Causes and Effects of World War 1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Militarism
Policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army prepared for war.

Alliances
Agreements between nations to support each other in case of war.
Nationalism
Strong belief in the interests and culture of one's nation; often leading to competition and conflict between nations.
Assassination
The act of killing a prominent person, often for political reasons.
Mobilization
The act of assembling and making both troops and supplies ready for war.
Total War
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort.
Nationalization
The process of a government taking control of private industry or assets for national interest.
Bolsheviks
Members of the Russian Social Democratic Party, which seized power in the October Revolution of 1917.
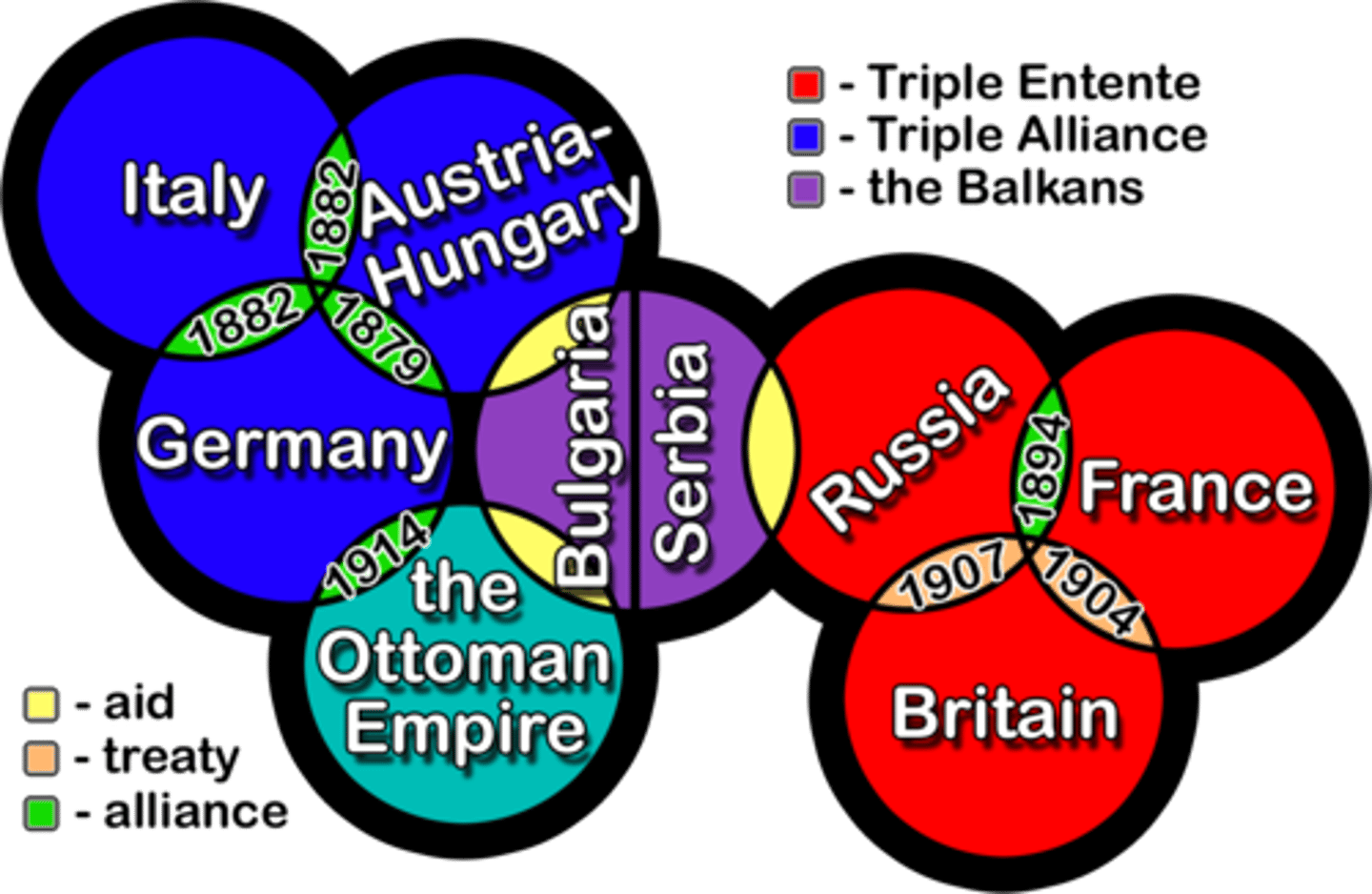
The Balkans
A region in Southeastern Europe known for its history of conflict and ethnic tension. The countries are Bulgaria and Albania. Serbia, Greece, Romania, and Montenegro. Serbia nationalists who were angry with A-H wanted a free Bosnia and Herzegovina, they killed the heir to A-H
Homefront
The civilian population and activities of a nation during war.
Conscription
Compulsory enlistment for state service, typically into the armed forces.
Belligerents
Nations engaged in active warfare.
Reparations
Payments and transfers of property and equipment that the losing countries were required to make after the war.
Armistice
A formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting.
Casualties
People who are killed, wounded, or missing during a war.
Neutrality
The state of not supporting or helping either side in a conflict or disagreement.
Propaganda
Information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote a political cause or point of view.
Self Determination
The process by which a country determines its own statehood and forms its own allegiances and government.
Triple Alliance (Central Powers)
A military alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy.
Triple Entente/Allied
A military alliance between France, Russia, and the United Kingdom.
Genocide
The deliberate killing of a large number of people from a particular nation or ethnic group with the aim of destroying that nation or group.
Sarajevo, Bosnia/Archduke Ferdinand
The city where Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated led to the start of World War I—capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina. A member of a Bosnian Serb nationalist group killed him.

