unit 2
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What type of tissue is bone?
connective tissue
Protects the ends of bones from wearing down
Articular cartilage
Full of red marrow
Spongy bone
The knobby end of your femur at the hip end
Proximal epiphysis
The long shaft of the bone
Diaphysis
makes up diaphysis and outside of long bones
Compact bone
Site of hematopoiesis
red bone marrow in spongy bone
When it degenerates or is used up you get arthritis
Articular cartilage
the type of bone that is full of stem cells
spongy bone
Layer that lines the medullary cavity
Endosteum
growth plates
epiphyseal plates
Layer that covers the outside of the bone
periosteum
Provides bone cells with nutrients and O2
Blood Vessels
What does the word foramen mean?
hole
Name means around the bone
Periosteum
Has layers called lamella
Compact bone
Hollow space inside the diaphysis
medullary cavity
The knobby end of your humerus at the elbow end
Distal Epiphysis
Space full of yellow marrow
Medullary cavity
How blood cells leave the red marrow
blood vessel
Little hole in the bone that the blood vessel goes through
Nutrient foramen
Protects against bone friction
articular cartilage
Stronger than spongy bone
compact bone
True/False Periosteum is vascular
True
True/False Articular cartilage is vascular
False
Adipose tissue found in the medullary cavity
Yellow Marrow
Tibia is an example of what type of bone?
long bone
The carpals are what type of bone?
Short Bones
What type of bone is the patella
sesamoid bone
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12) is an example of what type of bone
Irregular Bone
The scapula is an example of a type of bone
flat
Where is the calcaneus located?
heel of foot
Where is the pisiform located?
wrist
Where is the cuboid?
lateral side of foot
The talus bone is part of the_.
Foot
The sternum is an example of what type of bone
flat bone
How many bones are in the human body (adult)?
206 bones
How many bones are there in the axial skeleton?
80 bones
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
126 bones
The skull is part of the _ skeleton
axial
The normal curvature of the cervical spine is called
Lordosis
There are ___ lumbar vertebrae
five
The triangular bone at the base of the spine is called _
Sacrum
True/False The male pelvis is oval or round in shape
false
The ilium is part of the
pelvis
The radius can be found on the ___ side (anatomical position) of the arm.
Lateral
Name the longest and strongest bone in the body
Femur
The structure found in between the vertebrae of the spine that helps with shock absorption.
Intervertebral disc
Contains stem cells that produce red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
Red bone marrow
Name the bones of the wrist (hint: remember the mnemonic)
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Range of Motion
The range through which a joint can be moved.
An important component of general health
Why we assess range of motion
Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, injury to muscle, tendon, or ligament
Conditions that limit ROM
600
muscles in the human body
gluteus maximus
largest muscle in the body
In the ear
Smallest muscles of the body.
The Heart
Hardest working muscle of the body
Masseter
The strongest muscle of the body
skeletal and cardiac
striated muscles
smooth muscle
non-striated, involuntary
cardiac muscle
intercalated discs
Cardiac muscle
linked together with gap junctions
uninucleate
smooth and cardiac muscle
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
Perimysium
The connective tissue that surrounds fascicles.
Epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
fascia
Forms tendons
endocardium
Contains heart chambers and valves
Myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
Epicardium
Outermost layer of the heart
Smooth muscle
Contracts slower than skeletal but remains contracted longer.
skeletal muscle
attached to bones
muscles of endurance
slow twitch
Muscles of strength
Fast twitch
hypertrophy
increase in muscle size
atrophy
muscle wasting
oxygen debt
delayed onset muslce soreness
RICE
rest, ice, compression, elevation
Strain
injury to muscle or tendon due to overstretching or tearing
Tendonitis
inflammation of a tendon due to overuse

Fracture
More pressure is put on on a bone than it can stand until it will split or break.
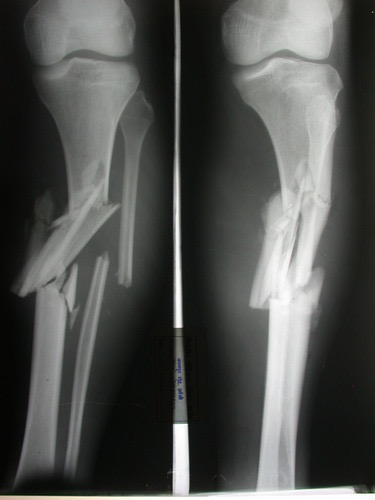
Open fracture
Bone breaks through skin and can be seen outside the body.

