Nucleotides and Nucleic Acid Structures
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What are the three components of a nucleotide? Include RNA vs DNA difference
A nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group.
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Nucleoside = base + sugar. Nucleotide = base + sugar + phosphate.
What type of bond connects the base to the sugar?
A β-glycosidic bond between the C1′ of sugar and N9 (purines) or N1 (pyrimidines).
Which bases are purines? Which are pyrimidines?
Purines: Adenine (A), Guanine (G). Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U).
What type of bond connects phosphate to the sugar?
Phosphoester bond at the 5′ carbon of the sugar.
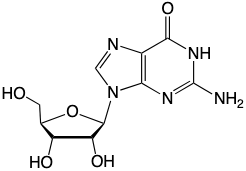
Guanosine
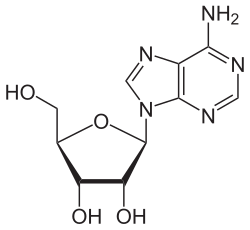
Adenosine
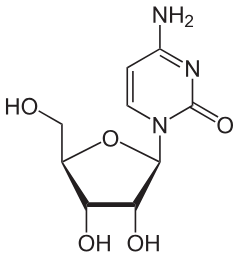
Cytidine
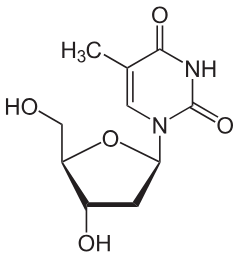
Thymidine
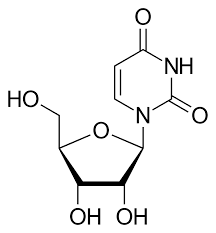
Uridine
What defines the primary structure of nucleic acids?
The sequence of nucleotides linked by 3′–5′ phosphodiester bonds.
What interactions stabilize secondary structure? what is secondary strucure.
Hydrogen bonds between base pairs (A–T, G–C) and base stacking through π–π interactions. sec structure is double helux formed by comp base paring.
What is tertiary structure in nucleic acids?
supercoiled and folded arrangements (3D): supercoiling, bending, and looping (e.g., closed circular DNA, tRNA folding).
What is quaternary structure DNA?
Association of nucleic acids with proteins: chromatin (beads on a string) or ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). Nucleosome (Dna+ histone, one bead
How does the backbone form?
The 3′-OH of one nucleotide binds to the 5′-phosphate of the next → phosphodiester bond.
Why is the backbone negatively charged? |
The phosphate group’s oxygen atoms carry negative charges, giving DNA its acidic property.
Why is GC-rich DNA more stable?
G–C pairs form 3 H-bonds and stronger stacking → higher melting temperature (Tₘ).
Describe A-DNA.
Right-handed, 11 bp/turn, short & wide (24.6 Å pitch). Forms under dehydrated conditions
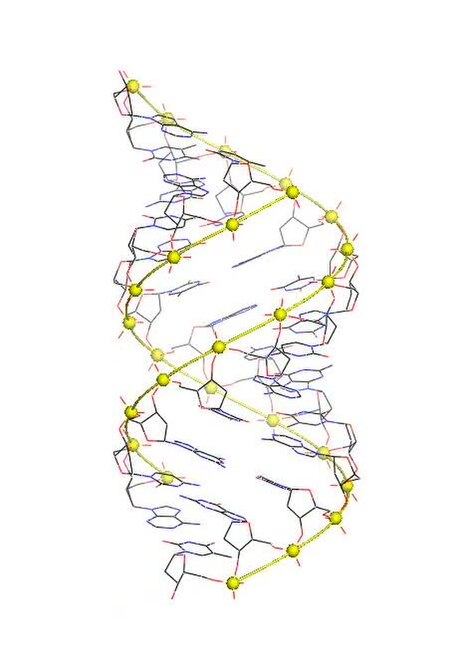
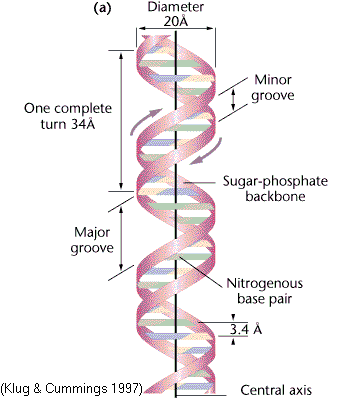
Describe B-DNA
Right-handed, 10 bp/turn, 3.4 Å spacing; major and minor grooves; physiological form found in cells.
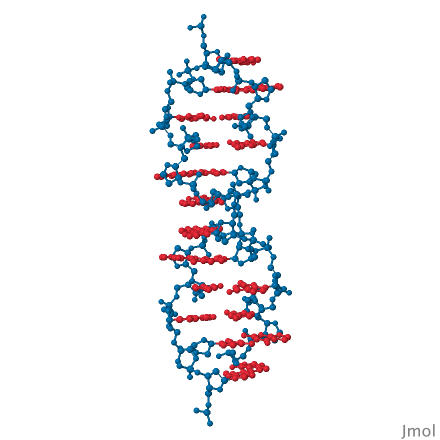
Describe Z-DNA. |
Left-handed (IMPORTANT), zig-zag backbone; forms in GC-rich or methylated regions; may regulate gene expression.