Armenian Genocide
The systematic mass murder and expulsion of 1.5 million ethnic Armenians by the Ottoman government from 1915 to 1923. Armenians wanted independence, but the Ottomans were threatened due to their self-determination and breaking up their empire. They thought it was justified because some of them supported the Russians. The U.S government knew strongly about it and did not act.

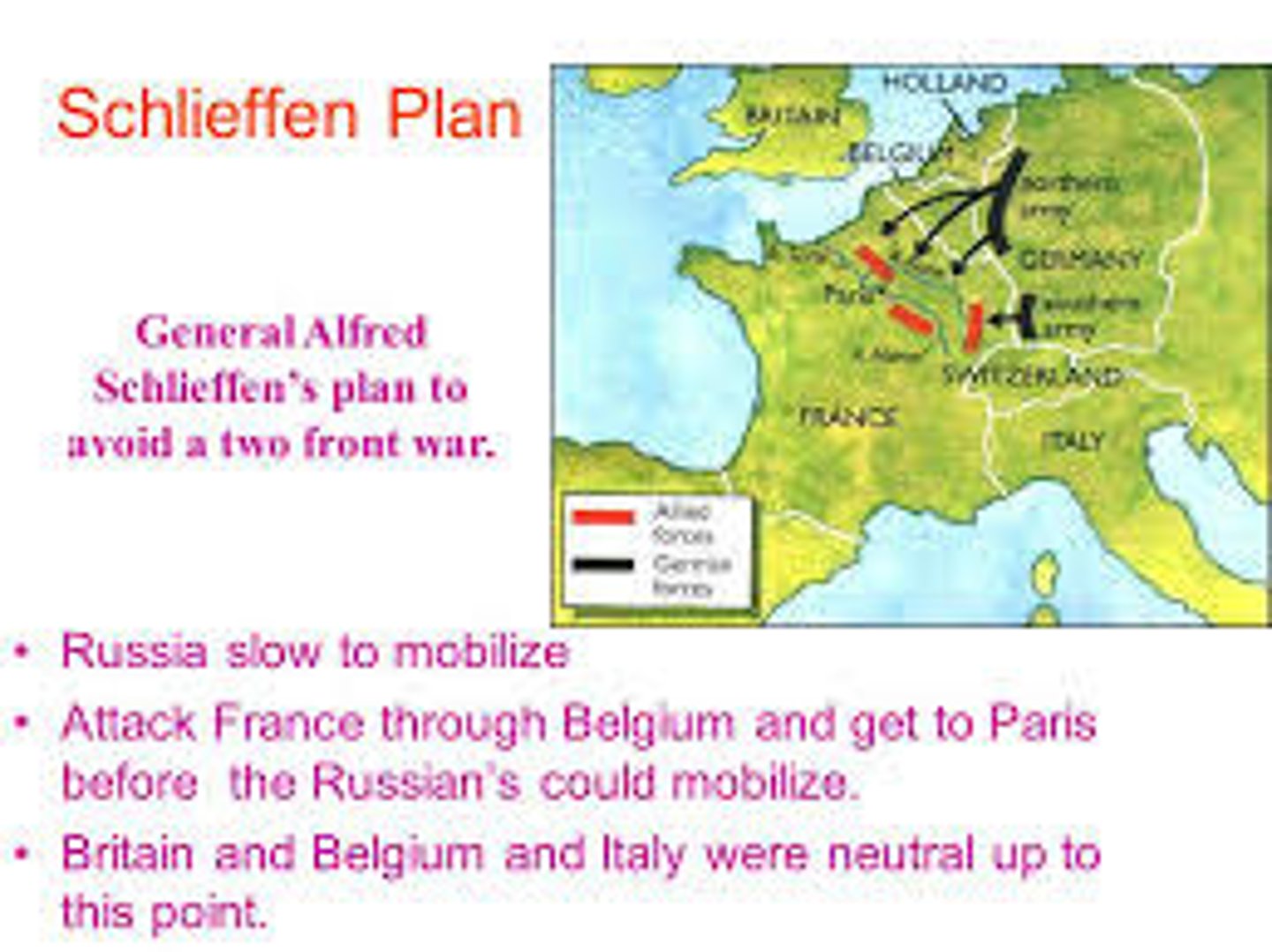
Schlieffen Plan
The German military plan to quickly defeat France and then turn to fight Russia, which ultimately failed.
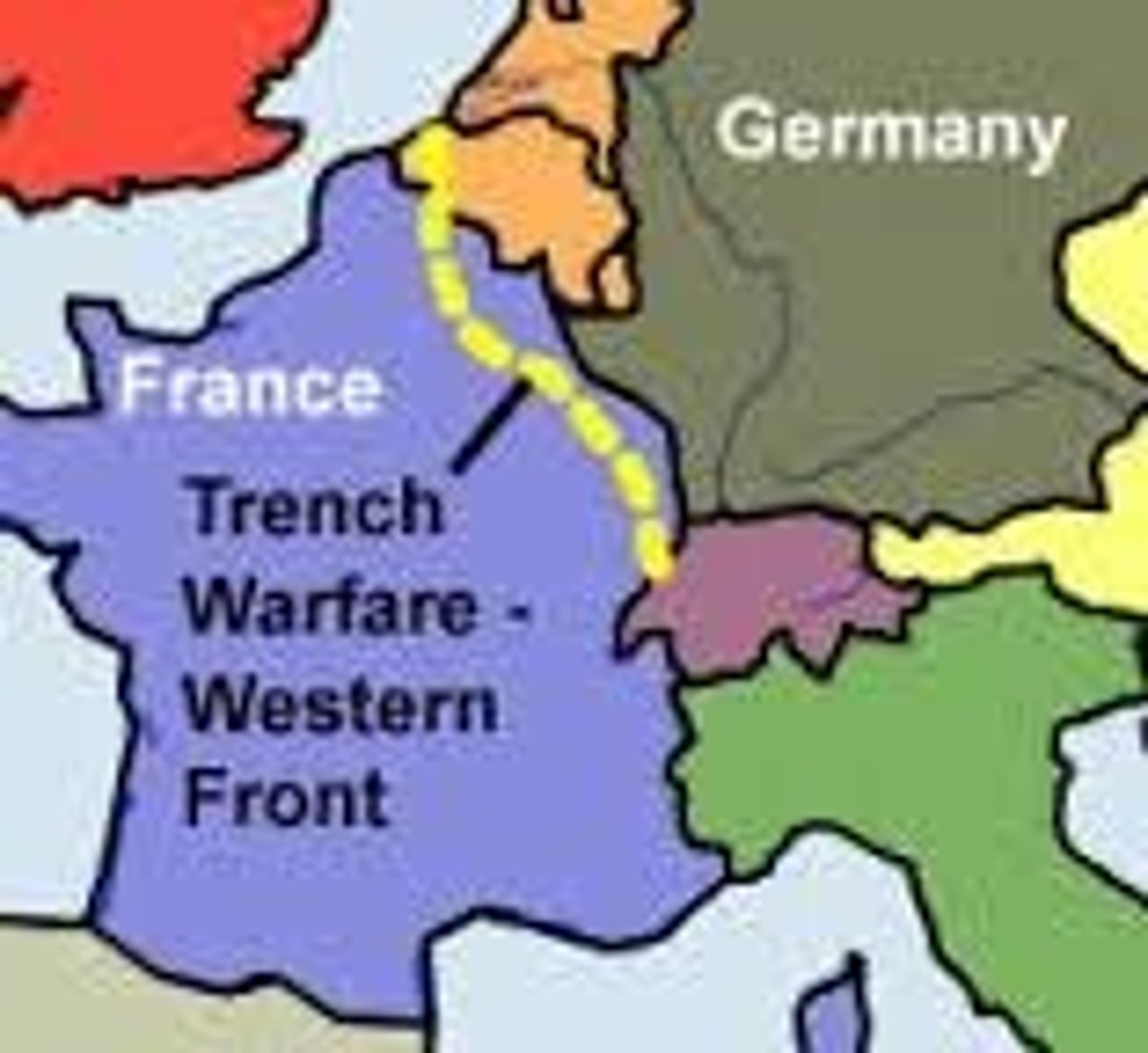
Stalemate on the Western front
A situation in which neither side is able to win a decisive victory due to trench warfare, they could not break through each other's defenses.

