Section 4 9 Genetic diversity
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Chromosome mutations
Changes in the whole set of chromosomes, when the organism has three or more sets of chromosomes rather than two
Changes in the number of individual chromosomes, when homologous pairs of chromosomes fail to separate during meosis.
The steps of Meosis
Interphase: The cell replicates chromosomes and and organelles
Meosis 1: Separation of homologous chromosomes
Phrophase 1: The chromosomes condense and become visible. Homologous chromosomes link together to form chiasmata, crossing over takes place - exchanging alleles between the homologous chromosomes. Nuclear membrane breaks down, and centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell, commencing spindle fibers.
Metaphase 1: Pairs of Homologous chromosomes line at the equator of the cell [Independent segregation]
Anaphase 1: Spindle fibres contract (shorten) spindle fibres move to opposite sides of the cell.
Teleophase 1: The chromosomes reached to opposite poles of the cell, and condenses back to chromatin. Also, nuclear membrane reformed.
Cytokensis: Forming haploid cells that are not genetically identical.
Meosis 2: Separation of Sister chromatids
Phrophase 2: Chromosomes condense to become visible, nuclear membrane breaks down, spindle fibres form [No crossing over]
Metaphase 2: Chromosomes line up at equator [Independent segregation does not occur]
Anaphase 2: Centromere of each chromosomes divides, spindle fibres shorten. Chromatid pulled to opposite poles of the cell.
Teleophase 2: The chromatids reach the opposite poles of the cell and condenses back to chromatin, and membrane formed
Cytokenesis: Forming 4 genetically different haploid cells
