Topic 10/11 - Electricity, Circuits and Static Electricity
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
In a closed circuit, if there is a potential difference on the circuit there will also be a…..
Current.
Define: Current
Rate of flow of charge/electrons.
What is the unit for current?
Ampere (A).
Current will only flow if ___.
There is a potential difference in a closed circuit.
Which two factors does the current in a circuit depend on?
Potential Difference + Resistane.
Which piece of equipment measures current?
Ammeter.
In which direction does current flow?
From the positive to negative terminal of the power supply.
How does potential difference affect the current?
As the total potential difference of a circuit increases, the current flowing through the circuit also increases.
What is potential difference also known as?
Voltage.
What is voltage also known as?
Potential difference.
Define potential difference in terms of charge.
Work done per unit charge.
What is one volt equivalent to?
1 joule per coulomb.
What are some sources of potential difference?
Cell, batteries/cells and electrical generator.
How does resistance affect the current?
As the total resistance of a circuit increases, the current flowing through the circuit decreases.
How can the current in a circuit be varied?
Using a variable resitance.
What is the unit for resistance?
Ohm, Ω.
A volt can also be described as a….
Joule per coulomb.
Which piece of equipment measures voltage?
Voltmeter.
State the equation linking potential difference, energy transferred and charge.
Energy Transferred = Potential Difference x Charge.
State the symbols for potential difference, energy transferred and charge.
Potential Difference = V
Energy Transferred = E
Charge = Q
State the units for potential difference, energy transferred and charge.
Potential Difference - Volts
Energy Transferred - Joules
Charge - Coulombs
State the equation linking potential difference, energy, current and time.
Energy = Potential Difference x Current x Time.
State the equation linking time, current and charge.
Charge = Current x Time.
State the symbols for time, current and charge.
Time = t
Current = I
Charge = Q
State the units for time, current and charge.
Current - Amperes
Time - Seconds
Charge - Coulombs
State the equation linking potential difference, resistance and current.
Potential Difference = Current x Resistance.
State the symbols for potential difference, resistance and current.
Potential Difference = V
Current = I
Resistance = R
State the units for potential difference, resistance and current.
Potential Difference = Volts
Current = Amperes
Resistance = Ohm, Ω
What is the circuit symbol for a switch?

What is the circuit symbol for a cell?
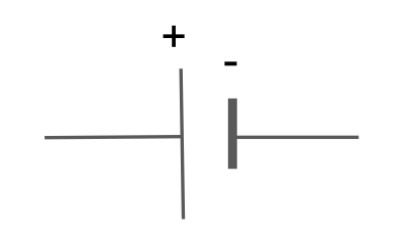
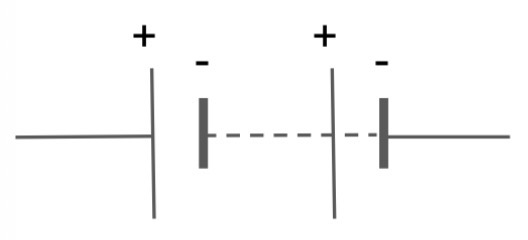
What is the circuit symbol for a battery?
What is the symbol for an open switch?
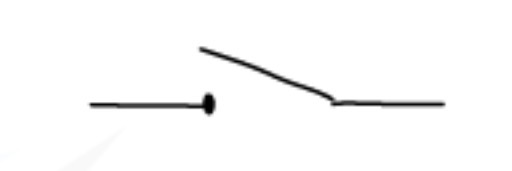
What is the symbol for a closed switch?

What is the symbol for a power supply?

What is the symbol for AC and DC power supply?

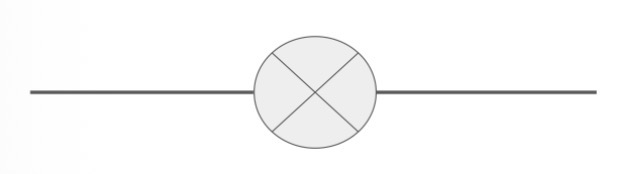
What is the circuit symbol for a lamp?