Russian Revolution
It was a period of political and social revolution across the territory of the Russian Empire, commencing with the abolition of the monarchy in 1917-1923. People were unhappy with the czarist imperial government . It ended with a socialist government and the end of the monocracy. USSR

Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The peace treaty was signed by the new Bolshevik government of Russia and the Central Powers, marking Russia's exit from World War I. Russia lost much land. German soldiers went to the Western Front.

Treaty of Versailles
The peace treaty that ended World War I, imposing heavy reparations and territorial losses on Germany.

14 Points
The principles for peace proposed by President Woodrow Wilson aimed to prevent future wars. They were made in 1918. It was successful in the short term, but two decades later, WW2 happened.

Lusitania
A British passenger ship sunk by a German U-boat, contributing to the U.S. entering World War I.

Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
The use of submarines to sink without warning any ship (including neutral ships and unarmed passenger liners) found in an enemy's waters. Because of this, the U.S. moved closer to declaring war on Germany.

Role of Women
Women took on new roles in the workforce and volunteer organizations during the war, contributing to the war effort. After the war, they were forced back into low-paying jobs or domestic work.
Total War on the Homefront
The complete mobilization of a nation's resources and population towards the war effort affects all aspects of life. Women took over men's jobs, food rationing, and businesses changed to produce for war.

Imperialism
the practice by which a country increases it's power by gaining control over other areas of the world

