A: Unit 1: Human Lifespan & Development
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is meant by Life stages?
Life stages are the number of distinct phases people pass through during their lives
What are the 7 life stages
Infancy: 0-2 years
Early Childhood: 3-8 years
Adolescence: 9-18 years
Early Adulthood: 19-45 years
Middle Adulthood: 46-69 years
Late Adulthood: 70-84 years
Later Adulthood: 85+ years
Age range of Infancy?
0-2 years
Age range of Early Childhood?
3-8 years
Age range of Adolescence?
9-18 years
Age range of Early Adulthood?
19-45 years
Age range of Middle Adulthood?
46-69 years
Age range of Late Adulthood?
70-84 years
Age range of Later Adulthood?
85+ years
What does PIES stand for?
The 4 aspects of growth and development Physical
Intellectual
Emotional
Social
Growth
Physical and measurable changes that increase throughout a persons life
Human Development
A change in a persons skill and capabilities
Life stages
The phases of growth and development a person goes through
Life span
The length of time between a persons birth and death
Life expectancy
The number of years a person can expect to live for
Life course
The pattern of events and experiences that a person goes through during their existence
What are Gross motor skills?
The ability to control the movement of the large limbs of the body e.g Crawling, Walking, Running
What are Fine motor skills?
The ability to control the movements of hands and fingers e.g Writing, Painting, Tying shoelaces
By what age can a child walk up the stairs unaided and hold a crayon or pencil to draw or write?
5 years old
By what age can a child usually catch and throw quite well and will have good sense of balance?
8 years old
What is Group Identity?
{Primary school years (6-8 years)}
A persons sense of belonging to a social group
What is Gendered play?
the ways in which societal expectations and traditional gender roles influence the toys, activities and behaviours that children engage in creating a divide in what’s appropriate for boys and girls
What is the key physical feature of Adolescence?
Puberty, where the reproductive organs demand mature
What hormone causes the physical changes seen in puberty in girls?
Oestrogen
What hormone causes the physical changes seen in puberty in boys?
Testosterone
What is Oestrogen?
A hormone produced in a women’s ovaries that controls sexual development in women and stimulates the changes of the reproductive organs
What is Testosterone?
A hormone produced by the testes that controls the development of male sexual characteristics
Common features of Early Adulthood?
Starting work
Meeting a partner
Settling down and starting a family
What are common features of physical development in Early Adulthood?
People reach their physical peak in early adulthood, and towards the end of early adulthood physical capabilities start to decrease and fertility levels also decrease. Peoples metabolic rate also decreases and as a result people to begin to burn less calories and may gain weight
What is Menopause?
The natural and permanent stopping of menstruation (periods) which usually occurs between ages 45 and 55
How does physical development develop in Middle Adulthood?
Physical capabilities decline and muscle tone is not as good as it was. People may feel that they have lower energy levels and sight and hearing begin to decline. Skin loses its elasticity, and wrinkles become more noticeable. Hair becomes greyer and some men lose some of their hair and become bald.
How does physical development change in Late Adulthood?
The persons skin is thinner, joints are stiffer, muscles are weaker and bones are often more brittle. Physical development at this life stage involves the loss of skills and physical capacities
What is Object Permanence?
Knowing an object still exists even when outside of of view (Develops around 18 months)
Maturation
The gradual process of becoming physically mature
Norms
Average milestones that are expected in all individuals of certain ages
Examples of Gross motor skills
Sitting up unaided (6-8months)
Crawling (9-10months)
Walking (12-15months)
Riding a Bike (24-60months)
Examples of Fine motor skills
Using a spoon (12-18months)
Tying a shoelace (60-72months)
Holding a crayon (12-24months)
Picking up a pea (10-15months)
What is Attachment?
A strong emotional bond babies form with parents or carers
According to John Bowlby, What happens if there is failure to form attachment?
Failure to form attachment within the first 2 years can lead to a hinderance in social + emotional development as it’s a blueprint for all future relationships
Jean Piaget’s stages of cognitive development
Sensorimotor (0-2 years)
Pre operational (2-7 years)
Concrete operational (7-11 years)
Formal operational (11-18 years)
Piaget’s Model
A sense of self develops as children develop the cognitive skills to understand the world around them
What is meant by Egocentric thinking?
