Final - Vertebrates evolution
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
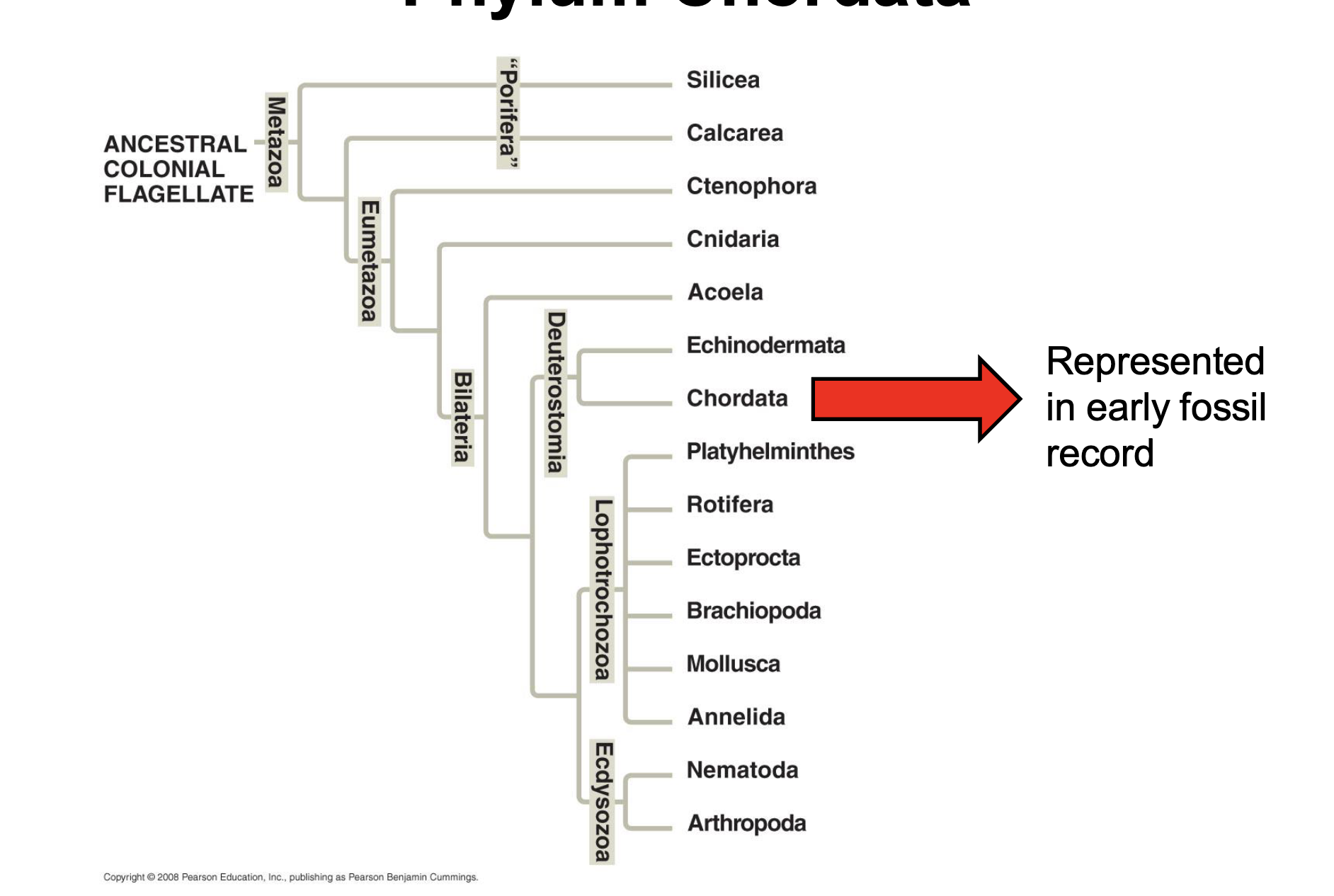
Phylum chordata
ancestral “missing link” between invertebrates and vertebrates
chordata characteristics
Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and post-anal tail
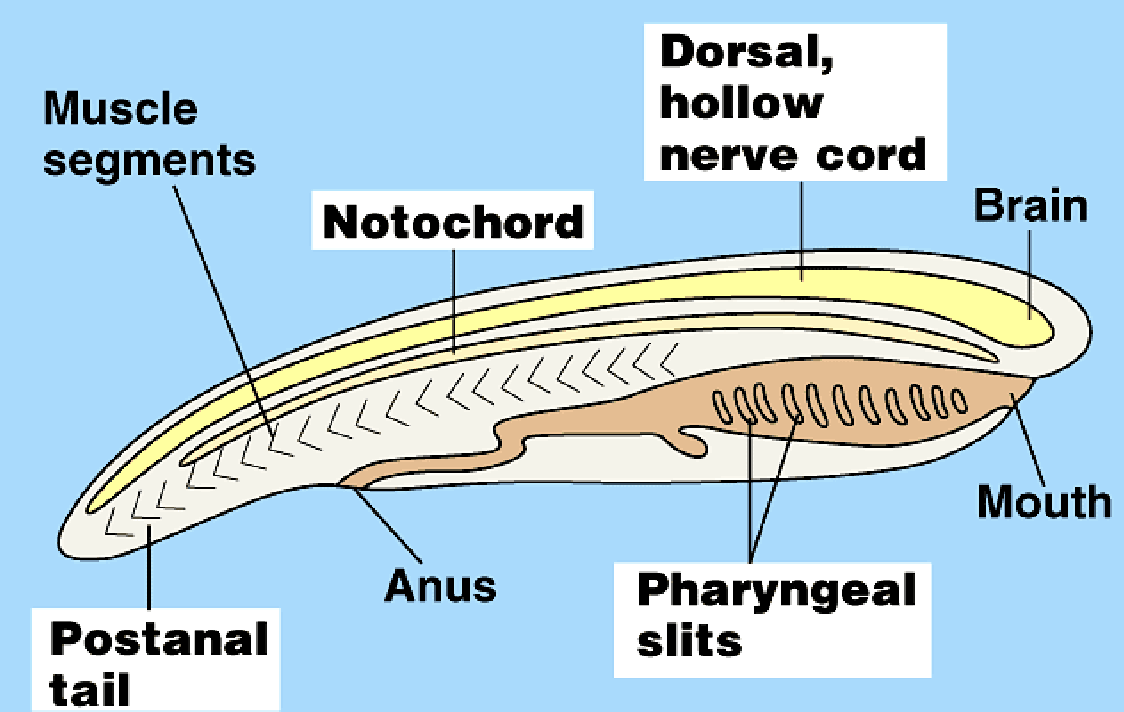
Notochord
longitudinal, flexible rod between digestive tube and nerve cord
provides skeletal support
in vertebrates, jointed skeleton develops and only remnants of the embryonic notochord retains
Dorsal, Hollo Nerve cord
develops from a plate of ectoderms
develops into cns
Muscular, Post-Anal tail
Tail posterior to anus
contains skeletal elements and muscle blocks
provides propelling force in many aquatic species
tail is greatly reduced following embryonic devlopment
Pharyngeal clefts/slits
slits on outside of the body
function: suspension feeding in invertebrate chordates and gas exchange in aquatic vertebrates
Pharyngeal pouches