abdicate
to give up a position, right, or power
mandates
terms set by the national government that states must meet whether or not they accept federal grants
war front
a region where a battle is being (or has been) fought
Pre and Post WW1 map
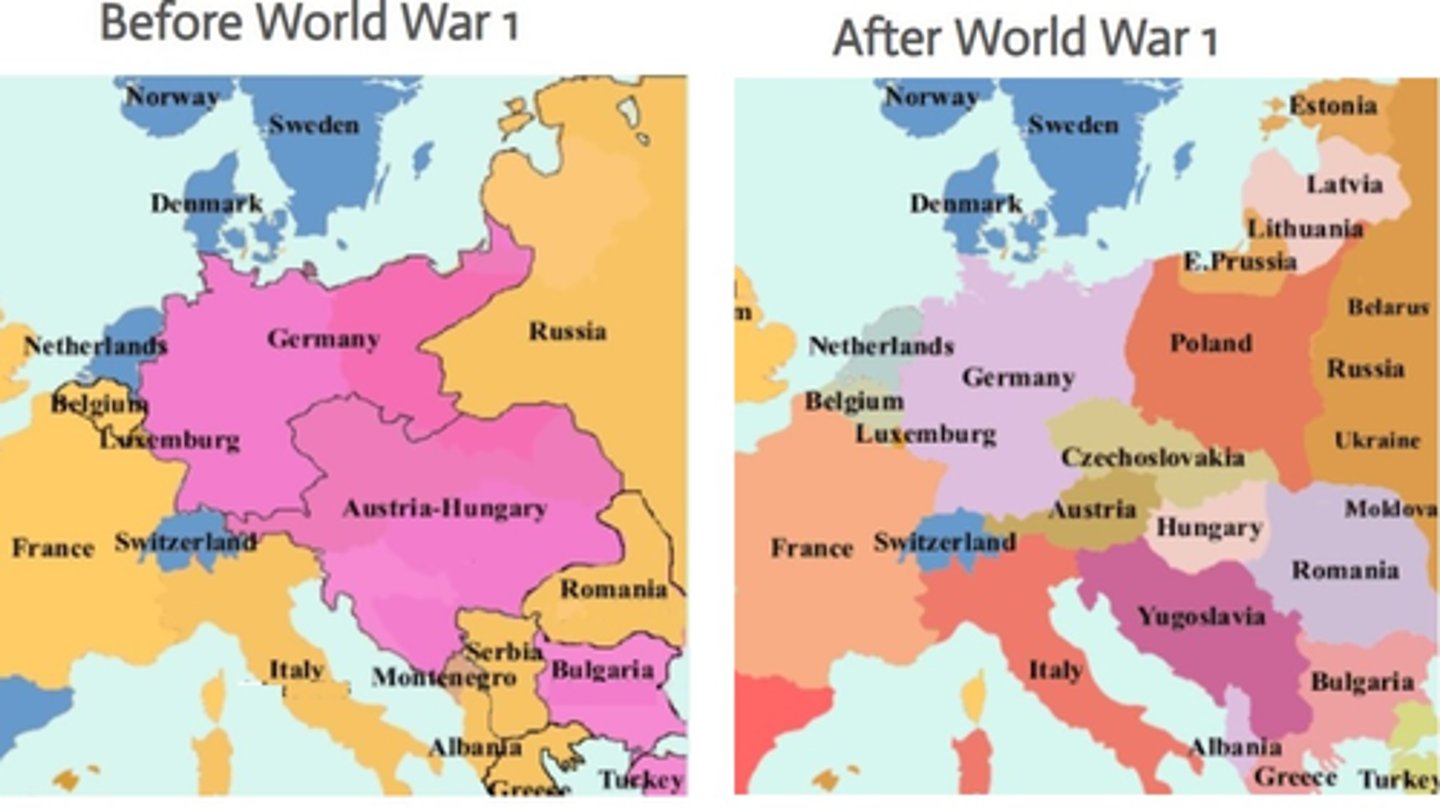
annexed
Took control of
Wilhem II
Kaiser of Germany during WWI
Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield. They were very deadly
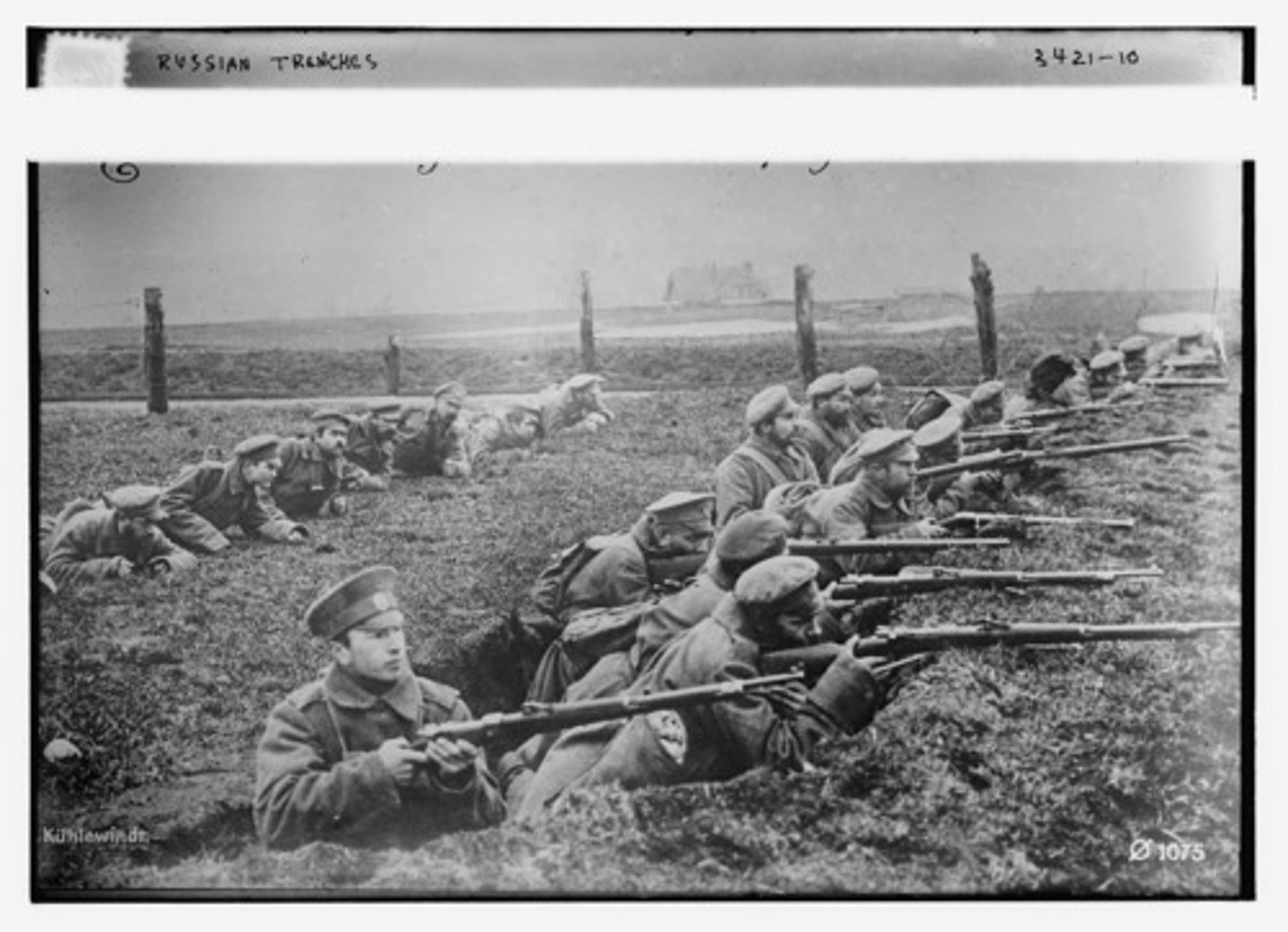

