Photosynthesis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
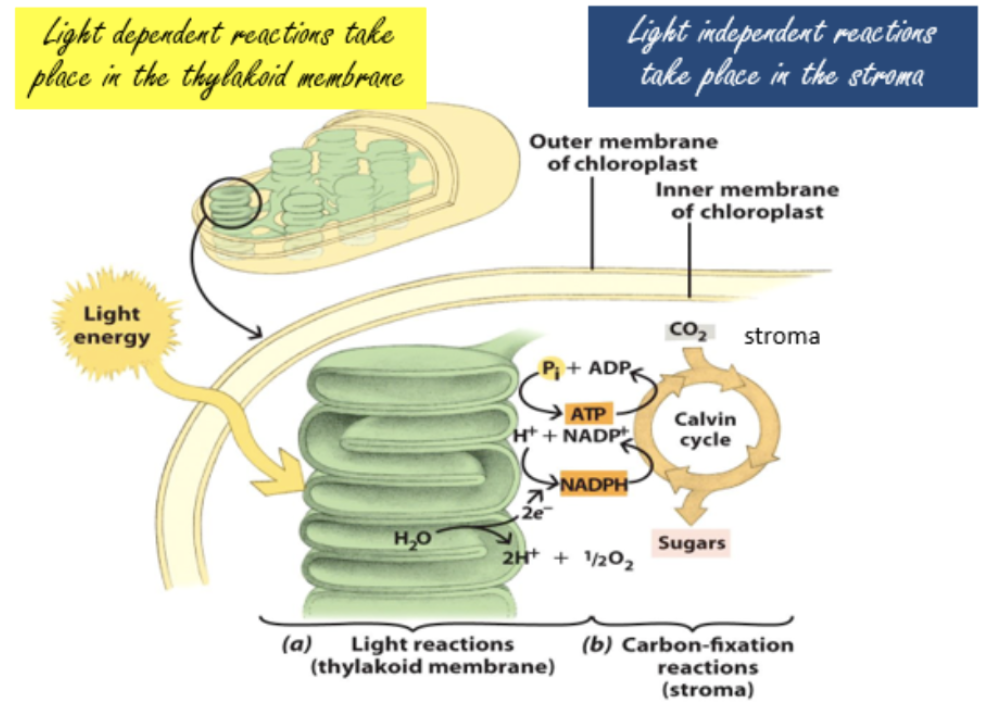
light-dependent reactions overview
take place in thylakoid membrane, converting light energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH
photoactivation and photolysis (oxidation) in photosystem II
electron transport chain and proton pump
reduction in photosystem I
chemiosmosis
net production of O2, NADPH, and ATP
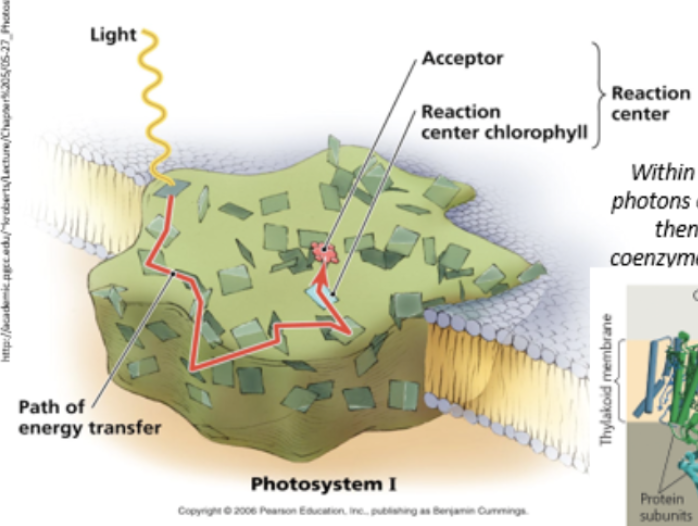
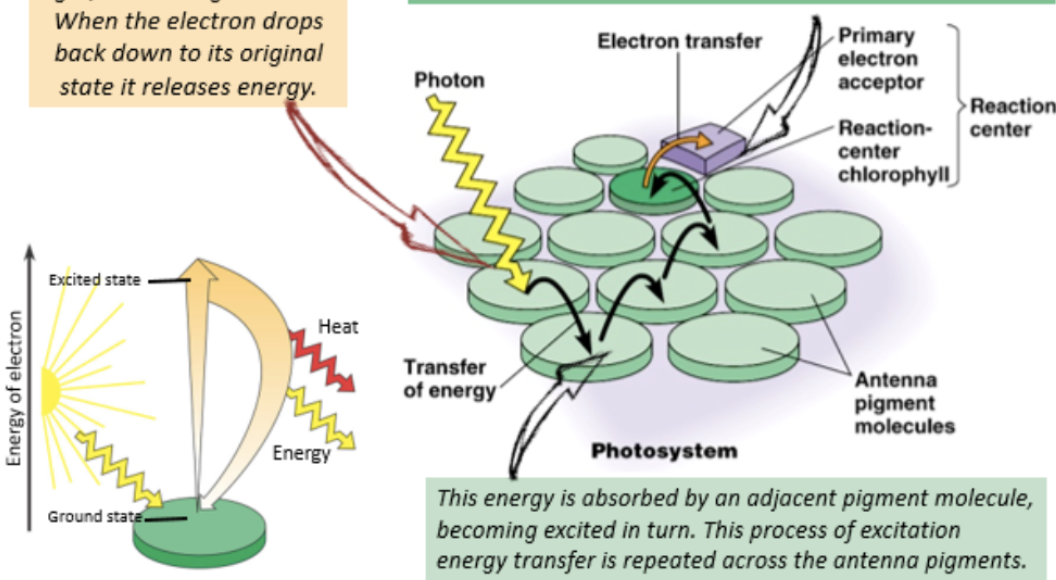
photosystem structure
light-harvesting protein complex with accessory pigments (e.g. chlorophyll b, carotenoids, xantophylls, pheophytins)
reaction center - two chlorophyll a molecules
