Patho- Module 3: Respiratory (EXAM 2)
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
infectious rhinitis (aka the common cold)
-upper respiratory infection
-highly contagious (caused by the rhino virus)
-the very young, very old, and immunocompromised are at risk
-incubation of 2-3 days (if longer we are highly concerned)
-inspiratory vs expiratory

what are the manifestations of infectious rhinitis?
-sneezing
-nasal congestion/nasal discharge
-sore throat
nonproductive cough
-malaise
-myalgia
-low-grade fever,
-hoarseness, headache, and chills
What is rhinosinusitis?
-upper respiratory infection
-inflammation of the sinus cavities
-causes: viruses, bacteria, and fungi
-exudate collects and blocks sinus cavities
-acute: 4 weeks or chronic: more than 12 weeks with constant pain and leaking
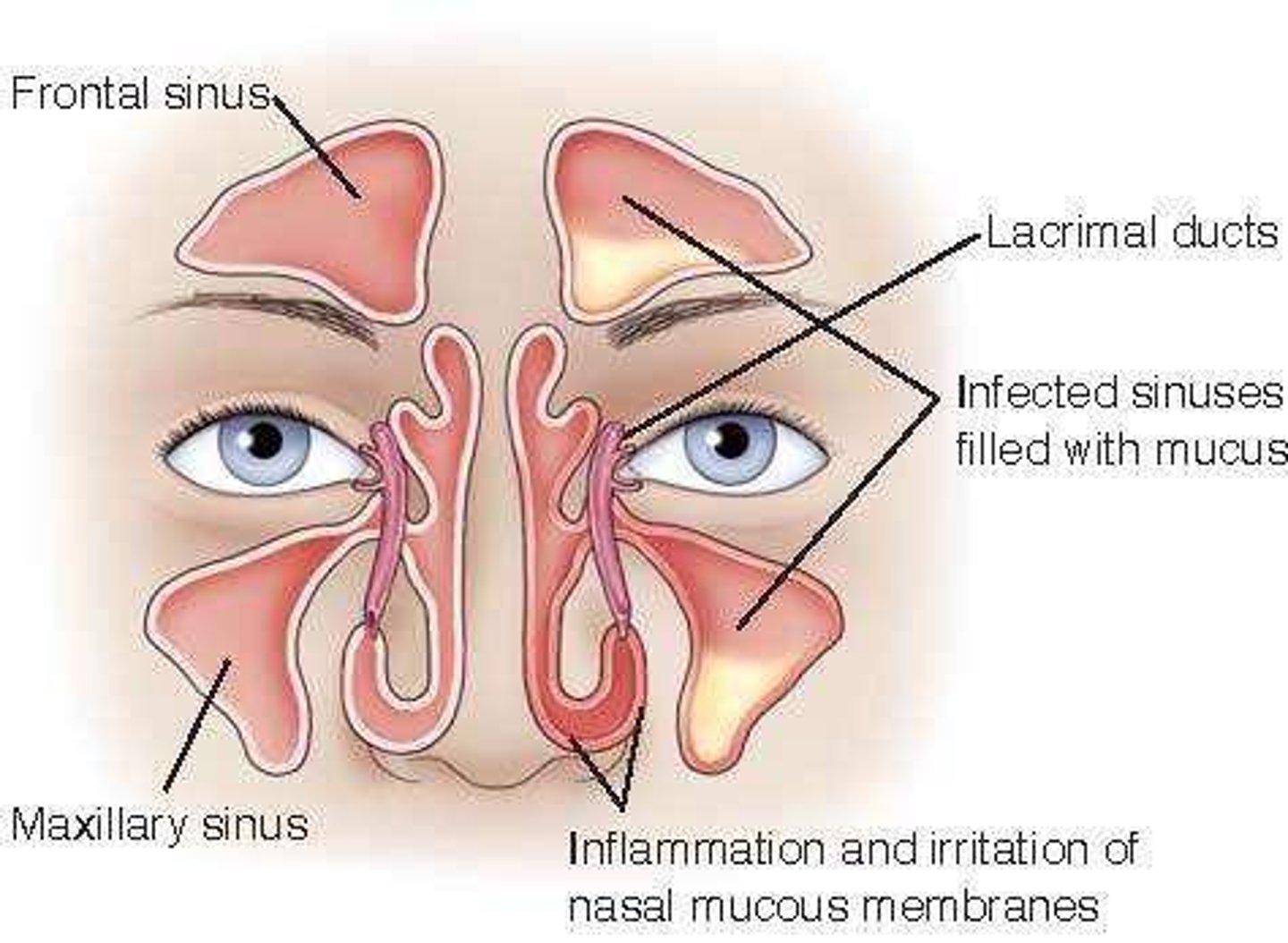
what are the manifestations of rhinosinustitis?