A form of thinking typical of the pre operational child in which the child can only view the world from his or her owns perspective and can’t take the perspective of others
What happens during the Sensorimotor stage (0-2 years) ?
Infants build their understanding of the world by exploring through physical actions and sensory experiences. Here they develop object permanence
What happens during the Pre operational stage (2-7years) ?
Children begin to use symbols and language to represent the world but still struggle with logical reasoning. This phase is characterised by egocentrism and a lack of conservation leading them to judge quantity based on physical appearance

What happens during the Concrete operational stage (7-11 years) ?
Children develop logical reason along allowing them to master conservation and understand that physical changes do not alter an objects quantity - They also begin less egocentric, gaining the ability to mentally reverse actions and consider the perspectives/ feelings of others
What happens during the Formal operational stage (11+ years) ?
Adolescents transition to abstract thinking allowing them to solve hypothetical scenarios and concepts not tied to physical reality. They gain the ability to reason systematically about complex subjects
What are some ways to encourage Physics development in children?
Encourage active play
Provide appropriate equipment
Focus on fun not competition
Leading by example
What is meant by Primary sexual characteristics?
The reproductive organs you are born with
What is meant by Secondary sexual characteristics?
these are characteristics which are developed during puberty e.g Pubic hair, Breasts
What is the meaning of decentring?
Can see things from others point of view and are no longer egocentric
Changes to males in puberty:
Shoulders widen
Growth spurt
Facial hair
Body hair
Voice changes
Changes to females in puberty:
Hips widen
Growth spurt
Body hair
Voice changes
What is the meaning of self concept?
The combination of self image and self esteem
What is self image?
How people view themselves based on others reactions to them
What is self esteem?
How highly we think about our abilities and ourselves
Influences to self concept
Life experiences
Age
Appearance
Gender
Culture
Emotional maturity
Education
Relationships
Meaning of the Mid life crisis?
A dramatic period of self-doubt caused by the passing of youth and move to later adulthood
What is Empty nest syndrome?
The sadness parents experience when their children have grown up and have moved out of home
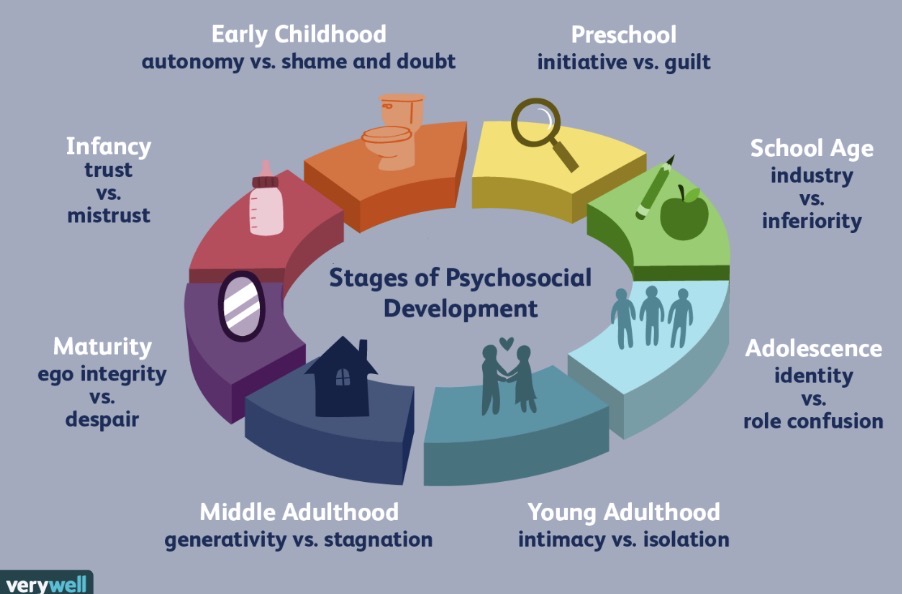
What are Erik Erikson’s stages of Psychological development
Erikson’s theory of outlines eight stages of development, each one defined by a core conflict that shaped personality and identity- successfully resolving these conflicts leads to healthy development
Expected changes of Early Adulthood
Physical peak and maturation
Peak fertility
Pregnancy & lactation
Perimenopause
Slowing metabolism
Subtle appearance changes
What is Perimenopause?
Transition period where oestrogen levels begin to decrease, cause symptoms such as hot flashes, mood swings, night sweats