tetrapods pouches develop into parts of the ear, head, and neck
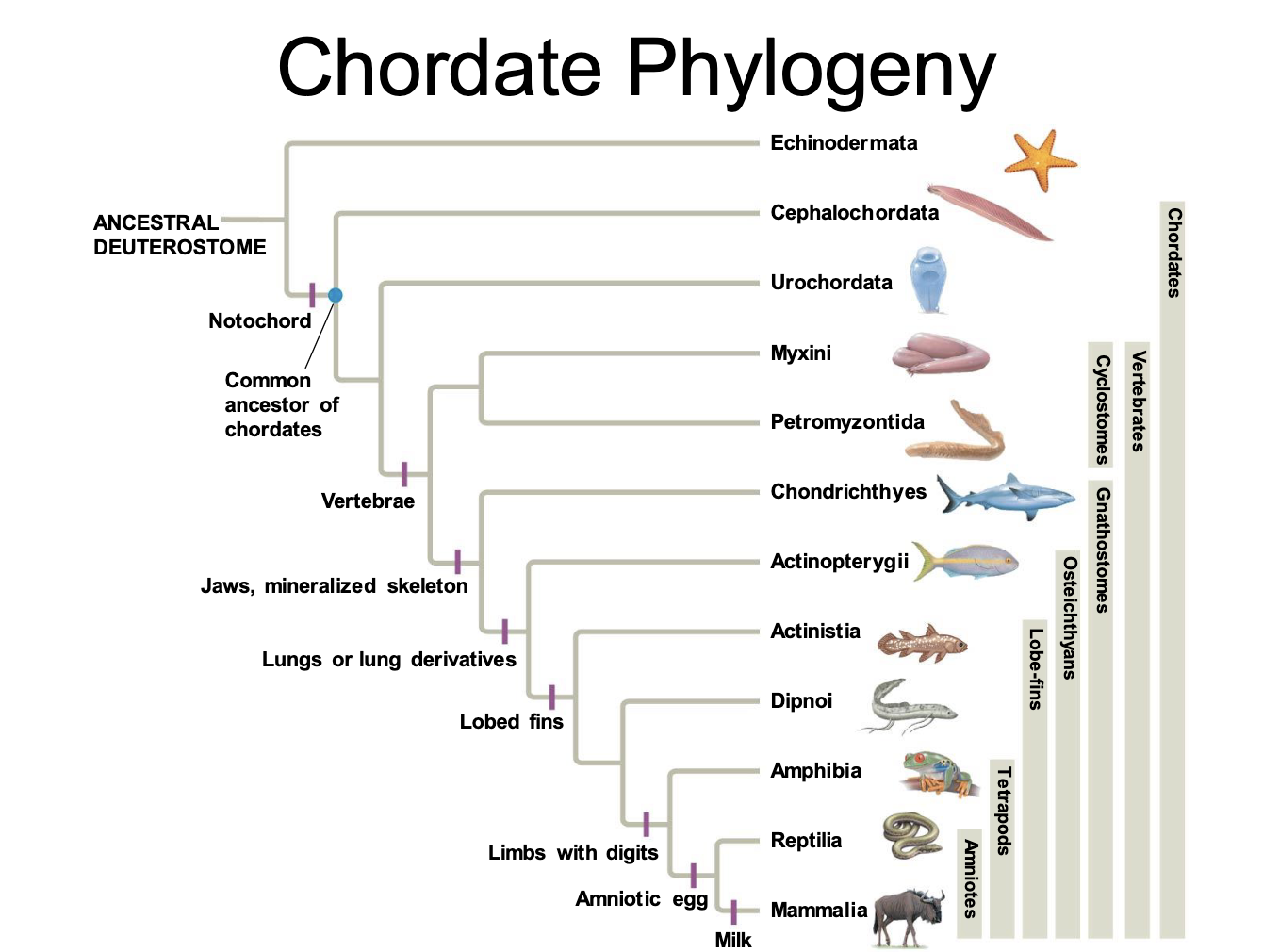
Chordate Phylogeny
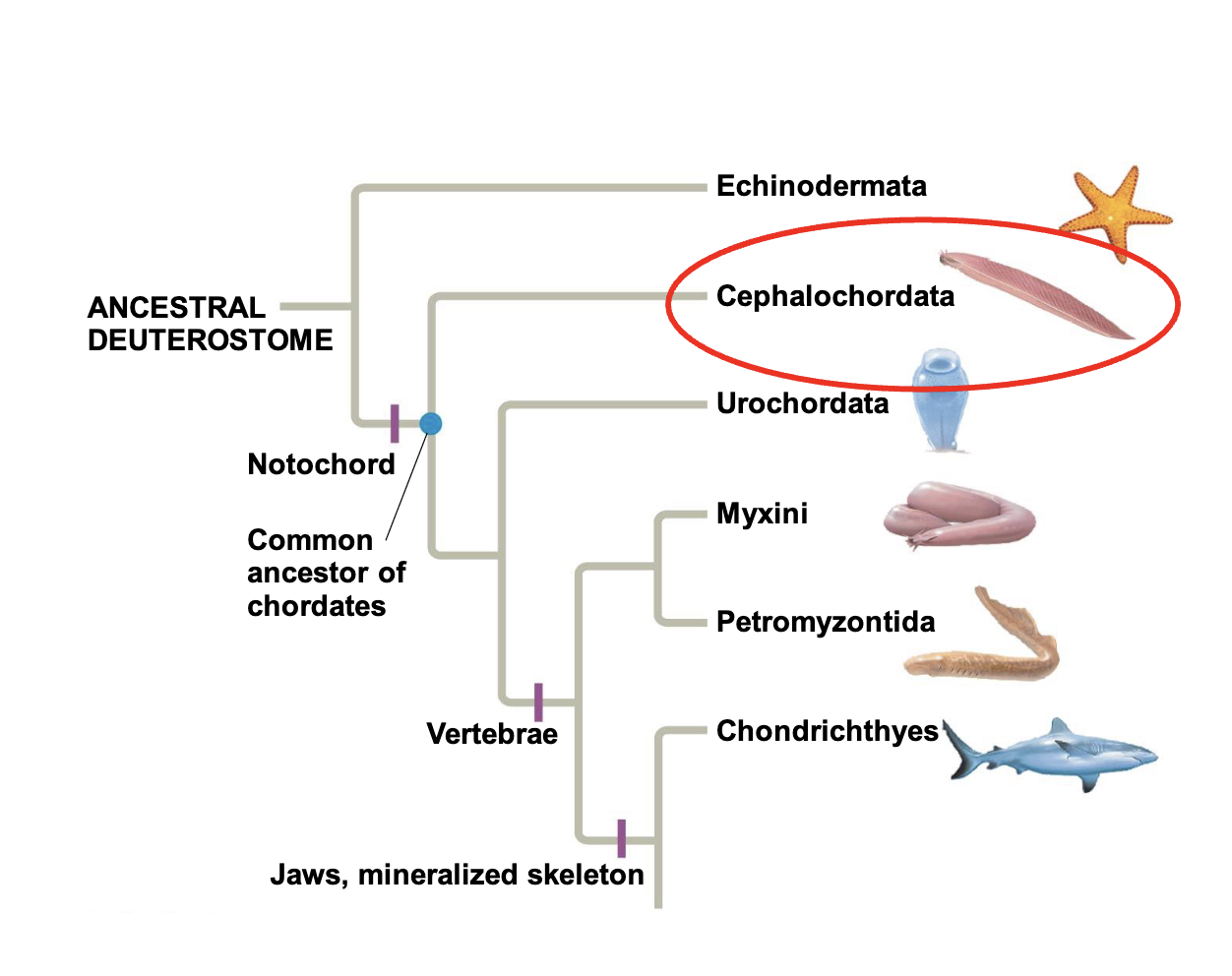
Subphylum cephalochordata
lancelets: hox genes & brain evolution
Hox genes
cluster of homeotics (hox) genes in the chromosome (anterior to posterior)
Colinearity
in time and space . Anterior genes expressed first and during devlopment and posterior later
Hox genes are transcription factors
binds to specific sequences of DNA (cis-regulatory elements) and control the transcription from DNA to RNA
Hox genes and the construction of body plans
DNA would up like spool, spool is unwound the emerging genes become actives
A new gene come out the spool every 90 mins-which corresponds to the time needed for a new layer of the embryo to be built
2 days for the strand to completely unwind - same time needed for all the layers of the embryo to be completed
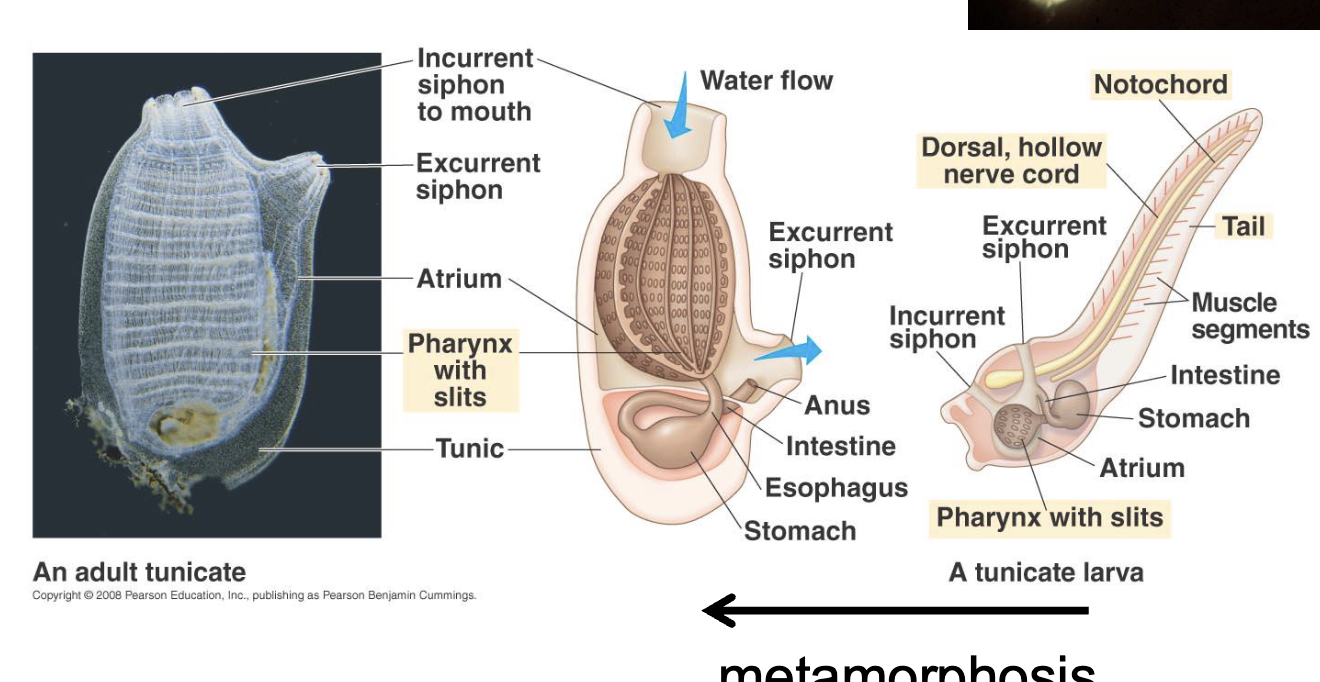