-facial pain
-nasal congestion lots of mucous
-fever
-sore throat
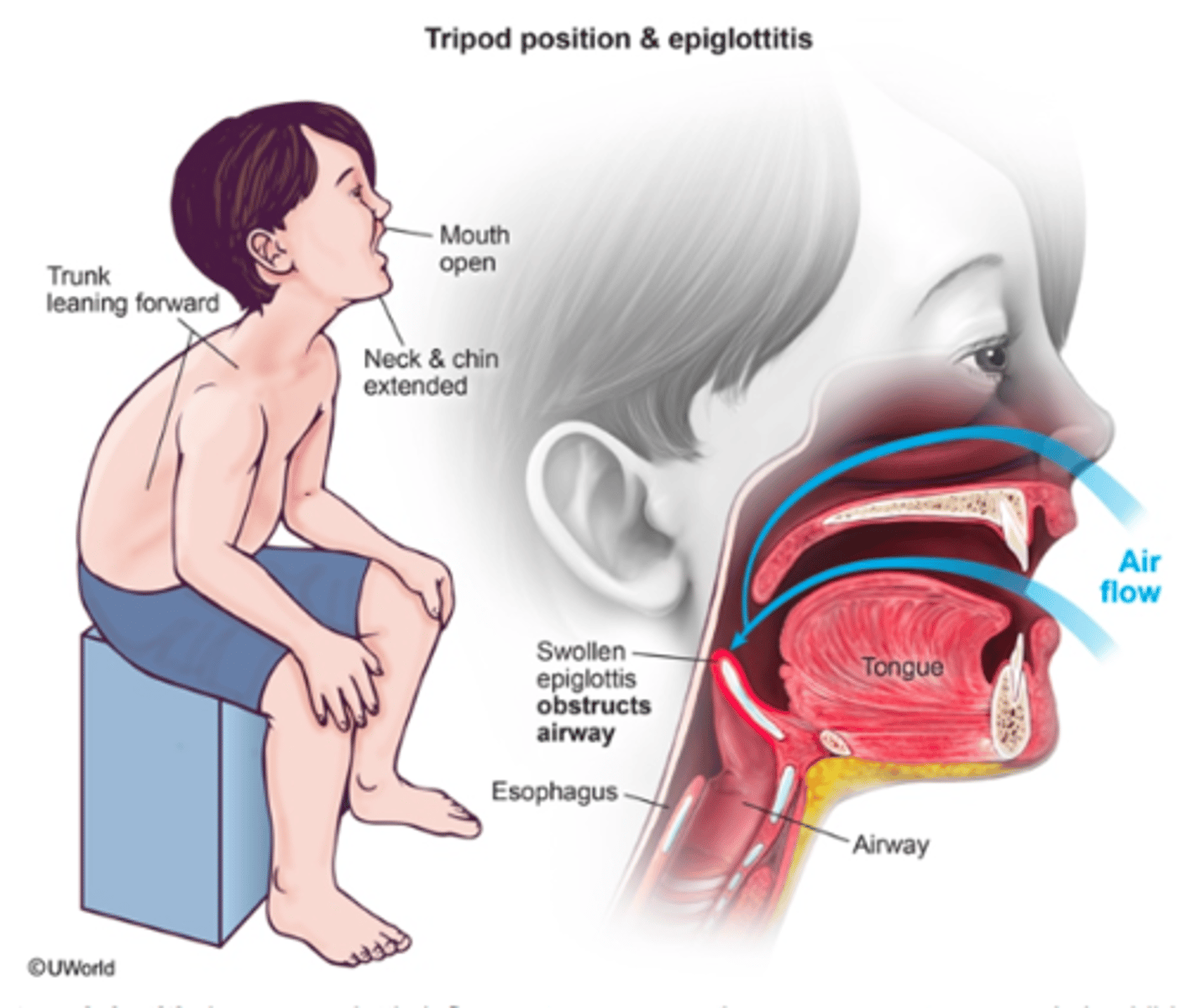
what is epiglottitis?
-upper respiratory infection
-it is an inflammation of the epiglottis (the lid that covers our tracheal opening aka we need it to breathe)
-it is a medical emergency!!
-these patients are extremely sick and low energy
what are the causes of epiglottitis?
-haemophilus influenzae type B
(Hib) (common infection in children)
-throat trauma
what are the manifestations of epiglottitis?
-drooling (cannot tolerate oral secretions aka cant swallow)
-odd sitting forward position (trunk leaning forward)
-inspiratory stridor
-respiratory distress
-central cyanosis
-pallor
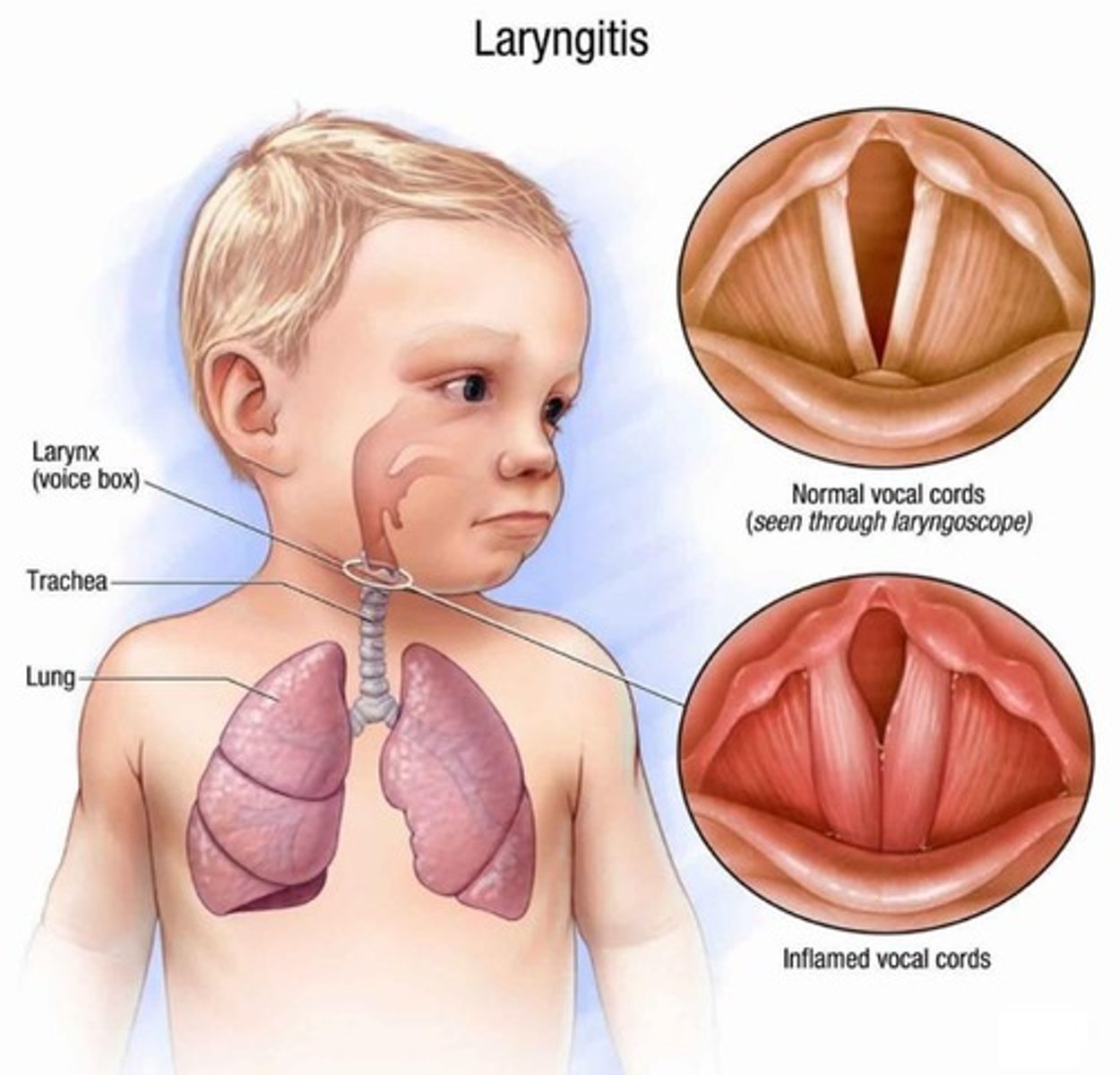
What is laryngitis?
