NeuroBio Intro (Transmembrane Proteins)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are action potentials/spikes in the brain a result of?
Changes in neuronal membrane voltage.
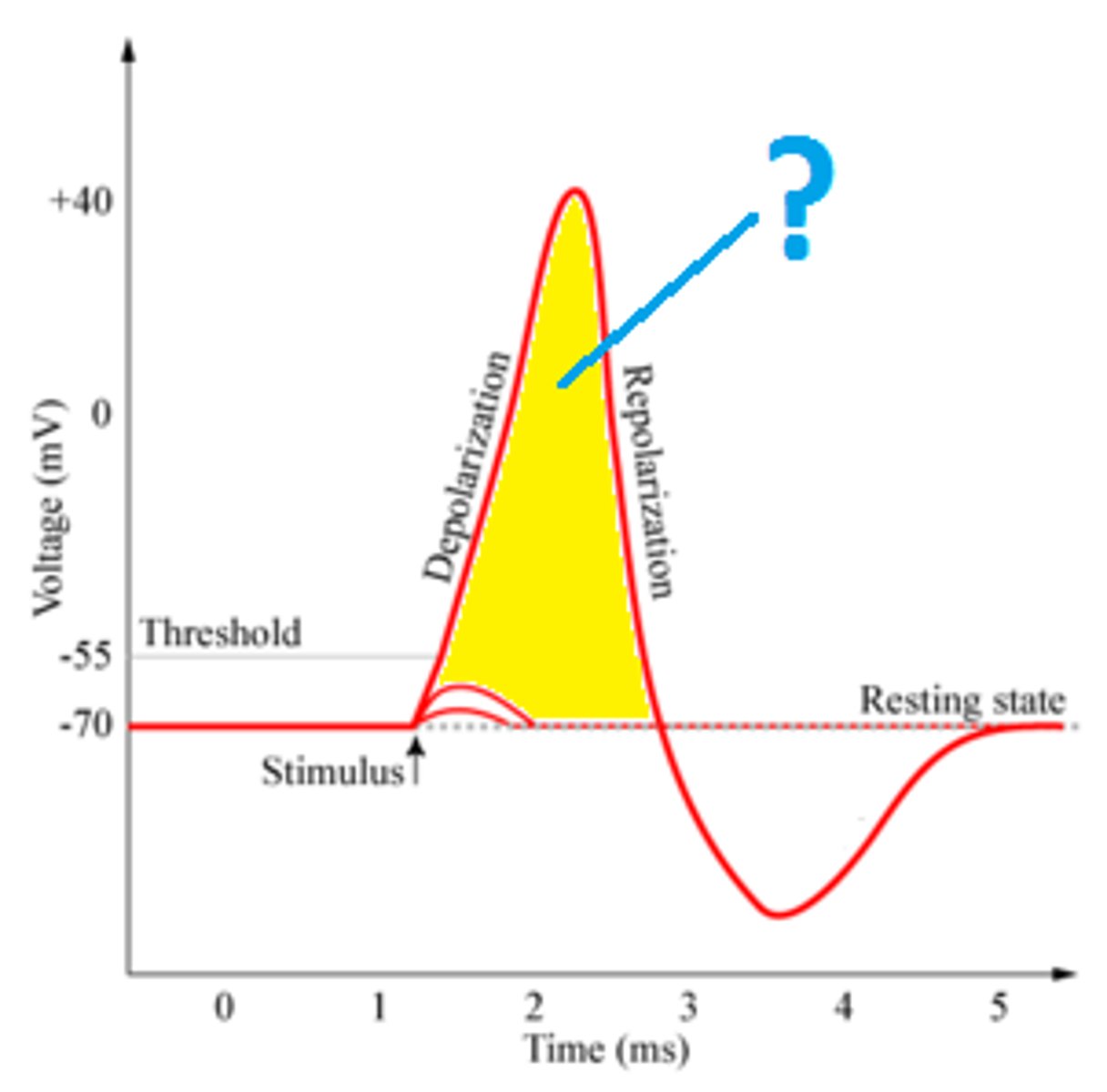
Which part of the neuron receives signals?
Dendrites
Which part of the neuron transfers signals?
Synapse
What state is the phospholipid bilayer (cell membrane) in?
Polar
The cell membrane is impermeable to:
Ions
The cell membrane is permeable to:
Water
Action potential patterns are:
Stereotypical/predictable
What is the speed of the action potentials in the brain?
mSeconds (Milliseconds)
What is a threshold?
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural signal.
What is the function of a Pump transmembrane polypeptide?
Using ATPase as energy to transport ions via conformational changes.
What is the function of a Symporter transmembrane polypeptide?
Using the electrochemical gradient of one molecule to drive the transport of another molecule against its electrochemical gradient. [SAME DIRECTION; One uphill, one downhill of respective gradients]
What is the function of an Antiporter transmembrane polypeptide?
Using the electroschemical gradient of one molecule to drive the transport of another molecule with its electrochemical gradient. [OPPOSITE DIRECTION; Both downhill respective gradients]
What are the primary active transport protein types?
Pump, symporter, antiporter
What is an ion channel?
A transmembrane polypeptide that converts electrochemical potential into currents.
What are the two primary properties of ion channels?
Selectivity and Gating
Ion channels can SELECT for which two properties?
Size and Charge
A closed Ion channel:
Deactivated state
An open ion channel:
Activated state
An ion channel blocked by a third-party gating mechanism:
Inactivation
An ion channel opens with a third-party gating mechanism:
De-inactivation
Function of MECHANICAL gating:
The membrane pulls on the protein, opening it to allow for the movement of molecules.
Function of LIGAND gating:
The binding of an activating substrate opens the protein. (Second messenger signals)
Function of VOLTAGE gating:
Opens and closes in response to changes in electrical charge across the cell membrane.