What causes B ↔ Z DNA transitions?
Cytosine methylation or GC repeat sequences can switch helical direction.
What are H-DNA and Cruciform DNA?
H-DNA: Triplex (1 purine-rich (A-G), 2 pyrimidine-rich strands(C-T)). Cruciform DNA: 4-way junction at palindromic regions.
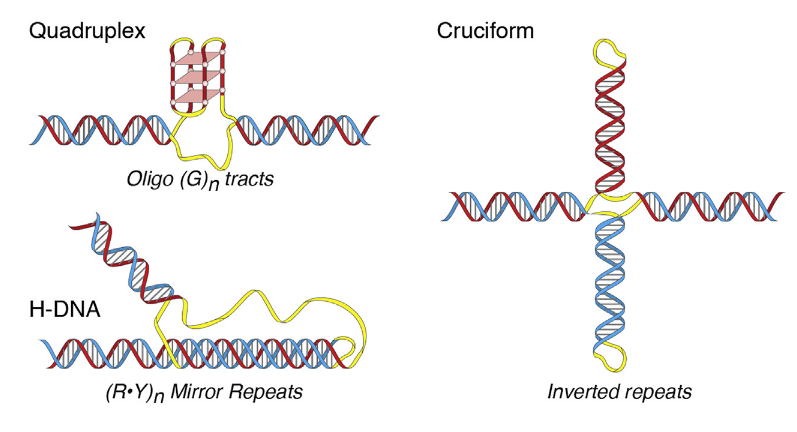
Describe RNA’s stability vs. DNA
less (its more flexible)
What are the 4 RNA secondary elements?
Stems, loops, bulges, and junctions formed by intra-strand base pairing. buge unpaired on one side, loop on both.
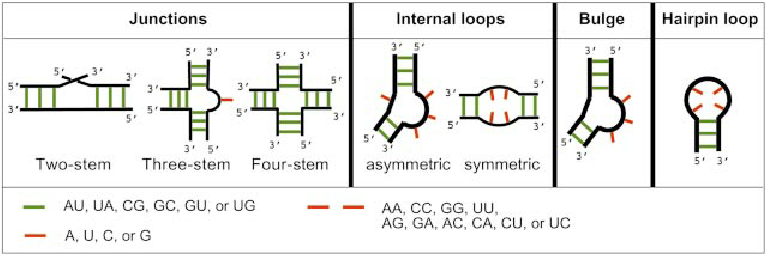
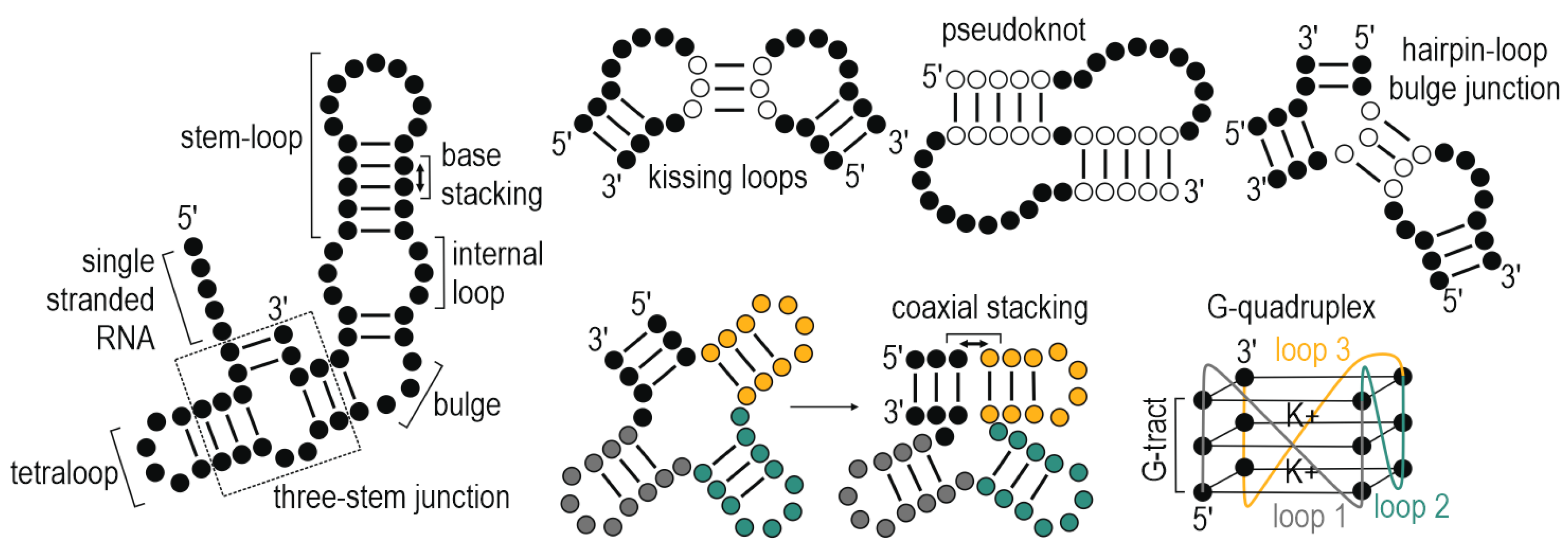
What are RNA tertiary interactions?
