Enzymatic catalyst 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Enzymology
enzymic reaction mechanisms, regulations and rates
subfields of enzymology
structural biology and kinetics
catalyst definition
speeds up the rate of reaction; is not altered or consumed.
there (is/isn’t) change in Keq or delta G0 of the process
isn’t
transition state
highly reactive, high-energy state.
∆G≠
free energy of activation or activation energy
what conformation is the transition state
half chair
∆G≠ ensures reaction (does/doesn’t) always occur
doesn’t
the numbers of molecules with energy is ___ transition state
>
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
graph depicting the fraction of molecules against energy
Rate of reaction (V) equation
V=k[Boat]
Arrhenius equation
k=Ae-∆G≠
to speed up a reaction ___ ∆G≠ and ____ Temp
lower; raise
∆∆G≠ =
∆G1≠ - ∆G2≠
degree of rate enhancement
k2/k1= e∆∆G≠/RT
enzymes and substrates are ____ between the active site of E and S
complementary
examples of weak noncovalent bonds
ionic, electrostatic forces, hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals interactions, H-bonding, geometric or electronic
tight binding between E and S is ___
bad
lock and key model of substrate binding
explains specificity but not stabilization of the intermediate shape of the substrate.
induced fit model of a substrate binding
explains stability of ES complex with limits- no real distortion
type of reactions catalyzed by oxidoreductases
oxidation-reduction reactions
type of reactions catalyzed by transferases
