2. small animal med- GI therapeutic principles
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is the gut microbiome?
aggregate of all microbes that live within the GI tract
includes bacteria, viruses, protozoa, fungi
what vital roles does the gut microbiome play for the host?
vital for host health, esp. health of GIT
-source of essential nutrients and vitamins (short chain fatty acids)
-immune system modulation
-gut epithelial health
-protection against enteropathogens
what is dysbiosis?
imbalance of gut microbial community, often reduced bacterial richness and diversity with disease
plays a role in pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory enteropathy and systemic disease
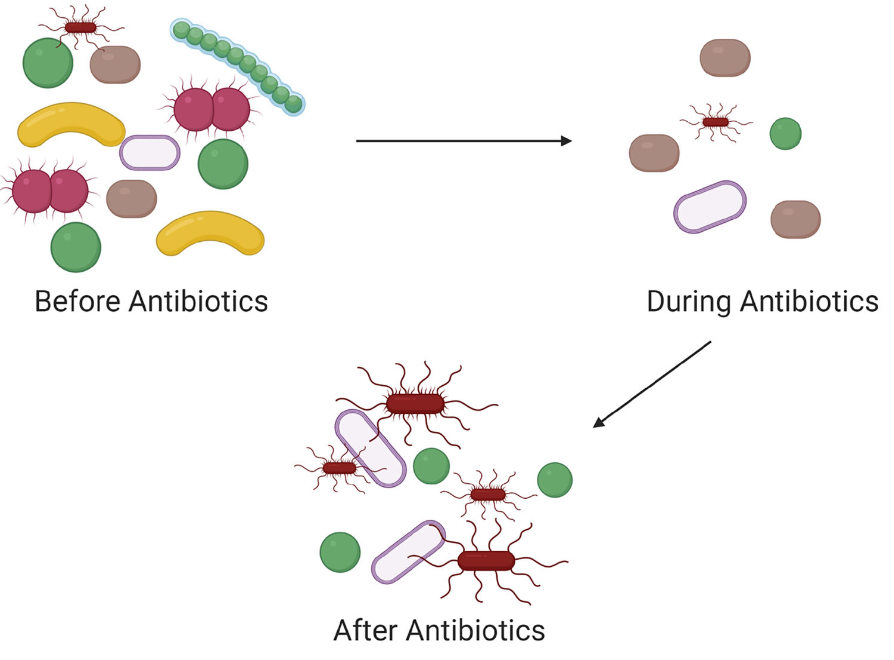
what can profound dysbiosis be caused by?
oral antibiotics
what antibacterial drugs are used for GI disease?
tylosin, metronidazole, amoxicillin most common
few and specific indications for antibiotics in dogs and cats with GI disease
can antibiotics be used for uncomplicated acute diarrhea?
no, abx should not be used routinely for uncomplicated acute diarrhea
what are adverse effects of using antibacterial drugs for GI disease?
-prolongs dysbiosis
-predisposes to enteropathogenic bacteria (c. diff)
-promotes antibiotic resistance
-worsens GI signs (V/D inappetence)
-increases susceptibility to disease
what are indications of using antibiotics for GI disease?
-parvovirus infection with neutropenia
-acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome (AHDS) with signs of sepsis
-antibiotics-responsive diarrhea trial (after appropriate workup, after strict diet trial)
-E. coli associated granulomatous colitis (based on FISH and C&S testing)
-enteropathogenic bacteria with signs of systemic illness (ie, fever)
what are contraindications of using antibiotics to treat GI disease?
-uncomplicated acute diarrhea
-AHDS without signs of sepsis
-antibiotic-responsive diarrhea trial (in lieu of workup, before diet trial)
-chronic large bowel diarrhea (in lieu of workup)
-enteropathogenic bacteria in nonclinical cases or mild, self-limiting disease
what are general therapies for the gut microbiome?
probiotics, prebiotics, fecal transplant
what are probiotics?
live microorganisms, which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit to the host
what are the common bacteria in probiotics?
most are lactic acid producing bacteria:
-lactobacillus
-enterococcus
-streptococcus
-bifidobacterium
BLES
does use of probiotics induce permanent changes in the intestinal microbiota/colonize the gut?
no- probiotics do not induce permanent changes
health benefits end once the probiotic is discontinued
what are indications for probiotic use?
-acute uncomplicated diarrhea
-prevention and treatment of stress diarrhea
-prevention of antibiotic associated GI signs
-adjunct therapy for chronic enteropathies
how should probiotics be administered?
-prefer high dose, multi-strain probiotics for chronic enteropathies
-probiotics and antibiotics should be administered at least 4 hours apart
-need 1-3 days to infer a health benefit (give prophylactically ahead of time for stress-induced diarrhea)
what are prebiotics?
non-digestible fermentable food ingredients (fiber) that promote growth and function of the beneficial bacteria already present in the gut
not all fibers are prebiotics
what is a synbiotic?
commercial products with probiotics and prebiotics combined
what are the 3 classifications of fiber?
1. fermentability
2. solubility
3. viscosity