![<p>Interphase: The cell replicates chromosomes and and organelles</p><p>Meosis 1: Separation of homologous chromosomes</p><ul><li><p>Phrophase 1: The chromosomes condense and become visible. Homologous chromosomes link together to form chiasmata, crossing over takes place - exchanging alleles between the homologous chromosomes. Nuclear membrane breaks down, and centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell, commencing spindle fibers.</p></li><li><p>Metaphase 1: Pairs of Homologous chromosomes line at the equator of the cell [Independent segregation]</p></li><li><p>Anaphase 1: Spindle fibres contract (shorten) spindle fibres move to opposite sides of the cell.</p></li><li><p>Teleophase 1: The chromosomes reached to opposite poles of the cell, and condenses back to chromatin. Also, nuclear membrane reformed.</p></li><li><p>Cytokensis: Forming haploid cells that are not genetically identical.</p></li></ul><p>Meosis 2: Separation of Sister chromatids</p><ul><li><p>Phrophase 2: Chromosomes condense to become visible, nuclear membrane breaks down, spindle fibres form [No crossing over]</p></li><li><p>Metaphase 2: Chromosomes line up at equator [Independent segregation does not occur]</p></li><li><p>Anaphase 2: Centromere of each chromosomes divides, spindle fibres shorten. Chromatid pulled to opposite poles of the cell.</p></li><li><p>Teleophase 2: The chromatids reach the opposite poles of the cell and condenses back to chromatin, and membrane formed</p></li><li><p>Cytokenesis: Forming 4 genetically different haploid cells</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c52f262d-71b0-499a-a910-acd72450fb5a.png)
The importance of meosis
For the formation of gametes which fuse together during fertilisation to introduce variation
The three ways meosis forms genetic variation
Crossing over of the homologous chromosomes, passing on alleles between each other, where each chromatid is genetically different from one another
During Metaphase 1, the way the homologous chromosomes are lined up at the equator (independent assortment) SHOWN IN PIC
Random fusing of gametes