-upper respiratory infection
-inflammation of the larynx
-self limiting (meaning that it gets better on its own)
-worst case scenario is that the larynx swells so much that breathing stops
what are the causes of laryngitis?
-infection
-increased upper respiratory exudate
-overuse
what are the manifestations of laryngitis?
-hoarseness
-weak voice or voice loss
-tickling sensation
-raw feeling in the throat (no mucous)
-sore throat
-dry cough and difficulty breathing
what is laryngotracheobronchitis? (aka croup)
-common viral infection in children usually parainfluenza viruses and adenoviruses
-larynx and surrounding area swell, leading to airway narrowing, obstruction, and respiratory failure

what are the manifestations of laryngotracheobronchitis? (aka croup)
-seal like barking cough
-congestion
-hoarseness
-inspiratory stridor
-dyspnea
-anxiety
-central cyanosis
what is influenza? *(aka the flu)
-viral infection that may affect the upper and lower respiratory tract
-a highly adaptive and intelligent virus
-incubation time of 1-4 days
-children, elderly, and immunocompromised are at risk!
what are the different types of influenza?
type a: most severe and most common in the united states
type b: less severe
type c: usually causes small outbreaks (seen more in animals)
what are the manifestations of influenza?
-fever
-headache
-chills
-dry cough
-body aches
-nasal congestion
-sore throat
-sweating
-malaise (you feel too sick to do anything else)
how can we prevent influenza?
-hand washing
-isolation and avoiding crowds
-annual vaccination
what is acute bronchitis?
-lower respiratory infection
-inflammation of the tracheobronchial tree or large bronchi
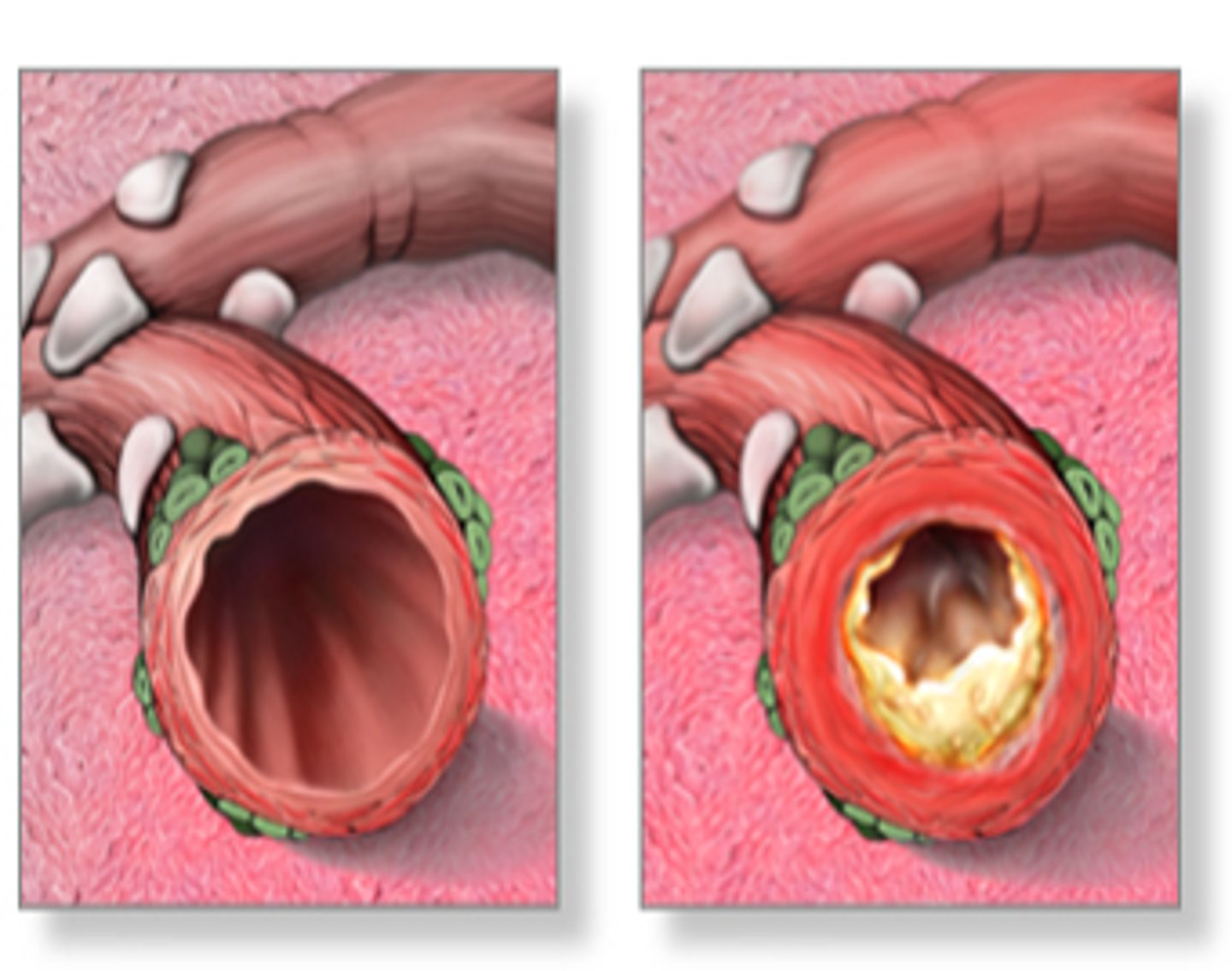
what causes acute bronchitis?
