Neurological imaging and diagnostic testing
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Focal sensory examination evaluates 3 things
light touch, 2 point discrimination, sharp/dull
The more distal, the more _____ sensory capabilities you have
focal
what does AVPU stand for
Alert, Voice (responds to), Pain (responds to), Unresponsive
What is the best score for GCS
15
What is the GCS of a totally unresponsive person
3
EVMS
Eye, Verbal, Motor, Score
"Dry" CT
CT w/o IV contrast
CT w/o contrast can help identify
intracranial bleeding, stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic), brain/spine tumors, fractures, spinal stenosis
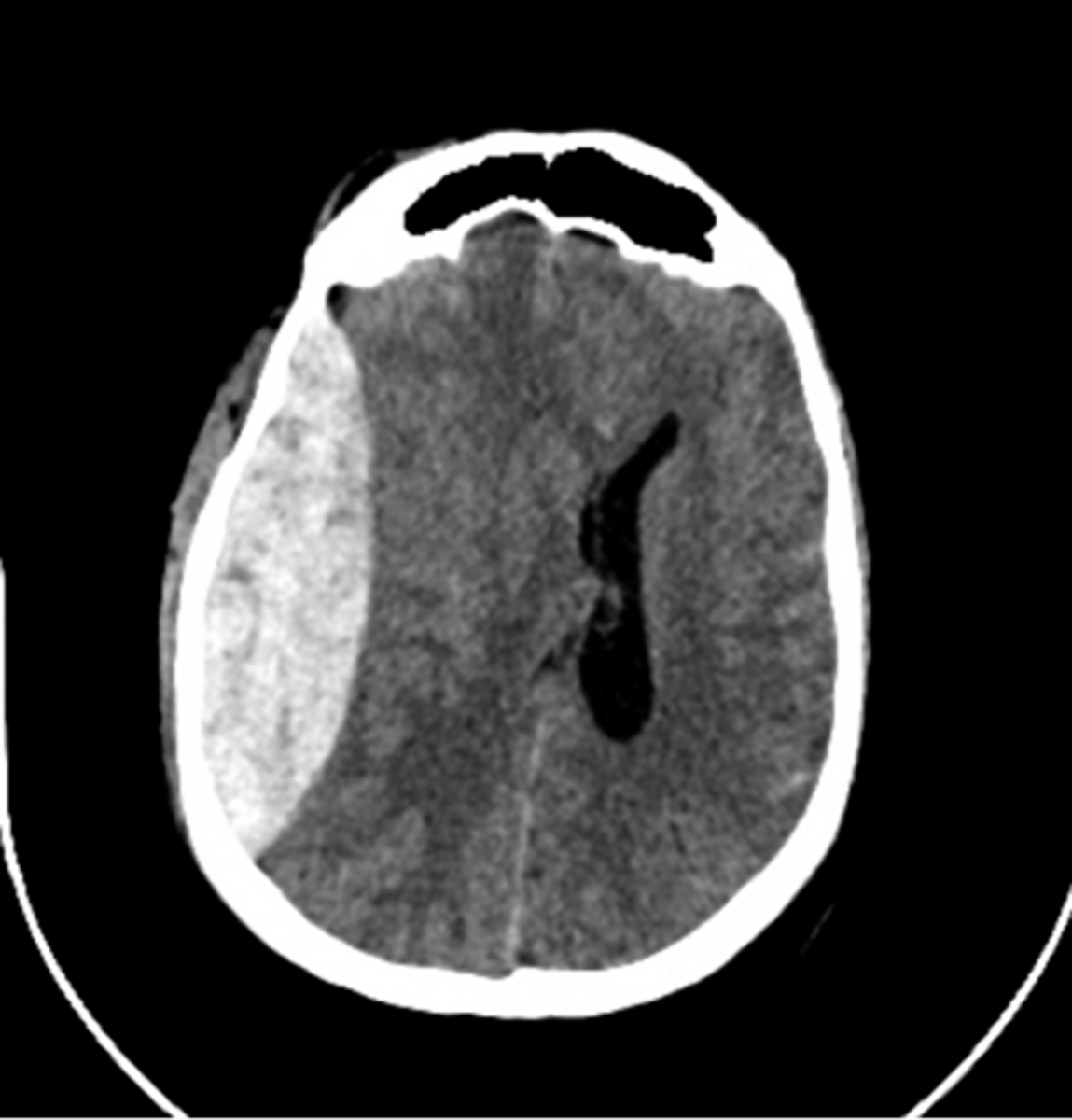
epidural hematoma
lemon shaped
normal mental status to completely unconscious
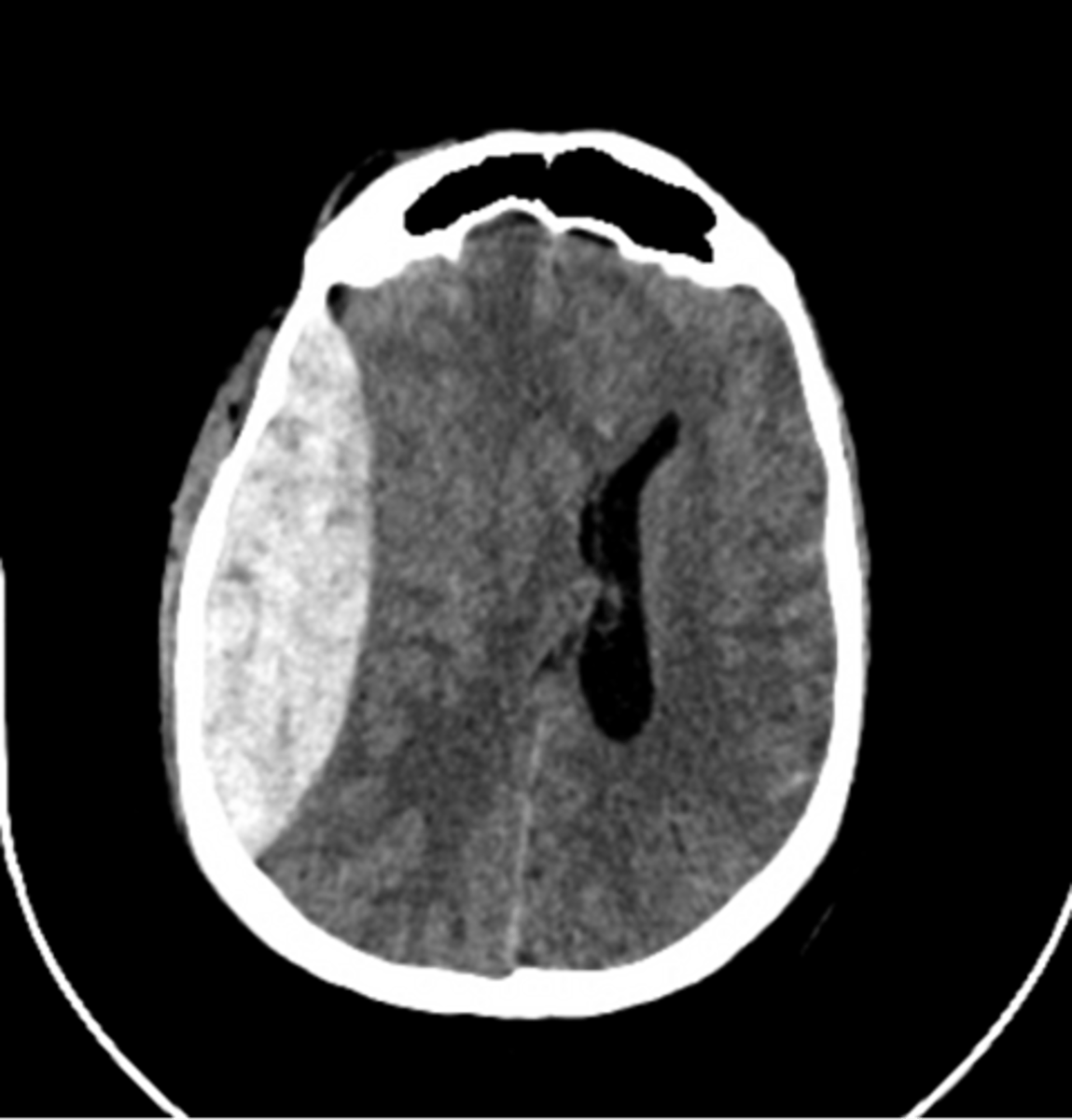
subdural hematoma
Crescent-shaped intracranial bleeding after head injury in the elderly; can be acute on chronic
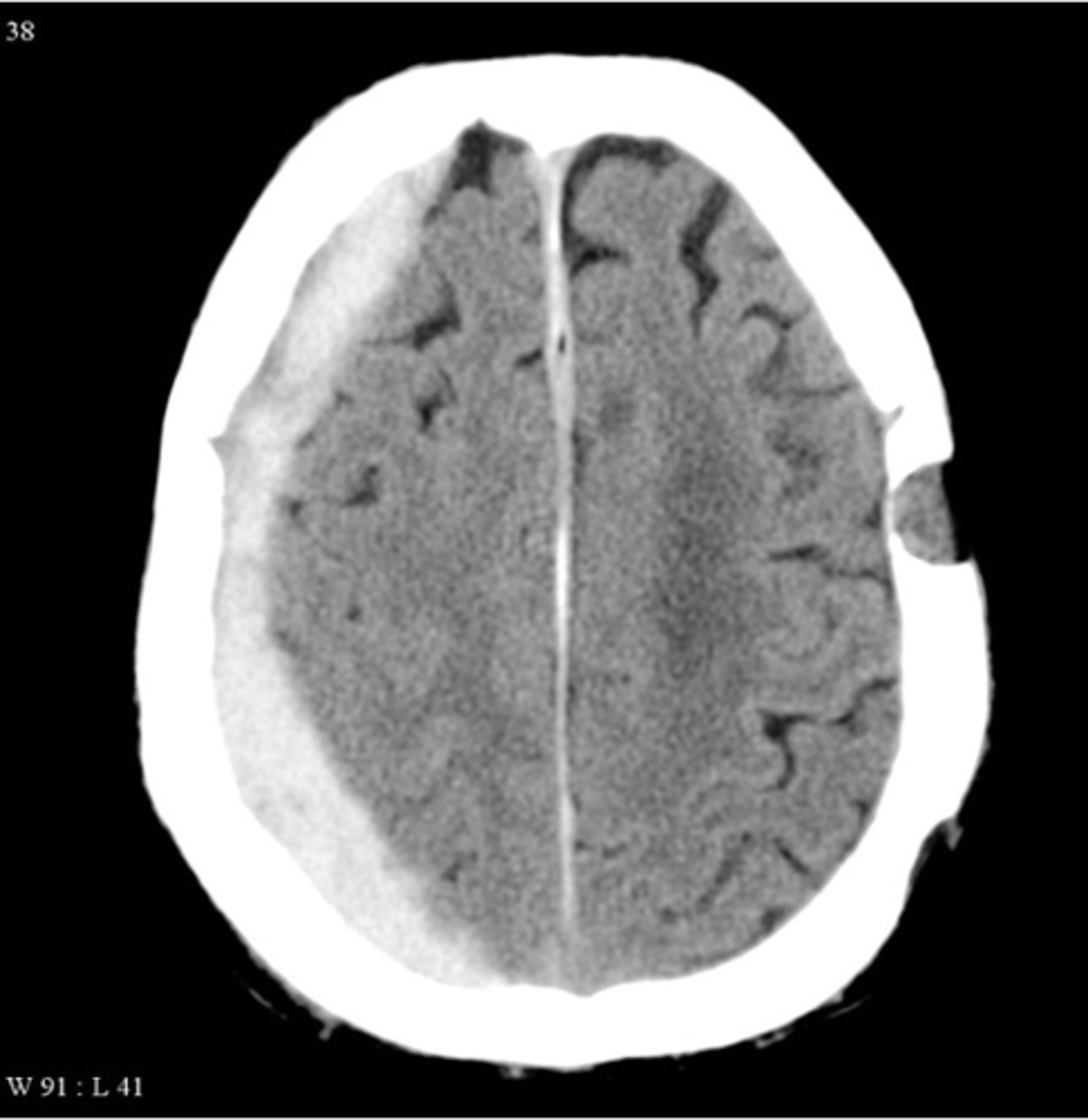
subarachnoid hemorrhage
