bio 314 wk 4 lab
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
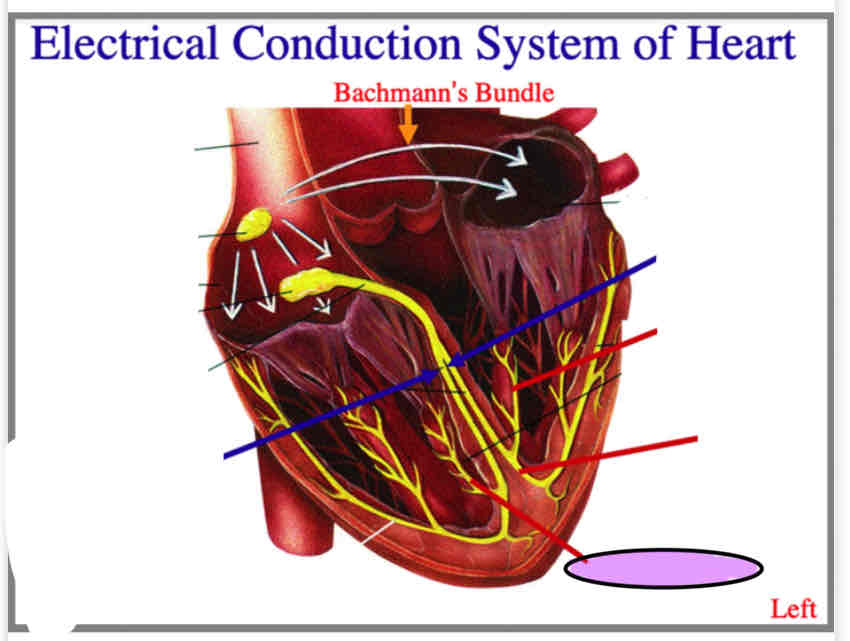
Sinoatrial node
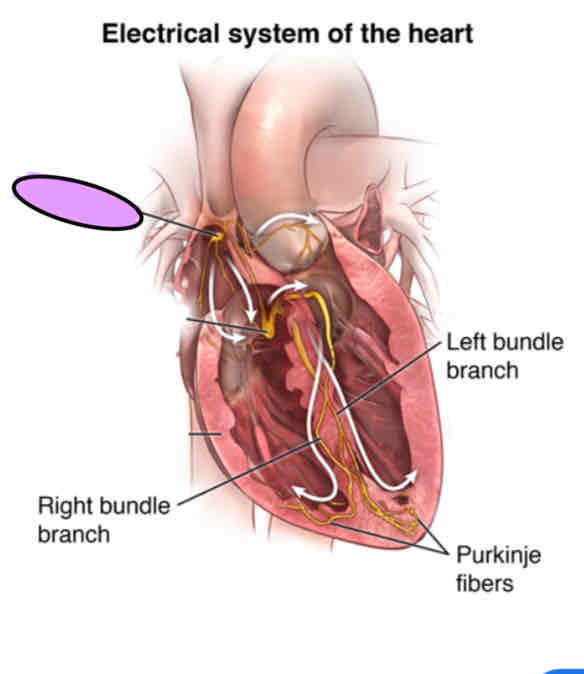
Atrioventricular node
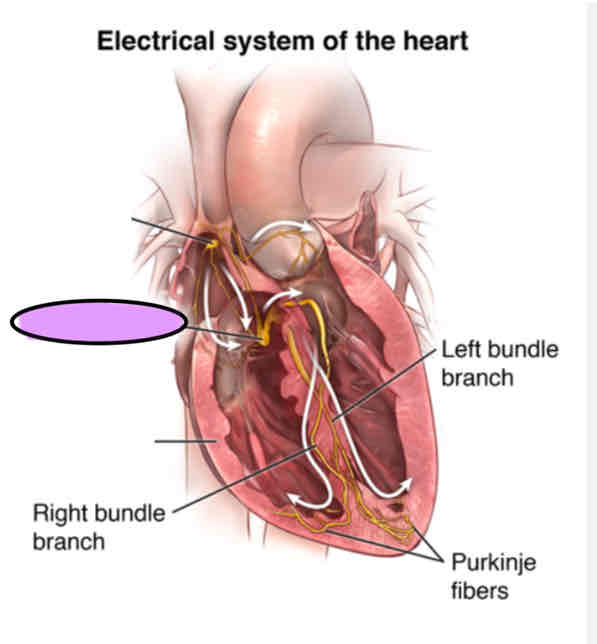
Atrioventricular bundle (or Bundle of His)
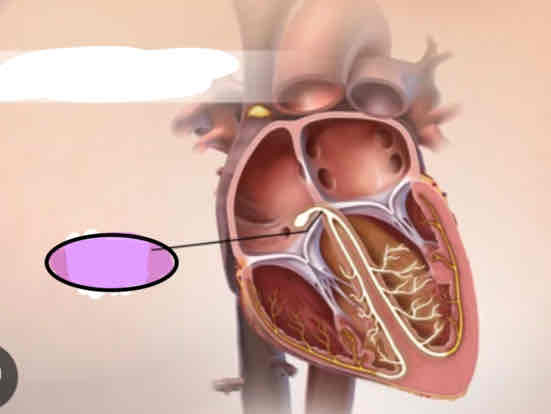
Bundle branch
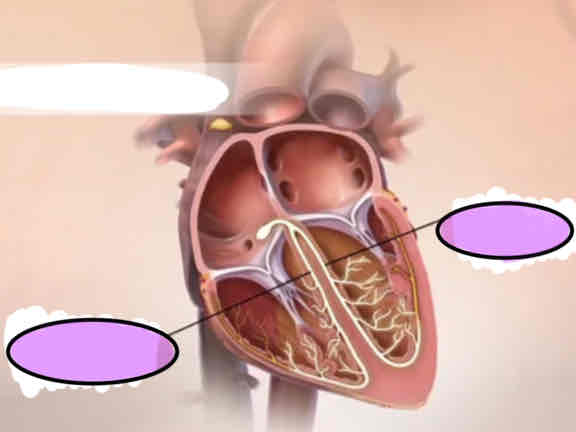
Purkinje fiber
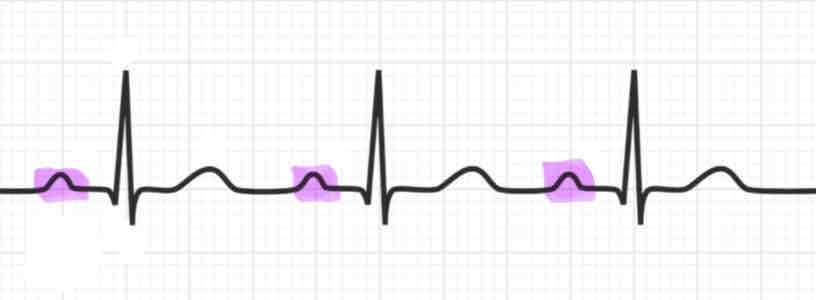
P wave
(Note: Explain what is happening during each)
the first small peak is called the P wave