-viruses
-bacteria
-irritant inhalation
-allergic reactions
what are the manifestations of acute bronchitis?
-productive and nonproductive cough
-dyspnea
-wheezing
-low grade fever
-pharyngitis
-malaise
-chest discomfort!
how do we diagnose acute bronchitis?
-history
-physical examination
-X-ray
what is bronchiolitis?
-lower respiratory infection (can go from upper to lower)
-common acute inflammation of the bronchioles, usually respiratory syncytial virus
-more frequent in children younger than 1 year and during the winter months
-can lead to atelectasis (partial or complete collapse of lung/lobe) AND respiratory failure
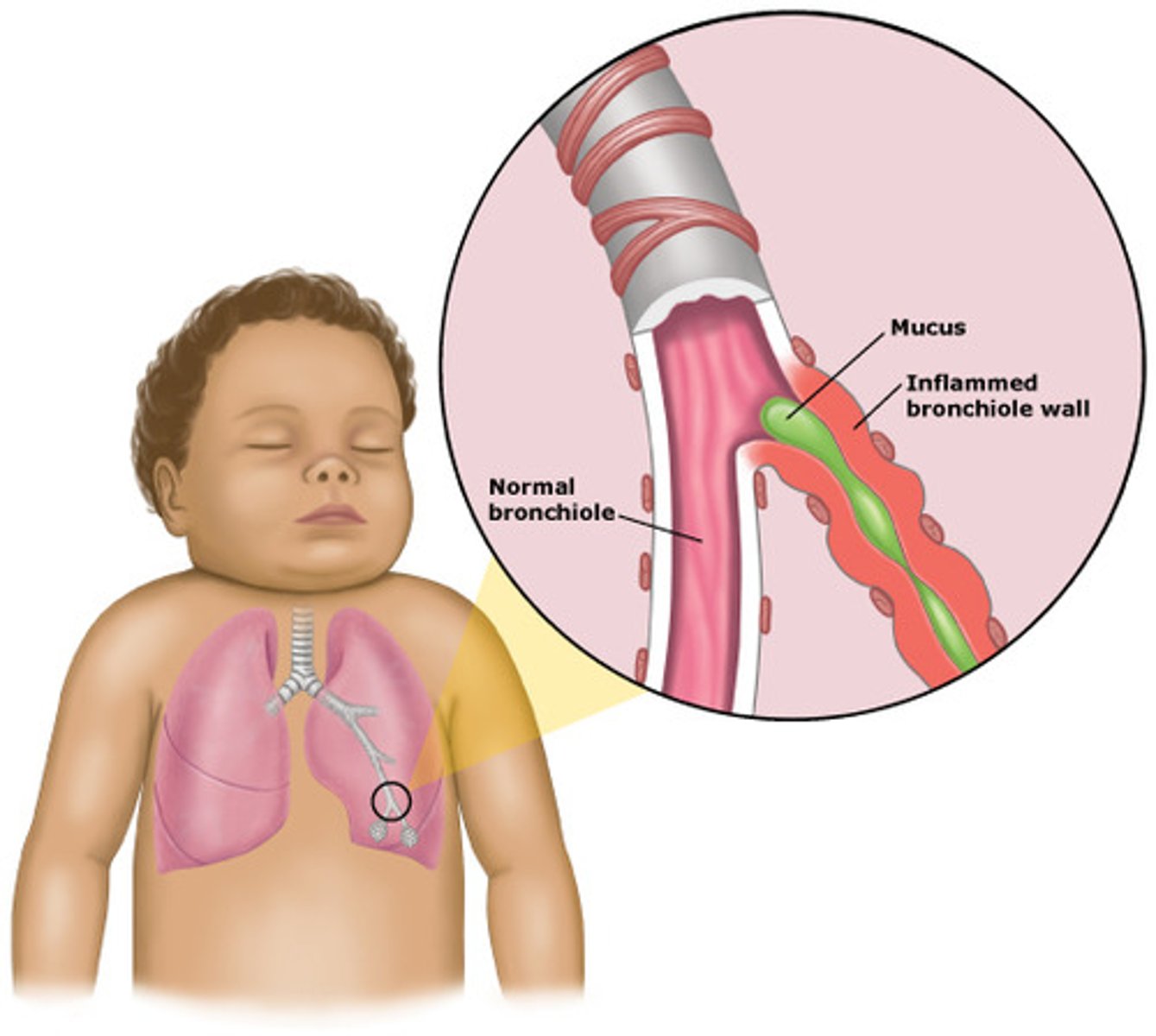
what are the manifestations of bronchiolitis?
-chest retractions!!
-nasal drainage
-nasal congestion
-cough
-wheezing
-rapid and shallow breathing
-dyspnea
-tachycardia
-malaise
what is pneumonia?