Simple fracture
Fracture does not break through skin. Also known as closed
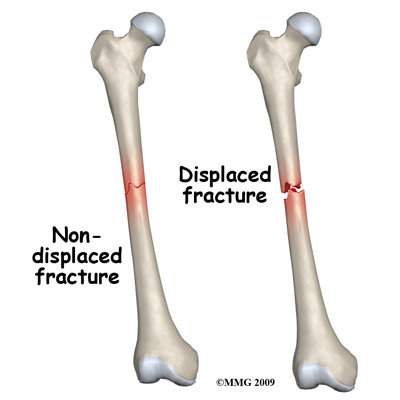
Non displaced fracture
The broken ends line up and have not moved out of place
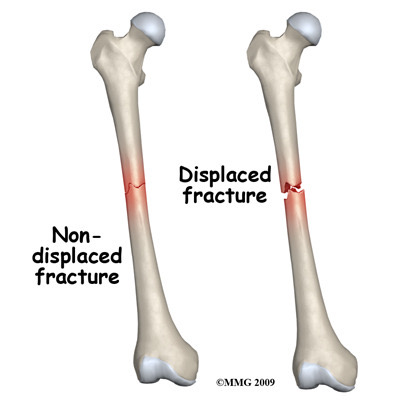
Displaced fracture
Bone ends are out of normal alignment. May require surgery
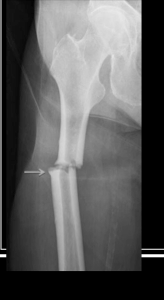
Transverse fracture
Complete fracture that is straight across a bone’s axis
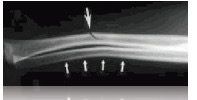
Green stick fracture
Bending an incomplete break of a bone; most often seen in children
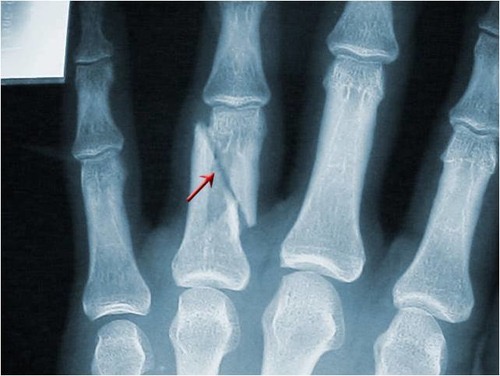
Oblique fracture
A fracture that is diagonal to a bone’s long axis
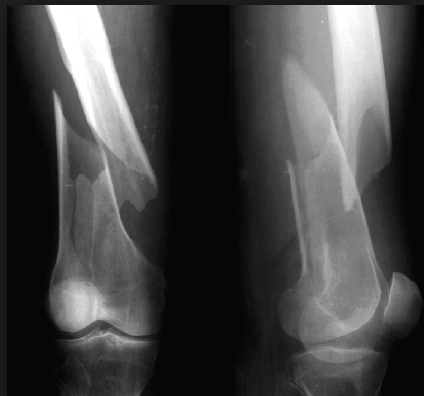
Spiral fracture
A fracture in which the bone has been twisted apart

Communited fracture
Direct impact that shatters a bone into several fragments.
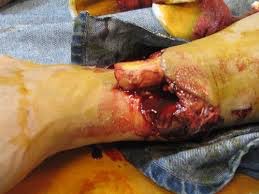
Compound fracture
Fracture that breaks the skin. Risk of serious infection. Also called open fx.