sybphylum urochordata
tunicates or sea squirts
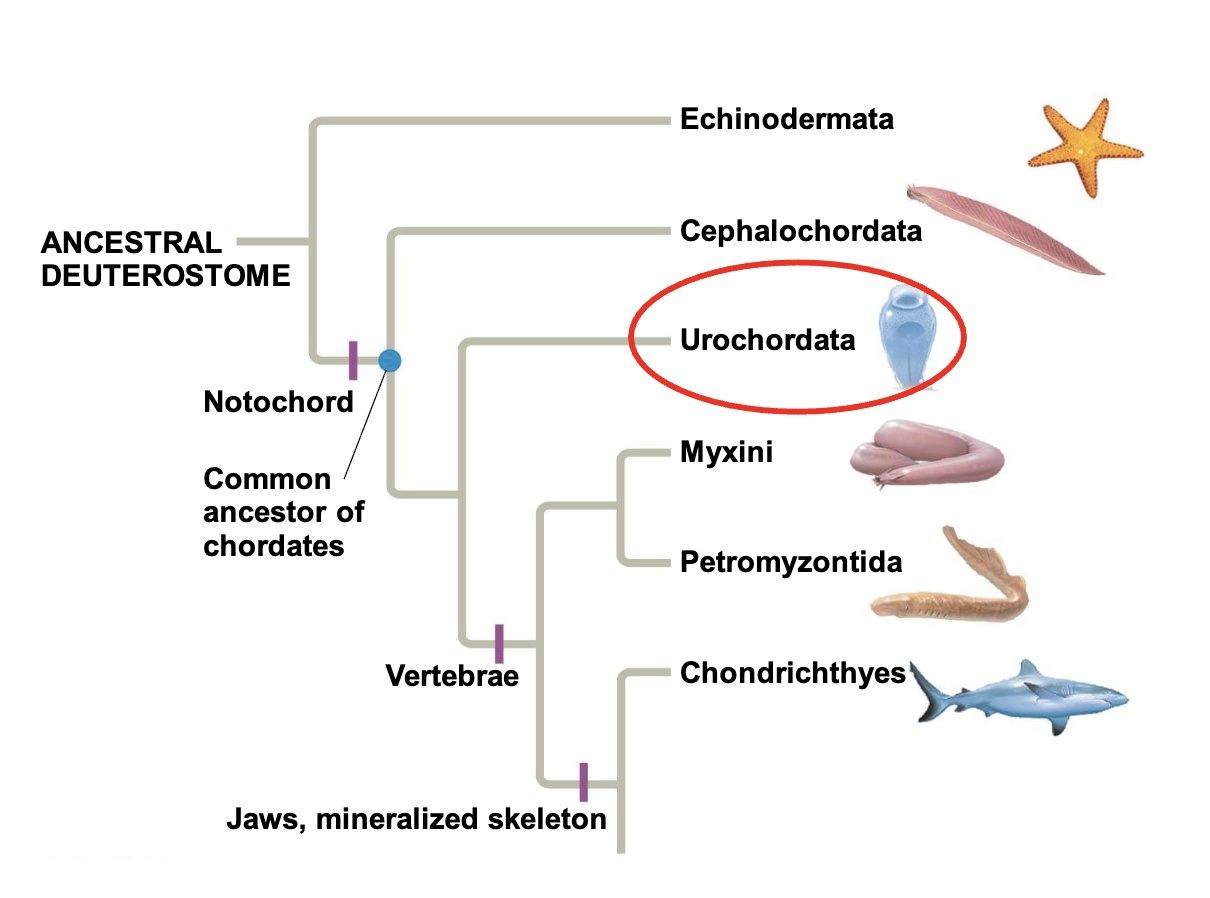
Tunicates
chordate-like larva
adult animals without a backbones
Appearance of self-recognition
whether tissue transplants graft or are rejected 0 based on sharing same allele for Fusion Histocompatibility Complex gene
high allelic diversity at FuHC
Vertebrates
A skeletal system and complex nervous system allows them to be efficient at 2 tasks: capturing food and evading predators
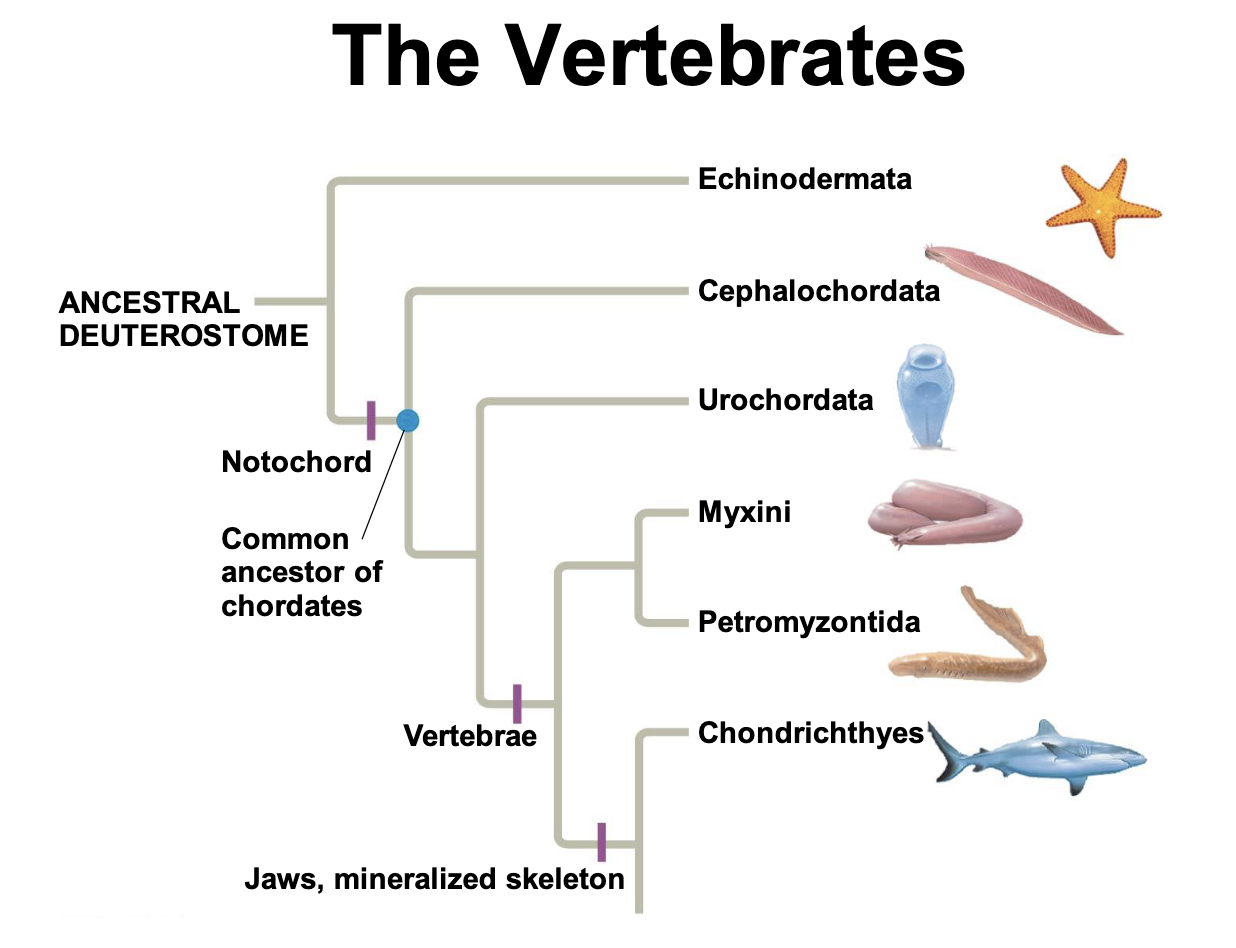
Spinal cord
vertebrae enclosed the spinal chord and replaced notochord
vertebrate hox genes
vertebrates have 2 sets of hox genes
Vertebrate neural crest
involved in formation of cranium
Subphylum Craniates
Chordates that have a head
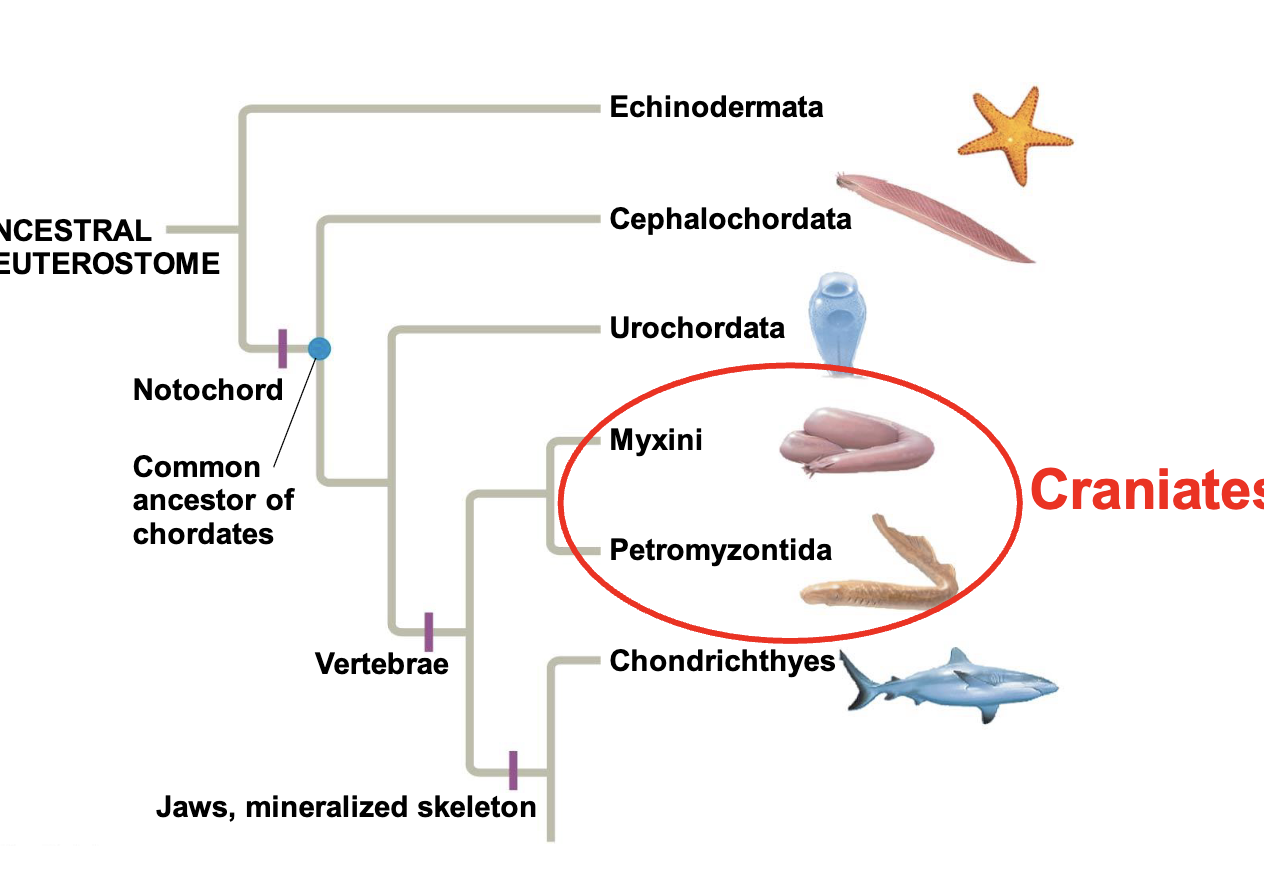
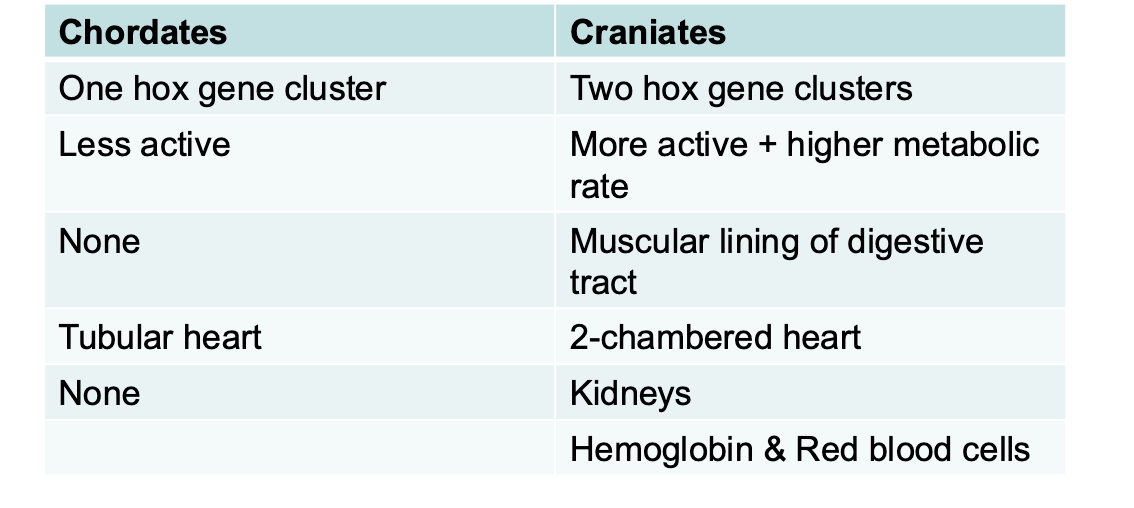
chordates vs craniates
Family Myxini - Hagfish
marine scavangers, cartilaginous skeleton and notochord, no jaw, produce slime
Family pretromyzontida - lampreys