-inflammation of the lungs and produces EXCESS fluid and causes an infection
-damage to the bronchial mucous membranes and alveolocapillary membranes
-infectious debris and exudate
-some microbes will release toxins from cell walls which will further lung damage
-top ten leading causes of death in the US
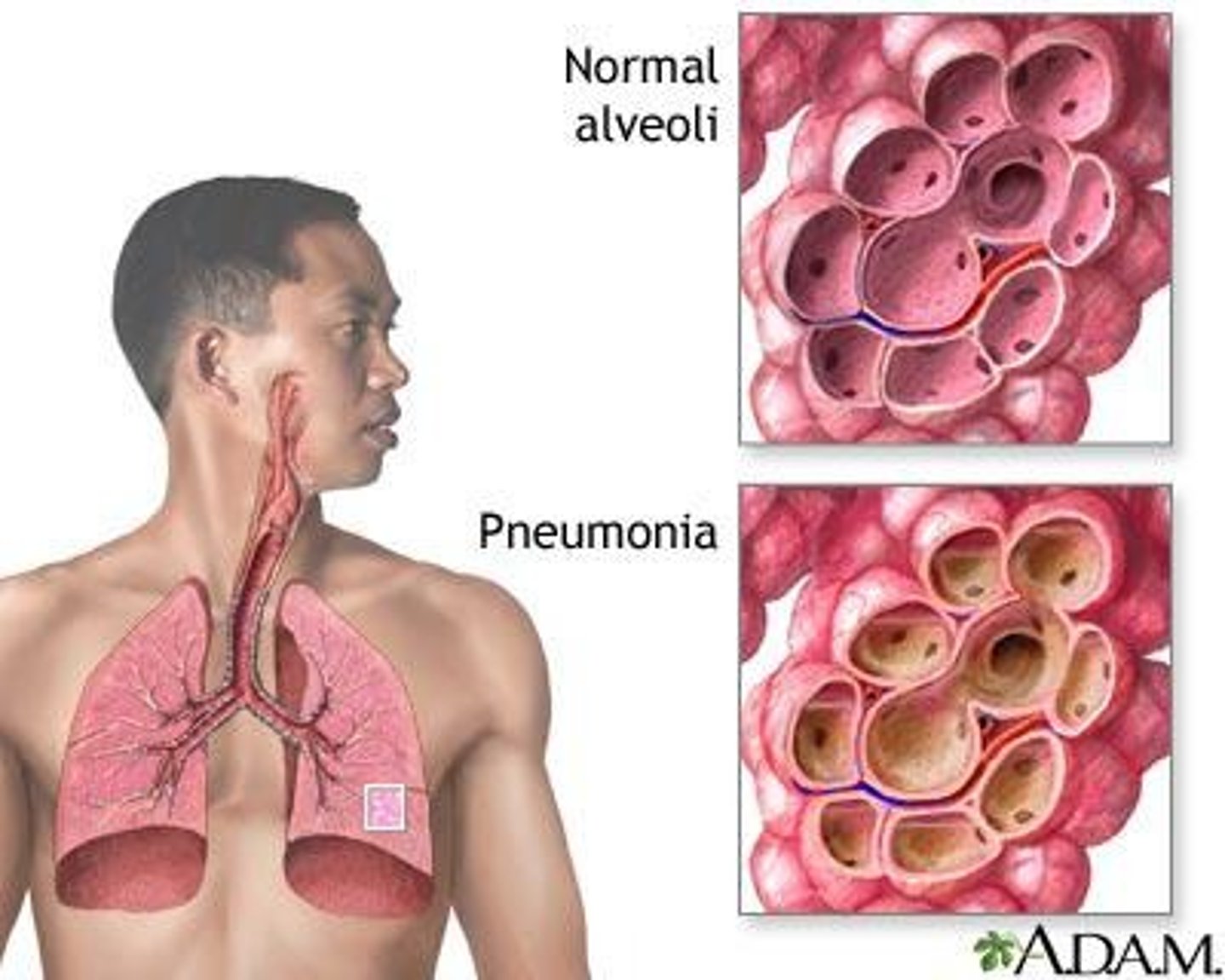
what is the most common route for lower tract infections and the most common cause for pneumonia?*
aspiration of oropharyngeal secretions!
what is primary pneumonia
when the agent is inhaled and causes pneumonia
what is secondary pnemonia?
-a complication from another disease
what populations are more susceptible to and the risks of pneumonia?
-children
-older people
-immunocompromised patients
what are some ways to acquire pneumonia?
-through inhalation of microorganisms that are released in the air (infected individual coughs, sneezes, talks)
-contaminated respiratory therapy equipment such as endotracheal tubes
what causes pneumonia?
-pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae) is the most common and lethal cause of outpatient and inpatient pneumonias
-infectious agents
-pulmonary secretion stasis
what are the manifestations of pneumonia?
-productive cough (sometimes nonproductive cough)
-fatigue
-crackles or rales in the lower basis
-tachypnea
-dyspnea
-fever
-chills
-pleuritic pain
-mental status change especially in the elderly
what is the most common cause of CAP (community acquired pneumonia)?
-influenza
how do we prevent pneumonia?
-turn, cough, deep breath (TCDB!)
-hand washing
-vaccinations
-smoking cessation
what is tuberculosis?
-infectious disease caused by bacillus mycobacterium tuberculosis
-airborne! only need one single micro droplet to contract it
-occurs mainly in lungs but can spread to other organs
what is latent tuberculosis?
-someone who is infected but do not have an active infection
-occurs during reactivation of dormant bacilli
*ONLY people with active tb can spread the infection to others
what are red flags for tuberculosis?
-hemoptysis
-night sweats
-fever
-chills
-fatigue
-unexplained weight loss
-anorexia
what are ways to prevent tuberculosis?
-vaccination
-respiratory precautions
-adequate ventilation
-appropriate isolation
what is asthma?
-REVERSIBLE but not curable!