more diffuse presentation
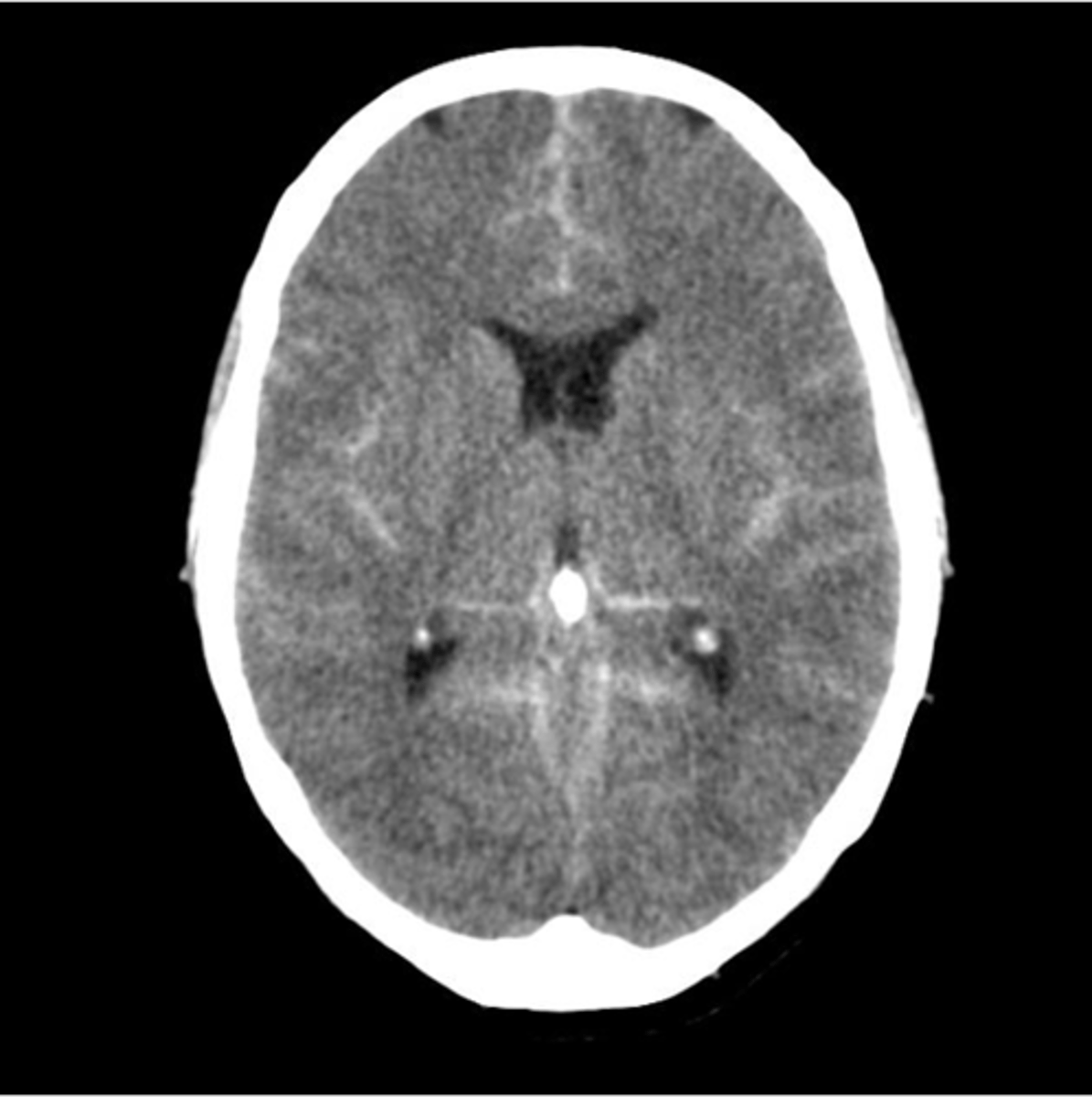
intracerebral hemorrhage
typically not trauma related; can often come from a ruptured AVM from uncontrolled HTN
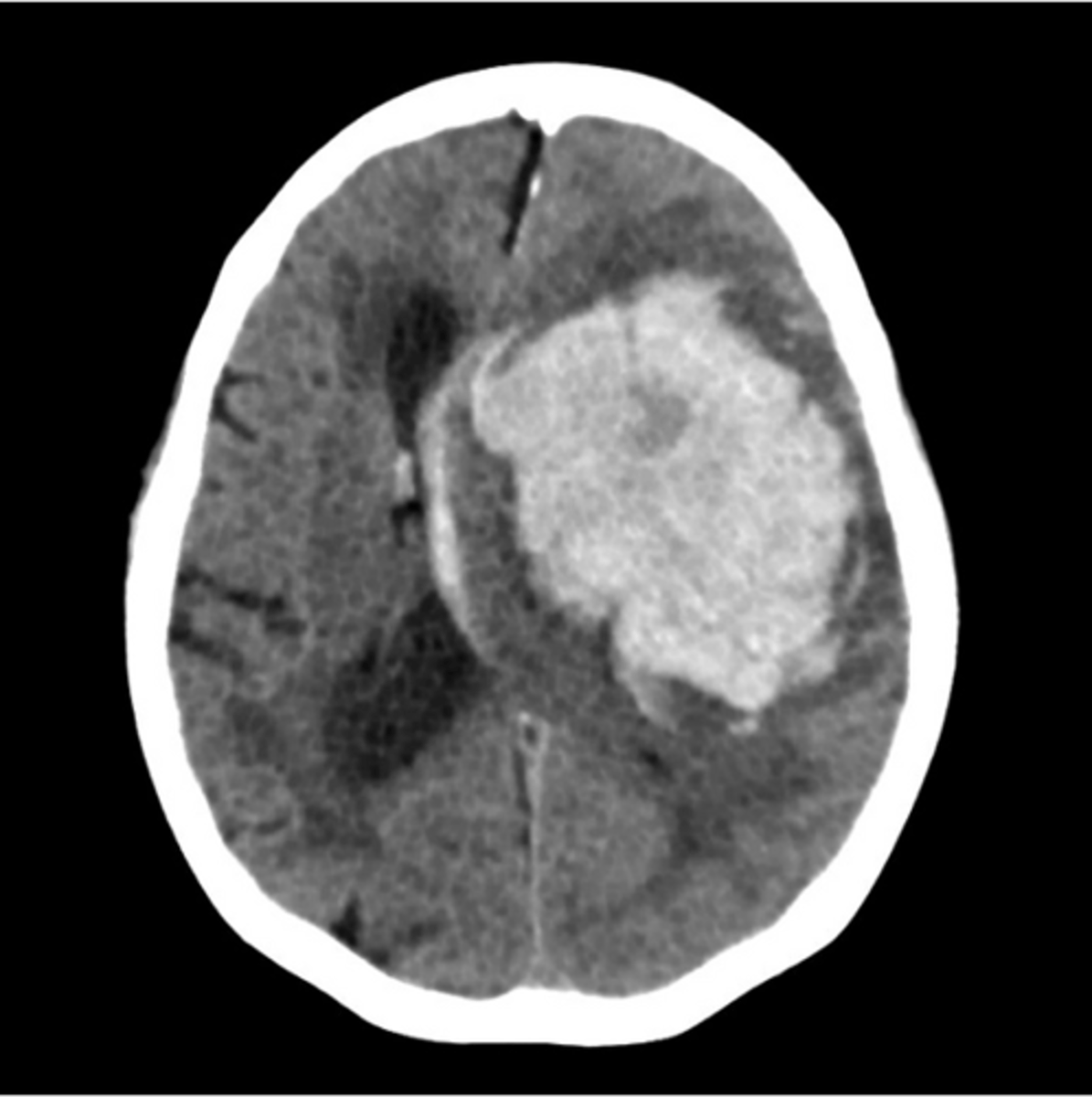
ischemic brain injury
are epidural or subdural hematomas more common?
subdural
Dark (on CT) means
old blood
White means
new blood or CSF
Can you have a subdural hematoma that is acute on chronic?
yes
CT w/ IV contrast head can help identify
stroke (ischemic), brain/spine tumors & vascularity, AVM, fractures/spinal stenosis
if you wanted both a CT w/ and w/o contrast, which would you do first?
Without contrast ("dry")
MRI head is most helpful in evaluating __________
soft tissue disturbances (tumors, brain infections, dementia, inflammation)
Before having an MRI, you must make sure the patient doesn't have
metal in the body
head MRA evaluates
magnetic resonance angiography
head PET Scans use ____ bound to glucose to show where the brain is _____