found in thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts of plants, algae, or cyanobacteria
advantage of antenna pigment molecules being close and in precise orientation to one another
photons of light avoid traveling large distances and disappearing, instead allowing for the seamless transition of energy
advantage of different pigment molecules
different pigments absorb different ranges of wavelengths and surround one chlorophyll pigment reaction center, ensuring the most efficient absorption of energy at any time of the day/season
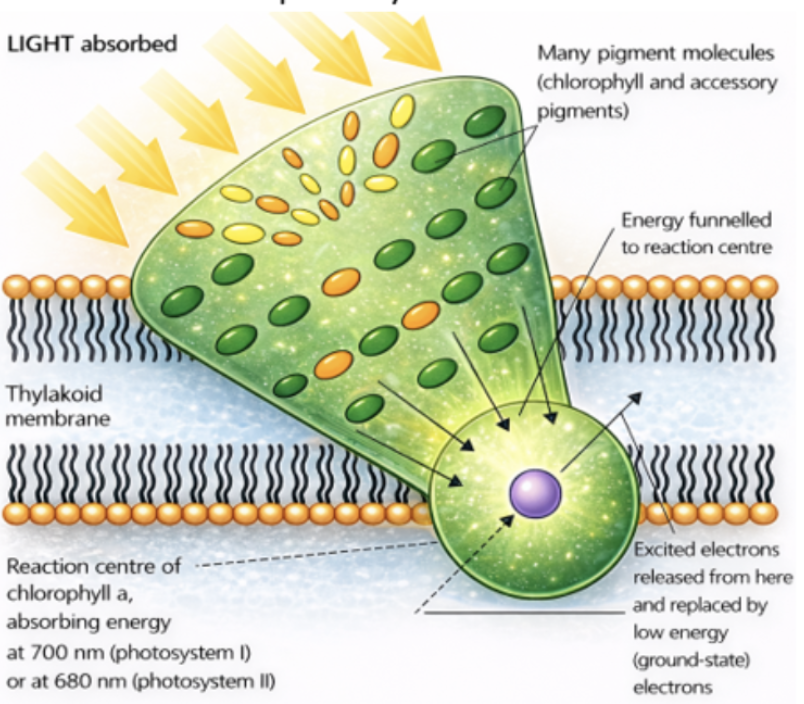
photosystem function
accessory pigments in photosystem absorb light, exciting electrons