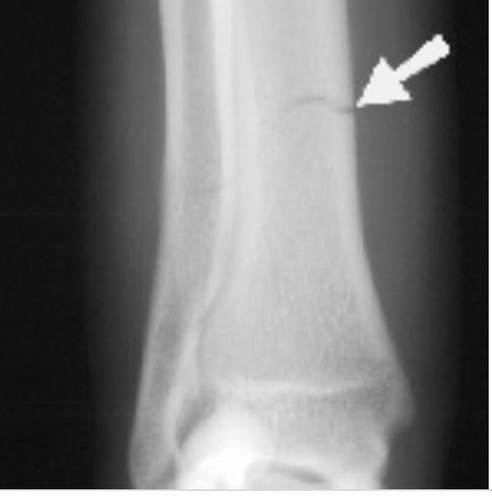
Stress fracture
Due to repetitive use. Also called hairline fracture. Appears like a crack on a x-ray
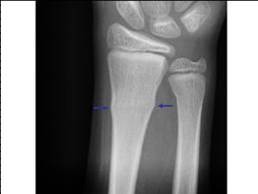
Impacted fracture
Broken bone ends are forced into each other
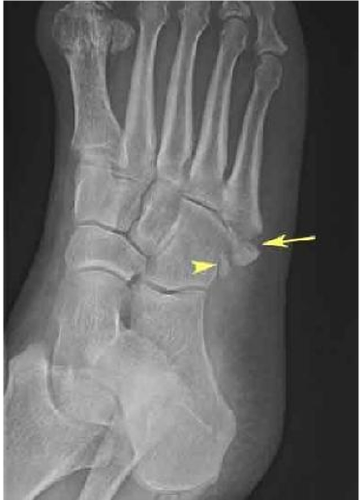
Avulsion fracture
A fracture in which a fragment of bone has been pulled away by a tendon and its attachment. Common in children

Compression fracture
Spiral fracture in which vertebra is flattened/crushed
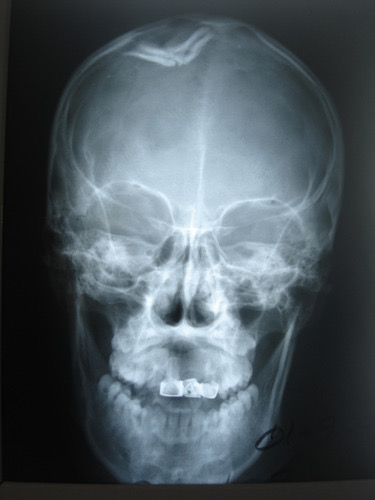
Depressed fracture
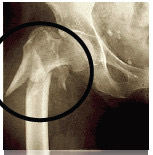
Pathological fracture
Fracture caused by an underlying disease or condition
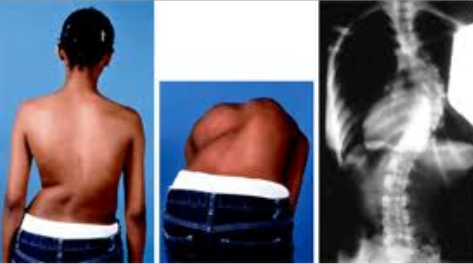
Scoliosis
Abnormal curvature of the spine
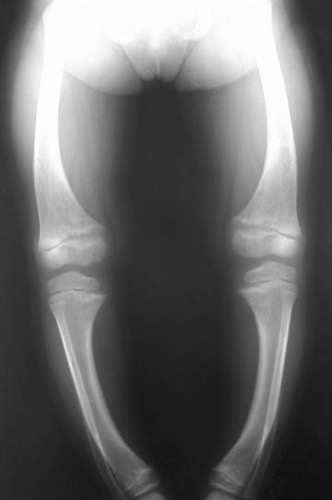
Rickets
A bone weakness disease caused by vitamin D deficiency. Causes bone to bend or bow
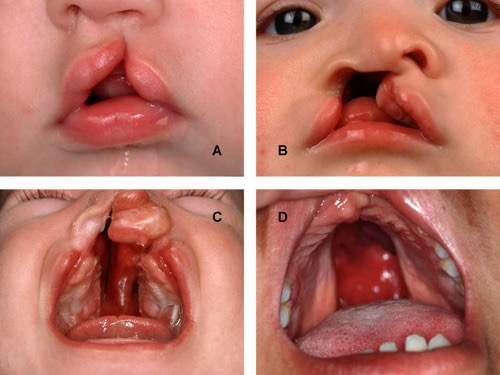
Cleft lip and palate
Bones of the mouth do fuse properly. Birth defect