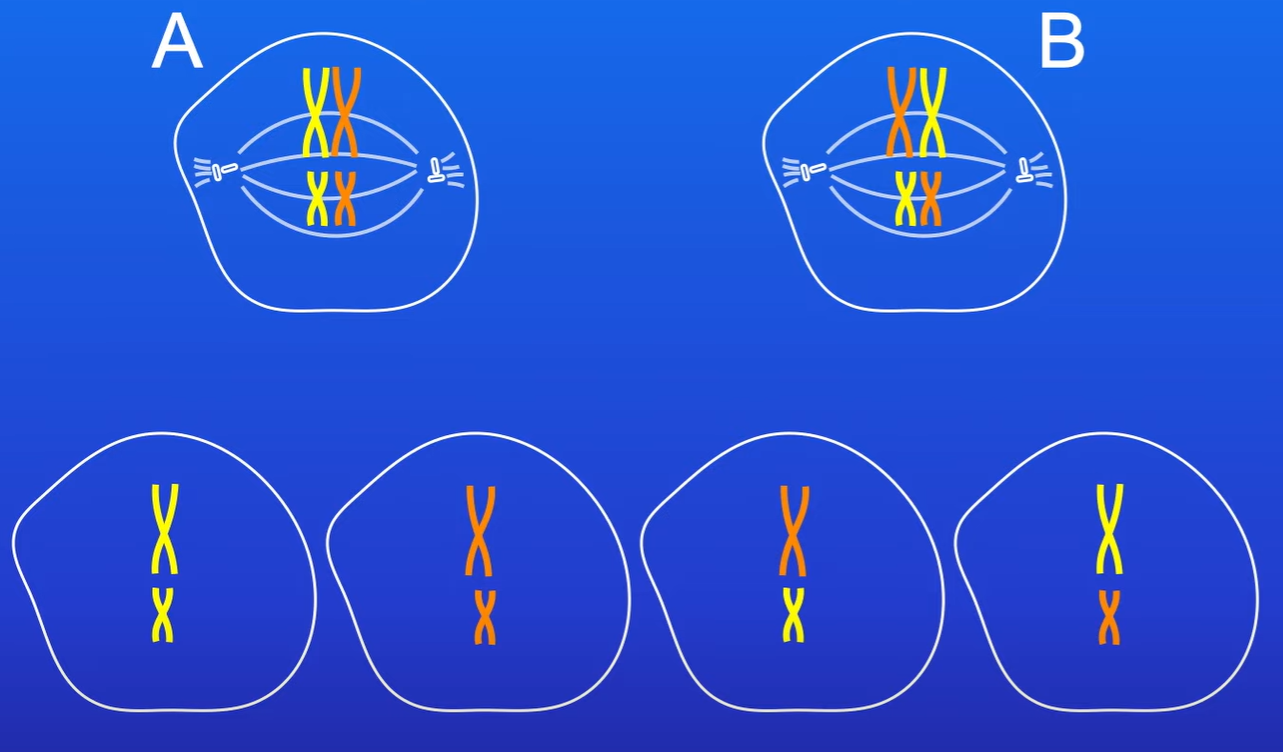
How to calculate the number of genetically different gamete produced by independent assortment?

How do organisms of the same species differ from one another?
All members from the same species have the same genes.
Organisms of the same species differ in their combination of alleles not their genes.
Define genetic diversity
Total number of different alleles in a population.
Define population
A group of individual same species that live in the same place and can interbreed to form fertile offspring.
Natural selection in the evolution of populations
Within a population there is a large number of different alleles that can be inherited.
Random mutation of alleles forms a new allele of a gene
However, in certain environments this allele will give advantage
These individuals are better adapted and survive
They reproduce sucessfully and pass on their alleles to next generation
Over many generation, this will increase the number of organisms with the advantageous allele, while the non-advantageous allele reduces.
KEY: the frequecy of the allele increases over many generation
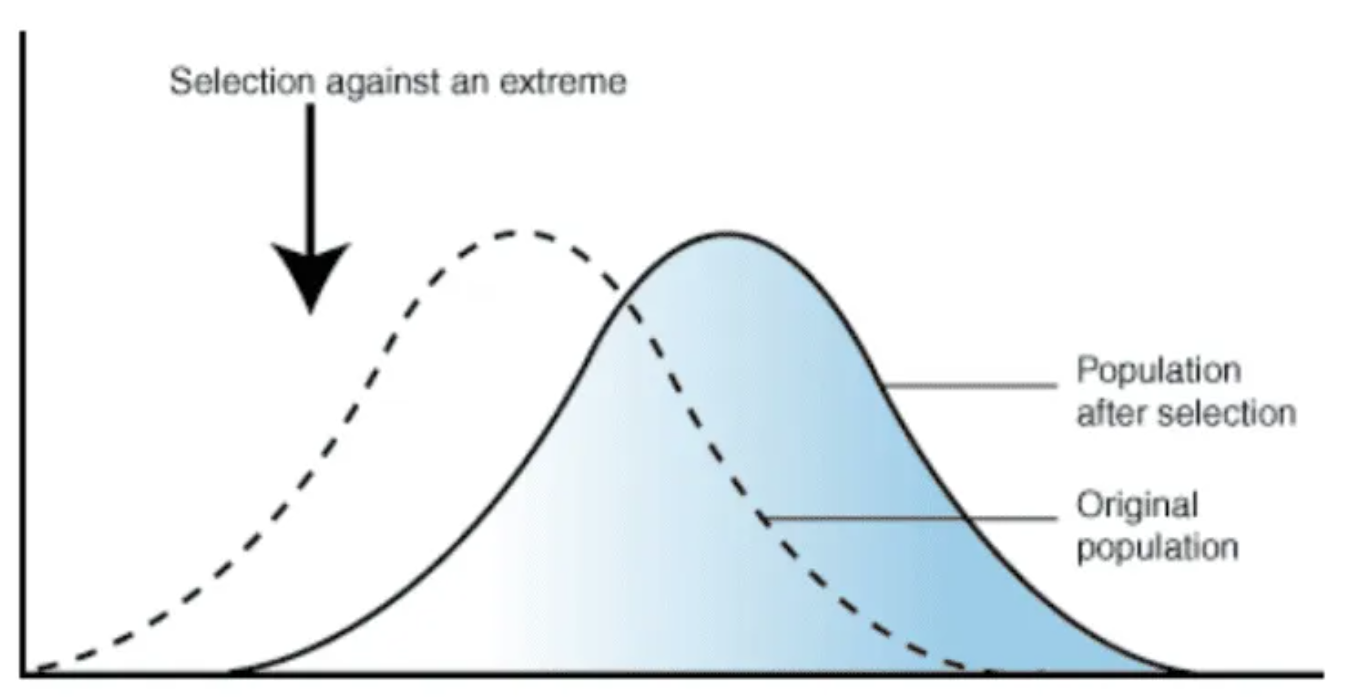
Directional selection
Alleles of an extreme type are selected, and causes the change in characteristic of population
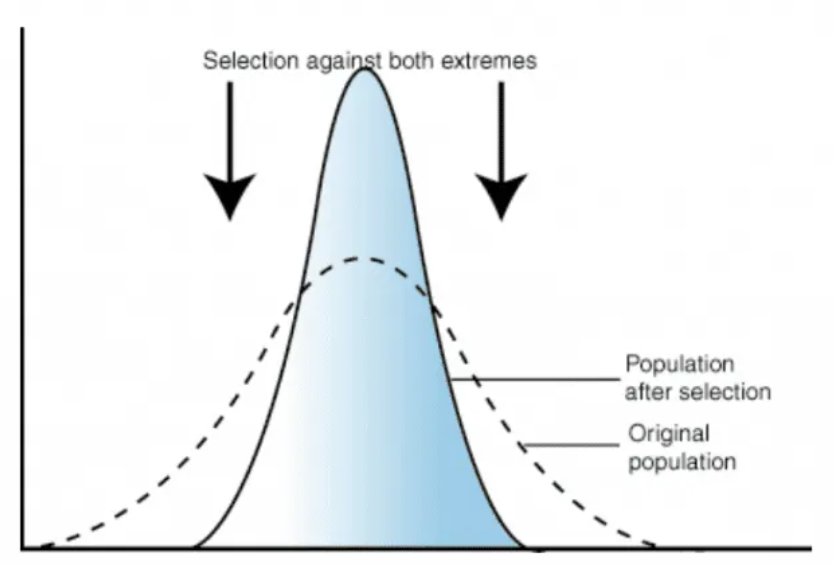
Stabilising selection
Selection pressure which favours average individuals, and preserves the characteristics of the population
That the alleles at the extreme ends are not valued that this causes a reduced frequency of the allele.
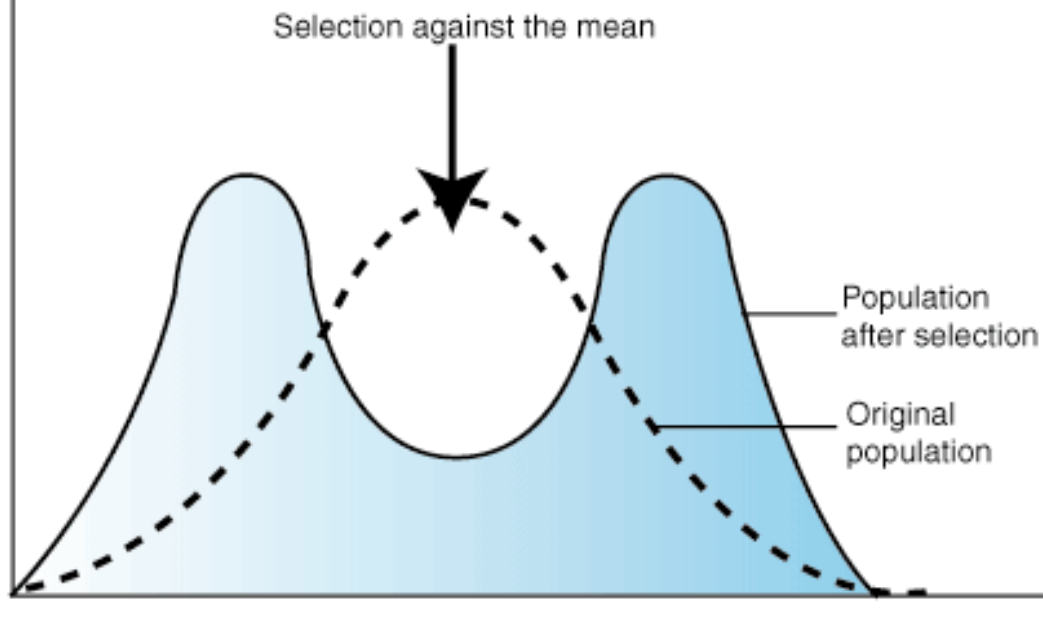
Disruptive selection
Selection pressure against the mean, which favour the extreme characteristics of populations.
How does Crossing over cause variation? (4-marker)
Homologous chromosomes form a bivalent
They form a chiasmata
Where lengths of chromosomes are exchanged (alleles are exchanged)
This forms a different combination of alleles