What is the circuit symbol for a fuse?

What is the circuit symbol for a voltmeter?
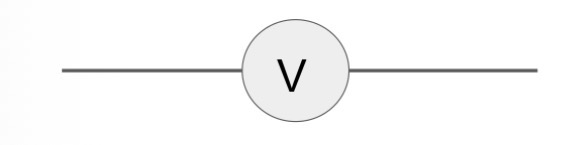
What is the circuit symbol for a ammeter?
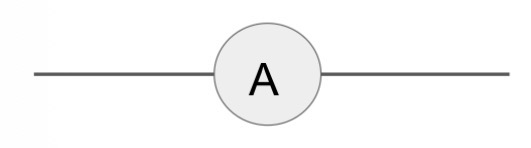
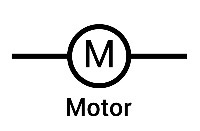
What is the circuit symbol for a motor?
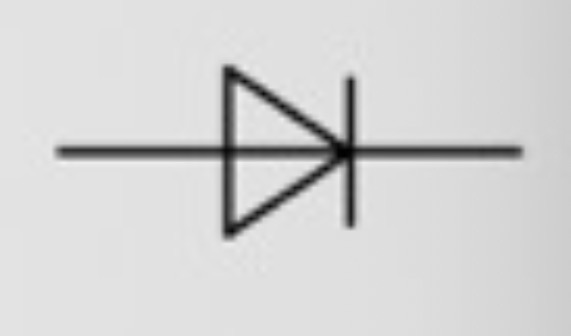
What is the circuit symbol for a diode?
What is the circuit symbol for a resistor?

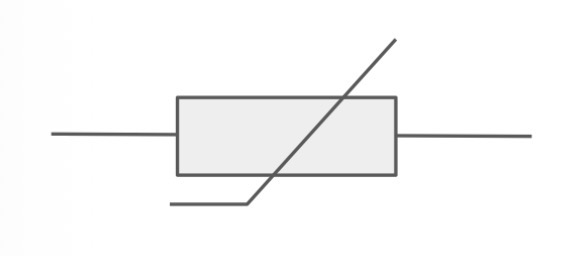
What is the circuit symbol for a variable resistor?
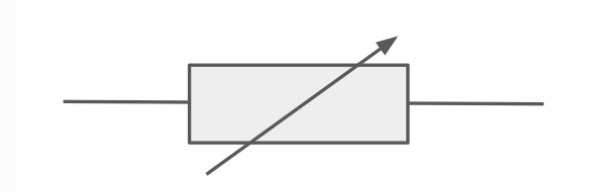
What is the circuit symbol for a thermistor?
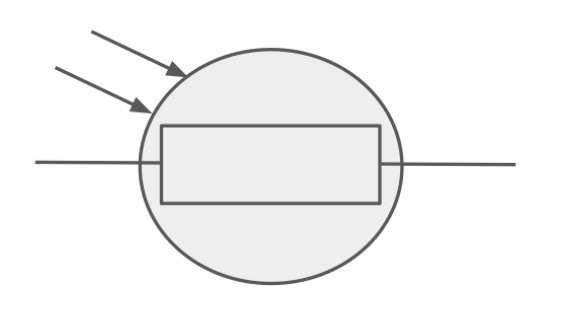
What is the circuit symbol for a LDR?
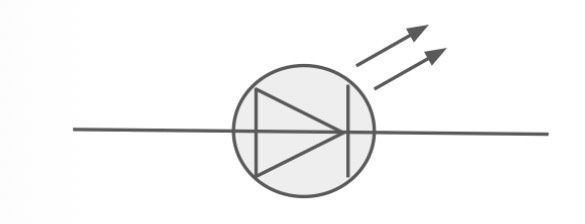
What is the circuit symbol for a LED?
Two or more cells is a ___.
Battery.
Which electrical component provides the circuit with a source of potential difference?
Battery or cell.
What is the role of a cell/battery in an electrical circuit?