-acute airway inflammation with broncho constriction, spasms, edema, and mucous production
-often the result to a strong immune reaction to an antigen but we do not really know
-chronic with periods of symptoms
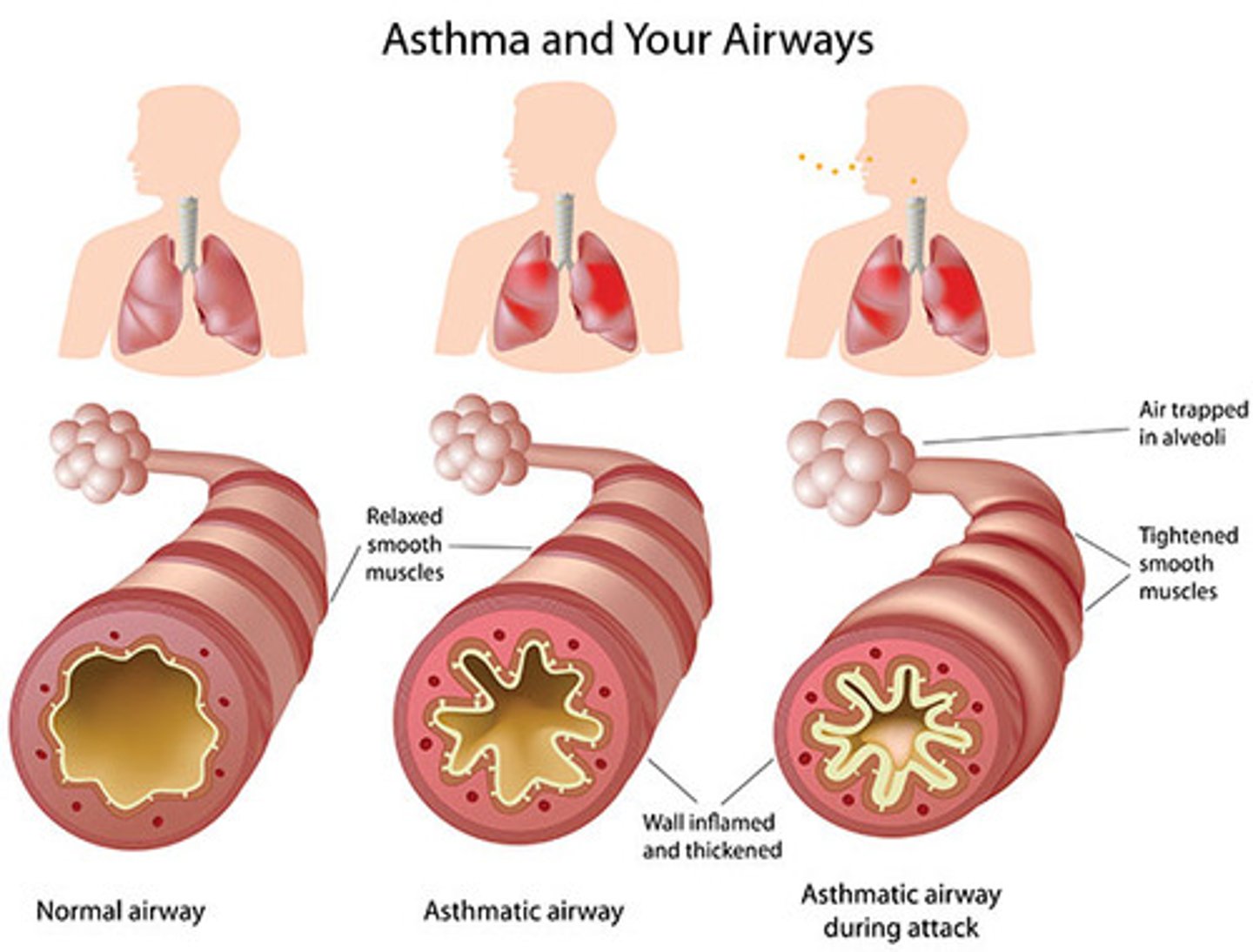
which asthma is more common in children?
-intrinsic asthma
-usually triggered by allergens such as food, pollen, dust, and medications
what is asthma is more common in adulthood?
-extrinsic asthma
-more common in women
-non allergic reaction
-can be triggered by upper respiratory infections, air pollution, emotional stress, smoking, exercise, and cold exposure
what is nocturnal asthma?
-usually occurs between 3:00 and 7:00 a.m.
-may be related to circadian rhythms - at night, cortisol and epinephrine levels decrease, while histamine levels increase, leading to bronchoconstriction
what is exercise-induced asthma?
a medical condition characterized by shortness of breath induced by sustained aerobic exercise
what is occupational asthma?
-like other types of asthma, it is characterized by airway inflammation, reversible airways obstruction, and bronchospasm, but it is caused by something in the workplace environment
what is drug-induced asthma?
-frequently caused by aspirin
-can be fatal
-reactions can be delayed up to 12 hours after drug ingestion
what is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
-COPD
-an umbrella term used to describe a group of respiratory disorders
-the two disorders are chronic bronchitis and emphysema!
-characterized by irreversible, progressive and causes tissue degeneration
-airway obstruction
-AKA structural changes in the lung
-often asymptomatic and masked by smoking
where is COPD found?
-lungs
-pulmonary circulation
*severe hypoxia and hypercapnia can lead to respiratory failure
what is the single most contributing factor to COPD?
-long term smoking!
what is cor pulmonale?