electrons drop back down to original state and release energy, exciting electrons in adjacent pigment molecules
process of excitation energy transfer repeated across antenna pigments until reaction center chlorophyll is reached
in the reaction center, electrons transferred to electron acceptor (main electron acceptor NADP+)
photosystem II (PSII)
wavelength absorption peak at 680 nm, strongest biological oxidizing agent (photolysis)
photolysis of water
H2O molecules split by light, creating H+ protons and waste product O2
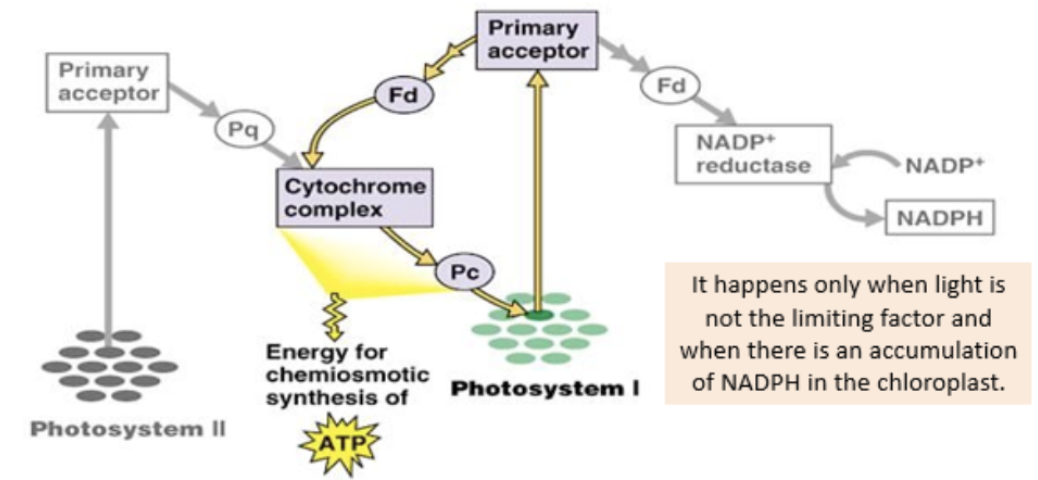
electron transport chain
passes excited electrons from primary acceptor chlorophyll a of PSII along several electron carriers (intermembrane proteins) to the primary acceptor of PSI
