Chemistry - Topic 5 - Moles
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
what is Avogadro’s constant and its symbol?
6.02×10²³/mol
L or Nₐ
gives the number of atoms/molecules/ions in one mole of a given substance
what is the molar mass of a substance?
the mass per mole of a substance in g mol-1
empirical formula
smallest whole number ratio/simplest ratio of atoms of each element in one molecule of a substance
molecular formula
indicates the number of atoms of each element in one molecule
is Ba(OH)2 soluble or insoluble?
soluble
what is a precipitation reaction?
two soluble salts reacting to form one insoluble salt i.e. a precipitate
core practical 1: measure the molar volume of a gas - why do we add a large spatula of sodium carbonate to the acid and wait until all of this solid has reacted?
CO2 is soluble, so some will dissolve in the solution - therefore, we must first saturate the solution with CO2. then, there will still be some HCl left over for the second reaction, and all of the CO2 gas produced in the second reaction will be pushed into the gas syringe.
describe how to carry out an experiment to determine the water of crystallisation (x) in CuSO4.xH2O
weigh a known mass into a crucible
heat (avoid the formation of black CuO if possible)
heat and reweigh and repeat until constant mass
DRAW A DIAGRAM
core practical 1: Measure the molar volume of a gas - safety precaution
ensure the delivery tube does not become blocked with liquid
core practical 2: prepare a standard solution from a solid acid and use it to find the concentration of a solution of sodium hydroxide - procedure
weigh a sample of a solid in a weighing boat
transfer to a beaker
reweigh the boat and subtract to get the mass of the solid transferred
add around 100ml of distilled water to the beaker and stir to ensure all solid dissolves
transfer to a volumetric flask . rinse the beaker with distilled water and add the rinsings to the flask
fill up to the line (disgram of volumetric flask with meniscus on line)
stopper and invert to thoroughly mix
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - the pipette should be rinsed with distilled water and then with some HCl - why?
rinse with water - to clean burette
rinse with HCl - to get rid of water which could slightly change concentration of HCl which would change moles of HCl
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - why do you only add a few drops on indicator?
indicators are themselves weak acids
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - why do you fill a burette below head height?
dangerous otherwise, acid could spill, danger to eyes and face
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - why do you use a white tile?
to make the colour change more apparent
how accurately can you read a burette?
+-0.05cm³
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - why do you swirl while adding the NaOH?
to evenly distribute/mix NaOH
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - what is the end-point of a titration?
when the colour changes
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - what is the equivalence point?
when the moles of NaOH = moles of HCl therefore there is only NaCl + H2O
the point at which the acid has been exacly neutralised
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - what is a rough titration? what is the purpose of the rough titration?
open the tap
when you see the colour change, close
to get an idea of the end point of the titration so the accurate titration may be carried out more rapidly
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - what are concordant results?
at least two results which are within +-0.10cm³ of each other
what is an accurate result?
a result which is close to the real, true value
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - what are four random errors when carrying out a titration?
reading miniscus incorrectly on burette
misreading miniscus on pipette
not swirling conical flask frequently enough
misjudging colour change
core practical 3: find the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid - what are two systematic errors when carrying out a titration?
adding too much indicator
overshooting the end-point
what are random errors?
above or below the true value
cancelled out during average
what are systematic errors?
consistently above or below true value
not cancelled out during average
what are zero errors?
zero errors are a particular form of systematic error caused by measuring instruments that have a false zero
how to reduce percentage uncertainty in temperature rise recorded with a thermometer?
use a higher resolution thermometer
graduated every smaller interval
increase temperature rise
how to calculate the size of the error in a titre volume and how to reduce error?
2 measurements - initial reading and final reading
2×0.05/actual value x 100
increase actual value to reduce error by:
diluting the solution in the burette
(increasing volume of HCl)
(increasing concentration of HCl)
how to calculate the error in the pipette volume?
0.03 (written on pipette)/25 × 100
how to calculate the error in a mass reading using a 2d.p. balance and how to reduce error?
2×0.005 (every time you use the mass balance, you tear it)/actual value x 100
improve by using a greater mass
improve by using a 3d.p. mass balance
how to calculate % yield and 3 reasons why you may not get all the expected amount of product?
mass of product obtained/maximum theoretical mass of product x 100
the reaction may be reversible (both the forwards and backwards reaction can take place)
some of the product may be lost when it is separated from the reaction mixture
some of the reactants may react in other reactions
what is atom economy?
a measure of what proportion of the products of a reaction are the desired product and how much is waste. the higher the atom economy, the less waste that is produced.
how to calculate % atom economy?
mass of desired product as shown in equation/total mass of products as shown in equation x 100
alternatively Mr of desired product/Mr of all products x 100 - Mr includes balancing numbers
burning ethanethiol balanced equation (CH3CH2SH)
ethanethiol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + sulphur dioxide + water
lithium and water reaction
lithium + water → lithium hydroxide + hydrogen
ammonia and nitric acid reaction
ammonium nitrate
the student deduced that M was sodium. Comment on the value for Ar of the metal M by calculating the range of values of Ar.
experimental difference = 23.23 × 0.0168 = 0.390
range = 23.23 +-0.39 = 22.84-23.62
the Ar of sodium (23.0 lies within this range)
the burette is the largest source of experimental uncertainty. explain how the the percentage uncertainty of the mean titre could be reduced without changing the apparatus or simply repeating the experiment.
dilute the solution of HCl in the burette
gives a larger titration volume so smaller percentage
what is the mass of one silicon atom?
Mr/Avogadro's constant
what is the molar mass?
mass is the mass of one mole, which has the same value as the relative atomic mass or relative formula mass. So for glucose (relative formula mass = 180.0), the molar mass is 180.0 g/mol.
suggest how a chemical process could have a high percentage yield, but a low atom economy. (2)
(has a high % yield) if there is a good conversion of reactants to products
(has a low atom economy) if there are lots of waste products made
a student suggested that the same salt could also be made by reacting potassium metal with sulphuric acid.
suggest why this reaction is not the preferred method. (1)
potassium is a very reactive metal, so the reaction will be dangerously vigorous.
a student adds deionised water above the mark in a 250.0 cm3 volumetric flask.
state why the procedure has to be restarted rather than using a teat pipette to remove the excess water. (1)
removal of the excess solution will remove some of the dissolved sodium hydroxide (so that the exact concentration will be unknown)
OR
the concentration won’t be known because the total volume will be more than 250.0 cm3
describe how the student should prepare the 250.0 cm3 of ethanedioic acid solution from ethanedioic acid crystals. (4)
weigh the ethanedioic acid crystals in a weighted container e.g. beaker and record the exact mass
dissolve crystals in around 100 cm3 of distilled water
transfer solution into volumetric flask, rinse beaker and add rinsings to volumetric flask
fill volumetric flask with distilled water up to the mark, add a stopper and invert 5 times to thoroughly mix (draw a diagram)
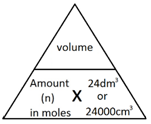
what is the equation related to gas volumes?
what is the equation relating pressure, volume, number of moles, the gas constant and temperature?
pV = nRT
p in Pa
V in m3 (dm3 × 10-3)
T in K