-right sided heart failure caused by high blood pressure
-caused by respiratory disorders especially COPD
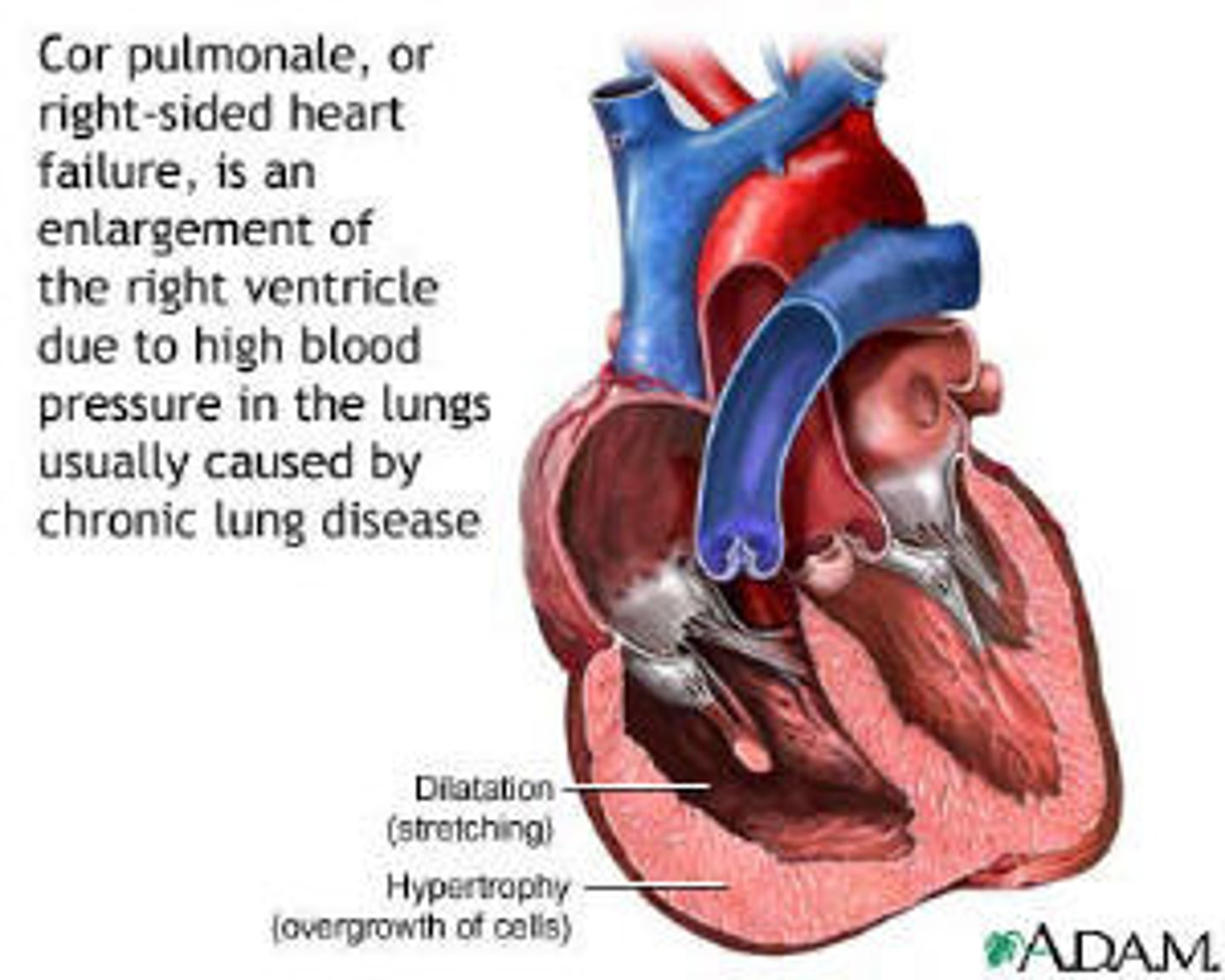
what is chronic bronchitis?
-inflammation of the bronchi, a productive cough, and excessive mucous production
-airway obstruction from excessive mucous and inflammation!
-not caused by an infection but by the nature of what is happening in their airways these patients will develop many infections
*think blue boater!
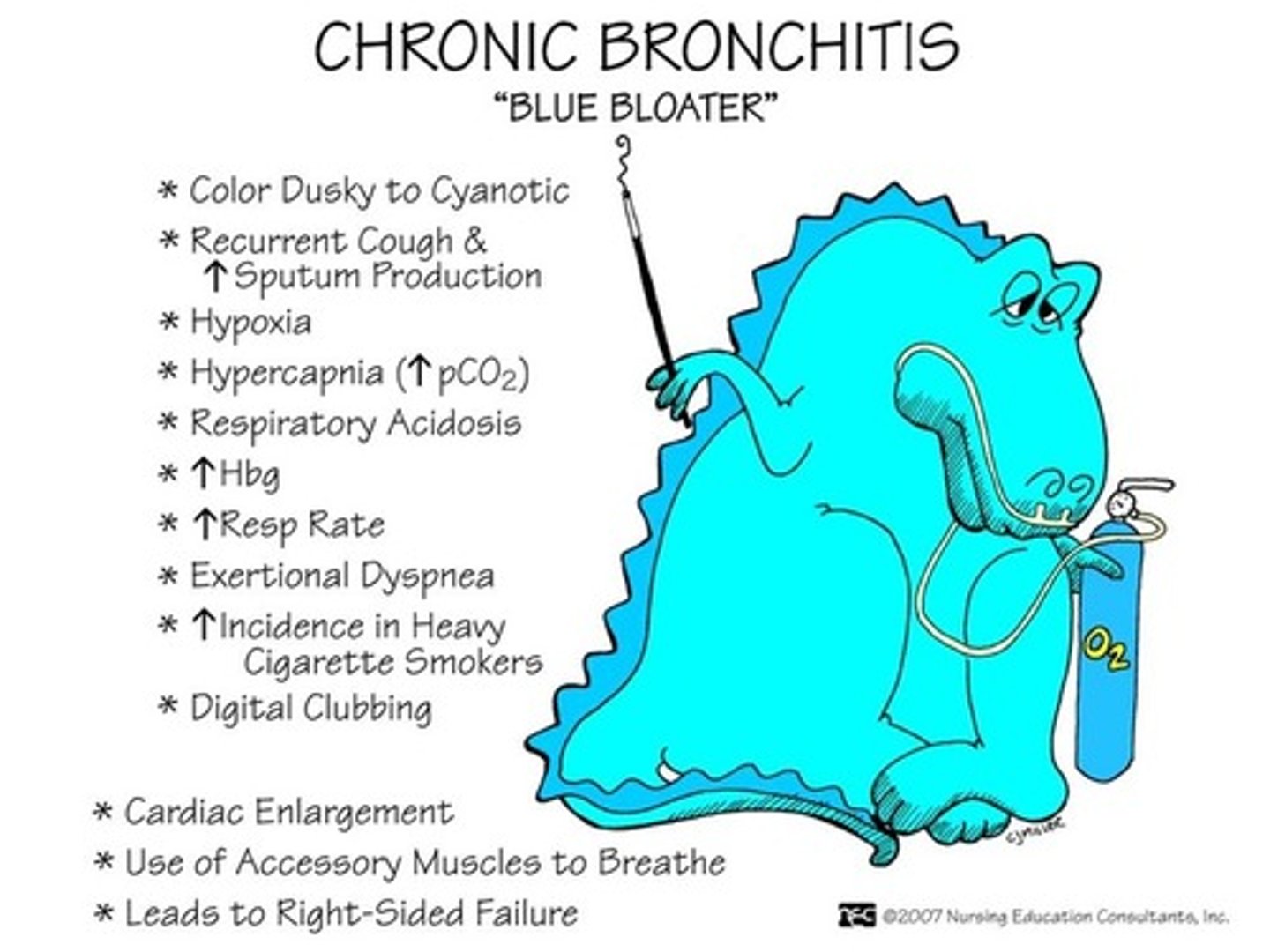
what are the complications of chronic bronchitis?