proton pump as a result of the electron transport chain
energy from photoactivated electrons used to pump protons across thylakoid membrane from stroma into lumen, causing the accumulation of H+ ions within the thylakoid (concentration gradient)
photosystem I (PSI)
wavelength absorption peak at 700nm, strongest biological reducing agent
activated electrons received by carrier ferredoxin, reducing NADP+ → NADPH to be used in light independent reaction
chemiosmosis
high concentration of H+ ions in thylakoid lumen
diffusion of H+ ions through ATP synthase to stroma generates ATP
alternative path of photoexcited electrons
occurs when light is not the limiting factor - there is an accumulation of NADPH in the chloroplast
photoexcited electrons become cyclic, synthesize ATP more rapidly through chemiosmosis, but no NADPH
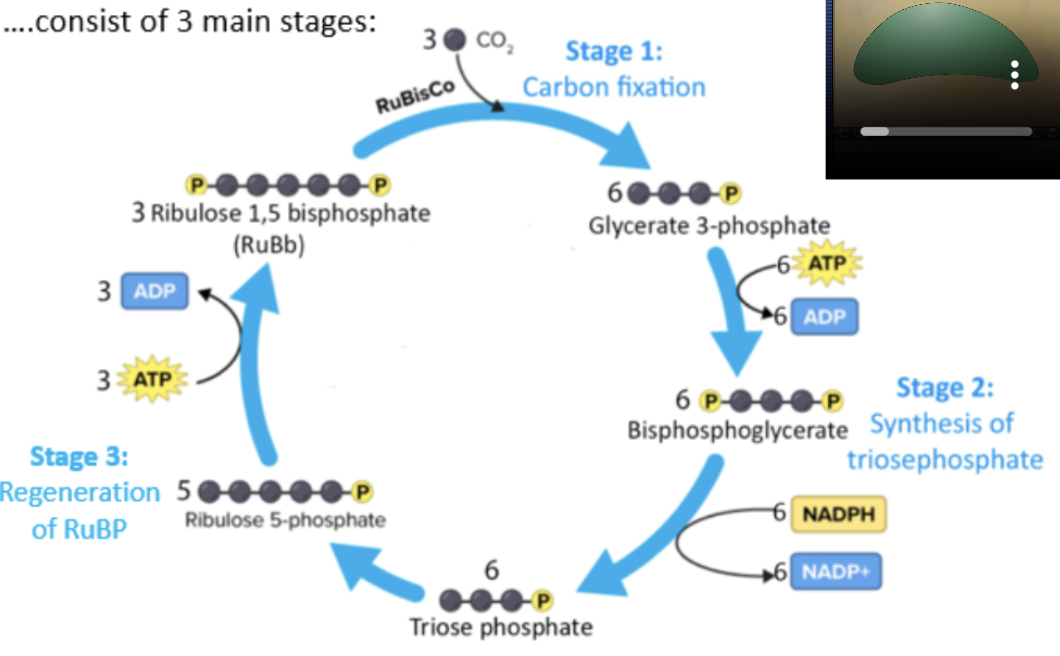
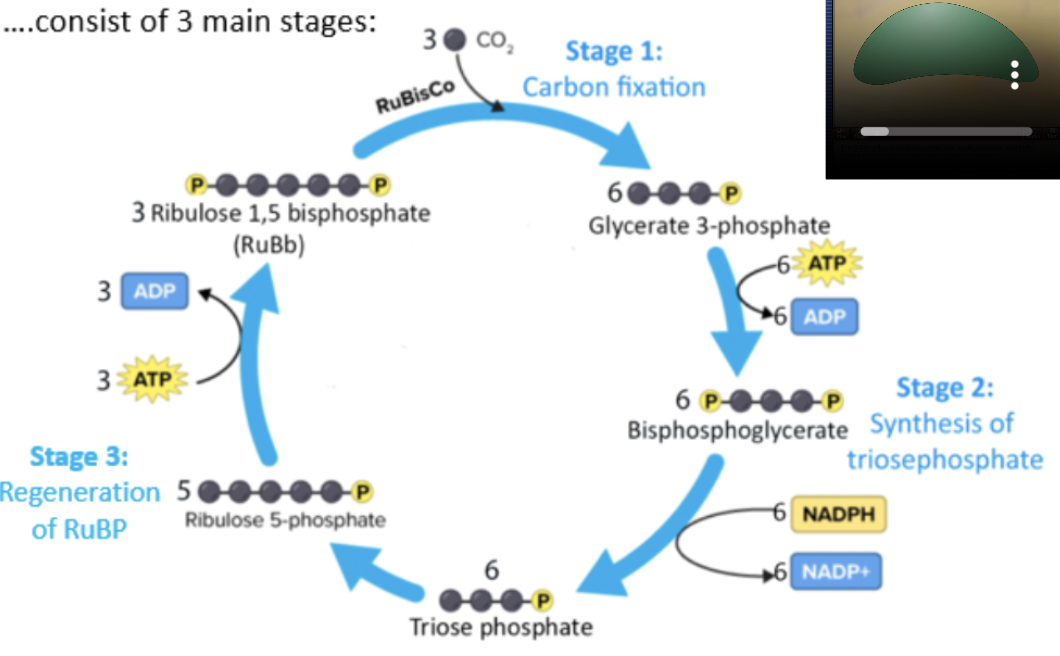
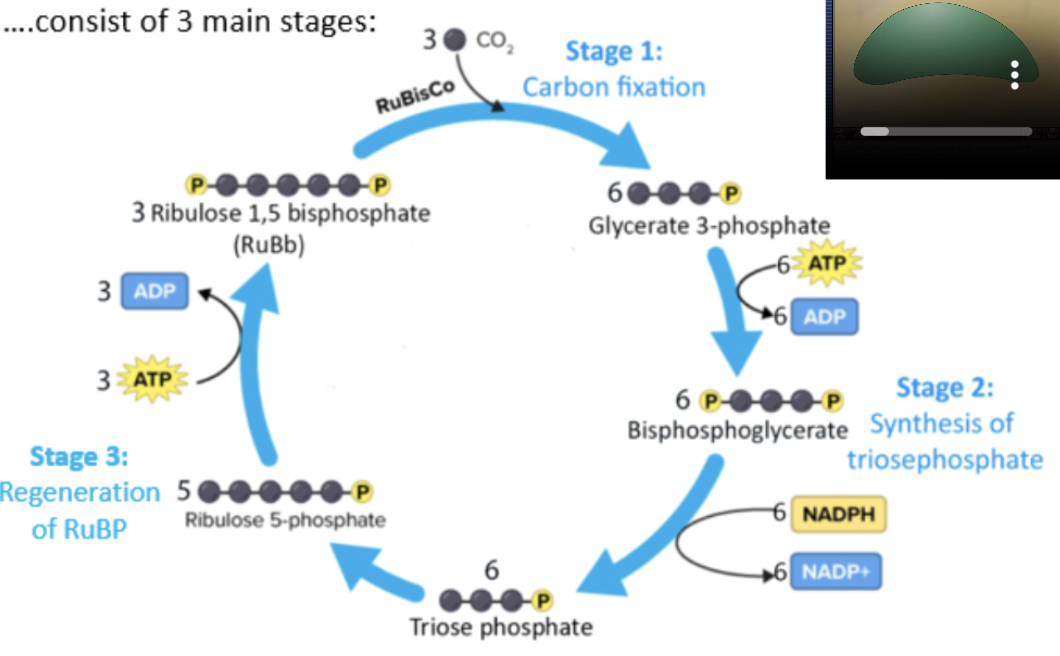
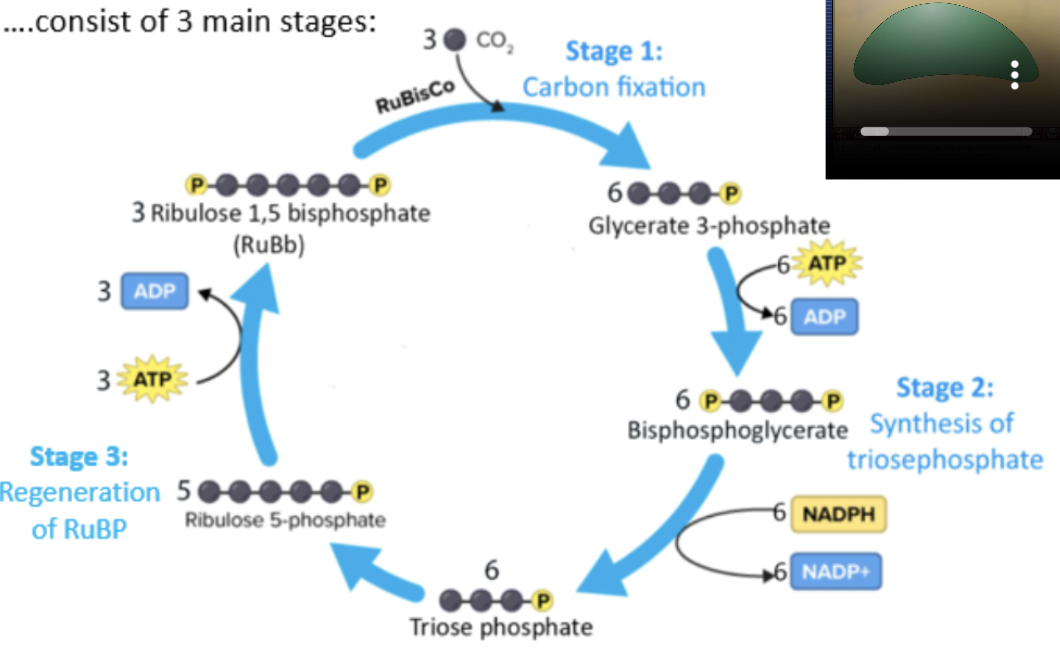
light independent/carbon fixation reaction/Calvin cycle
take place in stroma of chloroplasts, converting CO2 into sugars using energy synthesized in light dependent reactions
carbon fixation
synthesis of triose phosphate
regeneration of RuBP
carbon fixation
enzyme RuBisCo attaches ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP, 5C) with CO2 to fix carbon and produce intermediate products 2 glycerate 3-phosphate (3C each, 6C total)