the atria are depolarizing and contracting
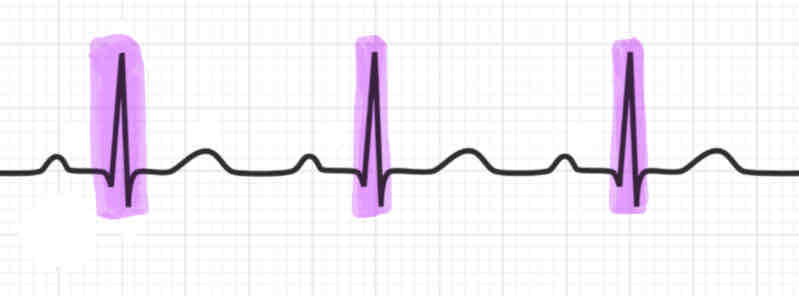
QRS Complex
(Note: Explain what is happening during each)
the sharp downward, upward, downward spike is called the QRS complex
the atria are repolarizing and relaxing. During the end of the QRS complex, the ventricles are depolarizing and contracting
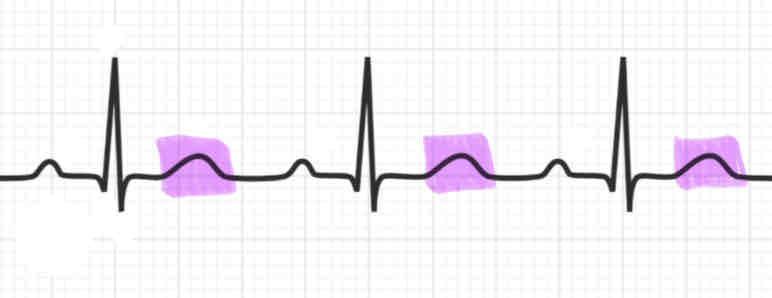
T wave
(Note: Explain what is happening during each)
the final small peak is called the T wave
