such as the sun. This property is known as being cold-blooded.
83
New cards
Viviparous
Where an animal gives birth to live young that have developed inside the body of the parent.
84
New cards
Oviparous
Where an animal lays eggs that then hatch after they have been laid.
85
New cards
Gregarious
Animals lives in groups or communities. Found in 40 shinosaurus in a mass bone bed that probably dies from red tide
86
New cards
Ichthopterygian Endothermy proof
1. Large size
2. Ring like growth patterns in limb bones
3. Viviparity - had 12 live young
87
New cards
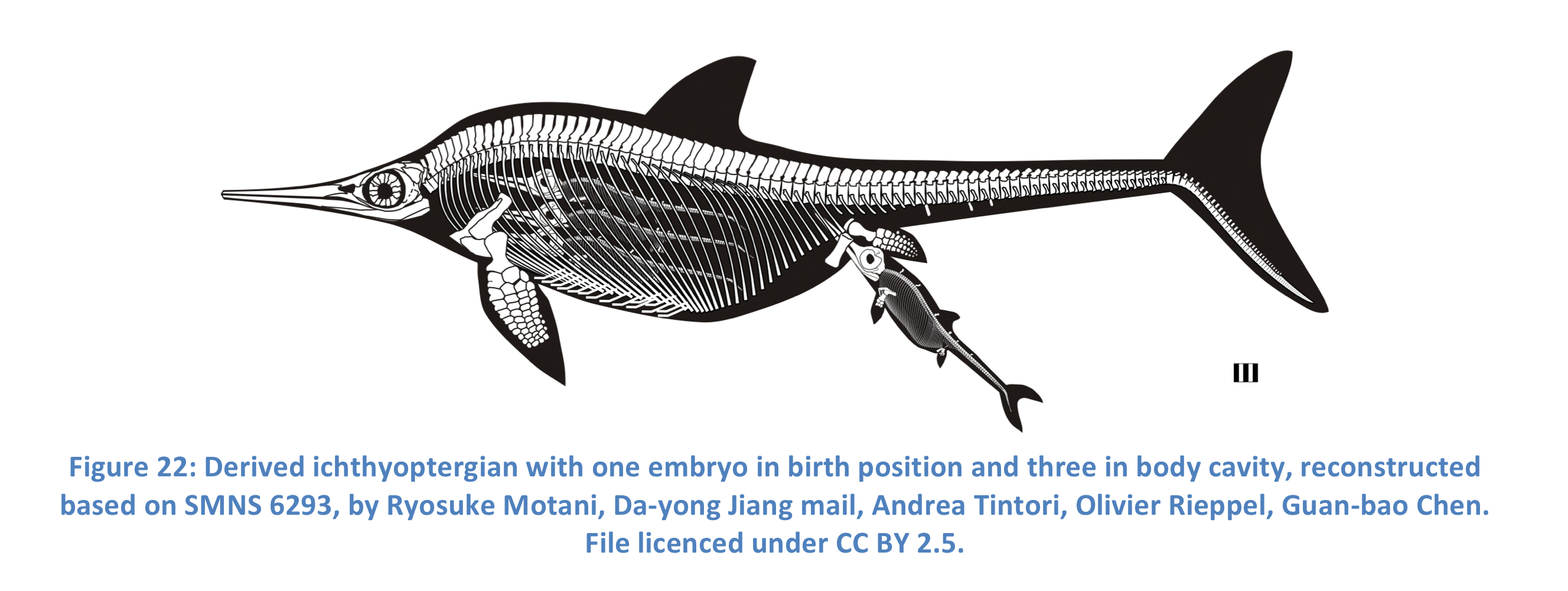
How baby’s are pushed out of dead moms
Gases from death provide pressure to expel dead fetus, can be preserved as fossils
88
New cards
Niche
The role an organism plays in its ecosystem.
