AP Chemistry: Unit 8
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Autoionization
pure water has an equilibrium in the production of H3O+ and OH- ions (It will act as a Bronsted-Lowry acid and base)
The equilibrium constant for the autoionization of water
Kw=[H3O+][OH-] Kw= 1 × 10-14
[H3O+]>[OH-]
acidic
[H3O+]<[OH-]
Basic (Alkaline)
[H3O+]=[OH-]
Neutral
What does “p” direct you to do?
to the usage of -log of the measurement we’re using
pH=
-log[H3O+]
[H3O+][OH-]=
1 × 10-14
[H3O+]=
10 TO THE -pH
[OH-]=
10 TO THE -pOH
pOH+pH=
14
pOH=
-log[OH-]
Ka*Kb=
1 × 10-14
As temperature increases, what happens to Kw?
It increases
Strong acids have
weak H-X bonds (HCl)
Weak acids have
strong H-X bonds (HF); do not experience a strong induced dipole force.
Oxoacids
contain an atom bonded to one or more oxygen atoms, sometimes with hydrogens attached.
Inductive effect
when electrons in adjacent bonds are attracted to more electronegative atoms. A stronger inductive effect creates more polarity in the molecule as e- move away to the electronegative atoms and makes it more ionizable (a stronger acid)
Weak acids in terms of polarity
weak acids will have a less inductive effect, which leads to less attraction of e- to electronegative atoms, making it less ionizable.
A strong acid will produce a
weak conjugate base
A weak acid will produce a
strong conjugate base
Strong bases
attract more protons
Factors that affect base strength
How easily the lone pair picks up a hydrogen ion
Stability of the ions formed
Strong base will produce a
weak conjugate base
Weak base will produce
a strong conjugate acid
As Kb or Ka increases
the strength increases
Relative concentrations of an acid and its conjugate base can be predicted by comparing
the pH of a solution to the pKa of the acid in that solution
pH<pKa
the acid form is greater in the buffer solution
pH>pKa
the conjugate base is greater in the buffer solution
Equivalence point
the number of moles of titrant added is exactly sufficient to react completely with the number of moles of the titrated species in the sample.
Endpoint
point at which the indicator undergoes a color change in a titration
Buffers
a solution that is resistant to changes in pH when a strong acid/base is added because it is a solution of a strong acid + conjugate base or strong base + conjugate acid
pH of a buffer
includes the pKa of the acid an
Key assumptions of the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Equil. concentrations of acid and conjugate base are approx equal to the initial concentrations
pH (according to the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation)
pKa + log([A-]/[HA])
The higher the buffer concentration
the greater the amount of acid or base it can neutralize - pH doesn’t change
What should you do in order to have the buffer solution be able to control the pH at the desired value?
Choosing an acid with a Ka close to the intended value of [H3O+] - Finding the ideal ratio of acid : conjugate base
Common strong acids
HCl, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4, HBr, HI
Common strong bases
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, RbOH, CsOH, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2, Sr(OH)2
What can you use to find pOH and pH of strong acids/bases?
Basic stoichiometric ratios to find the concentration of H+ or OH- when the strong base/acid dissociates
% ionization
[H+]equilibrium concentration/[Acid]initial concentration * 100
[OH-]equilibrium concentration/[Base]initial concentration * 100
Net ionic equation for strong base + strong acid
H+ + OH- → H2O(l)
Weak acid + Strong base
Weak acid + Strong base → Water + Conjugate base
Strong acid + Weak base
Strong acid + Weak base → Water + conjugate acid
Weak acid + Weak base
Check your Ka and Kb values (Ka>Kb - ACIDIC)
pH=pKa at the
half-equivalence point where the concentration of the weak acid/weak base is = to the conjugate acid/base
Strength of an acid
ELECTRONEGATIVE ATOMS - # OF OXYGENS
Common weak bases have
nitrogen and hydrogen (NH3)
An indicator should have a pKa value close to
the pH value of the equivalence point
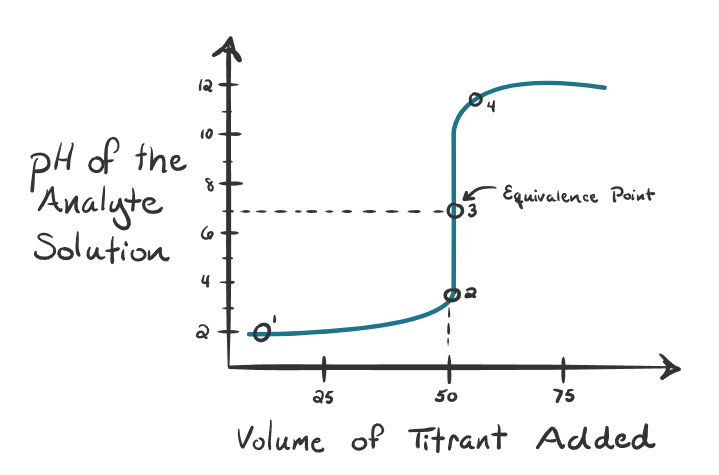
What kind of titration is this?
Strong acid titrated with strong base - Equivalence point is 7 pH
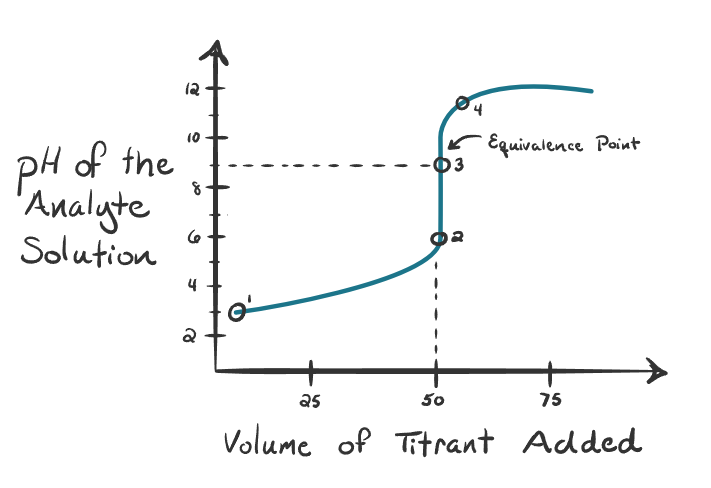
What kind of titration is this?
Weak acid titrated with strong base - Equivalence point is higher than 7 pH
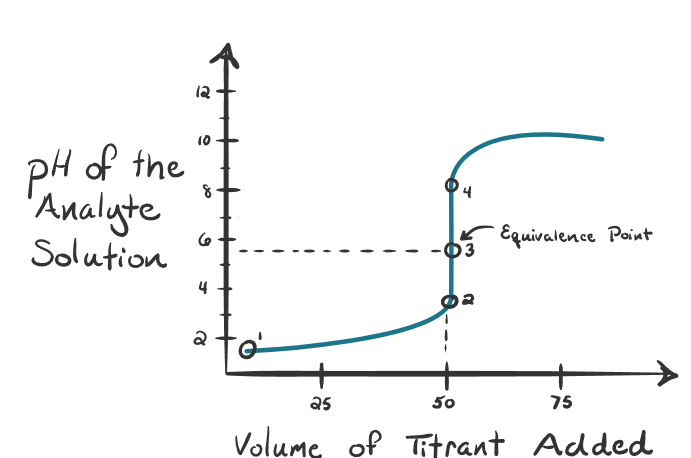
What kind of titration is this?
A strong acid titrated with weak base - Equivalence point is lower than 7 pH