transfer of functional groups
Type of reactions catalyzed by hydrolases
hydrolysis reaction
type of reactions catalyzed by lyases
group elimination to form double bonds
type of reactions catalyzed by isomerases
isomerization
type of reaction catalyzed by ligases
bond formation coupled with ATP hydrolysis
serine proteases
class of peptidases with a Ser in the active site
serine proteases are grouped into __ clans by _ and 40 families by ——
13; catalytic mechanism; sequential homology
Major clans in human
chymotrypsin-like; subtilisin-like; α/β hydrolase; signal peptidase
serine proteases participate in functions in _______
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase are synthesized by ___ and secreted into __
pancreatic acinar cells; small intestine
chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastases difference is the
peptide bond being cleaved
scissile bond
covalent chemical bond in a molecule that is susceptible to cleavage, or breaking, by an enzyme
__ of amino acids at the active sites are key
side chains
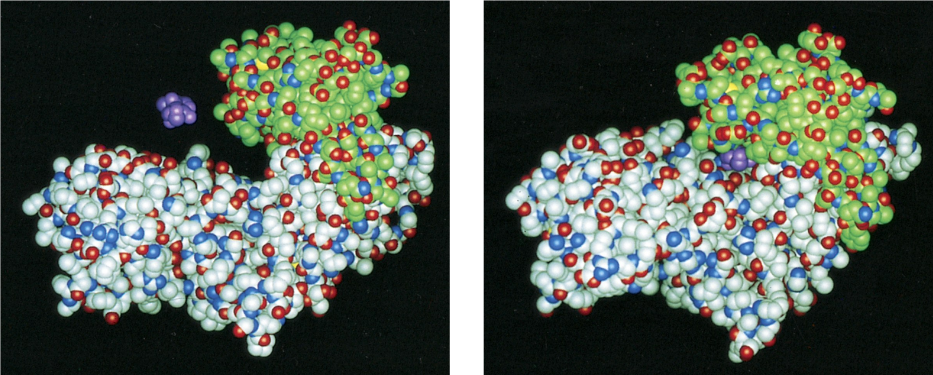
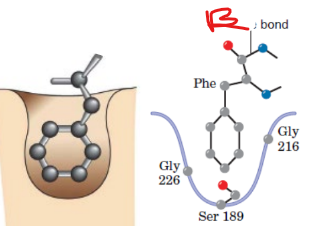
Chymotrypsin
has big hydrophobic pocket at active site
cleaves peptide bonds following a bulky hydrophobic amino acid
prefers Tyr, Trp, Phe, Met
Trypsin prefers
Lys or Arg
Elastase prefers
Ala, Gly, Val
catalytic triad
Asp, His, Ser
Catalytic triad is
conserved/essential for serine proteases
charge relay system
binding of S → release of N-term “half” → binding of water (another S) → release of C-term