Provides the circuit with a source of potential difference.
Which electrical component turns the circuit on or off?
Switch.
Which electrical component limits the flow of current?
Resistance.
What is the role of a resistor in an electrical circuit?
Limits flow of current.
Explain the role of a variable resistor in an electrical circuit.
Change resistance by changing the length of wire.
A longer wire has more resistance than a shorter wire and therefore the larger the resistance, the smaller the current.
A shorter wire has less resistance than a longer wire and therefore the smaller the resistance, the larger the current.
This is because electrons make their way through more resistor atoms so it’s harder to get through a shorter wire.
Does a longer wire have more or less resistance?
More.
Does a longer wire have more or less current?
Less.
Does a shorter wire have more or less resistance?
Less.
What does the resistance of a thermistor depend on?
Temperature.
Which electrical component’s resistance depends on its temperature?
Thermistor.
What happens to a thermistors resistance as temperature increases?
Decreases.
What does the resistance of an LDR depend on?
Light intensity.
Which electrical component’s resistance depends on light intensity?
LDR - Light dependent resistor.
What happens to the resistance of a light dependent resistor as light intensity increases?
Decreases.
Which electrical component converts electrical energy to mechanical energy?
Motor.
What is the role of a diode in an electrical circuit?
Allows current to flow in one direction only. It converts AC to DC.
Which electrical component allows current to flow in one direction only?
Diode.
Which electrical component converts AC to DC current?
Diode.
What is the role of an ammeter in an electrical circuit?
Measures current.
Which electrical component measures current in a circuit?
Ammeter.
Is an ammeter connected in series or parallel with other components?
Series.
What is the role of a voltmeter in an electrical circuit?
Measures potential difference.
Which electrical component measures potential difference?
Voltmeter.
Is a voltmeter connected in series or parallel with other components?
Parallel with relevant component.
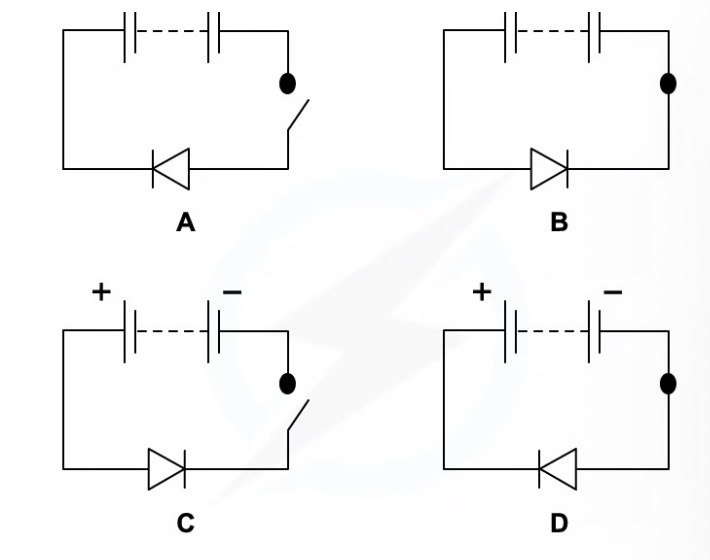
Which circuit diagram correctly represents a circuit with current flowing through? Why?
B.
For a circuit to be connected, the switch must be closed
The other circuit symbol is a diode, which only allows current to flow in one direction. Since current flow is from positive to negative, a forward-biased diode must point in this direction in order for the current to flow.
Name the two types of circuits.
Series and parallel circuit.
How does potential difference vary across series and parallel circuits?
Series - Shared between each component.
Parallel - Each component has the same potential difference.
Compare current in series and parallel circuits.
In a series circuit, the current is the same at all points whereas in a parallel circuit, the current splits at junctions.
Why does current flow from the negative to positive terminal?
Current is the flow of electrons. Electrons are negatively charged so flow away from the negative terminal and towards the positive one.
How is current shared in a series circuit?
Same value at any point.
What happens when current reaches a junction in a circuit?
Current is conserved; total current remains the same and is split between the two branches.