radioactive substance bound to glucose to see where the brain is working
PET Scans are used to identify brain
function
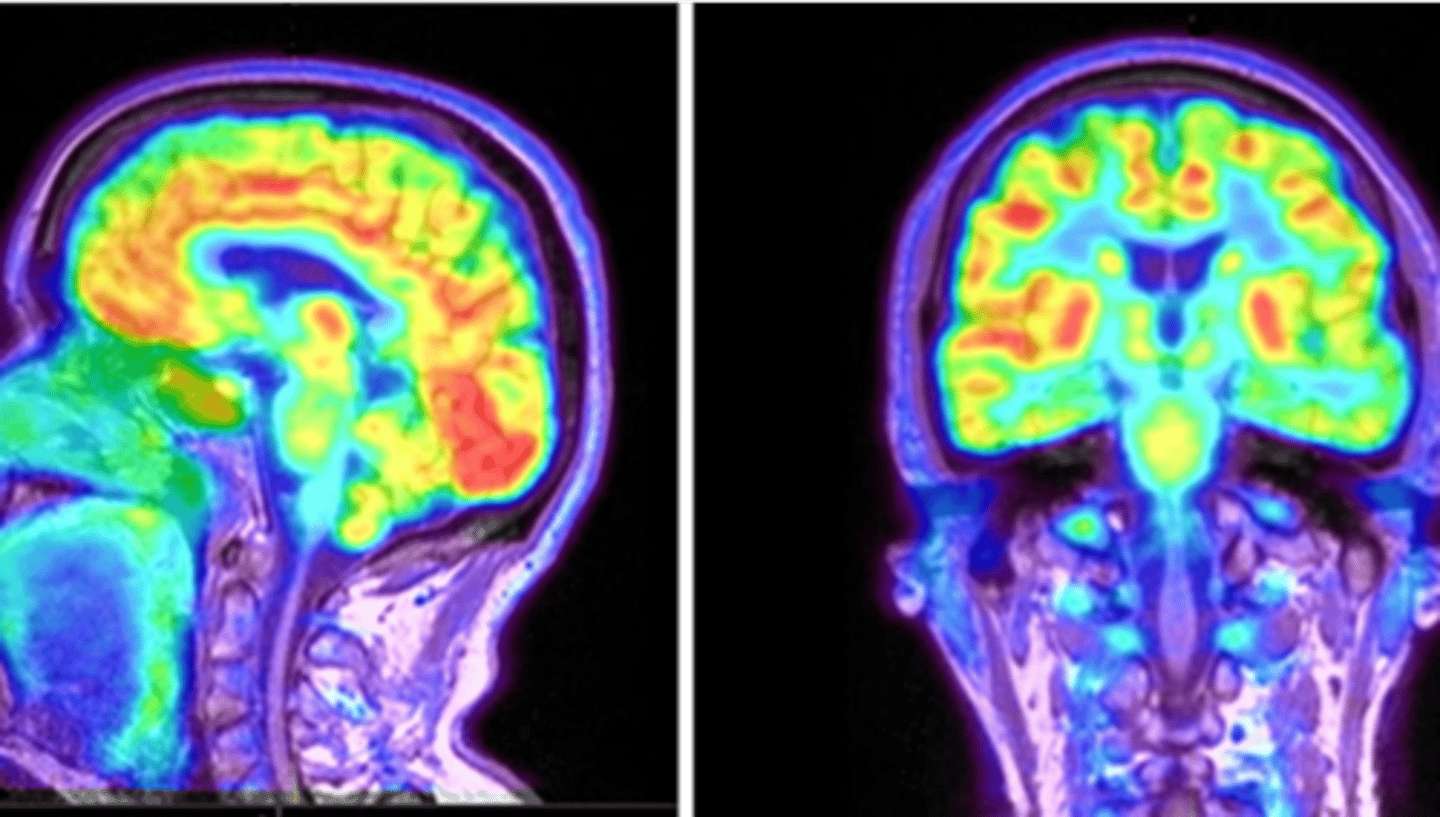
PET Scans are useful in evaluation of
alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, parkinson's disease, mets
EEG measures the pattern of
electrical activity in the brain
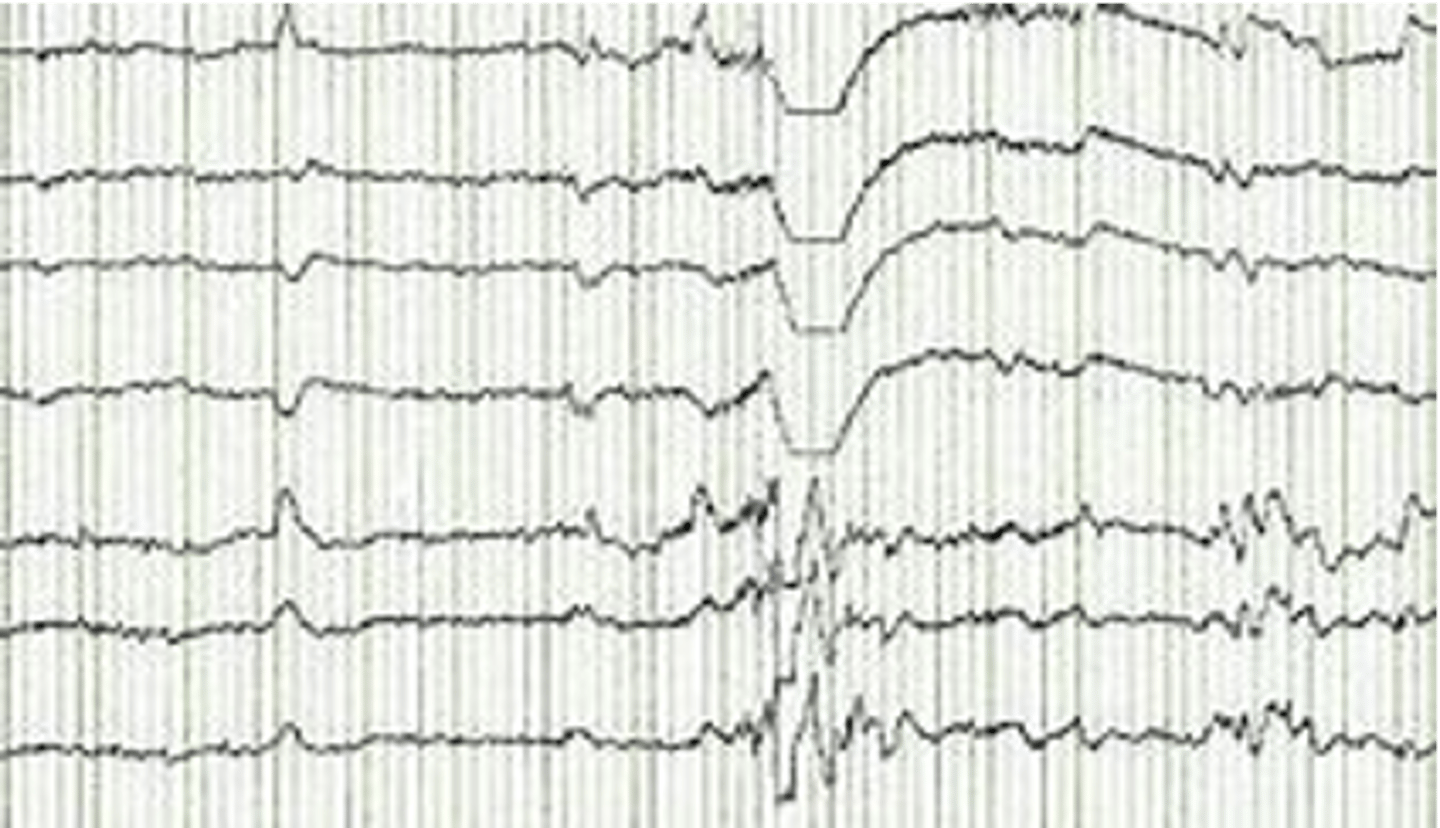
EEG can find brain wave patterns a/w
epilepsy, seizure, tumors, alzheimer disease, psychoses, sleep disorders, brain injury/death
brain death on EEG
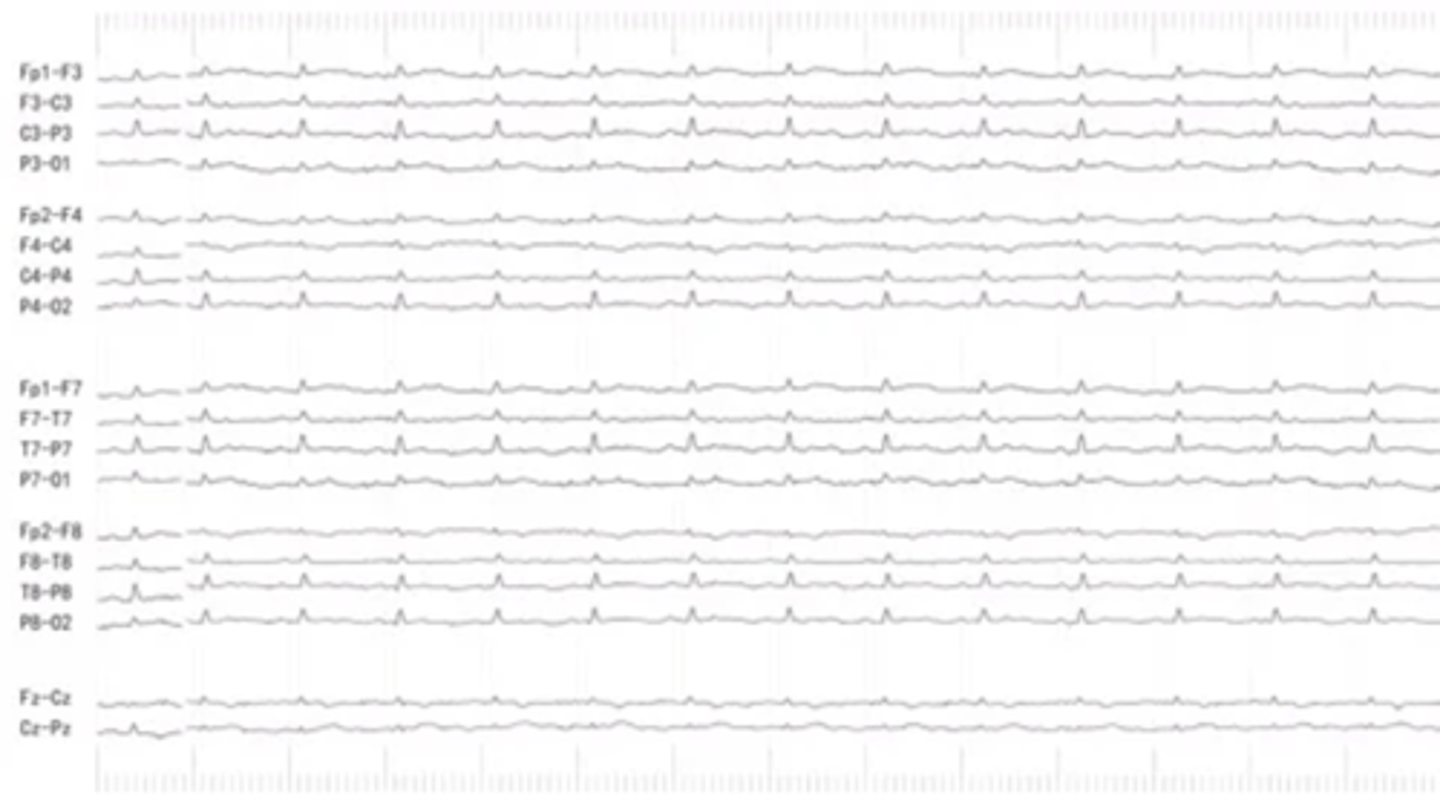
normal EEG
in CSF analysis what do tubes 1,2,3,4 represent
1: CBC w/ dif
2: gram stain
3: C&S
4: Cell count
Positive cell count on LP could indicate
traumatic tap or intracranial hemorrhage
do you have to draw tubes 1,2,3,4 in consecutive order?
YES
what is a major contraindication for performing an LP
space occupying lesion in the brain (this could cause the brain to herniate because you are quickly decreasing the intracranial pressure)