Coaxial stacking and pseudoknots (hairpin loop base-paired with another region).
Describe tRNA secondary and tertiary structure.
tRNA (~73–94 nt): Cloverleaf secondary, L-shaped tertiary formed by interactions between D-loop and TψC loop.
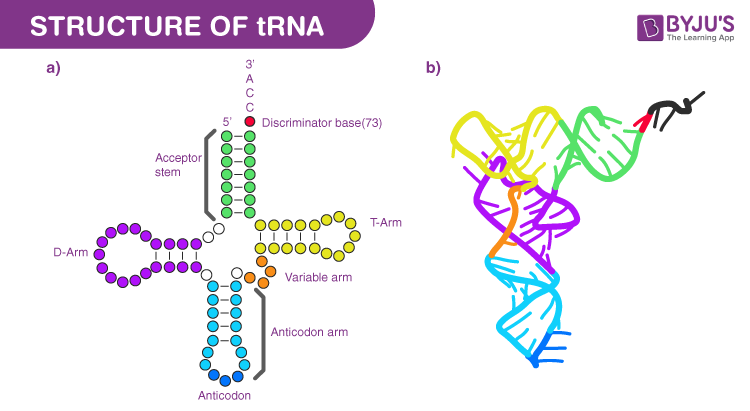
What happens when DNA is heated and cooled?
Hydrogen bonds break, strands separate (denaturation). Upon cooling, they reanneal.
What determines the melting temperature (Tₘ)?
GC content (↑GC = ↑Tₘ), ionic strength, DNA length, and sequence complementarity.
What is DNA hybridization?
Mixing DNA from different sources; similar sequences form hybrid duplexes — used to measure genetic similarity
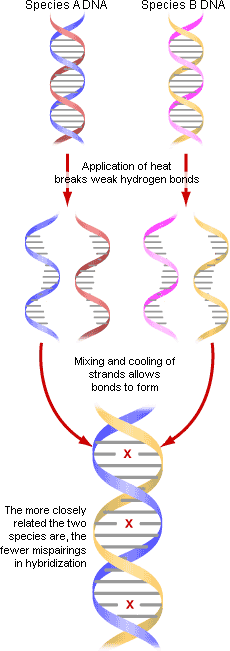
What is the role of intercalating agents?
Flat molecules (ethidium bromide, acridine orange) slide between base pairs, distorting the helix and interfering with replication.
What is adenosine and function. what does caffeine do to it
its a nucleotide. regulates Heart beat, promotes blood vessel dialation, sleepiness. caffeine blocks adenosine receptor.
NDP and NTPs (high energy) nucleotides contain addtional phosphates linked by
phosphoric anhydride linkages
What are histones?
Positively charged proteins that help wrap and organize DNA.
What does the β-configuration of the glycosidic bond mean?
The base is attached above the plane of the sugar ring.
How many degrees of freedom exist per nucleotide unit?
Six torsional angles in the sugar–phosphate backbone.
How many base pairs per turn in B-DNA?
About 10 bp per turn.
What may be the function of Z-DNA?
Possible role in gene regulation.
What is mRNA’s function?
Carries genetic information from DNA for protein synthesis.
What is rRNA’s role?
Structural and functional core of the ribosome.
What is tRNA’s role?
transfers amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
What are small RNAs like siRNA and miRNA used for?
Gene silencing and regulation
Which of the following can also be called "beads on a string" motif?
Nucleosomes
T/F DNA’s 2-deoxyribose increases resistance to alkaline hydrolysis compared with RNA.
true
Ribose is deoxygenated “2-deoxyribose” → causes greater resistance to ____ _____; strong base may denature DNA but won’t cleave the
phosphodiester bond
alkaline hydrolysis
What makes nucleotide soluble?
hydrophilic, charged sugar-phosphate backbone
Examples of secondary structure
A DNA, B DNA, Z DNA, H DNA, Cruciform
snRNA
Functions in various nuclear processes (ex. slicing)
snoRNA
Facilitates chemical modifications of RNAs
miRNA
regulates gene expression
siRNA
silences gene expression
lncRNA
regulates gene expression
RNA quaternary structure
Ribosome: rRNAs plus
ribosomal proteins; shows
tertiary and quaternary
interactions when assembled