the ventricles are repolarizing and relaxing
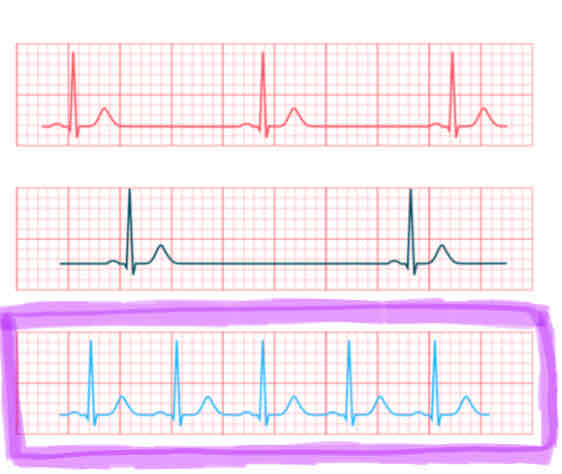
Tachycardia
the heart is pumping too fast
a heart rate of 100 to 150 BPM
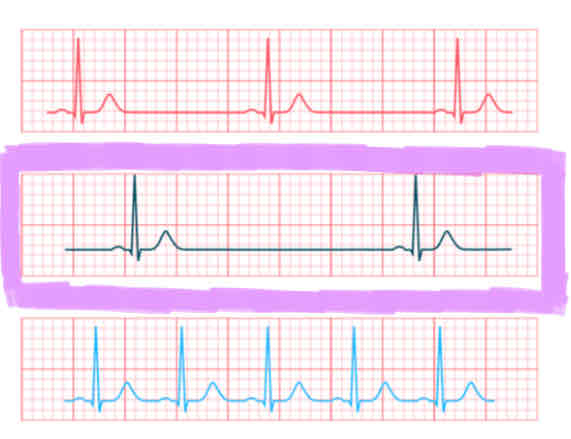
Bradycardia
the heart is pumping too slow
a heart rate of <60 BPM
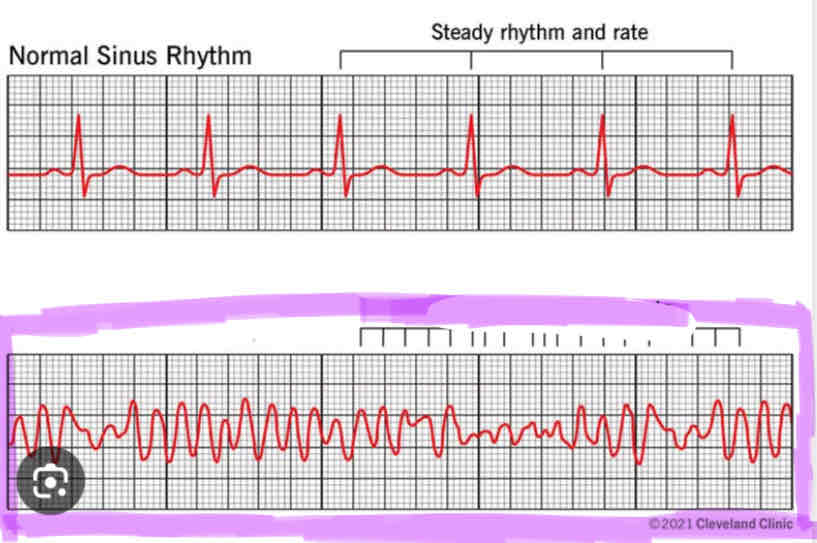
Fibrillation
a heart condition that causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate
Blood pressure
refers to the force of blood against the walls of the arteries as it circulates through the body.