serine (195) acts as a ___ and attacks the carbonyl carbon of a __ bond of the substrate
nucleophile; scissile
Histidine (57) has ability to accept H from ___ -OH group and coordinates the attack of the __ bond by the serine
serine; peptide
Aspartic acid (102) makes H-bond with the ___ and makes the pair of electrons on the ___ (same as the first) much more ___
histidine; electronegative
Zymogen
inactive precursors; activated only at the right location
large inactive structure →
smaller activated enzyme
active site is hidden or distorted (S cannot bind)→
no proteolysis
cofactors
non-protein
has “chemical teeth”
chemical teeth
broadens the range of enzymes’ catalytic properties
holoenzyme (active) =
apoenzyme (inactive) + cofactor
Types of cofactors
metal ions
coenzymes
coenzymes
cosubstrates; prosthetic groups
cosubstrates
loosely bound, cycle on and off
prosthetic groups
tightly/covalently bound
subtypes
metabolic coenzymes; vitamin-derived coenzymes
metabolic coenzymes
synthesized by common metabolites
vitamin-derived coenzymes are supplied from the
diet
water-soluble subtypes of cofactors
vitamins B and C
lipid-soluble vitamin-derived coenzymes of coenzymes
vitamins A, D, E and K
many vitamins are
coenzyme precursors
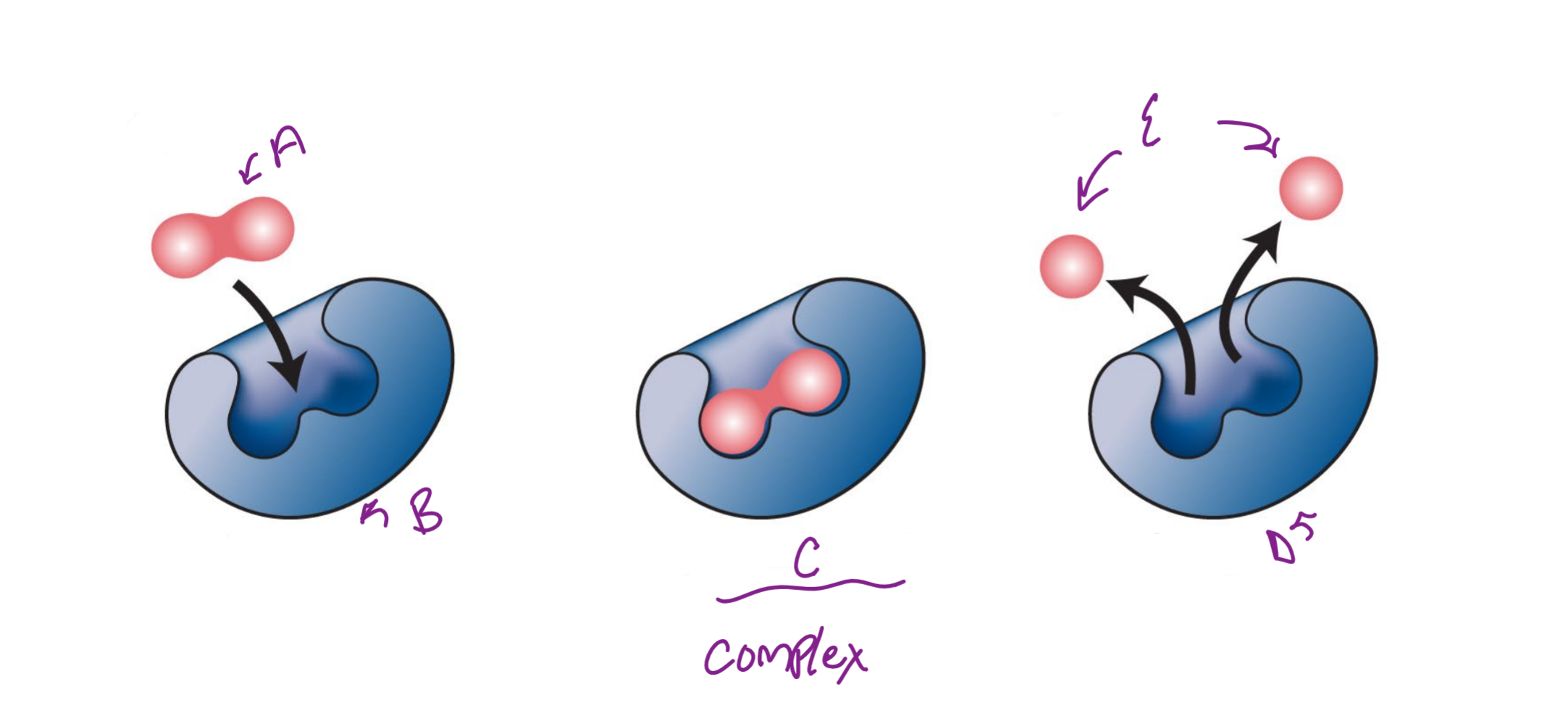
A
substrate
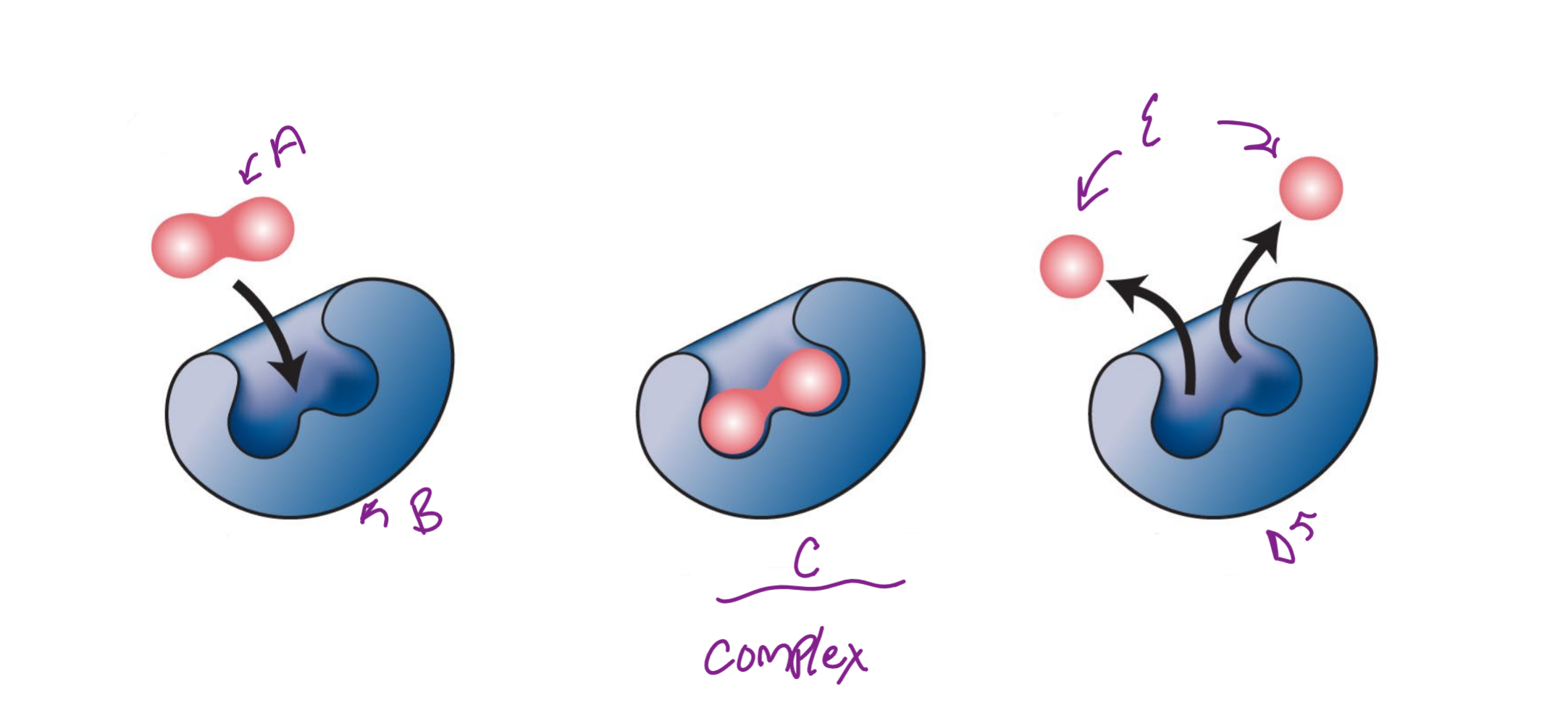
B
Enzyme

c
enzyme-substrate complex
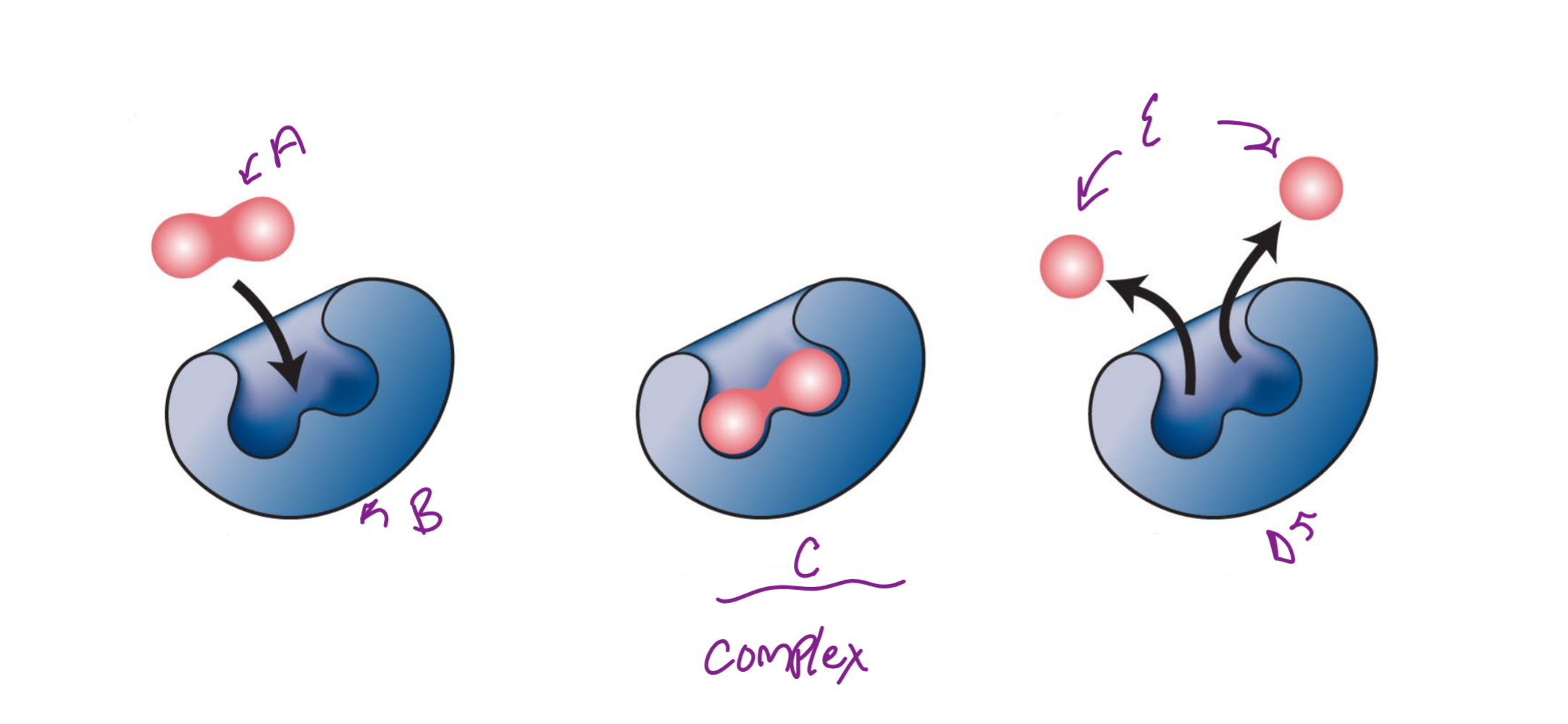
d
enzyme
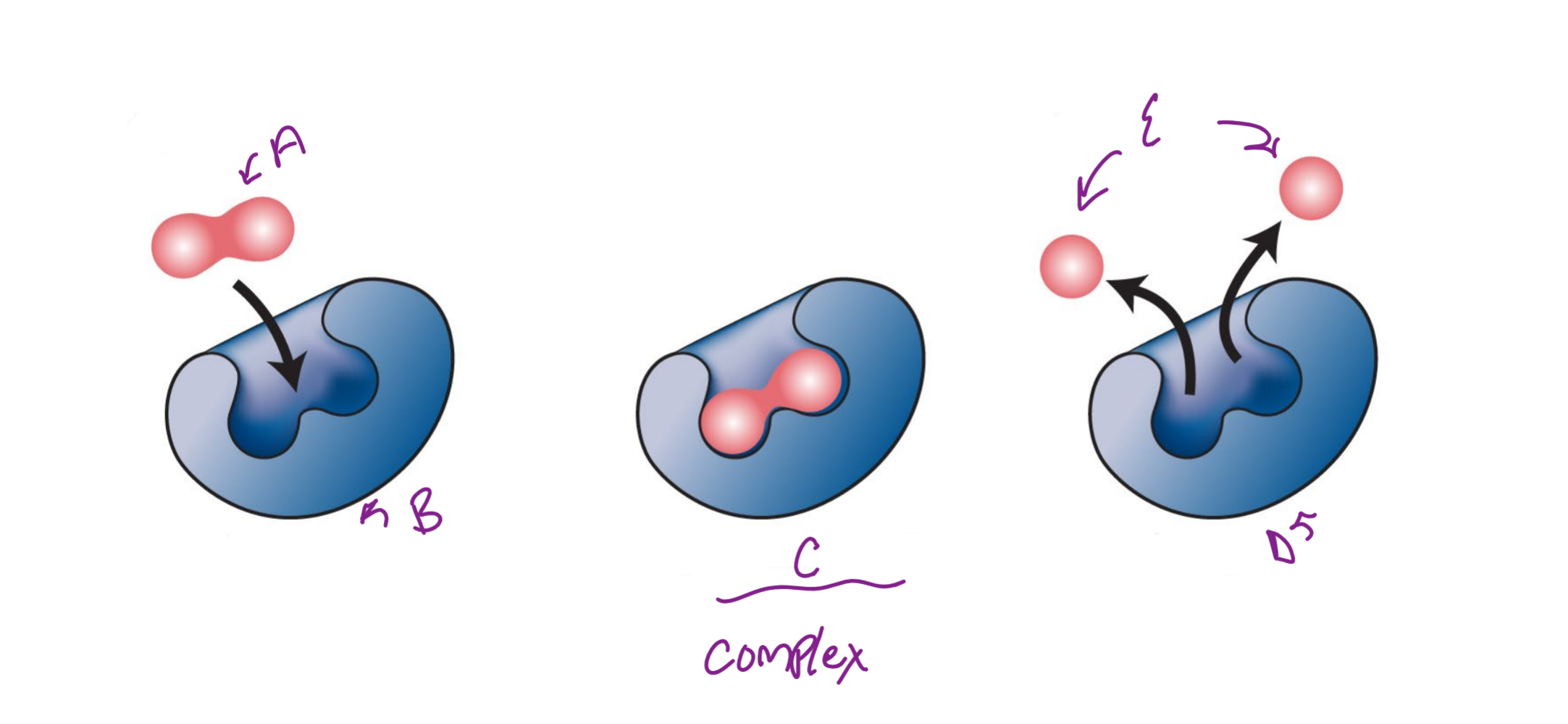
e
product
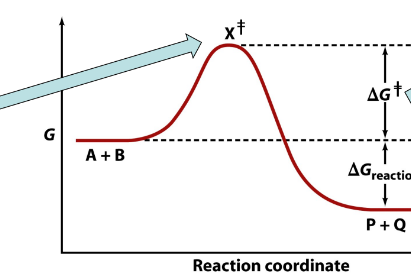
arrow is pointing to___
transition state
