Joint Mobilizations (week 6)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Effects of Joint Motion
Stimulates biological activity by moving synovial fluid
Prevents atrophy of the articular cartilage due to immobilization
Maintains extensibility and tensile strength of articular tissues
Cause afferent nerve impulses to be sent from joint receptors to the CNS regarding position and motion
Loss of sensory input can lead to impaired balance
Joint Mobilizations by PTAs
Controversial topic
Not prohibited by the Texas Practice Act
APTA article The Joint Manipulation Debate
Indications
Pain, muscle guarding and spasm
Reverse Joint Hypomobility
Position Faults/Hypomobility
Progressive limitation
Functional Immobility
Contraindications
Necrosis of ligament or capsule
Hypermobility
Joint effusion
Inflammation
Precautions
Malignancy
Bone disease
Unhealed fracture
Excessive pain
Weakness of connective tissue due to injury, surgery, disease (RA)
Elderly with weakened tissue
Pain as the Guide
Pain before tissue limitation
Gentle pain-inhibiting joint techniques
Pain concurrently with tissue limitation
Gentle stretching to tight tissue that doesn’t exacerbate pain
Pain after tissue limitation
Joint play techniques
Non-Thrust Oscillations
Grade I – Small amplitude oscillations at beginning of range. Rapid oscillations
Grade II – Large-amplitude rhythmic oscillations performed within the range. 2-3 osc./second, 1-2 minutes
Grade III – Large amplitude rhythmic oscillations performed up to the limit of the available range and tissues are stressed. 2-3 osc./second, 1-2 minutes
Grade IV – Small-amplitude rhythmic oscillations at the limit, stressed into tissue resistance. Rapid oscillations
Non-Thrust Sustained Joint-Play Techniques
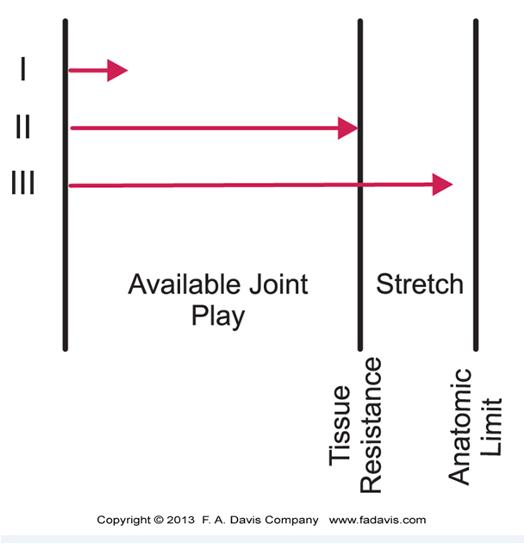
Grade 1 – Small amplitude distraction, no stress to capsule
Grade II – Distraction or glide to tighten tissues. “Taking up the slack”
Grade III – Large amplitude stretch or distraction to stretch joint capsule and surrounding periarticular structures
Oscillating
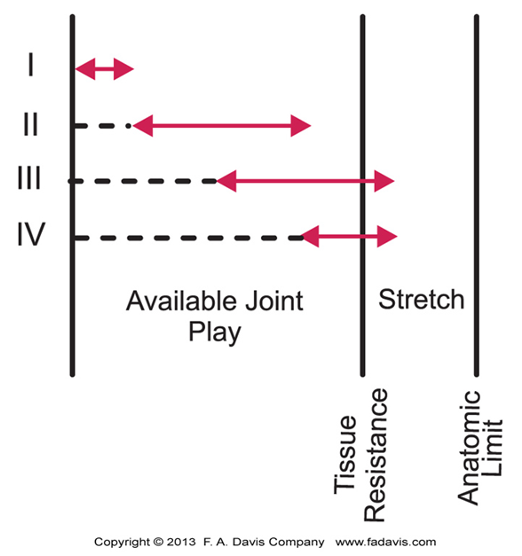
sustained
Comparing Oscillations and Sustained Techniques
Main differences are in the rhythm and the speed of force application
Remember:
Grade I and Grade II for both techniques are low intensity and do not cause a stretch force to the joint capsule
Grade III (both) and Grade IV (oscillations only) are applying a stretch
Thrust Manipulation/ High Velocity Thrust
Small-amplitude , high-velocity thrust performed at end range to snap adhesion or reposition.
One repetition only
Also called Grade V mobilization
Traction
Longitudinal pull.
Distraction
•separation, or pulling apart.
•Important to prevent damage to the joint with mobilization
Direction and Target of Treatment Force
The treatment force is applied as close to the opposing joint surfaces as possible (Get your hands close to the joint line)
Applying the force through a larger surface (hand vs. finger tips) will make it more comfortable for the patient
Remember the convex and concave rule!!
Mobilization with Movement
Treatment concept developed by Brian Mulligan
Application of pain-free accessory mobilization with active and/or passive physiological movement
Pain is the barrier
Documentation
Rate of application of the force
Location in range of available movement
Direction of force as applied by the PT/PTA
Target of the force
Patient position
Adverse Effects
Tearing/ Damage of tissue, joint surfaces, etc.
Damage to surgical repair
Inflammation
Swelling
Impaired function
Hypermobility
Loss of patient trust