Systolic pressure
the pressure in the arteries when the left ventricle of the heart contracts (systole) and pushes blood into the aorta and the systemic circulatory system. It is the highest, or top, number in a blood pressure reading

Diastolic pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the left ventricle is at rest (diastole). It is the lowest, or bottom, number in a blood pressure reading.

Pulse Pressure
(Note: Be able to calculate)
the difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures. It is calculated by subtracting the diastolic pressure from the systolic pressure.
Pulse pressure= Systolic Pressure- Diastolic pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
(Note: Be able to calculate)
the average pressure in the arteries over the course of a complete cardiac cycle. There are two equally correct ways to calculate MAP: choose the one which works best for you. If you already have pulse pressure, divide it by three and add it to the diastolic pressure.
MAP= (pulse pressure/ 3) + diastolic pressure
A second way to calculate MAP is to add one-third of the systolic pressure to two-thirds of the diastolic pressure.
MAP= (1/3 x systolic pressure) + (2/3 x diastolic pressure)
MAP is a way to measure how much blood is moving through the body.
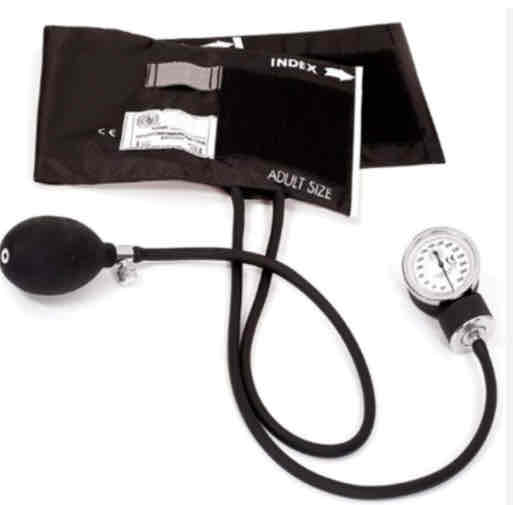
Sphygmomanometer
a medical device used to measure blood pressure. It consists of an inflatable cuff that is wrapped around the upper arm and connected to a gauge that displays the pressure.
Korotkoff sounds
refers to the series of sounds heard through a stethoscope when measuring blood pressure with a sphygmomanometer. These sounds are produced by the turbulent flow of blood through the arteries as the pressure in the cuff is gradually released.
Procedure for measuring blood pressure
Ensure that the person is relaxed and comfortable. They should be seated with their back supported and feet flat on the floor. This is important because the body’s physical orientation, or where on the body the measurement is taken, can influence blood pressure readings.
Locate the brachial artery in the upper arm, just above the elbow crease. This is where the blood pressure cuff will be placed.
Place the cuff snugly around the upper arm, about 2.5 cm above the brachial artery. The cuff should be centered on the arm and the tubing should be aligned with the brachial artery.
Inflate the cuff by squeezing the bulb or pressing the button on the sphygmomanometer. Inflate the cuff to a level that is about 20 to 30 mmHg above the expected systolic pressure (the top number of a blood pressure reading).
Place the stethoscope earpieces in your ears and place the diaphragm of the stethoscope over the brachial artery, just below the cuff. (Figure 21.2)
Slowly release the pressure in the cuff by opening the valve on the sphygmomanometer. As the pressure in the cuff decreases, you should begin to hear a “whooshing” or “swishing” sound through the stethoscope. This is the sound of blood flowing through the brachial artery.
Note the pressure reading on the sphygmomanometer when you first hear the sound of blood flow through the artery. This is the systolic pressure.
Continue to slowly release the pressure in the cuff. Eventually, the sound of blood flow will stop. Note the pressure reading on the sphygmomanometer at this point. This is the diastolic pressure (the bottom number of a blood pressure reading).
In Table 21.2, record the systolic and diastolic pressures, along with the arm used for the measurement and the date and time of the measurement.
Deflate the cuff and remove it from the arm.
Baseline blood pressure
Baseline blood pressure refers to the initial blood pressure measurement taken before any interventions or treatments are administered. It is used as a reference point for subsequent measurements to track changes over time.