what is the fermentability of fiber?
readily metabolized by the gut bacteria (prebiotics)
what is the solubility of fiber?
2 types:
-soluble fiber: dissolves in water
-insoluble fiber: does not dissolve in water (non-fermentable, bulks stool, e.g. wheat bran, cellulose, lignin)
what is the viscosity of fiber?
if/how much thickens in the presence of water
what is psyllium husk powder?
soluble, viscous/gel forming, poorly fermentable fiber
exerts stool-normalizing effect, to firm loose stool
creates gel that is good for constipation

What is the dose of psyllium husk powder for a cat? dog?
cat - start ¼ to ½ tsp per day
dog - start 1-3 tsp per day
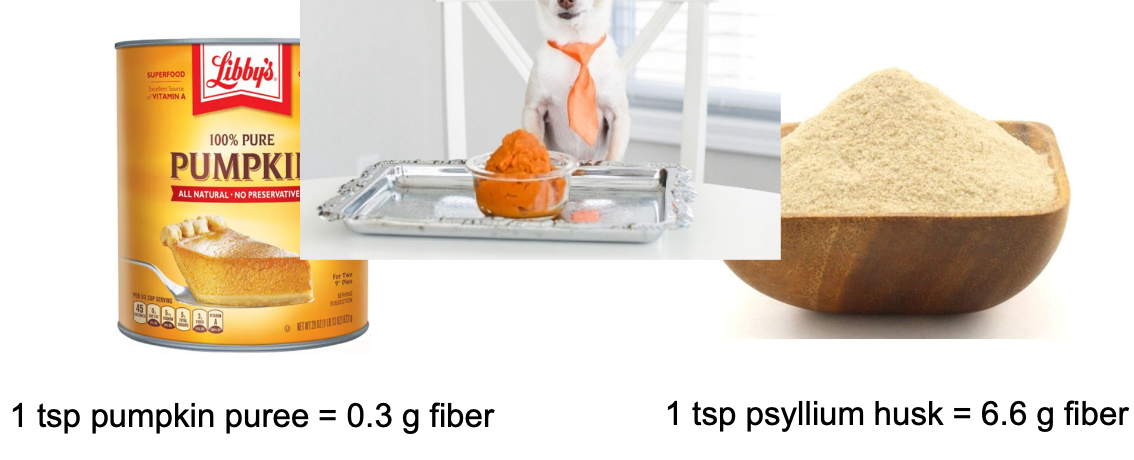
True or False? Pumpkin puree is an equal substitute to psyllium husk powder.
False. 1 tsp of pumpkin puree is only 0.3 g of fiber, 1 tsp of psyllium husk is 6.6g of fiber!

what is a fecal microbiota transplant (FMT)?
administration of a feces (oral capsule or enema) from a healthy individual (donor) to a patient with disease
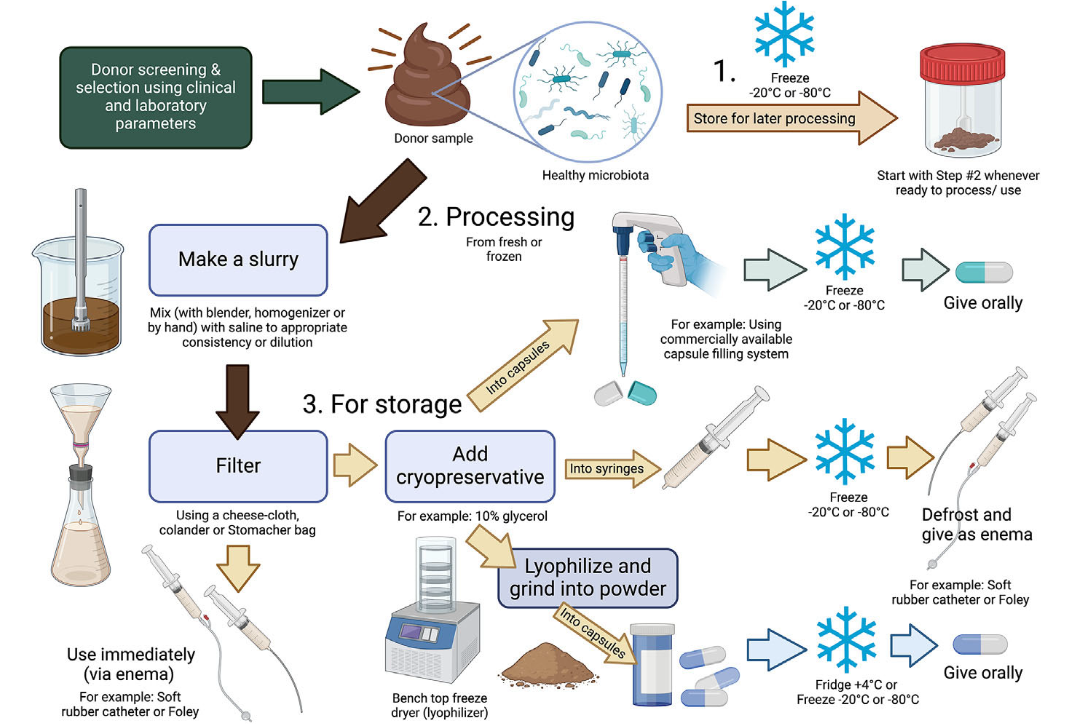
what are fecal transplants beneficial in treating?
-antibiotic-associated diarrhea/dysbiosis
-acute diarrhea
-clostridium difficile infections
-maybe chronic enteropathies
What is AnimalBiome FMT oral capsules?
commercially available to public freeze-dried fecal microbiota in enteric-coated capsules or powder for dogs and cats (expensive!)