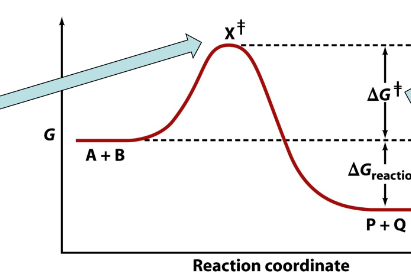
delta G≠
spontaneous reaction

delta G reaction
nonspontaneous
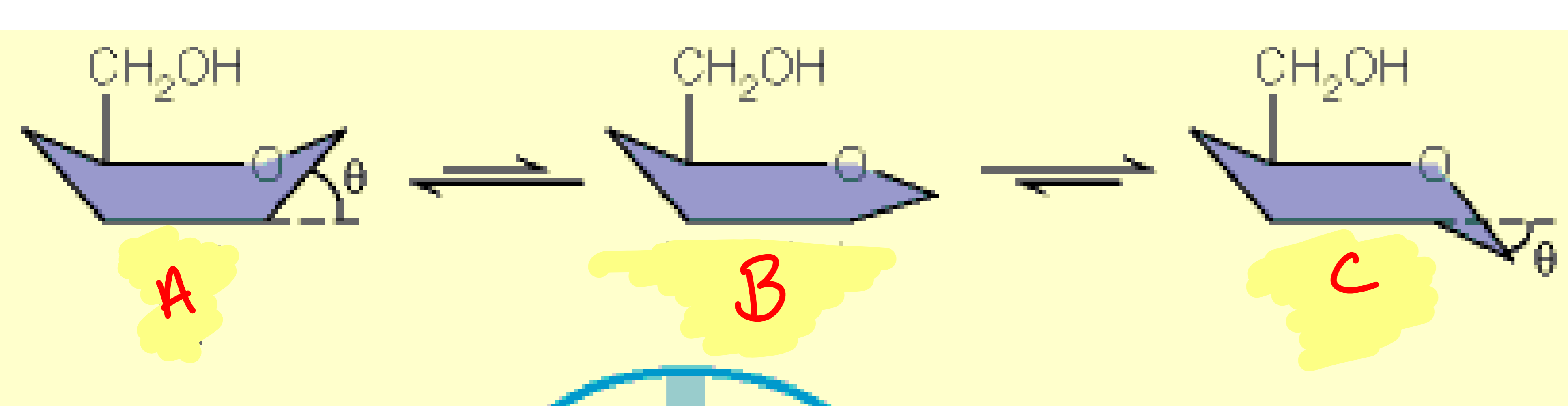
a
boat
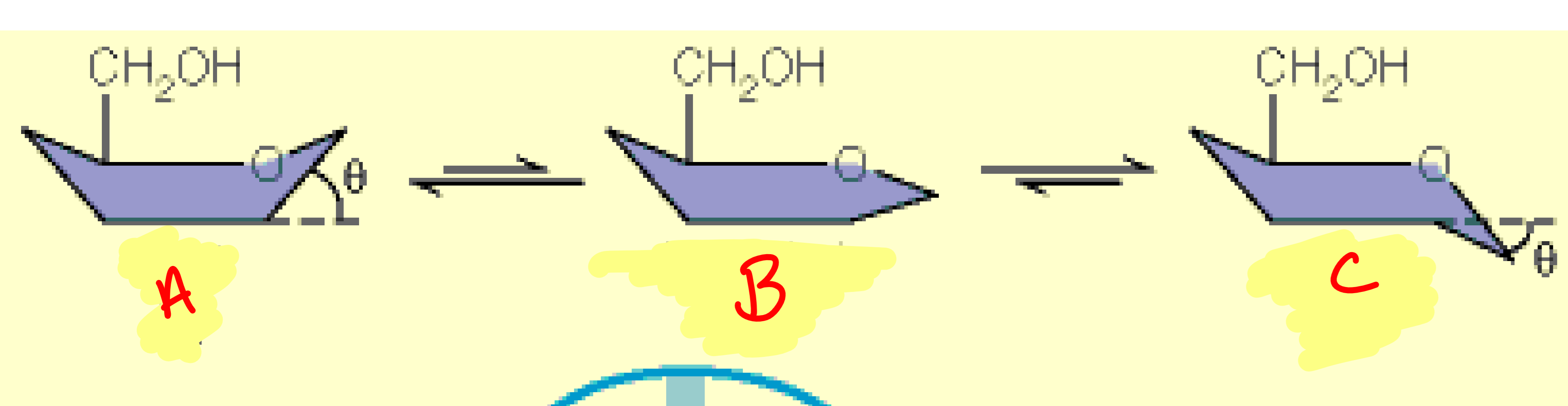
b
half-chair
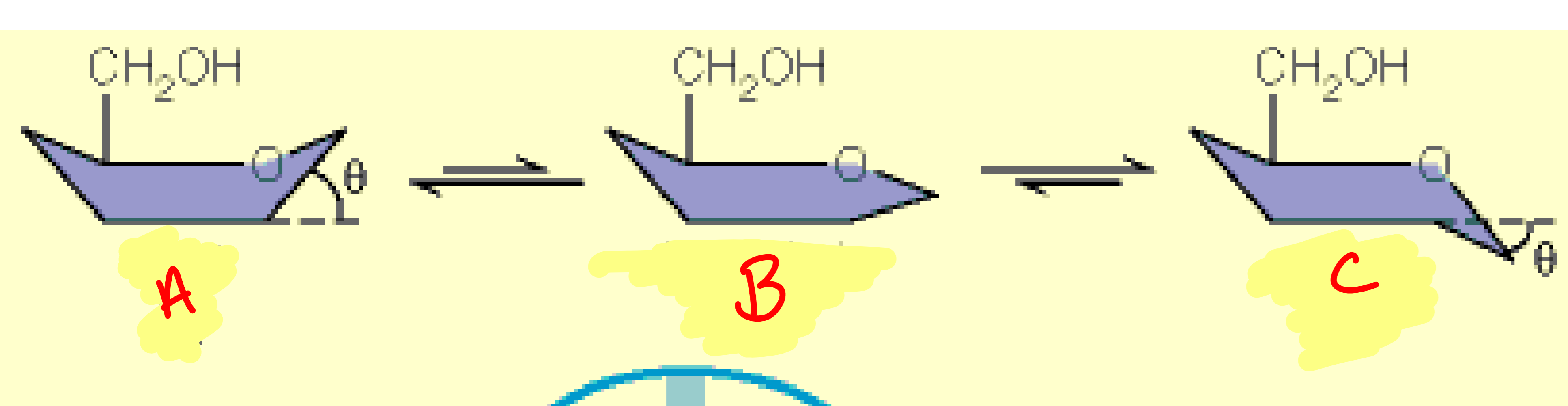
c
chair
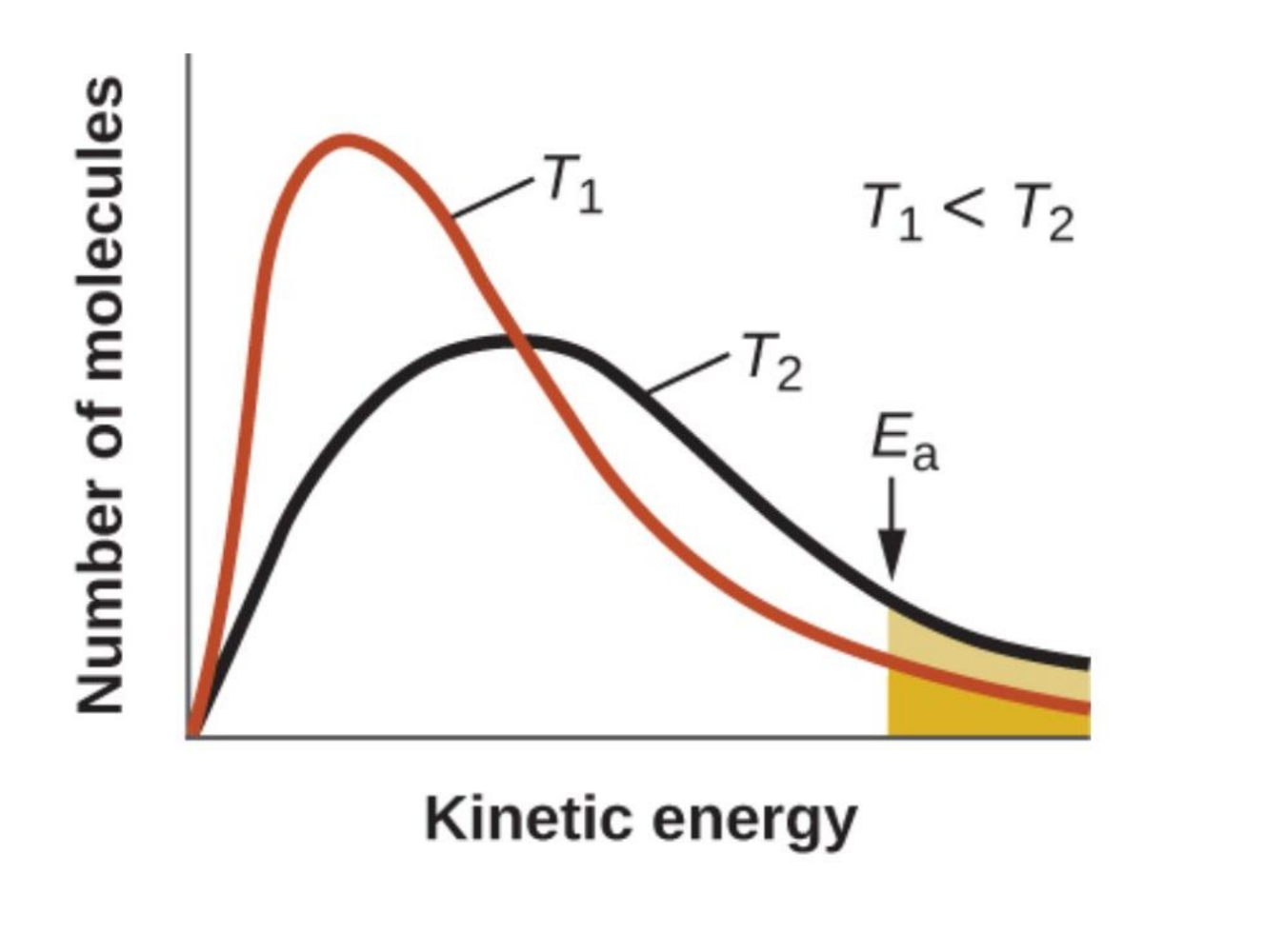
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution

a
acids, bases or metals
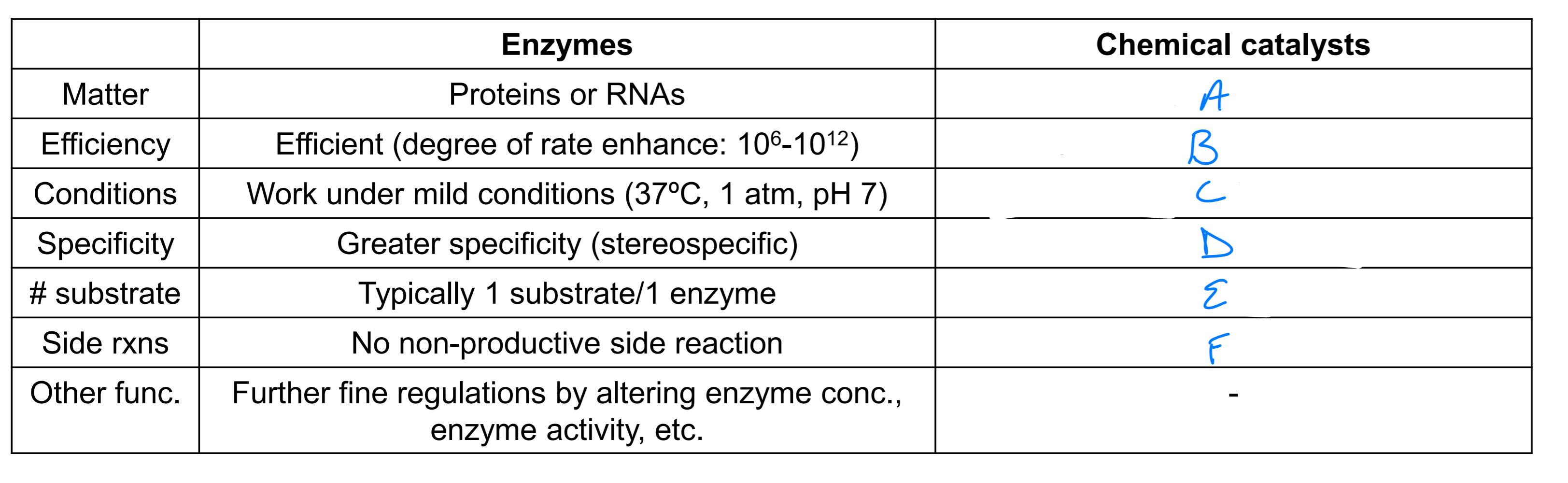
b
10^4 - 10^8 slower than enzymes
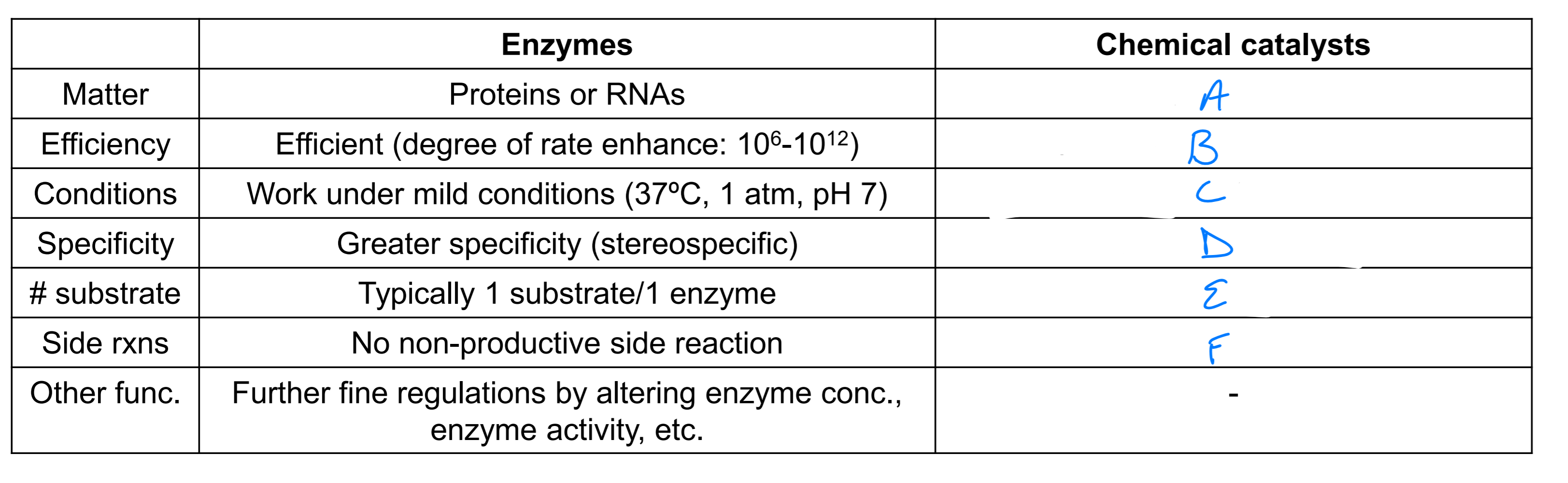
c
optimal under extreme conditions

d
lower specificity
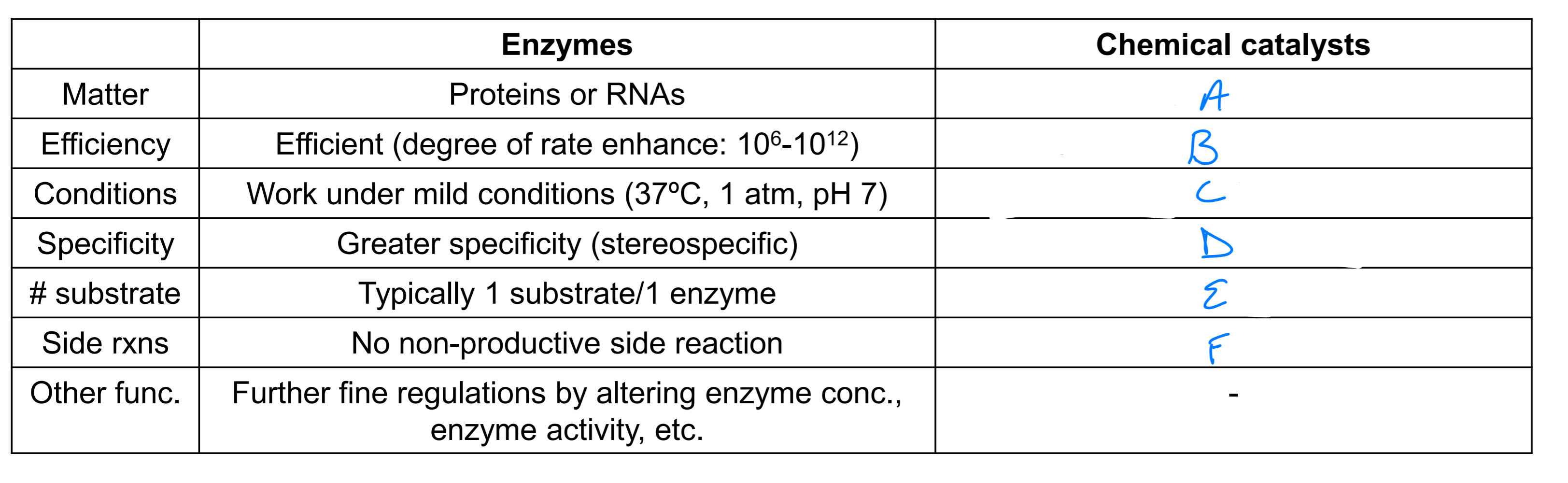
e
vary
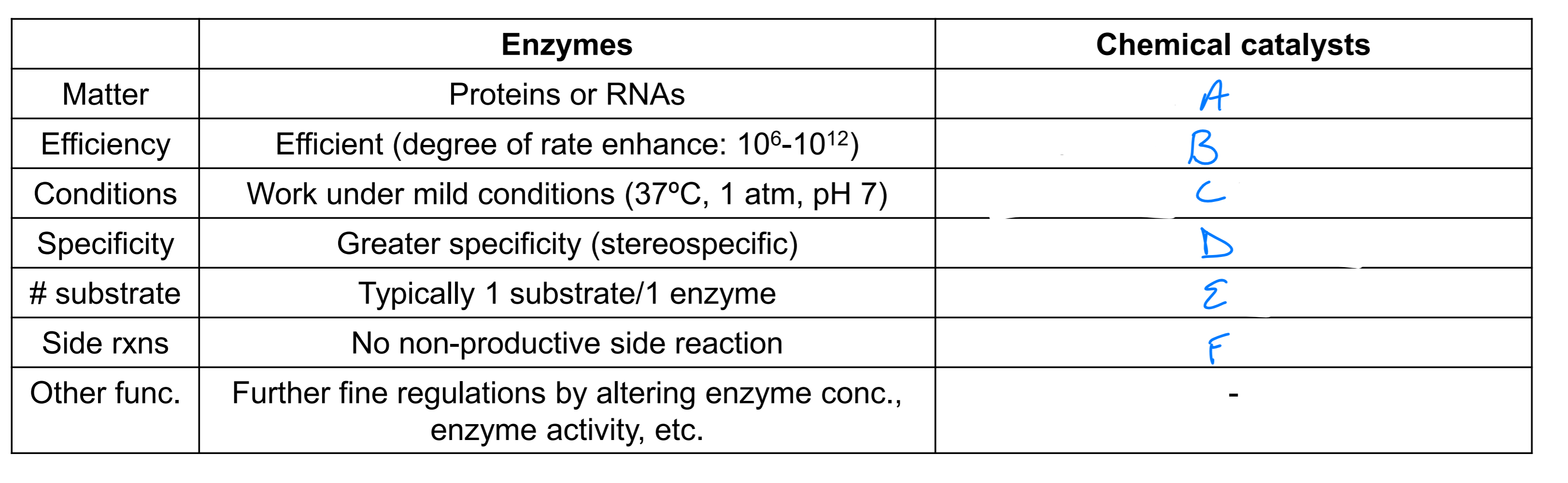
f
potential side rxns
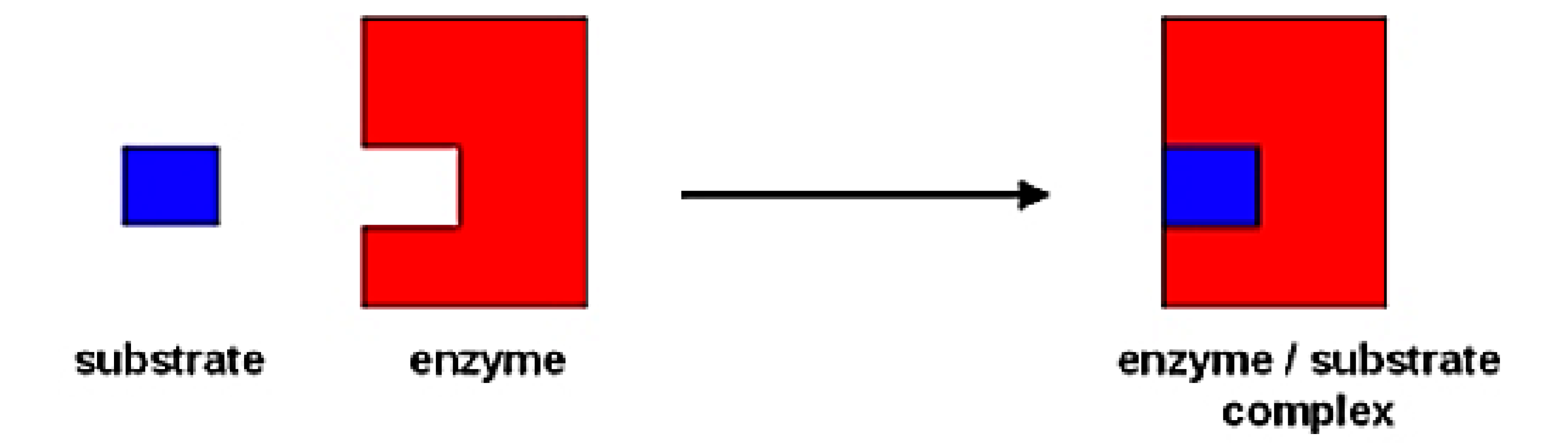
lock and key model of substrate binding
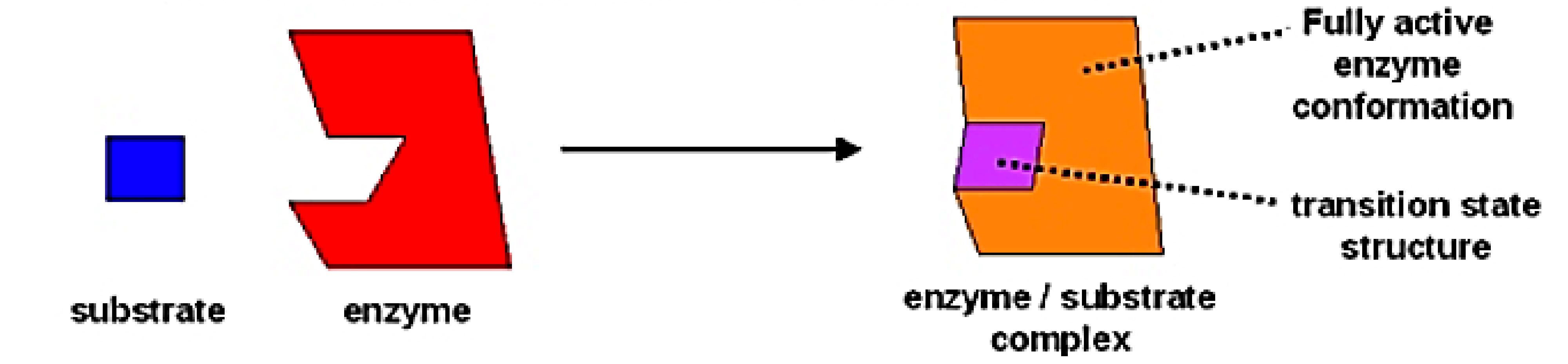