what are some signs and symptoms that would make you concerned about a space occupying lesion
progressively worsening HA, ne HA w/ focal neuro symptoms, unexplained HA in pt with cancer or HIV, new onset seizure
doppler US of the head can help identify
blood clots, arterial stenosis, vascular vasospasm
EMG can be used to evaluate _____ nerves
peripheral
EMG evaluates the ___ and ____ of electrical nerve impulses
speed and strength
what are some conditions that EMG is used for
peripheral nerve compression syndromes, peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome
what is some lab testing that you can order to evaluate peripheral nerve testing
vit deficiencies (vit b12, e, b6) , diabetes (glucose and HgbA1c) , immune function abnormalities, chronic renal failure (uremia), exposure to heavy metals (lead)
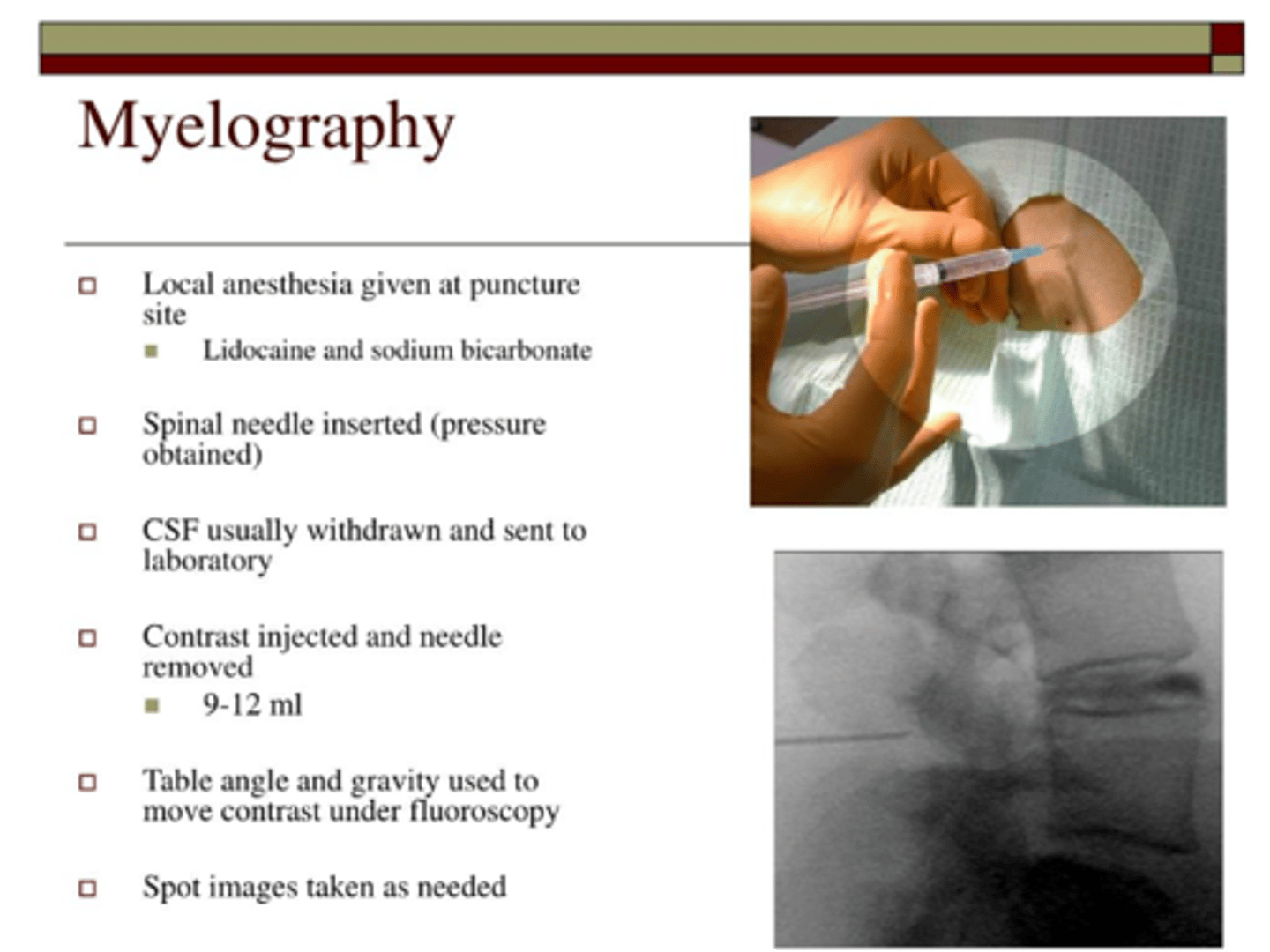
CT myelography can be used to evaluate the ____ and _____
spinal cord and canal
CT myelography is a good alternative to MRI to identify