what are the 4 categories of therapeutic foods for the GI tract?
1. highly digestible/low residue (aka GI diet)
2. low fat
3. elimination diet
4. fiber-enhanced
what is a “gastrointestinal” diet?
no standard formula but mostly are considered highly digestible, low residue foods
what are highly digestible, low residue diets?
aka “GI” diets:
-relatively low in soluble fiber to promote stomach emptying and high in complex carbohydrates
-low residue= low fecal bulk (very digestible)
-some low in fat for dogs (<3g/100kcal)
when are highly digestible, low residue diet indicated?
used for treatment of acute gastroenteritis, megacolon in cats
what are commercial options for highly digestible, low residue foods? FYI
RC GI
Purina EN
Hill’s i/d
Blue Buffalo GI Gastrointestinal support
what are low-fat canine diets?
GI diets that are also low in fat
-dogs: fat <3g/100kcal
-cats are not designated as low fat but can find options <4g/100kcal

when are low-fat diets indicated?
-non-specific acute gastroenteritis cases
-pancreatitis
-gastric retention disorders
-lymphangiectasia
-hypertriglyceridemia
what is an option to reach ultra low-fat diet <2.0g/100kcal? what situation would you recommend this?
formulated home-cooked diet
best for some PLE cases like lymphangiectasia

what are elimination (hypoallergenic) diets?
hydrolyzed protein or limited ingredient (novel protein) or elemental foods
when are elimination (hypoallergenic) diets indicated?
-chronic inflammatory entropathy
-atopy (skin allergies)
-feline triaditis (chronic pancreatitis, cholangitis, enteropathy)
what are the 3 categories of elimination diets?
1. hydrolyzed
2. limited ingredient/novel protein
3. elemental
what are elemental diets?
protein source consists of purified amino acids
no source of complete protein

what are limited ingredient/novel protein diets?
protein source the pet has never been exposed to
what are hydrolyzed diets?
protein source broken down into peptides (pre-digested) in hope that allergen goes undetected by immune system
what protein sources may be used in hydrolyzed protein diets?
soy, chicken, poultry feather, salmon
variable carb sources
PROTEIN AND CARB CAN VERY BETWEEN CANNED AND DRY DIET! Try to stick to one type
what are some commercial options for hydrolyzed protein foods? FYI
RC hydrolyzed (soy and/or chicken [canned only])
RC GI hydrolyzed
RC ultamino (poultry feather)
Hill’s z/d (chicken)
Purina HA (soy and/or chicken)
Blue Buffalo HF Hydrolyzed (salmon)
Peptides need to be ___ kD to abolish all antigenicity, for example the ___ diet. Most diets achieve size of __ kD where type __ reactions abolished BUT type__ still possible.
<1kD, RC ultamino
7-10 kD, I (mast cell degranulation), 4 delayed cell-mediated reactions
how long should elimination diet trials be for dermatologic disease and GI disease?
derm dz: 8-12 weeks
GI dz: at least 2 weeks
can animals on elimination diet trials have treats?
no, have to remove all other foods, treats, and snacks during the elimination diet trial
also d/c flavored meds and wash all bowls/scoops/storage bins
what are 2 types of fiber-enhanced diets?
1. soluble fiber: preferred for small intestinal or pancreatic disease
2. insoluble fiber: preferred for weight loss, colitis, anal sac disease
what are fiber enhanced diets used to treat?
-chronic small bowel diarrhea (first choice is hypoallergenic diet)
-acute or chronic large bowel diarrhea
-constipation