What can be said about the value of current at any point in a single closed loop?
Current is the same at all points.
Is current the same everywhere in parallel or series circuits?
Parallel.
Is current the split at multiple junctions in a series or parallel circuit?
Parallel.
Explain how a greater resistance affects current.
Greater resistance makes it harder for charge to flow through the component, making current smaller.
How is total resistance affected by two resistors in a series circuit?
The total resistance increases and is equal to the sum of the two resistors.
In a series circuit, what does increasing the number of resistors do to the overall resistance? Why?
Increases overall resistance.
This is because the charge has to push through multiple components when flowing around the circuit. The more components the charge has to travel through, the higher the number of collisions that occur.
How is total resistance affected by two resistors in a parallel circuit? Why?
Total resistance decreases and is less than the resistance of the resistor with the lowest resistance.
This is because the charge has more than one pathway to take, so only some charge will flow along each path. The more pathways there are, the smaller the amount of charge in each path.
Why does total resistance decrease when two or more resistors are connected in parallel?
Each resistor creates an extra path along which the charge can flow so more charge can flow, reading to an smaller overall resistance.
Compare the resistance in series and parallel circuits.
In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the resistance in each component.
In a parallel circuit, the total resistance decreases and is less than the resistance of the resistor with the lowest resistance.
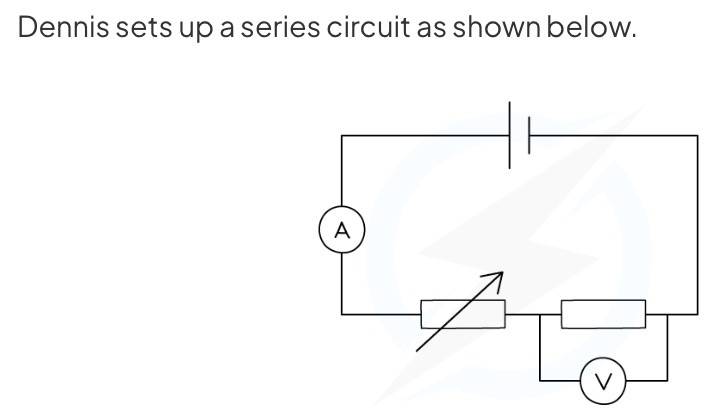
The cell supplies a current of 2 A to the circuit, and the fixed resistor has a resistance of 4 Ω. How much current flows through the fixed resistor?
Since current is conserved in a series circuit, it is the same size if measured anywhere in the series loop. This means that since the cell supplies 2A to the circuit, current is 2A everywhere, including at the fixed resistor.
The cell supplies a current of 2 A to the circuit, and the fixed resistor has a resistance of 4 Ω. What is the reading on the voltmeter?
V = IR so 8V.
Describe the current and potential difference in a series circuit.
The current is the same at all points around the loop.
The potential difference of the power supply is shared between the individual components.
What are the disadvantages of a series circuit?
If one of the components breaks, all of the others will stop working.
The components cannot be controlled (switched on and off) separately.
What is an Ohmic Conductor?
A conductor for which current and potential difference are directly proportional.
Resistance and temperature remain constant.
What is electricity in metals caused by?
The flow of electrons (current).
When an electrical current flows through a resistor, why does it heat up?
There are collisions between the electrons and ions in the resistors lattice.
This causes a transfer of kinetic energy to thermal energy which is released into the surroundings.
How do low resistance wires reduce unwanted energy transfers?
A smaller resistance will mean there are fewer collisions therefore less energy will be wasted through heating.
What are some advantages of the heating effect?
It is useful for appliances like toasters, ovens, heaters or electrical fires which are intended to heat up.
What are some disadvantages of the heating effect?
The loss of energy as wasted thermal energy can make an appliance inefficient.
If an appliance overheats it can catch fire or burn someone when they touch it.
How can the amount of heat created in wires be reduced?
Reduce current in wires or use wires with lower resistance.
Why is copper often used in electrical wiring?
It has a relatively low resistances and is fairly cheap.