spinal stenosis, disc herniation, spondylosis, arthritis
plain radiography of the head/neck is good to determine
flexion and extension of the spine (evals stability)
herniated disc disease
pain related to a herniated disc will most oftentimes occur ____ to the injury
distal
spinal compression fracture
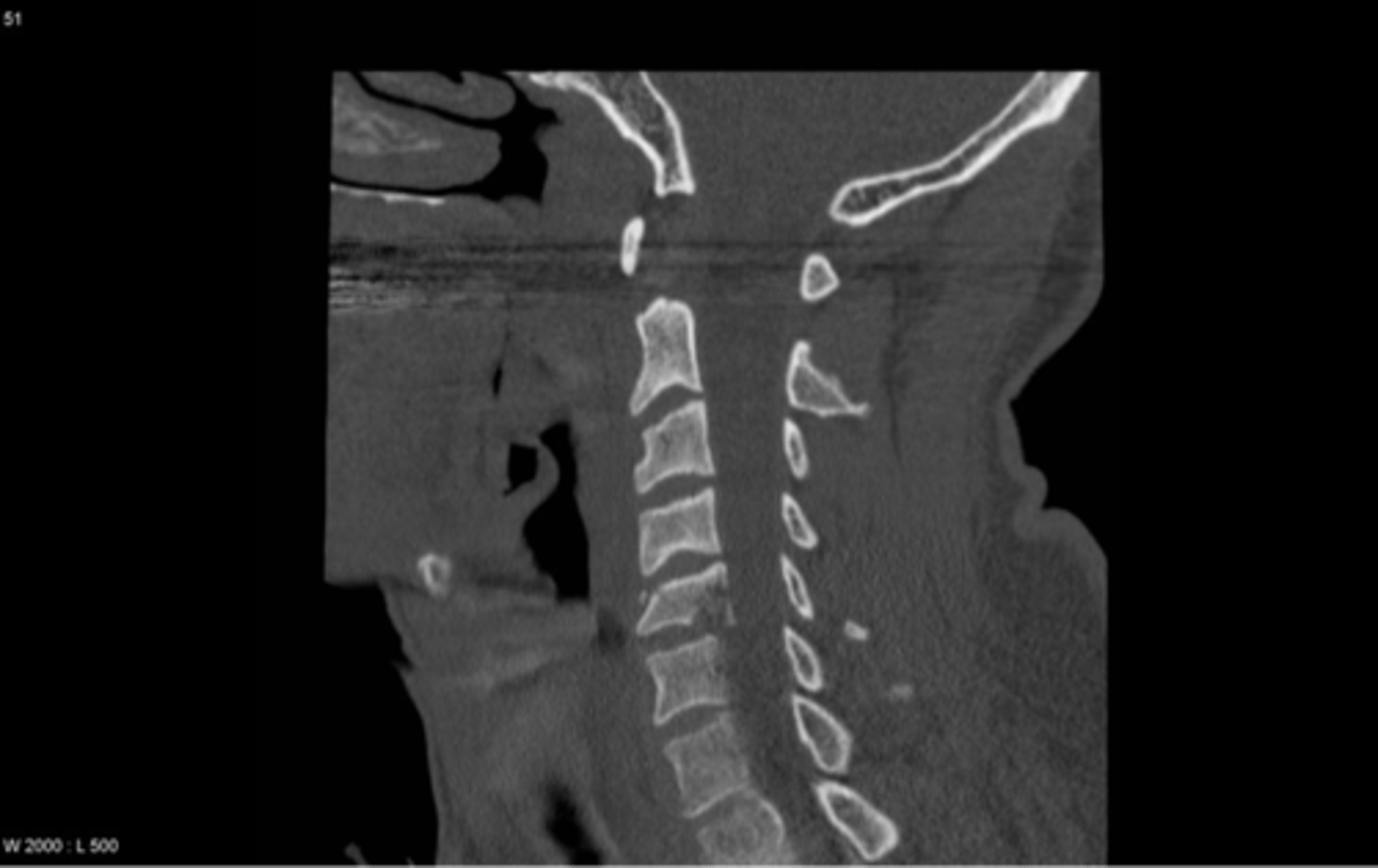
cervical burst fracture
clay shoveler's fracture
Fracture of C6 or C7 spinous process, relatively innocuous.
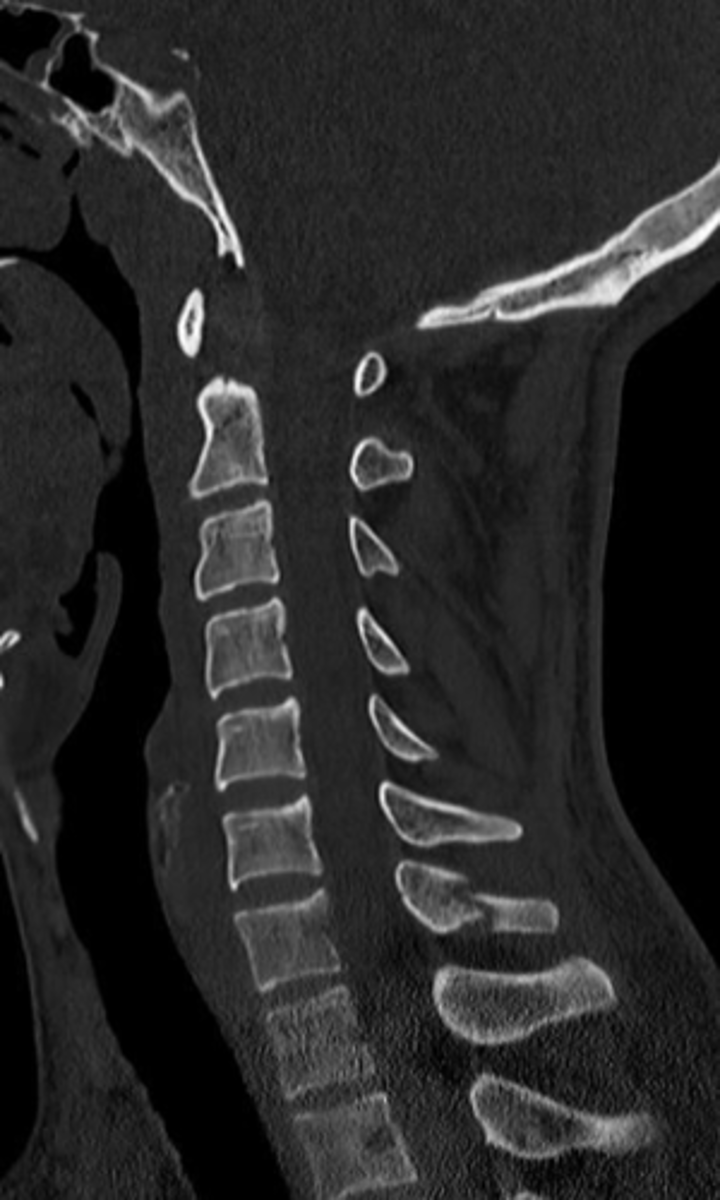
spondylosis
arthritic degeneration of the spine
spondylosis is generally accompanied by ____ formation and disc ______
osteophyte formation and disc thinning/collapse
_____ is a common cause of low back pain but can occur anywhere
spondylosis
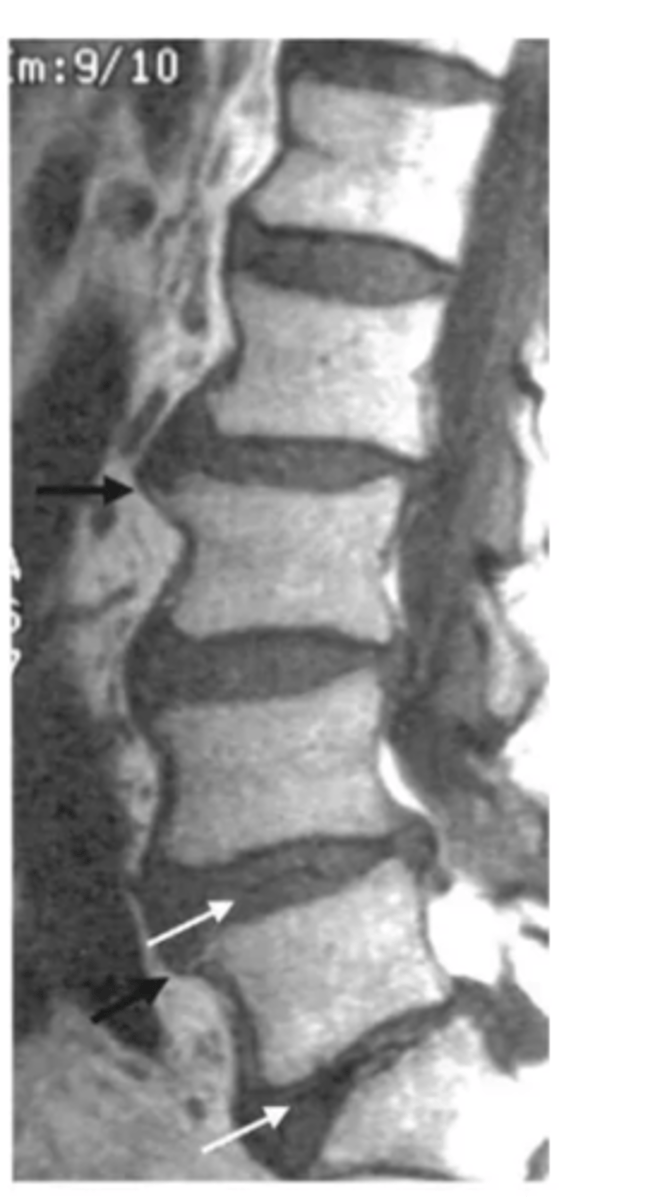
spondylolisthesis
forward slipping of one vertebra over another (caused by vertebral fracture at the pars interarticularis)
spondylolithesis can be caused by ____ or ______
degenerative or traumatic etiology