oldest living lineage of vertebrates, cartilaginous skeletons end cartilaginous projections that enclose nerve cord, jawless, and external parasites
Conodonts
extinct jawless vertebrates w mineralized dental elements
Ostracoderms
extinct jawless vertebrated w mineralized teeth and armor
Hypothesis: mineralization spread to endoskeleton
Gnathostomes
vertebrates w jaws and paired fins
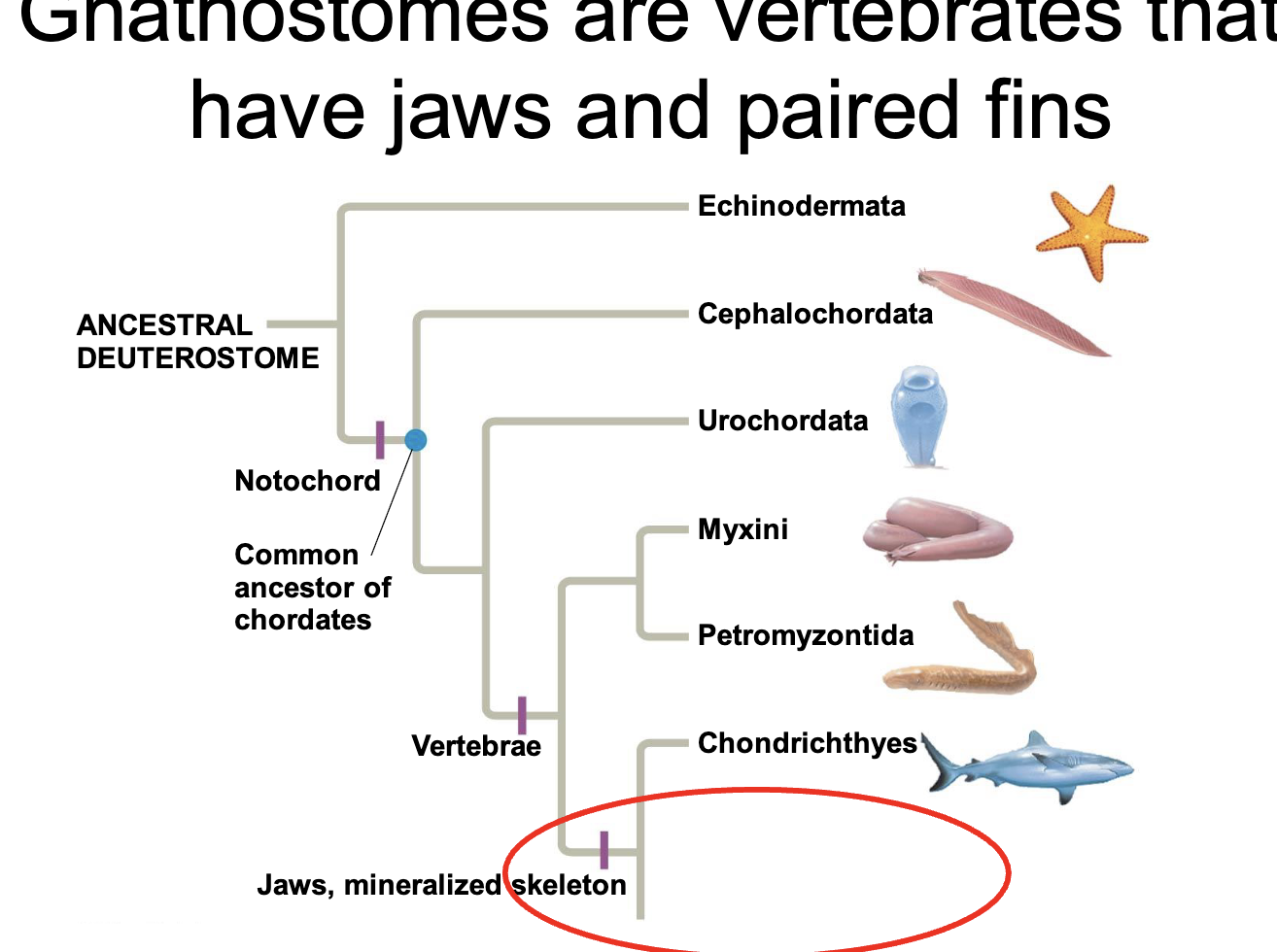
advantages of jaws & paired fins
to be active predators, diversification of lifestyles & nutrient sources
Jaw, skeletal support, and pharyngeal slita
Hypothesis: vertebrate jaws evolved by modification of skeletal rods that previously supported anterior pharyngeal slits
common to gnathostomes - Geneduplication
gene duplication, including hox genes
lateral line systems
rows of organs sensitive to vibrations that are located along each sidde of the body of aquatic gnathostomes
Age of fishes
440-360 MYa - increase in jawed fish in fossil record