synthesis of triose phosphate
2 glycerate 3-phosphate (3C each) —(2ATP→2ADP)→ 2 bisphosphoglycerate (3C each)
2 bisphosphoglyceratae (3C each) —(2NADPH→2NADP+)→ 2 triose phosphate (3C each
regeneration of RuBP
2 triose phosphate (3C each) —(ATP→ADP)→ RuBP (5C)
Calvin Cycle math
oxidized NADP+ and ADP molecules per CO2 molecule return to thylakoids to participate in light dependent reactions
6 cycles needed to fix 6CO2 from C6H12O6
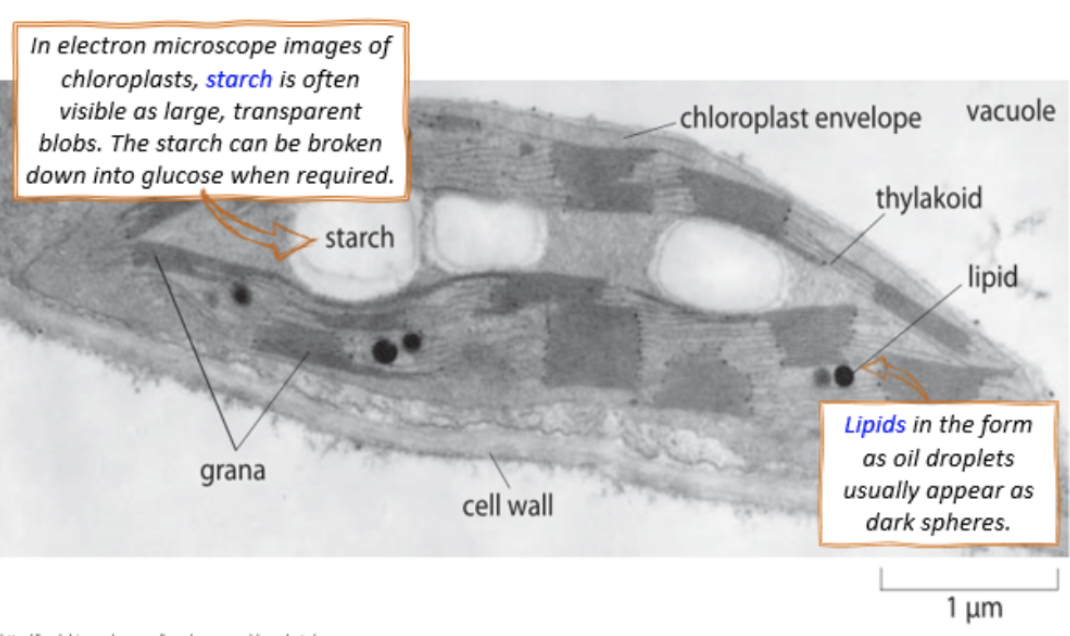
starch granules in the chloroplast under electron microscope
large, transparent blobs
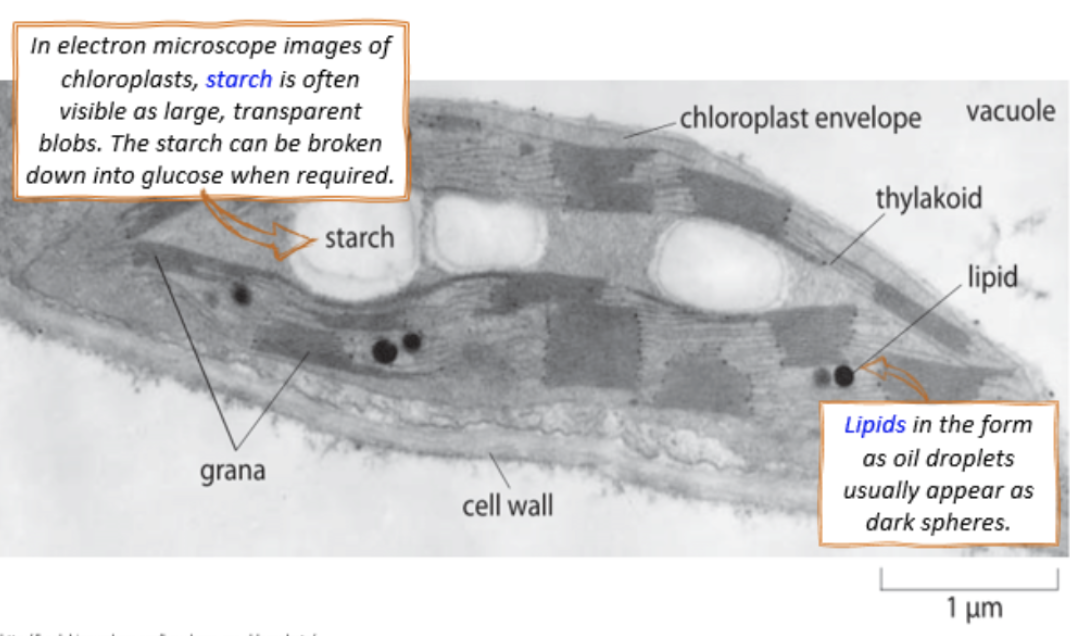
lipids in the chloroplasts under electron microscope
oil droplets appearing as dark spheres