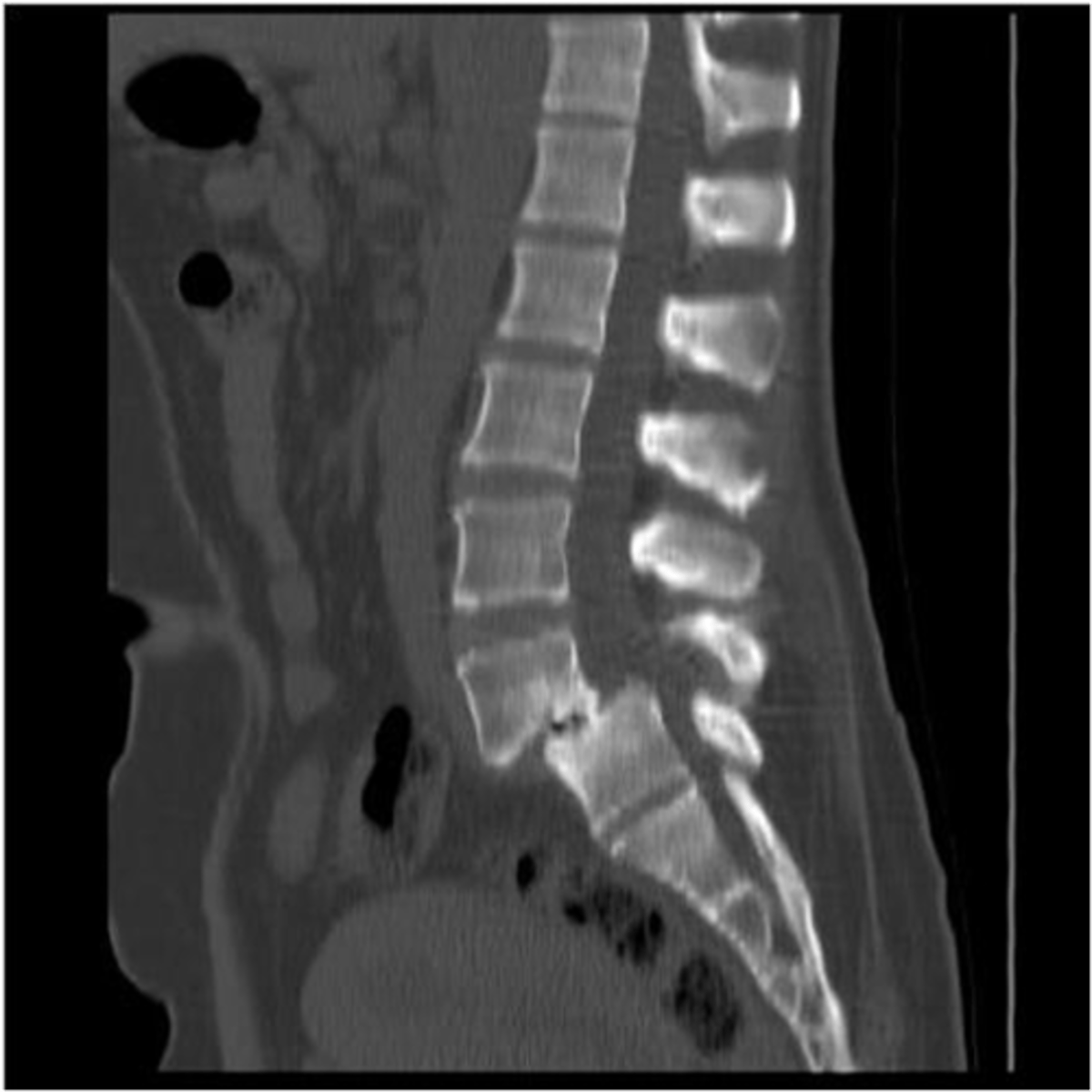
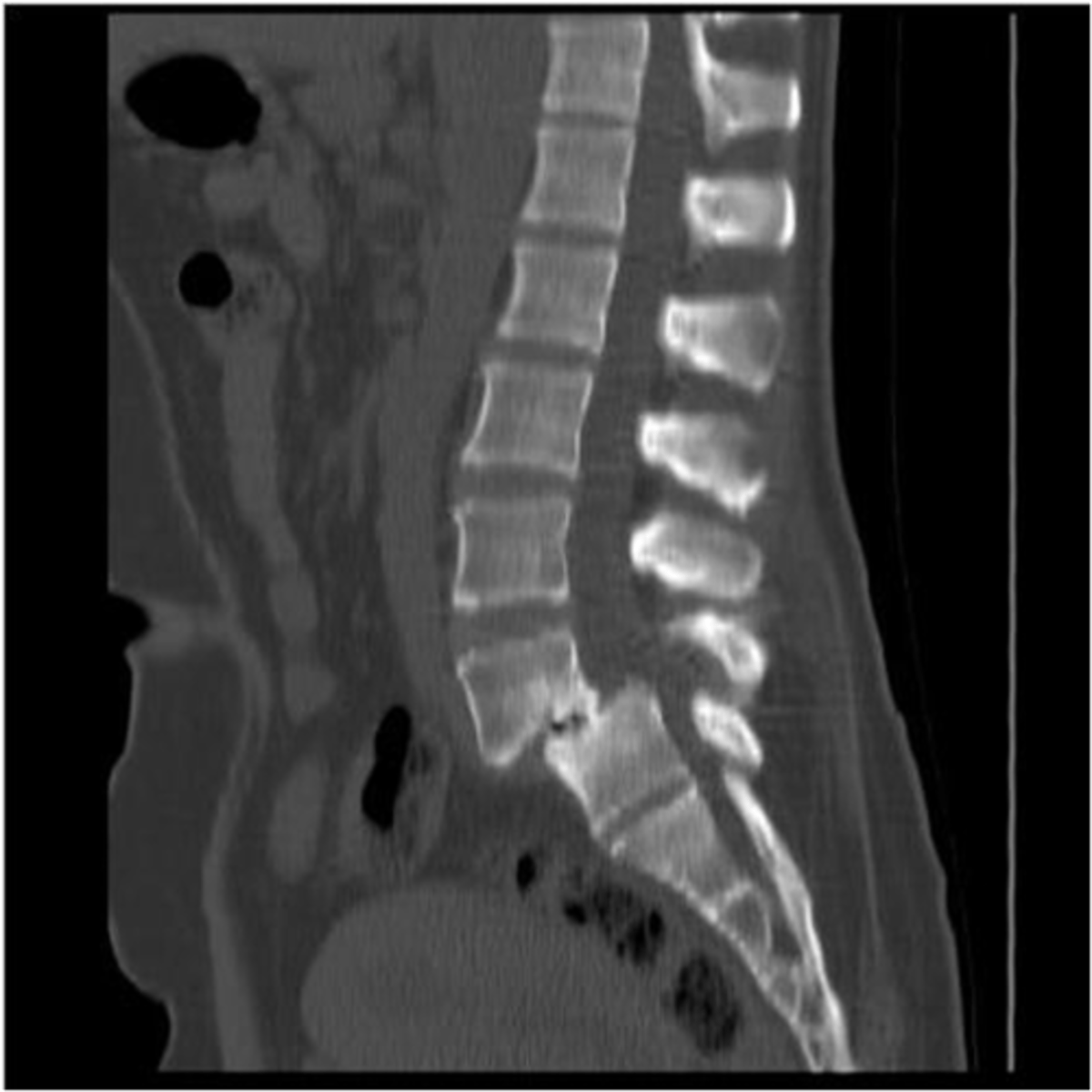
spondylolisthesis s/s can range from none to _______
severe low back pain with radiculopathy
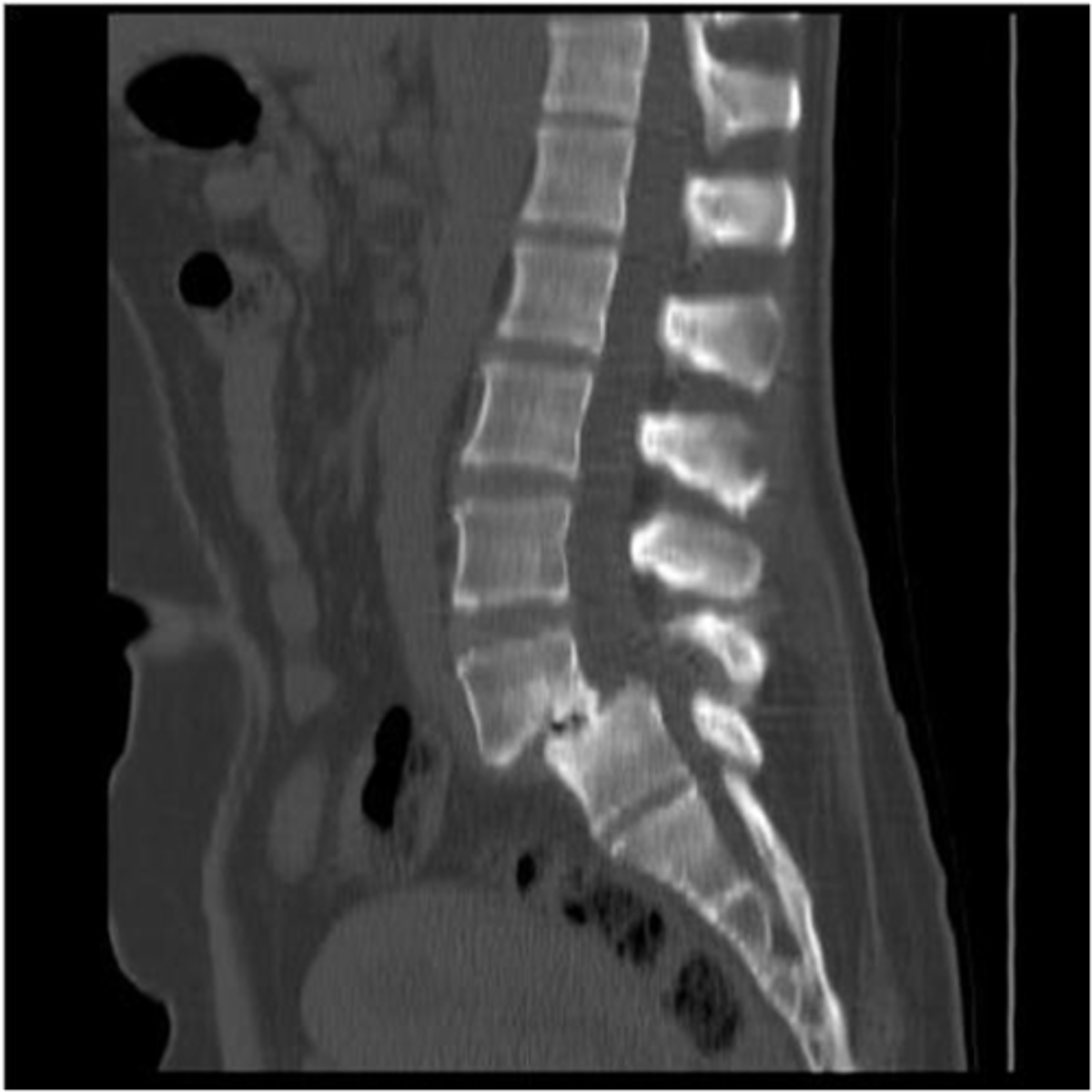
spinal stenosis
Narrowing of the spinal canal that causes pressure on the spinal cord (nerves)
spinal stenosis etiology
osteophytes, disc herniation, tumors, trauma
what are the s/s of spinal stenosis
mild-severe pain, paresthesia, and muscle weakness
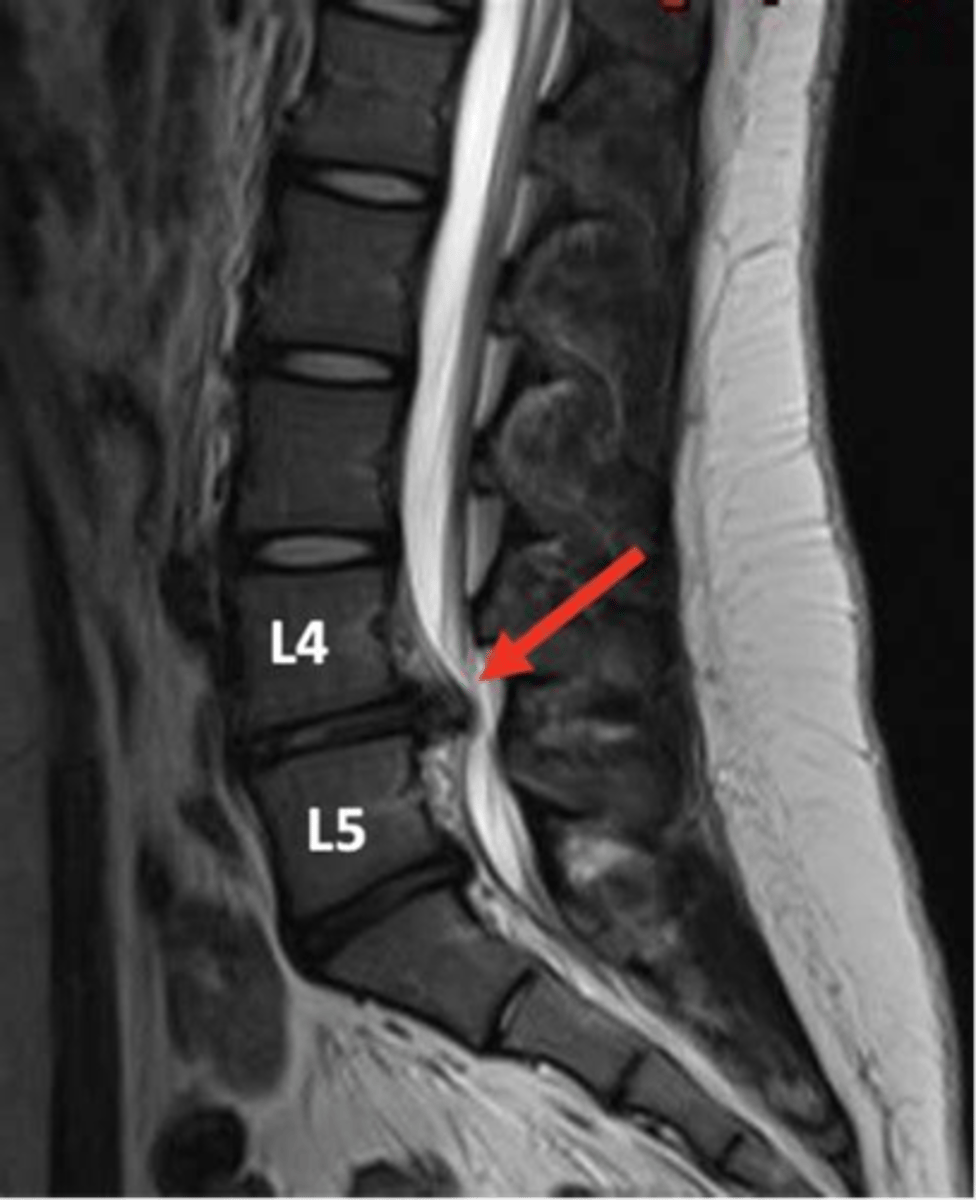
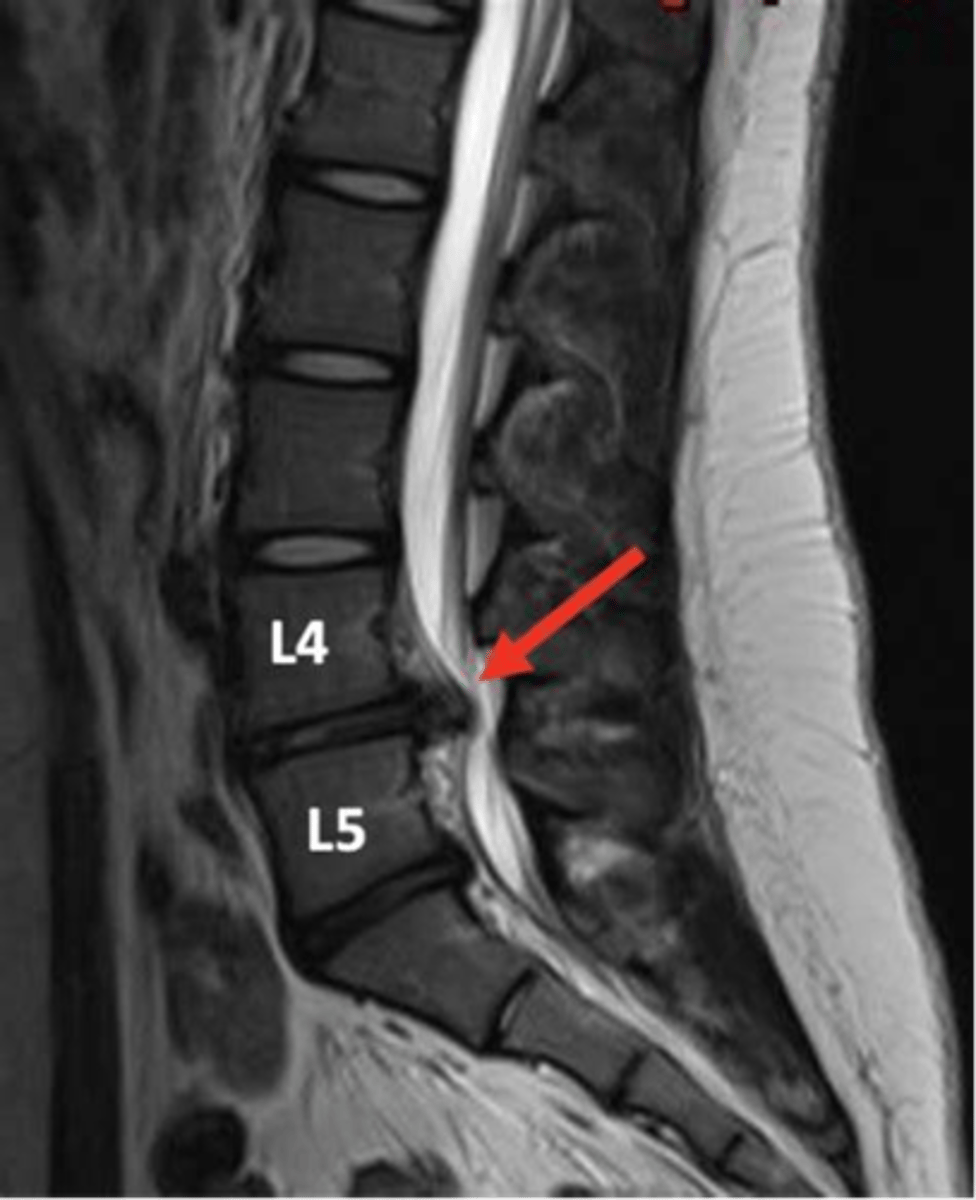
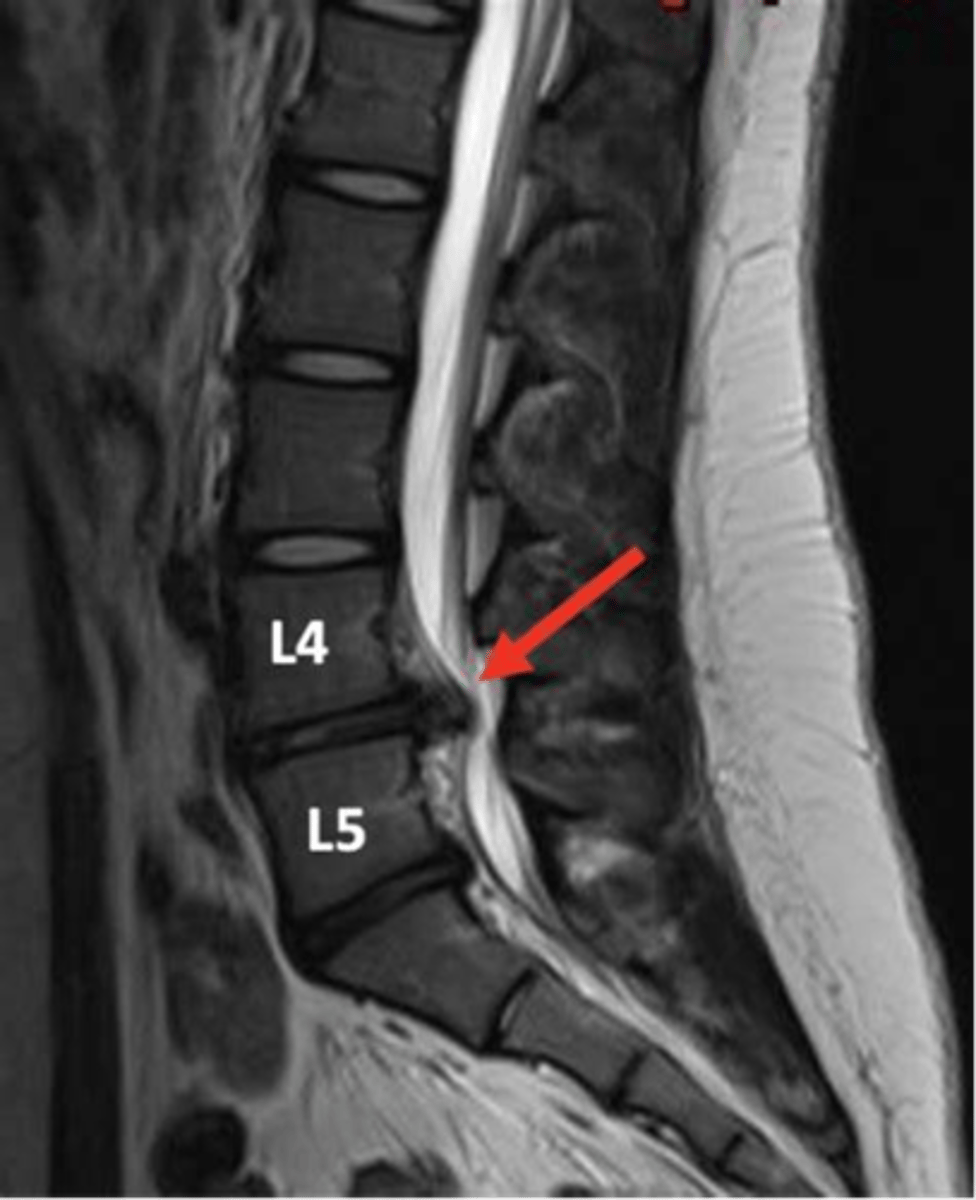
cauda equina syndrome is a form of _____ where all nerves in the lower spine are compressed
spinal stenosis
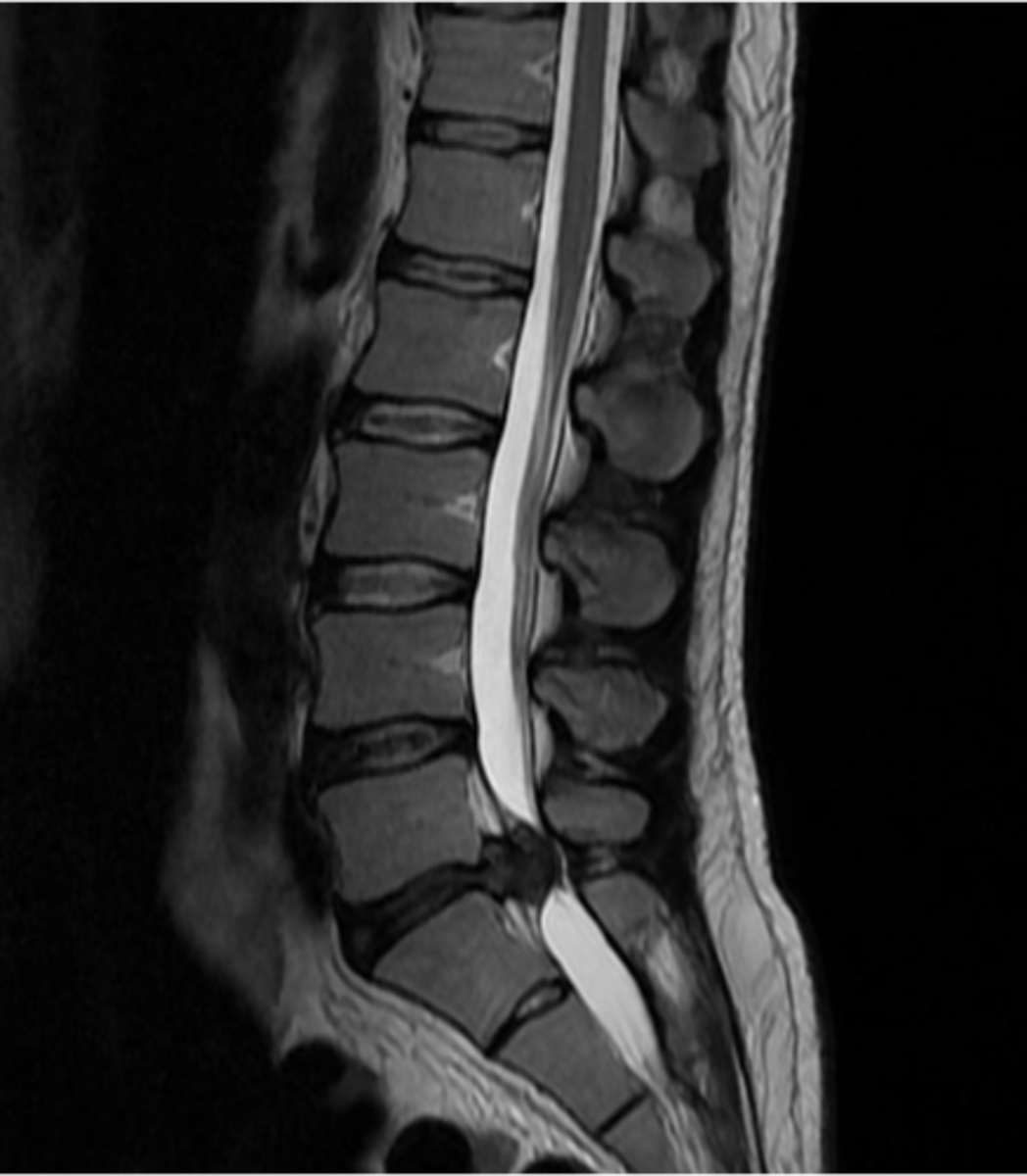
s/s of cauda equina syndrome
low back pain, radiculopathy, lower extremity weakness, reduced, incontinence of bowel/bladder
rank arthritis, cauda equina, spondylolithesis, and spinal stenosis from best to worst
Normal
arthritis/spondylosis
spondylolithesis
spinal stenosis