Chondrichthyes
flexible endoskeleton of cartilange rather than bone
derived condition
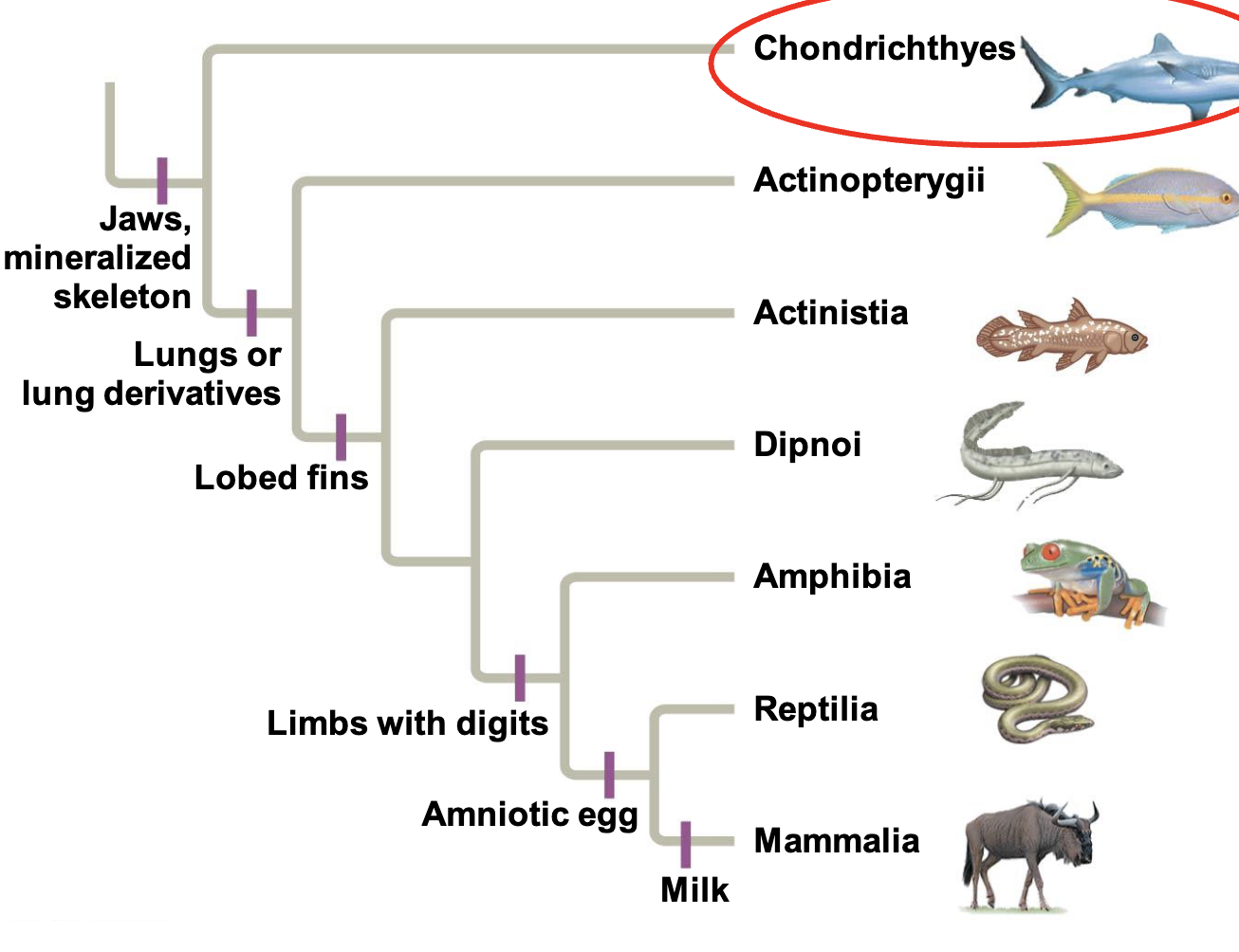
Sudden appearance of adaptive immune system
Jawed vertebrates t-cell, b-cell, MHC based immunity
Osteichthyes - bony fish
endoskeleton containing calcium phosphate and scales derived from bone
Actinopterygii - ray-finned fishes
bony rays that support fins
ex: bass, trout, perch, tuna, and herring
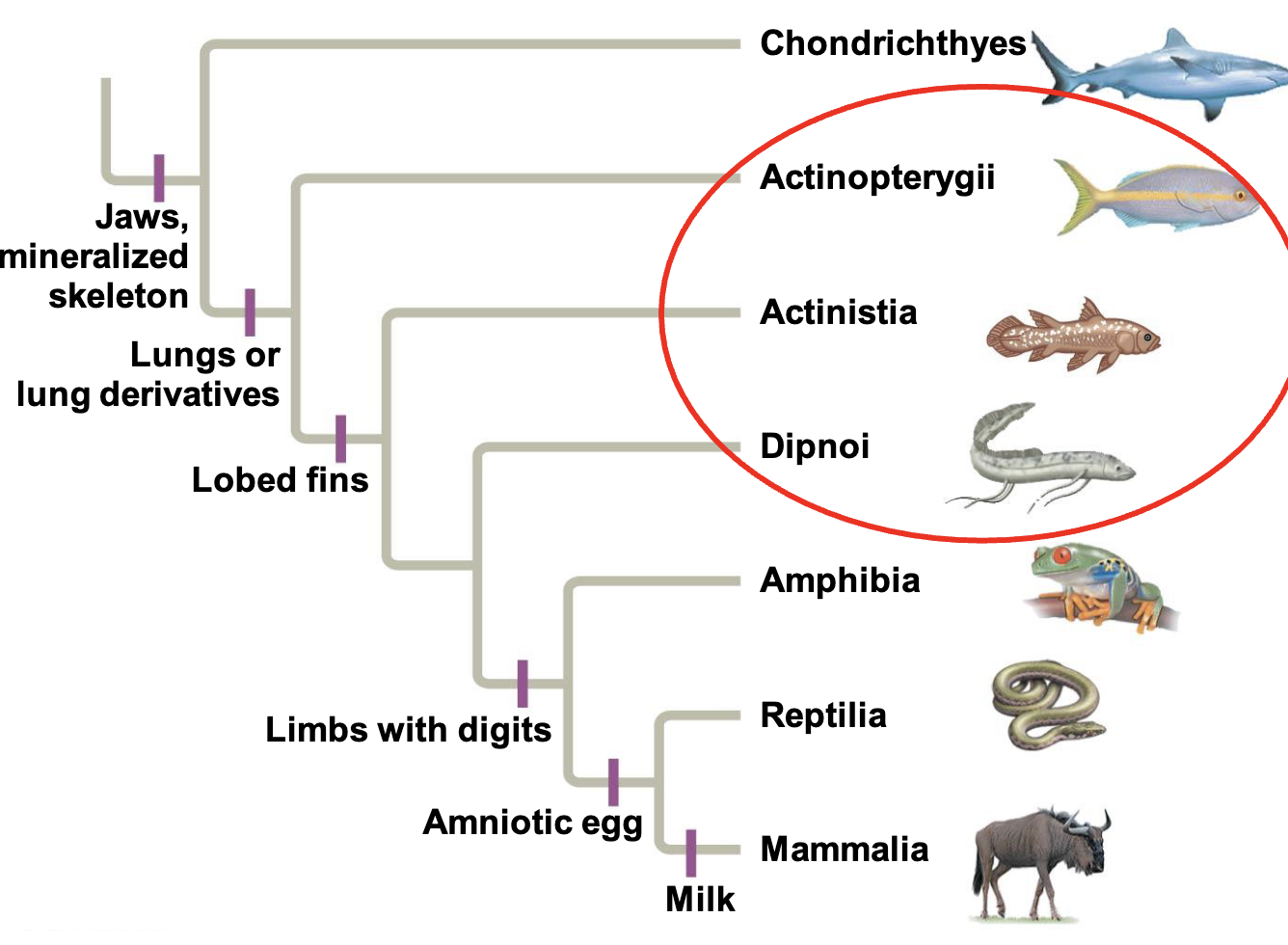
Actinistia - coelacanths
lobe-finned fished w muscular pectoral and pelvic fins supported by extensions of bony skeleton
2 living in S africa and S pacific
Dipnoi - Lungfishes
3 in southern hemisphere
Inhabit stagnant ponds and swamps
gulp air in lungs
can burrow in mud and aestivate
aquatic-terrestrial transition
420 mya-360mya, plants procided organic material at waters edge
lobe fin and lungfish abundant - buccal breathing and leg-ike paddes
Where would we find transitional species