89
New cards
Middle Triassic
Thalattoarchon (1st apex predator) evolved, took 30 million years to repopulate after end-Permian mass extinction occupied high variety of ocean niches
90
New cards
Early Triassic
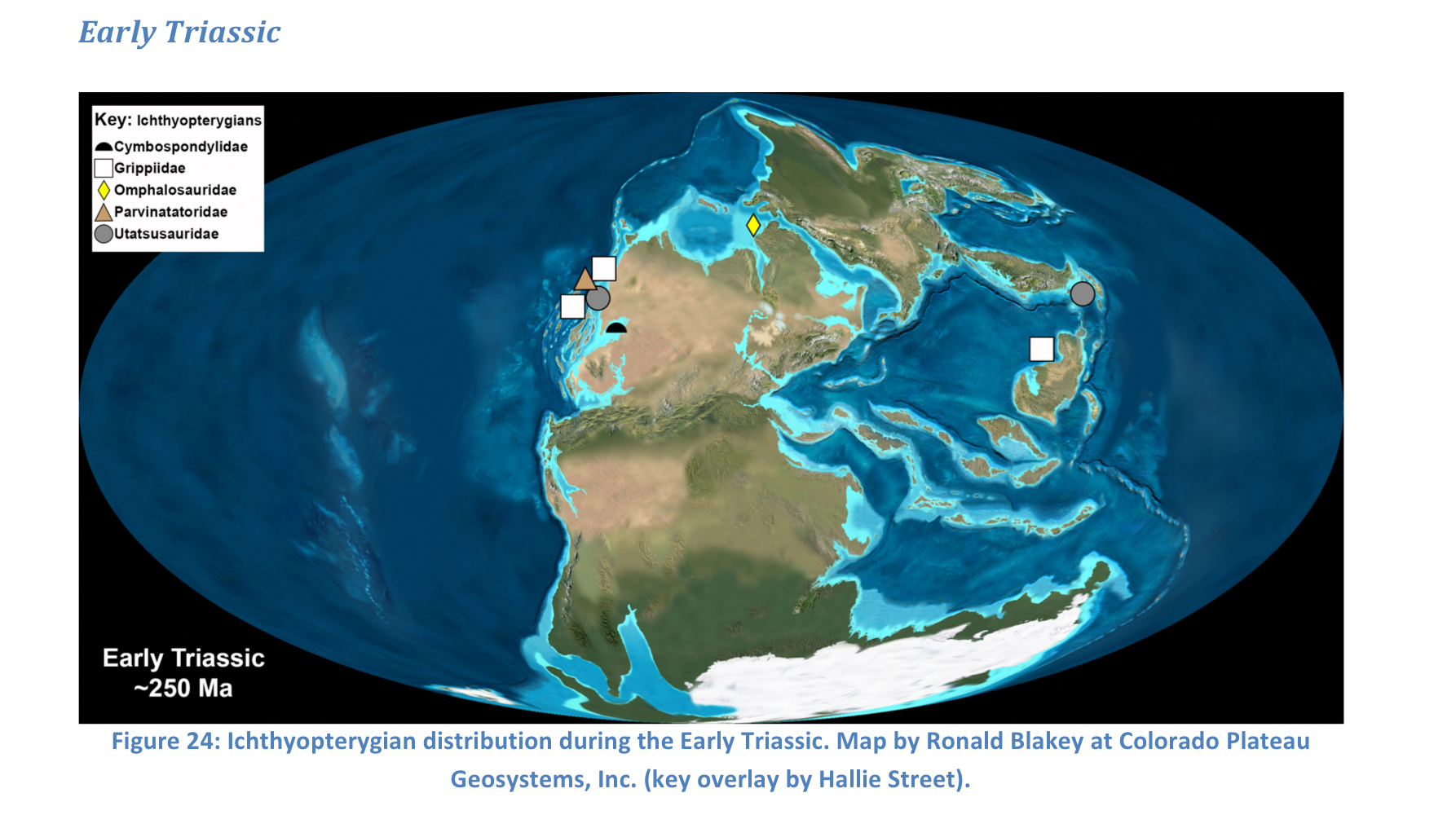
91
New cards
Middle Triassic