cauda equina syndrome
hangman's fracture is a fracture of the
bilateral pars interarticularis of C2
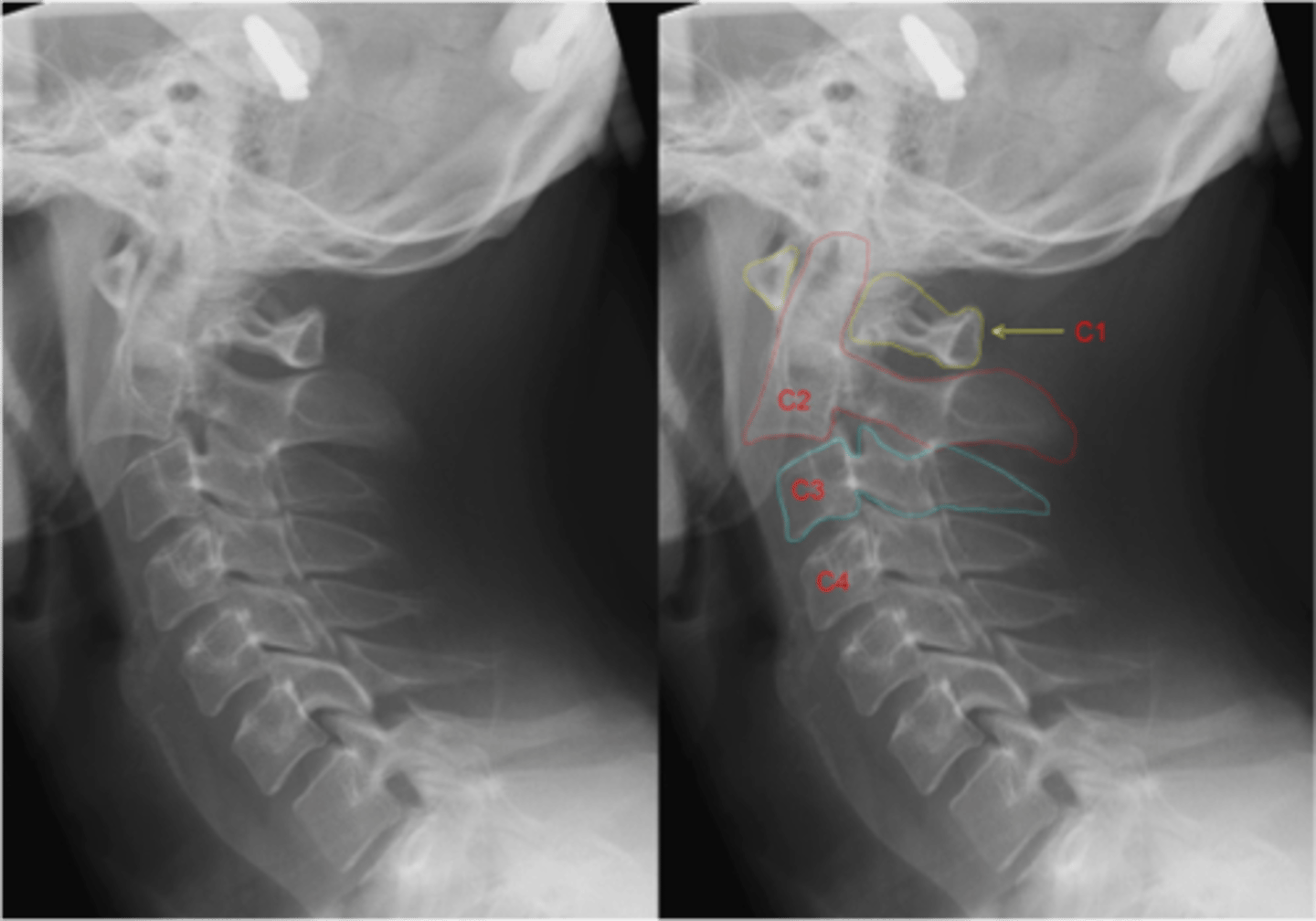
hangman's fracture is traumatic _____ of the atlas/axis
spondylolisthesis of the axis (C2)
what are the most common causes of a hangman's fracture
MVA, diving injuries, sports injuries, face first fall from standing position
Jefferson's fracture is a ___ fracture of the atlas/axis caused by axial loading of the cervical spine
burst fracture of the atlas (C1)
are jefferson's fractures usually accompanied by c-spine injuries?
yes, 1/3 have c2 fracture
Jefferson's fracture also usually causes a blunt ____ injury
cerebrovascular (ICA, CCA, vertebra artery)
chance "seatbelt" fracture
An unstable traumatic flexion-distraction fracture in the area of the thoracolumbar junction
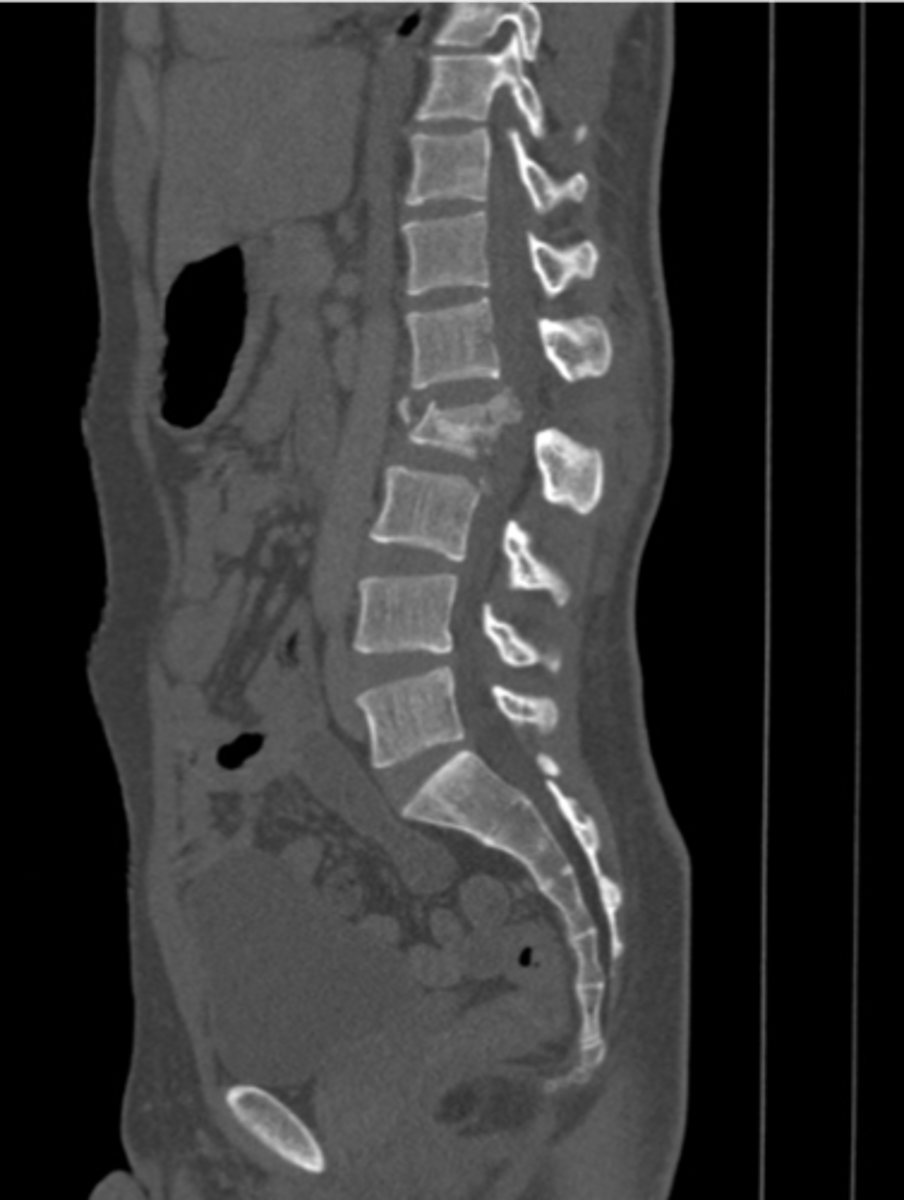
there is a high chance of severe ____ injury with chance fractures
abdominal