induced fit model of substrate binding
lock and key with conformational change (induced fit)
what type of binding
Chymotrypsin
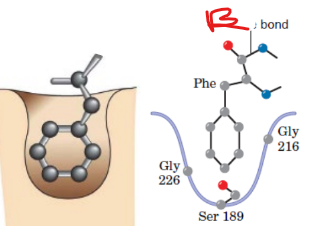
B
scissile bond
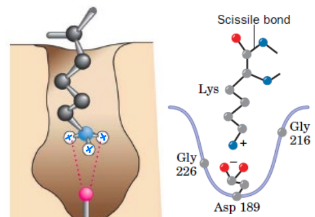
what type of binding is this
trypsin

elastase
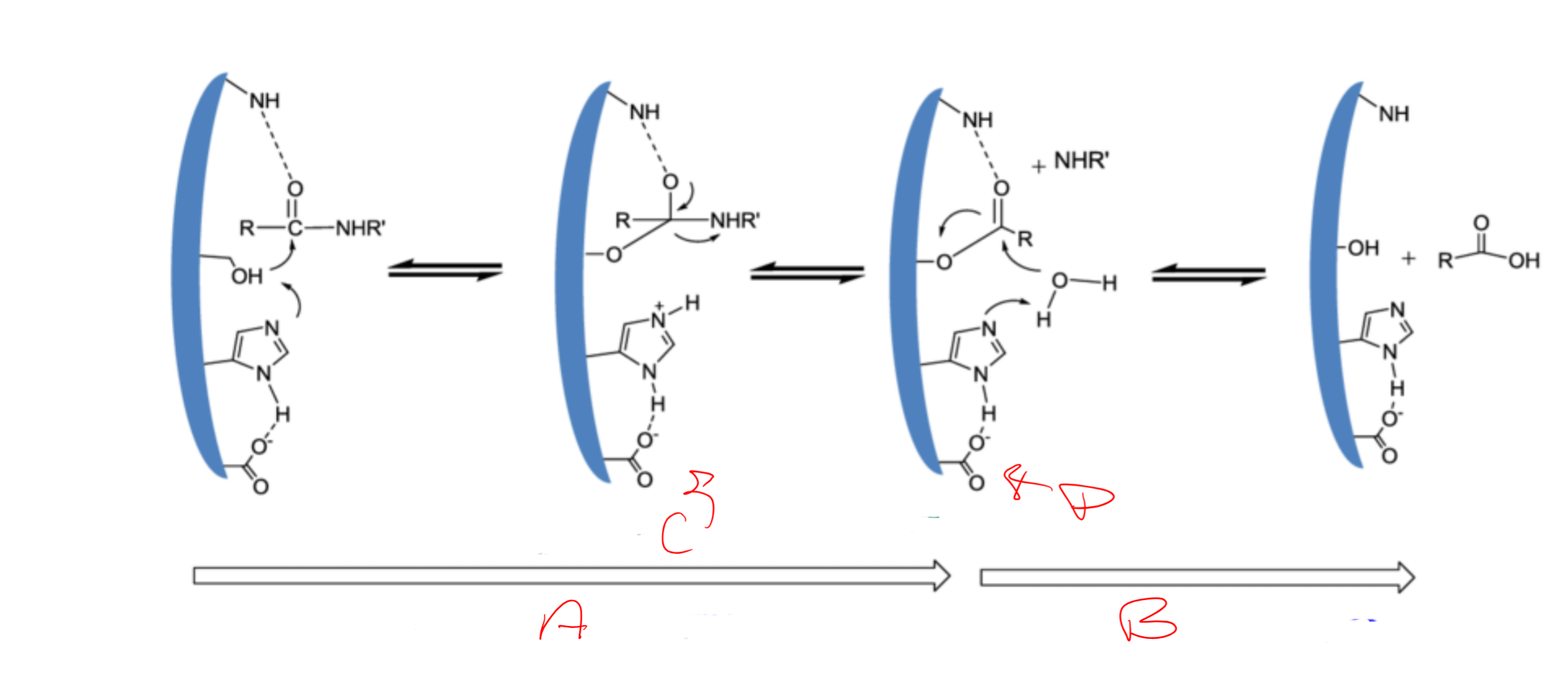
a
acylation of the enzyme
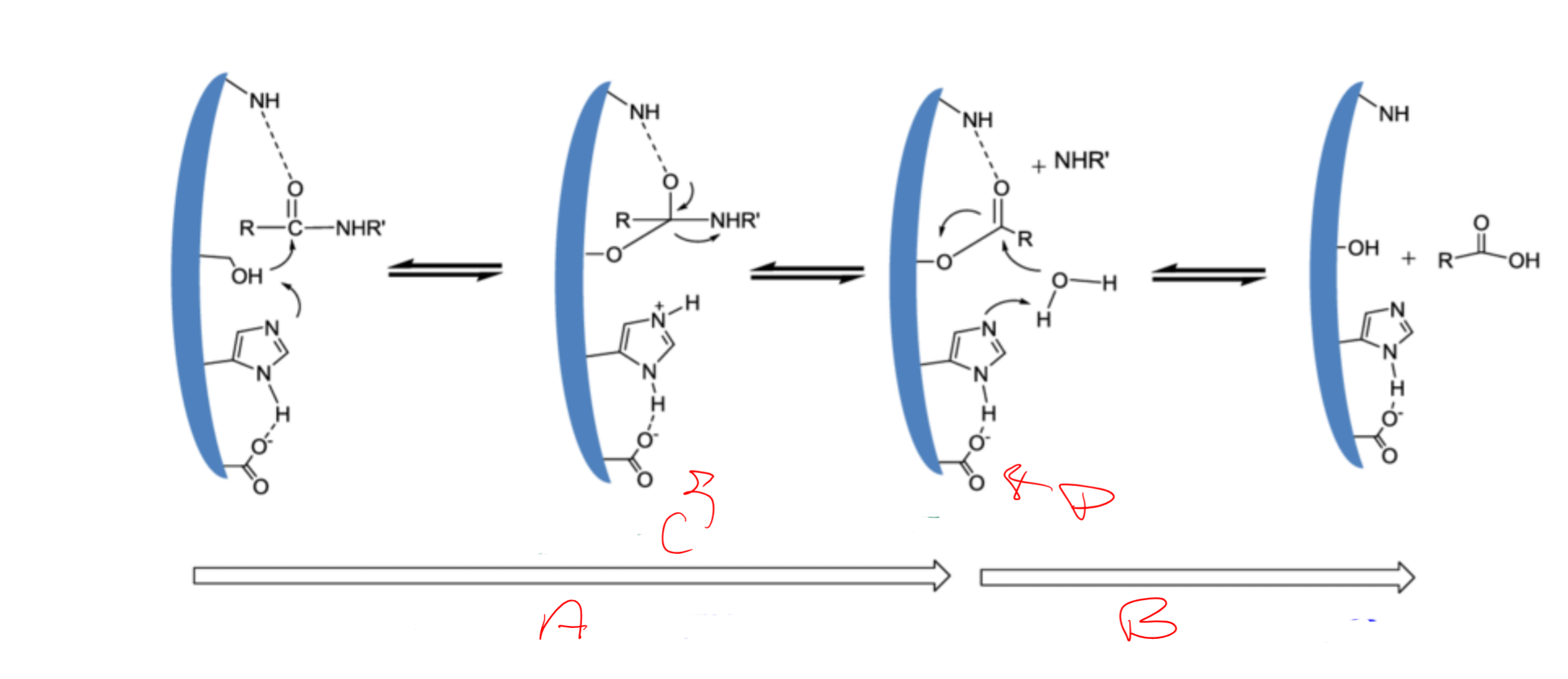
b
diacylation of the enzyme
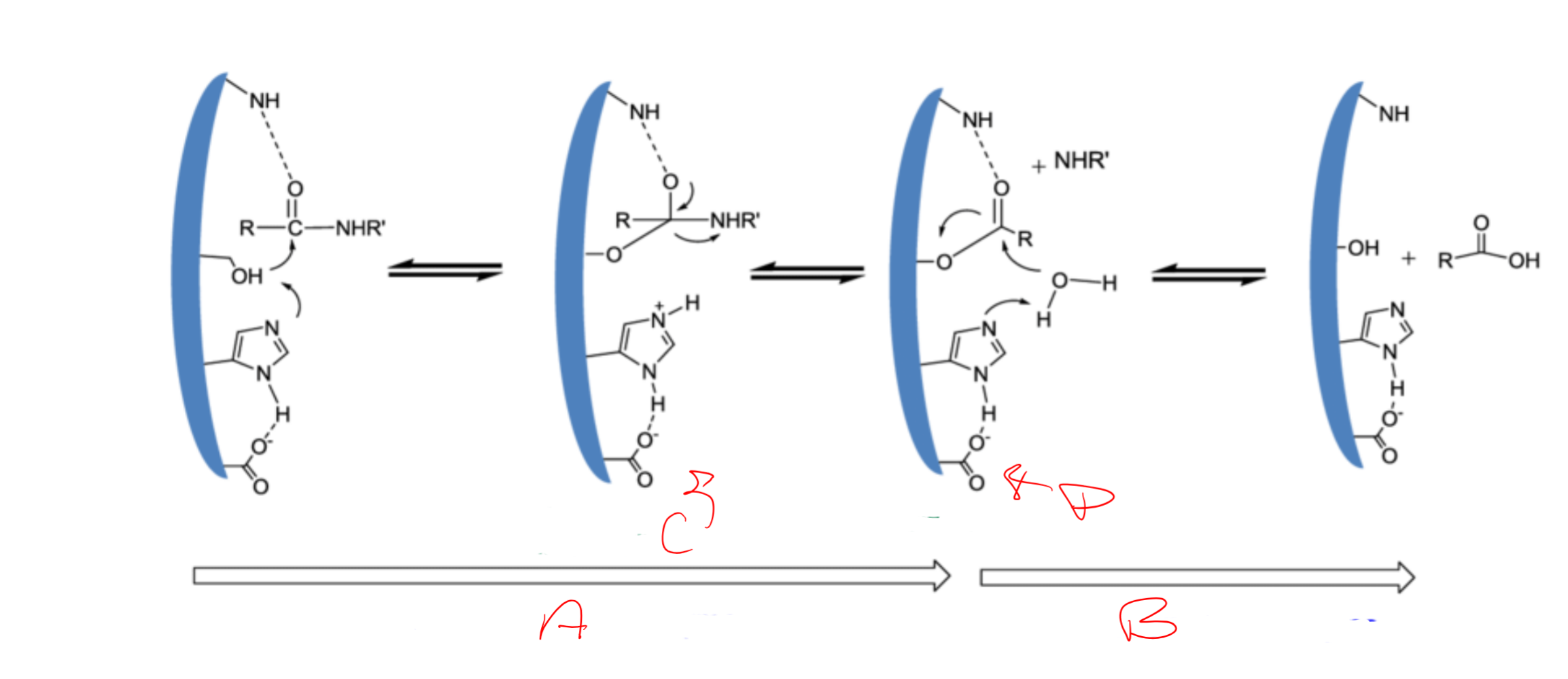
c
tetrahedral intermediate
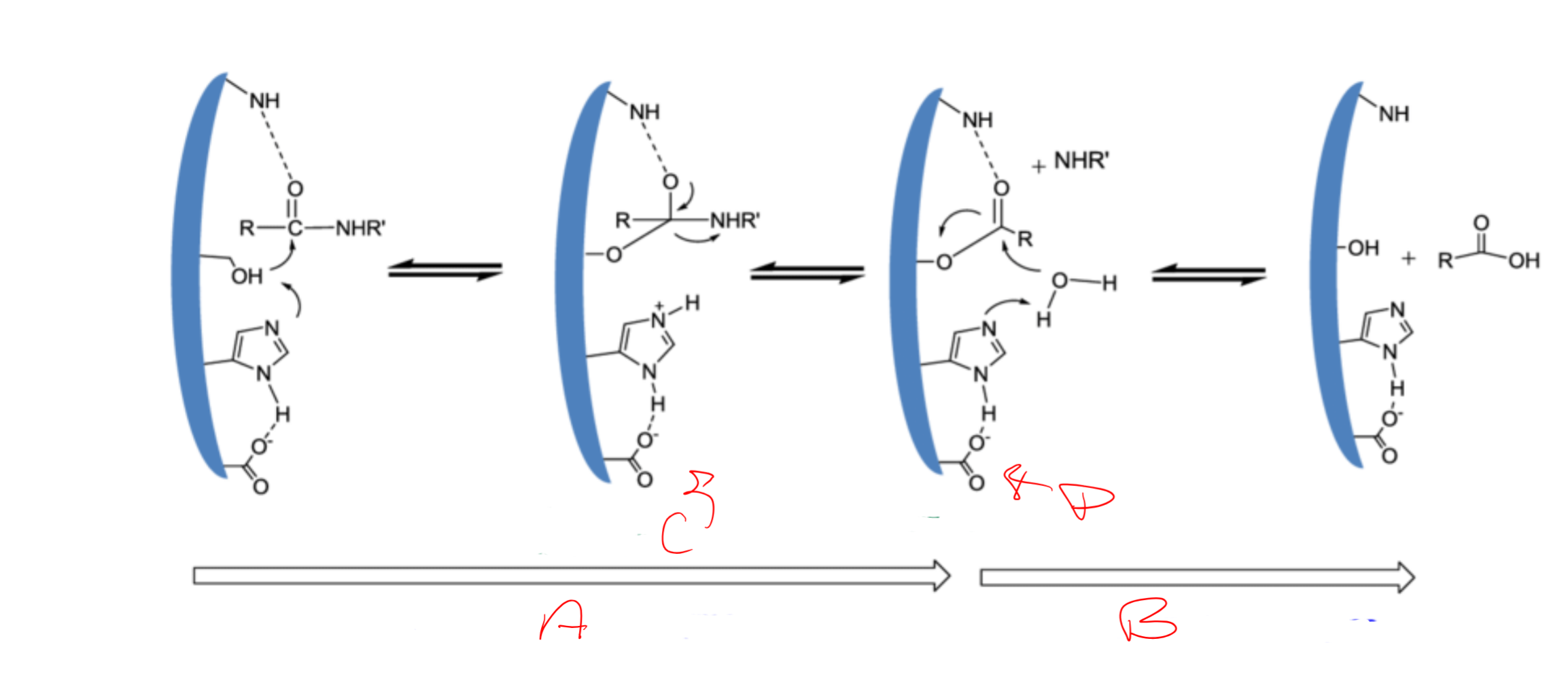
d
acylenzyme
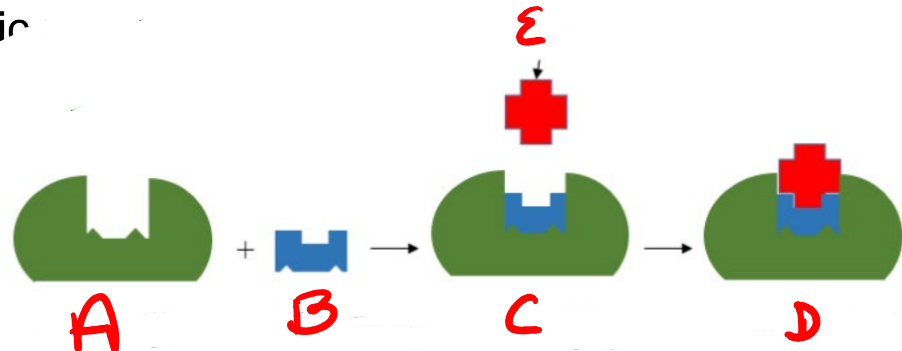
a
apoenzyme (inactive)

b
coenzyme (nonprotein compound)
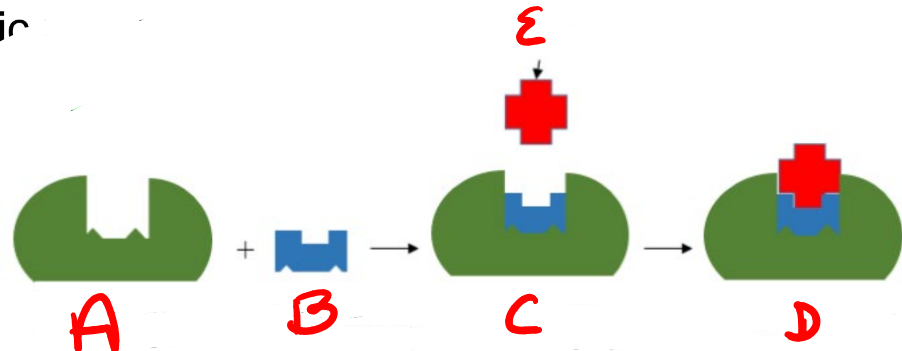
c
holoenzyme (active enzyme)

d
enzyme-substrate complex
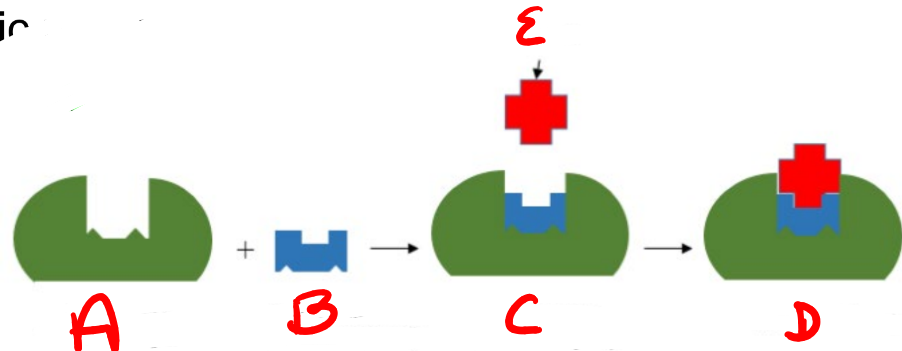
e
substrate