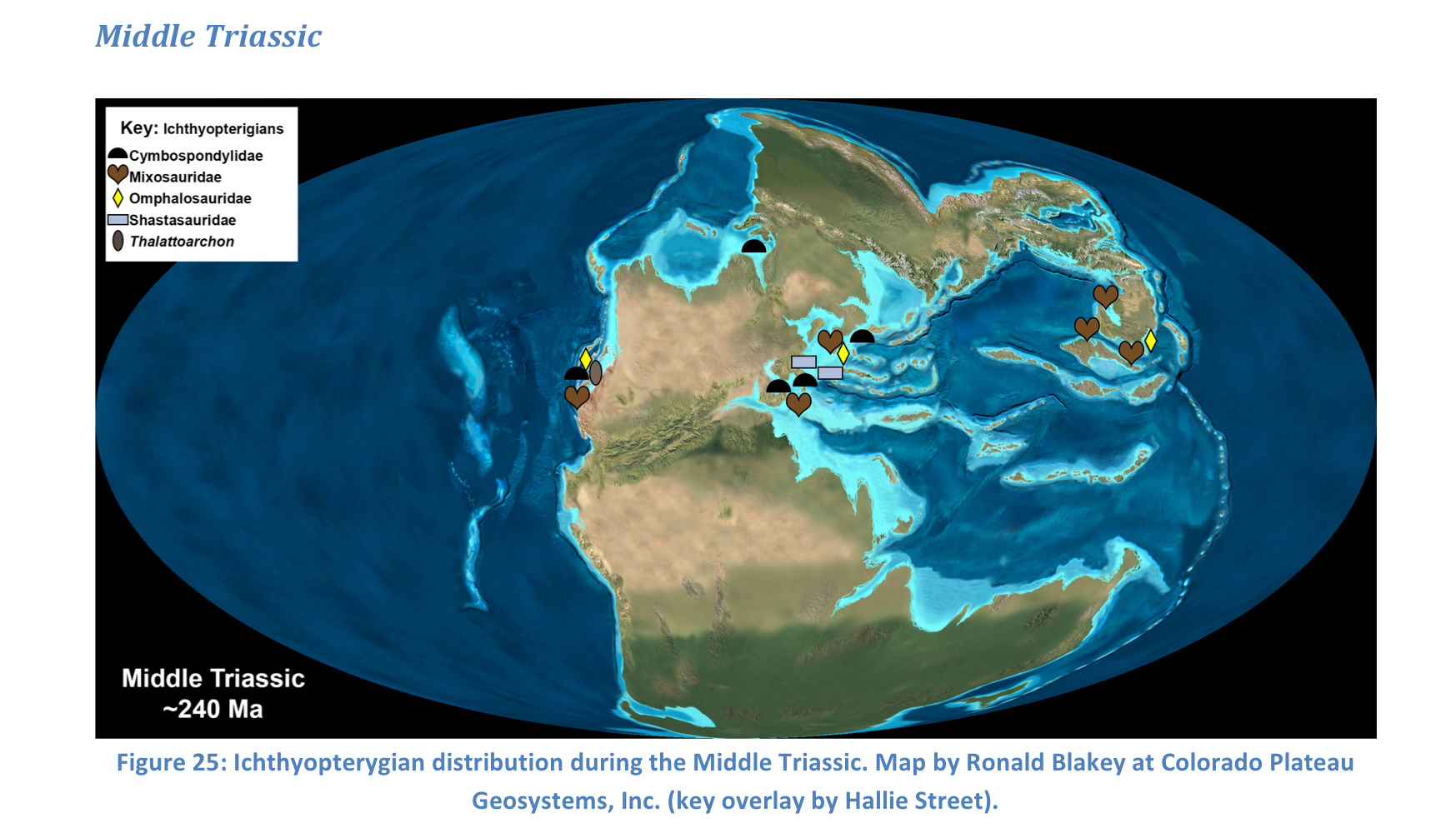
92
New cards
Late triassic
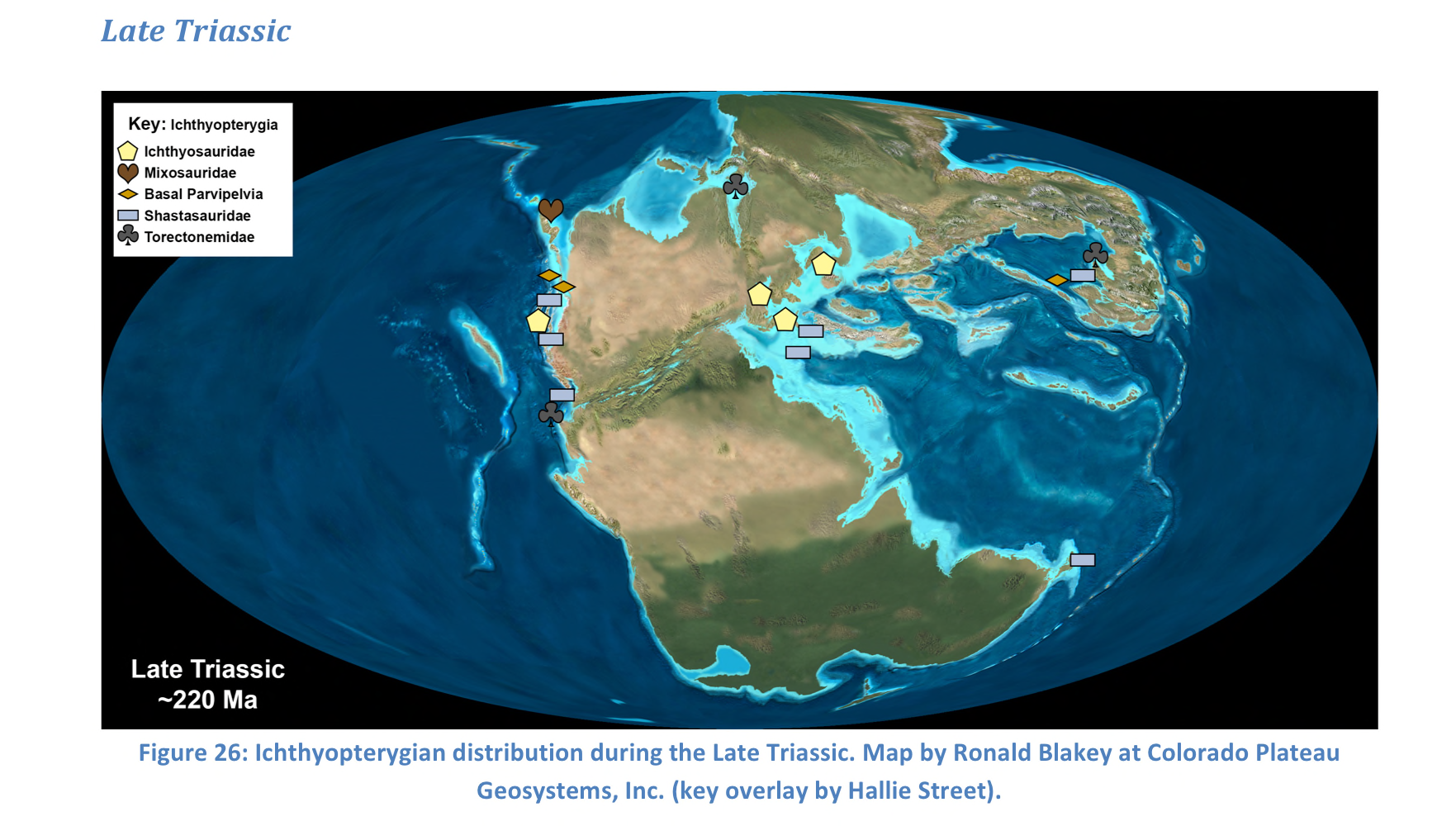
93
New cards
Late Triassic
High morphological and taxonomic diversity, extinction due to Pangea breaking up, deadly climate change (increased volcanic activity and tectonic activity, affected plankton), evolutionary bottleneck
94
New cards
Evolutionary bottleneck
When extinction reduces the number of individuals within a group, the number of species that make up a group (the diversity), the variety of morphologies within the group (the disparity), or a combination thereof.