odontoid fracture is a common fracture of the ____ dens caused by low-energy falls in geriatric patients and high energy trauma in younger patients
C2 dens
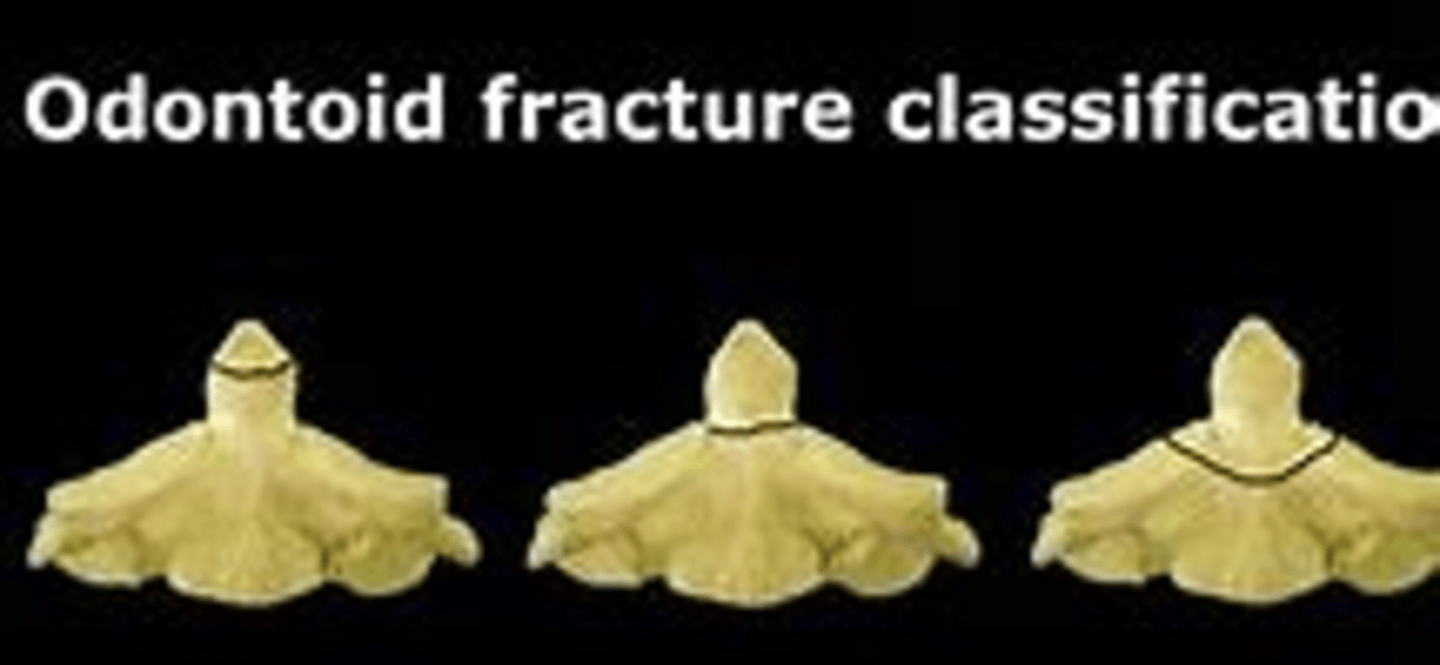
odontoid fractures are typically related to
hyperextension or hyperflexion
what are the 2 m/c primary spinal tumors
multiple myeloma and osteosarcoma
what are the m/c secondary spinal tumors
breast, lungs, prostate
multiple myeloma
Most common form of plasma cell cancer that develops in the bone and metastasizes throughout the body
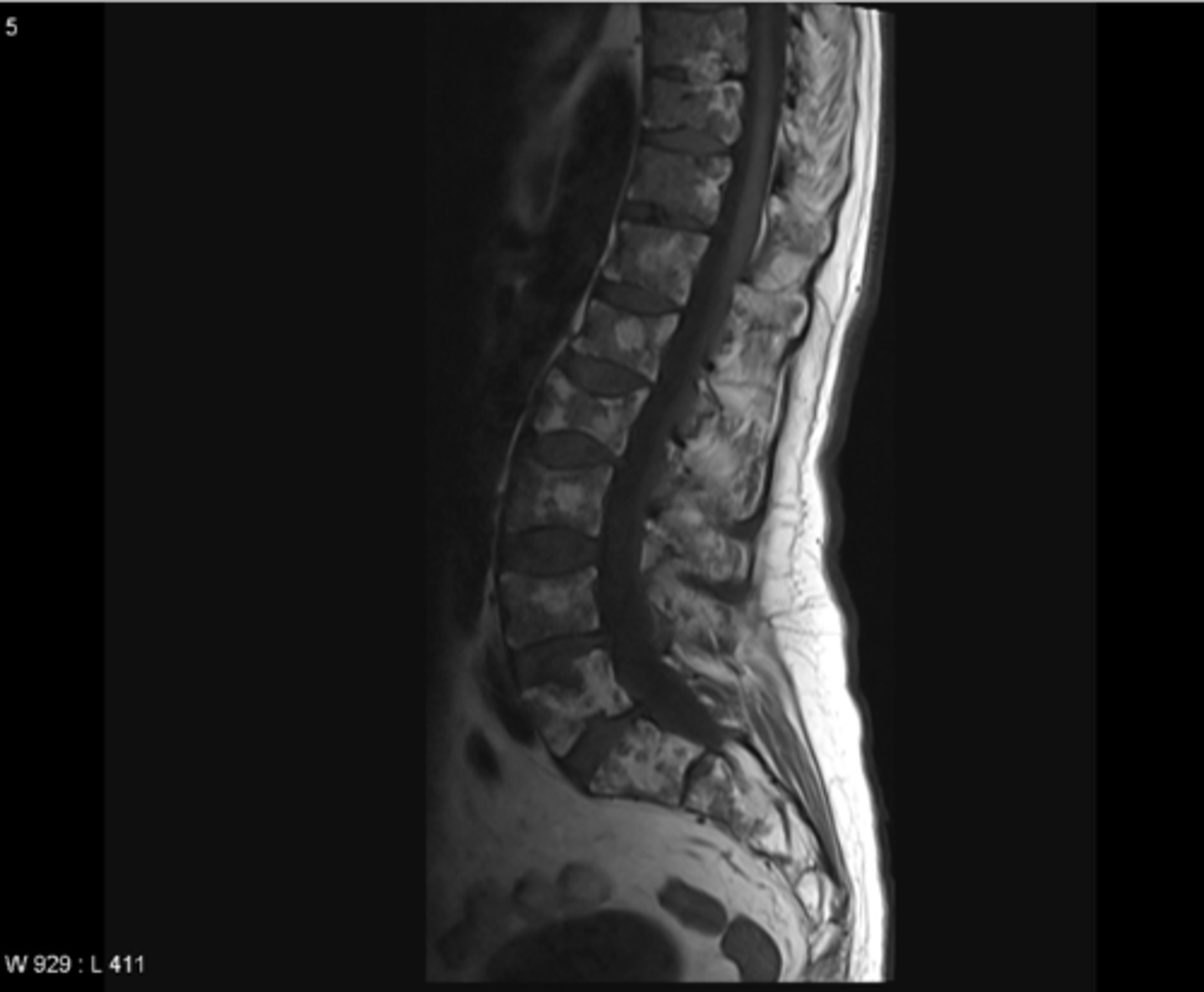
"moth eaten appearance" of bones indicates
multiple myeloma
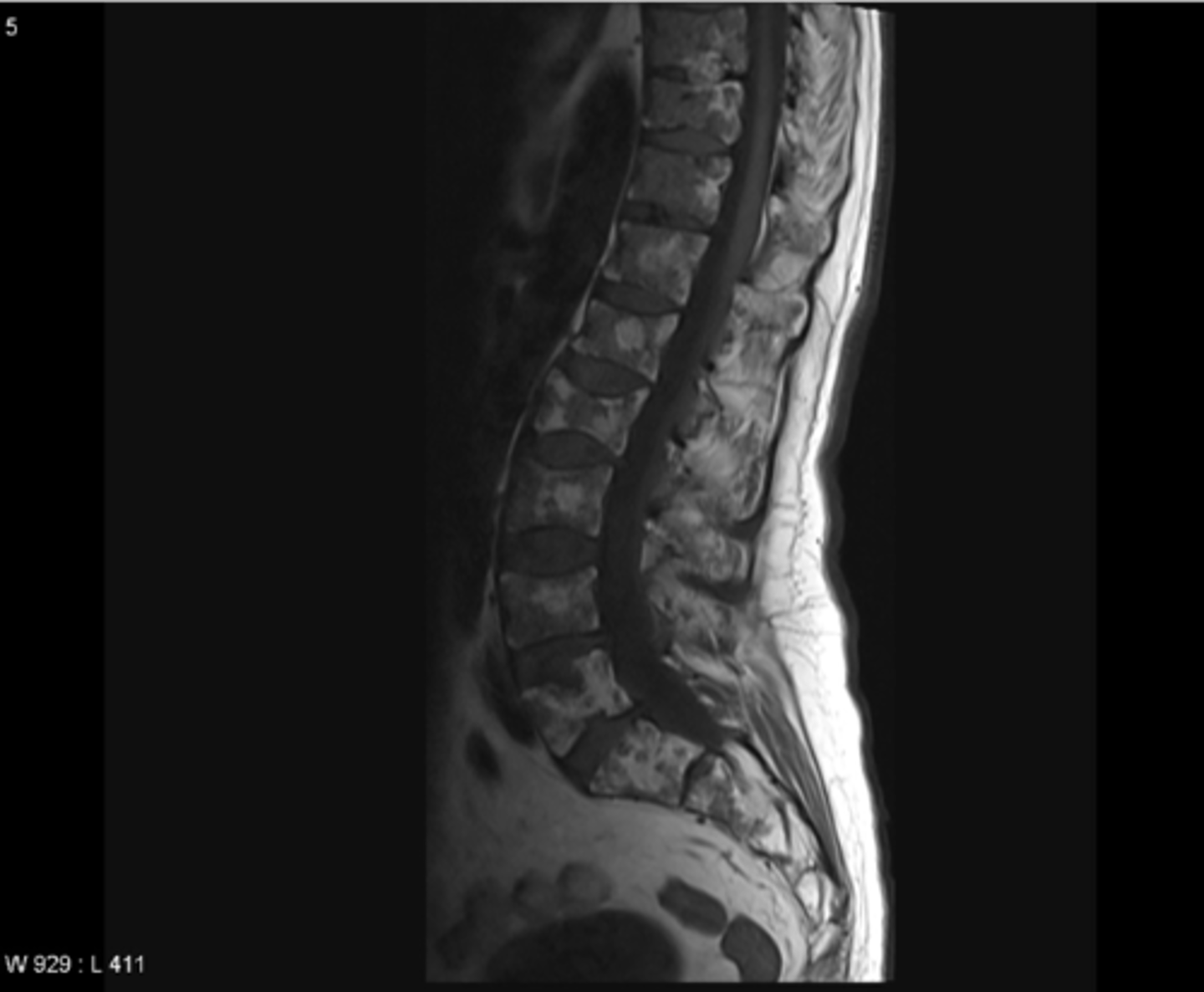
what are the s/s of multiple myeloma
bone pain, weakness, weight loss
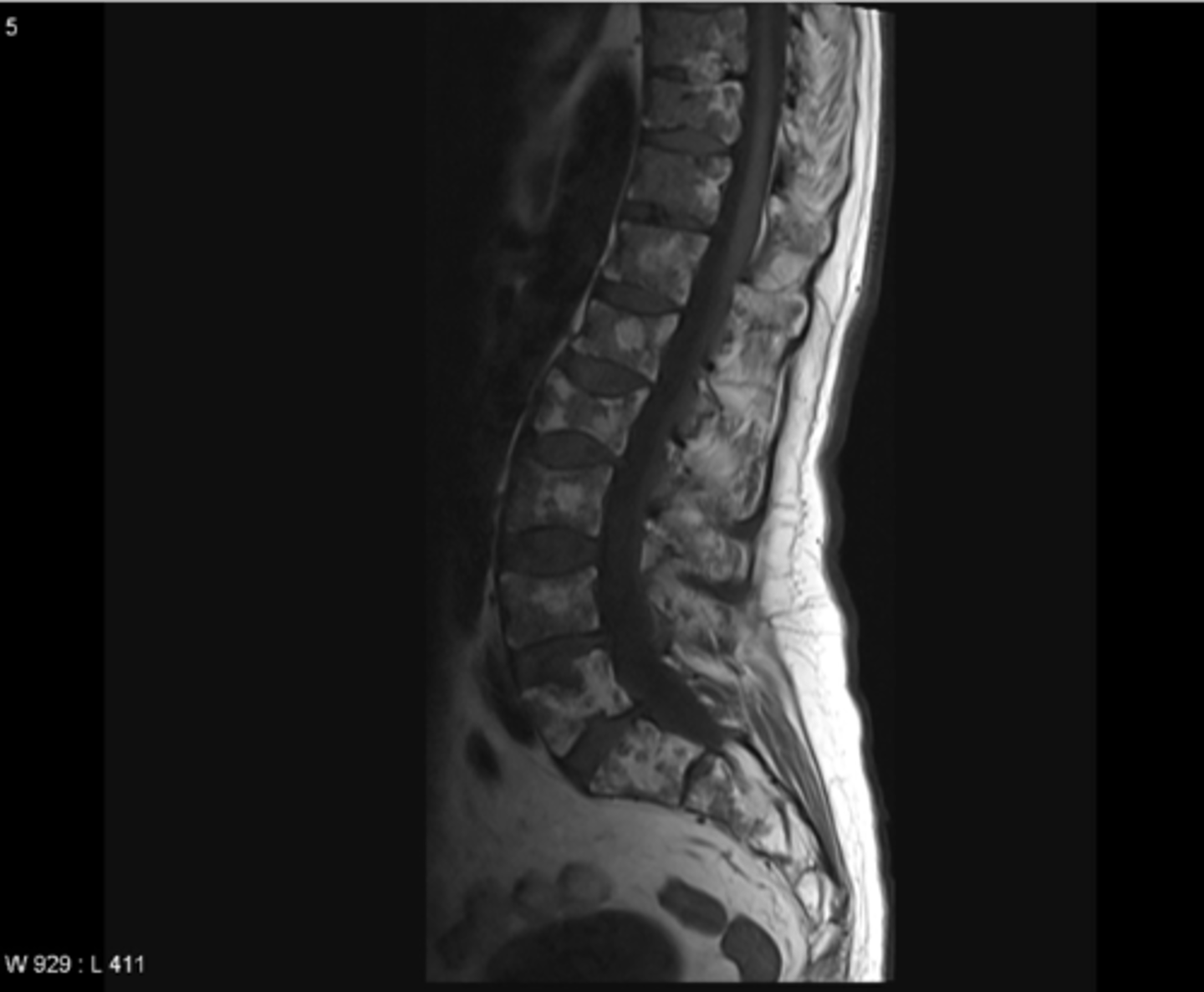
what is the m/c form of bone cancer that begins in the bone
osteosarcoma
what is the gold standard imaging for osteosarcoma
MRI (must confirm w/ bx)
secondary spinal tumors often present with nighttime _____ that wakes the patient up from sleep
neck or back pain