stalemate
A situation in which no progress can be made or no advancement is possible
artillery
large-caliber guns used in warfare on land- machine guns.

What does M.A.I.N mean and give examples?
Militarism - increasing spending on the navy, Alliances- triple Alliance, Imperialism - increased tensions between European countries, Nationalism- creates competition and assert independence
Which nations had to fight a two-front war?
During World War I, Germany fought a two-front war against France, Great Britain, Italy, Belgium and later also American forces on the Western Front and Russia and later Romania on the Eastern Front.
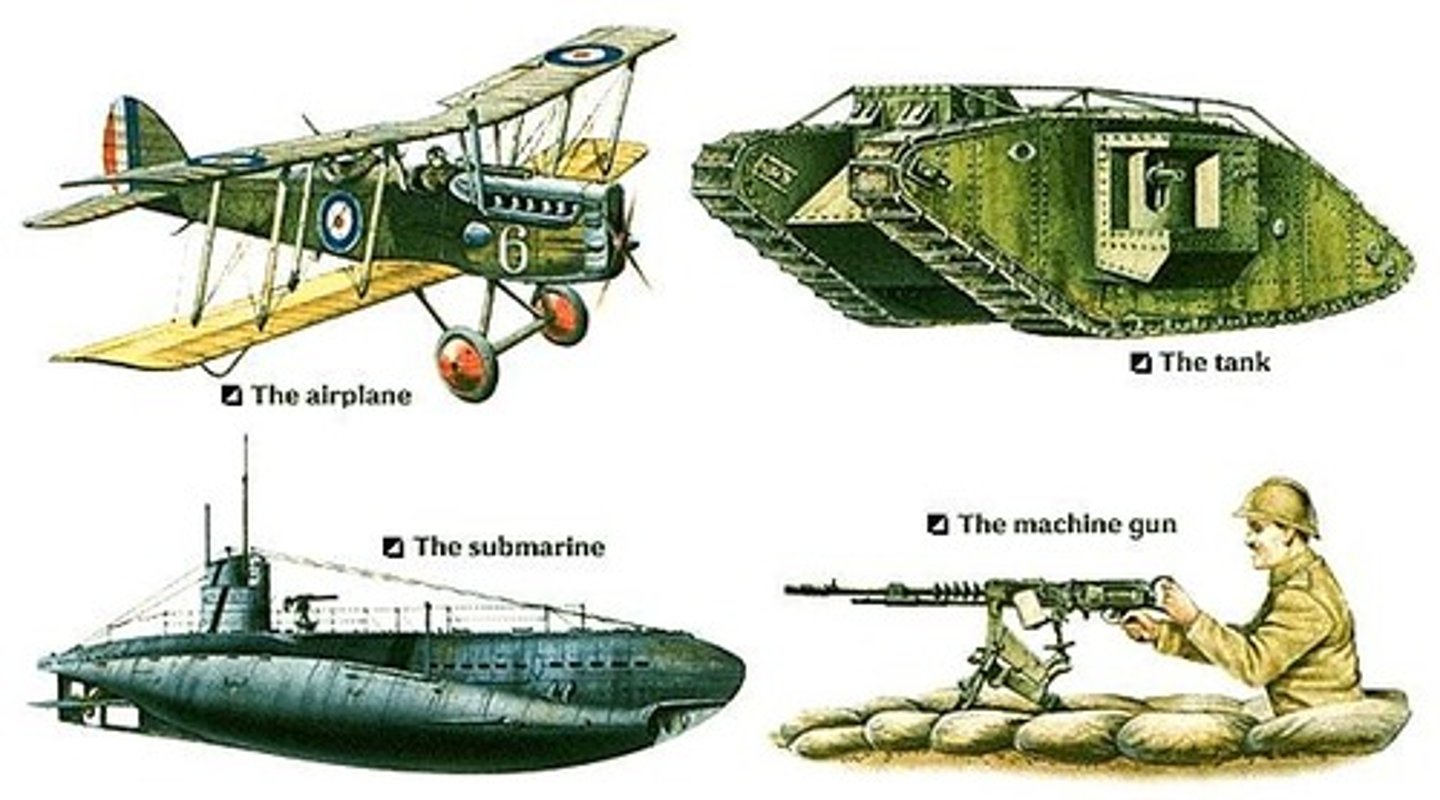
What were the new technology in WW1?
Military technology of the time included important innovations in machine guns, grenades, and artillery, along with essentially new weapons such as submarines, poison gas, warplanes and tanks.World War I popularized the use of the machine gun—capable of bringing down row after row of soldiers from a distance on the battlefield. This weapon, along with barbed wire and mines, made movement across open land both difficult and dangerous.
What was life like in the trenches?
bad conditions, diseases: trenchfoot, lice (big reason for stalemate)
What helped ended the stalemate?
the addition of American soldiers and tanks
What are the different types of propaganda?
The bandwagon (everyone else is), Fearmongering (appeals to one's fear), Flagwaving (patriotism), glittering generalities(sounds great, but you are not sure what it means), Good Ol' Boy(person who is down to Earth, football, corny jokes), Mudslinging(insults and suggests unethical behavior), Nostalgia (nice images of the past), Science and numbers, Shinning image (nice beautiful pleasant), Slogans and Jingles, Stereotyping, Testimonial(withfamous people and expects)
Russia leaving the war
March 1917 - Russian people not pleased how the government handled the scarcity of food and fuel. Russia became communist- Germany wasn't fighting Russia.
U.S in ww1
1917-1918. They join because the submarine attacks. The provided support to the Allies (I think).
What was the Zimmerman Telegram?
A telegram sent by Germany to Mexico asking them to join the war on the Central Powers' side.
How where the Central powers punished?
These treaties stripped the Central Powers (Germany and Austria-Hungary, joined by Ottoman Turkey and Bulgaria) of substantial territories and imposed significant reparation payments.
Which nation incurred the largest percentage of casualties?
A-H 90% death
Which nation incurred the most death?
Russia (maybe)
Which nations participated in the peace talks after the war?
United Kingdom, France, the United States, and Italy. Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey, and Bulgaria did not participate
The crime of ages- who did it?
"Crime of the Ages" is a US political cartoon suggesting peace in Europe has ended and all involved are to blame and also believe it the other sides' fault. The cartoon has all major players in World War I and each is pointing at another showing where the blame will lie

countries in wried fake Europe
Big thing - Tula/Russia, Square thing next to Tula - Petrovac/Serbia, Above Tula to the right - Klagfurt/Austria-Hungary, Right of Klagfurt - Metz/Germany, Island-Tobermory/UK, Hexagon top of Metz - Grenoble/France,
Triangle next to Grenoble - Tivoli/Italy