95
New cards
Early Jurassic
Only thunnosauria remained after bottleneck, long distance swimming helped to survive climate changes, 1 niche - squid eaters, sauropterygians, sharks, crocs, bony fish filled other niches, holzmaden lagerstatten
96
New cards
Early Jurassic
Fully aquatic
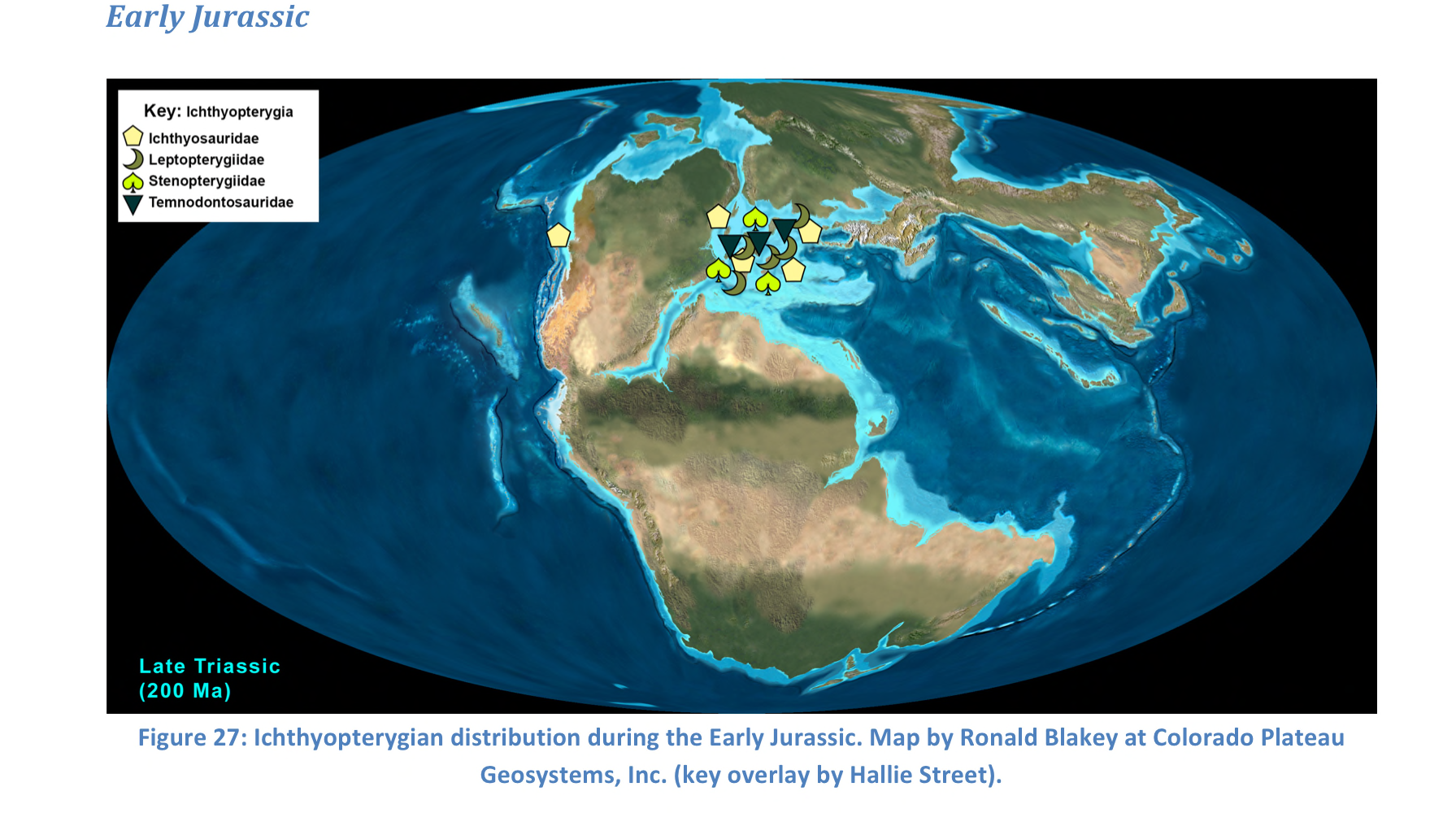
97
New cards
Middle Jurassic
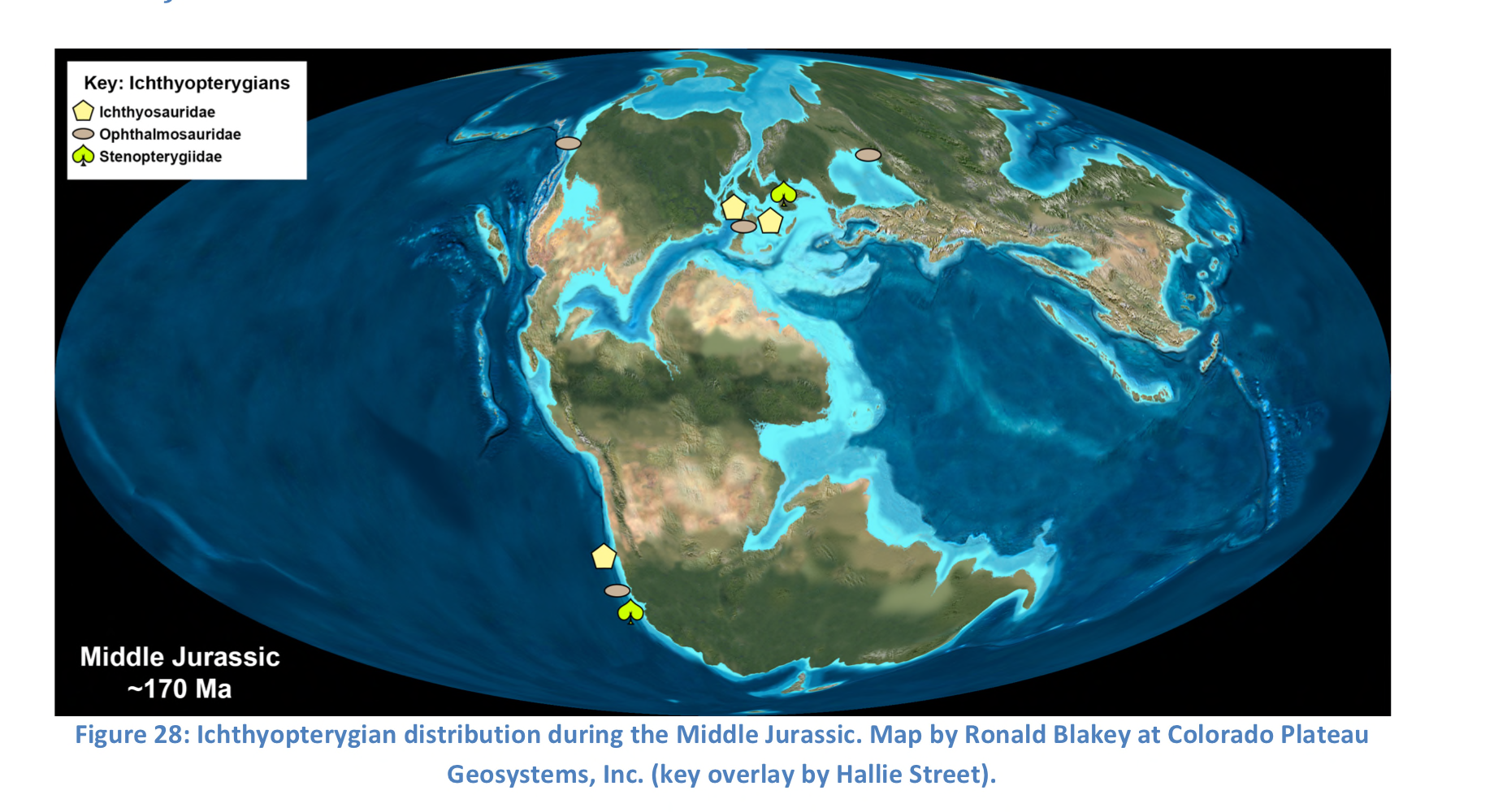
98
New cards
Laggerstatten
A deposit of extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation, sometimes including soft tissues.
99
New cards
Mary Anning
A young woman from the early 1800s of England. She was a fossil collector, dealer and paleontologist, and was responsible for many discoveries including the first correctly identified ichthyosaur, the first two plesiosaurs, the first pterosaur found outside of Germany, and numerous other discoveries.
100
New cards
Holzmaden
A laggerstatten from Germany preserved in oil shale. It is most famous for the large number of exquisitely preserved ichthyosaurs showing skin, muscle fibres, body outlines, embryos, and stomach contents.