shallow estuary or tidal flate
warm, equatorial climate
370 mya (devonian era)
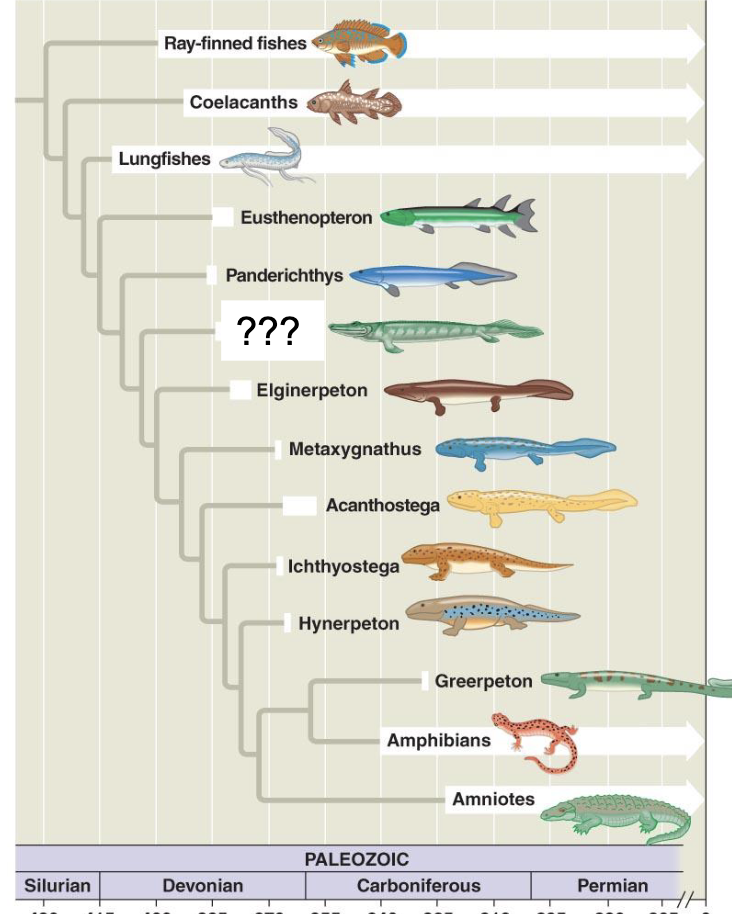
tiktaalik
tetra-pod like fish
gills and lung
gills had bony covering
scales
fins used for swiming
tiktaalik tetrapod characteristics
flat skulls, eyes on top of head, ear notches, full set of ribs, and had a neck
tiktaalik liffe styles
hunted small fish in shallows and terrestrial arthorods
innerfish
“fishapod”
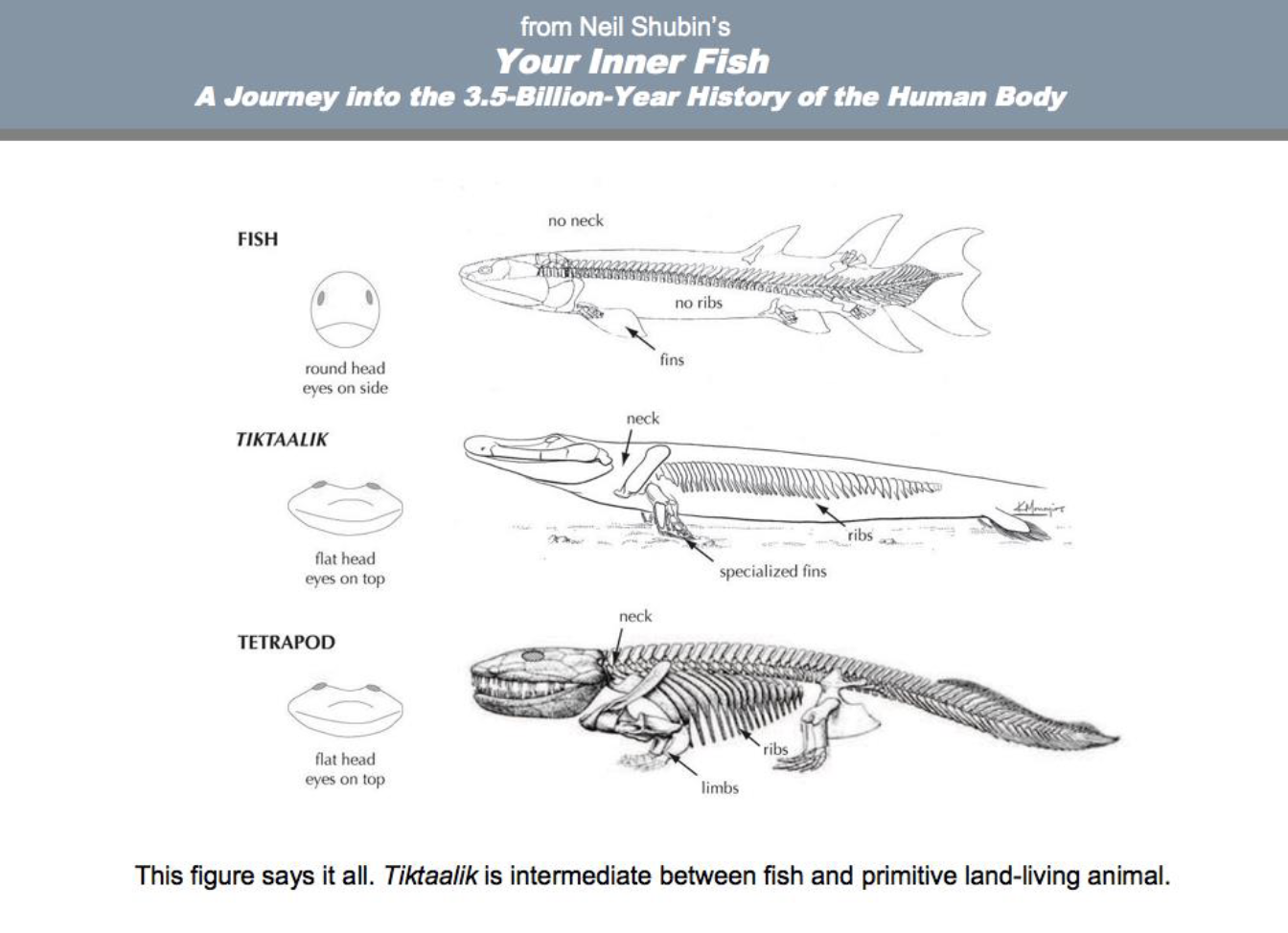
Characteristics of tetrapods
4 feets, digits, neck, pelvic girdle, and paryngeal clefts
Amphibia (age of amphibia 360-300mya)
earliest terrestrial tetrapods. Benefited from moist climates, abundant food, and little competition
need water - rely no mosit skin for gas exhange - eggs lack shells
Amphibious
both ways of life
aquatic and terrestrial
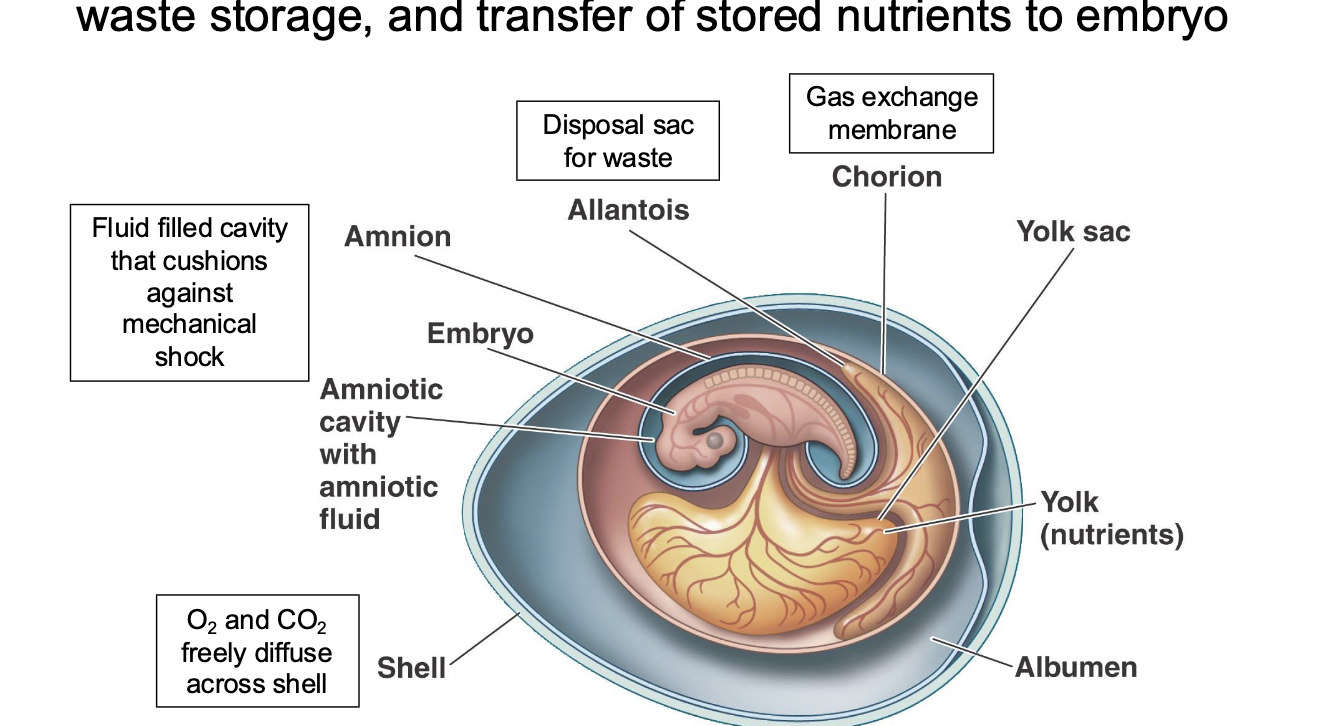
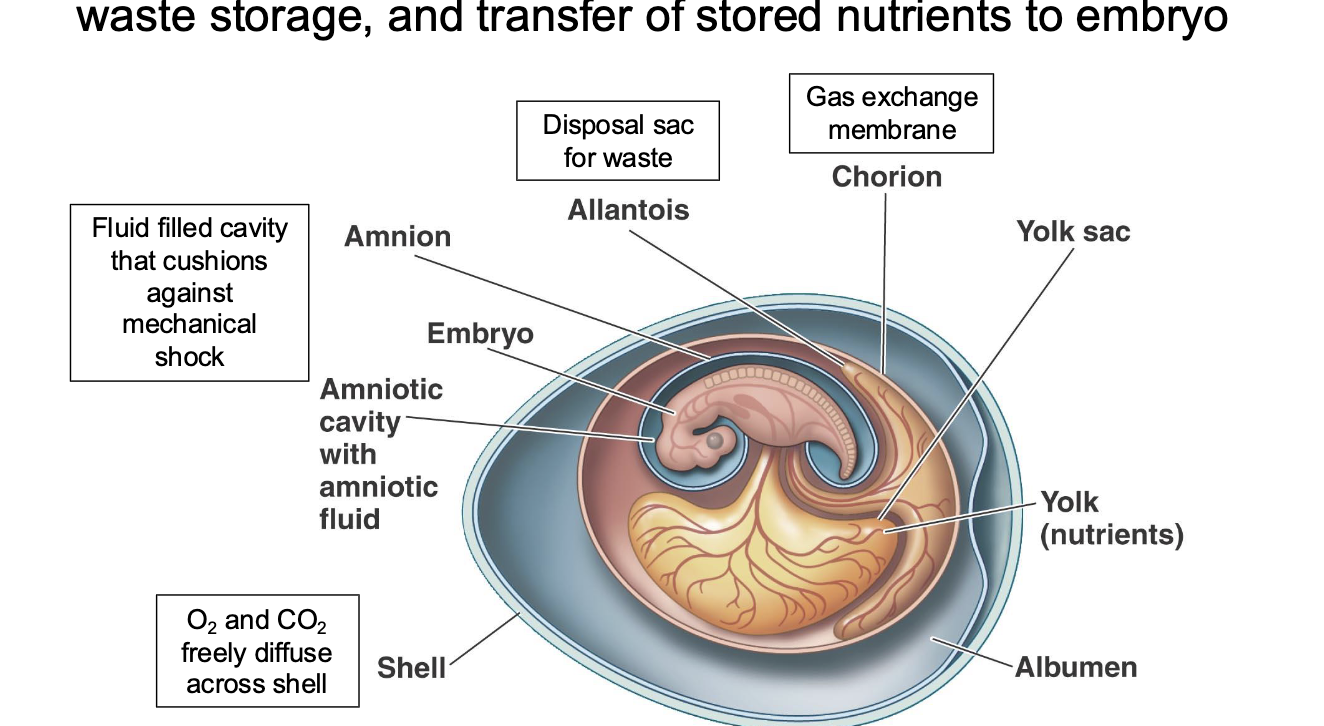
extraembryonic membrane
function in gas exhange, waster, storage, and transfer of nutrients to embryo
Reptilia - reptiles
320 ya - dry habitats
reptitlian traits
lungs, scales with keratin (waterproof skins), internal fertilization, ectothermic
ectothermic
abosording external heat as main source of body heat
age of reptiles
triassic, jurassic, and cretaceous (259-66 mya)
birds
feathered reptiles
clawes forelimbs, teeth, and long tail
dinosaurs
now believed to be endodermic or there being a middle ground
high metabolic rate, bone structurem and respiratory system
Distinguish between Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes
Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish like sharks) and Osteichthyes (boney fish)
The evidence that suggests the loss of bone in Chondrichthyes is a derived feature
an ancestral bony state followed by significant bone loss in this lineage
3 living lineages of lobe fins
Coelacanths (Actinistia), Lungfishes (Dipnoi), and Tetrapods
difference between gnasthromes, tetrapods, and amniotes
Gnathostomes are jawed vertebrates, the major group including most fish and all land vertebrates; tetrapods are a subgroup of gnathostomes with four limbs (or descended from four-limbed ancestors, like snakes); and amniotes are a subgroup of tetrapods (reptiles, birds, mammals) defined by an amniotic egg, allowing reproduction on land without a larval stage, distinguishing them from amphibians.
three ordered of living amphibians
Anura (frogs and toads), Caudata (salamanders and newts), and Gymnophiona (caecilians)
why does the reptile clade include birds
they evolved directly from a group of reptiles (theropod dinosaurs) and share a common ancestor with crocodiles and other reptiles
amonic egg
specialized, shelled egg that allows reptiles, birds, and mammals (amniotes) to reproduce on land, freeing them from water dependency by containing essential membranes (amnion, chorion, yolk sac, allantois) for moisture, nutrition, waste, and gas exchange, plus a protective shell,