-frequent respiratory infections and
-respiratory failure
what are the manifestations of chronic bronchitis?
-dyspnea at rest
-hypoventilation
-hypoxemia
-cyanosis (clubbing fingers)!
-peripheral edema
-weight gain
-rhonchi and wheezing
-chest pain (more like wall pain)
-fever
what is emphysema?
-destruction of the alveolar walls leads to large, permanently inflated alveoli
-loss of elastic recoil and hyperinflation of the alveoli which leads to air trapping
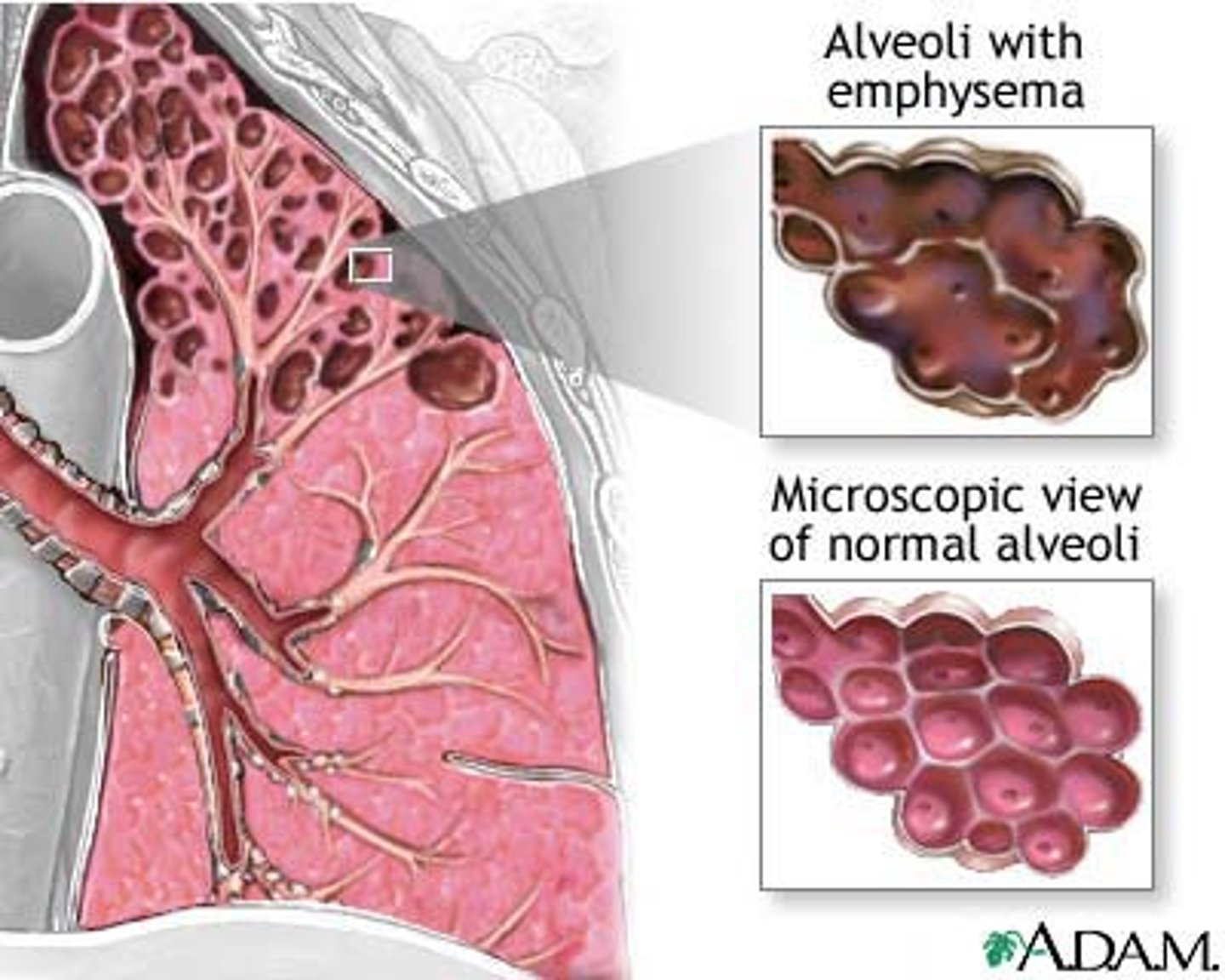
what causes emphysema?
-genetic predisposition
-smoking!
what are the manifestations of emphysema?
-dyspnea upon exertion (when the person is physically active)
-think pink puffer!
-barrel chest
-increased anterior-posterior
-thoracic diameter (from 1:2 to 1:1) AKA barrel chest!
-activity intolerance
-anorexia
-malaise
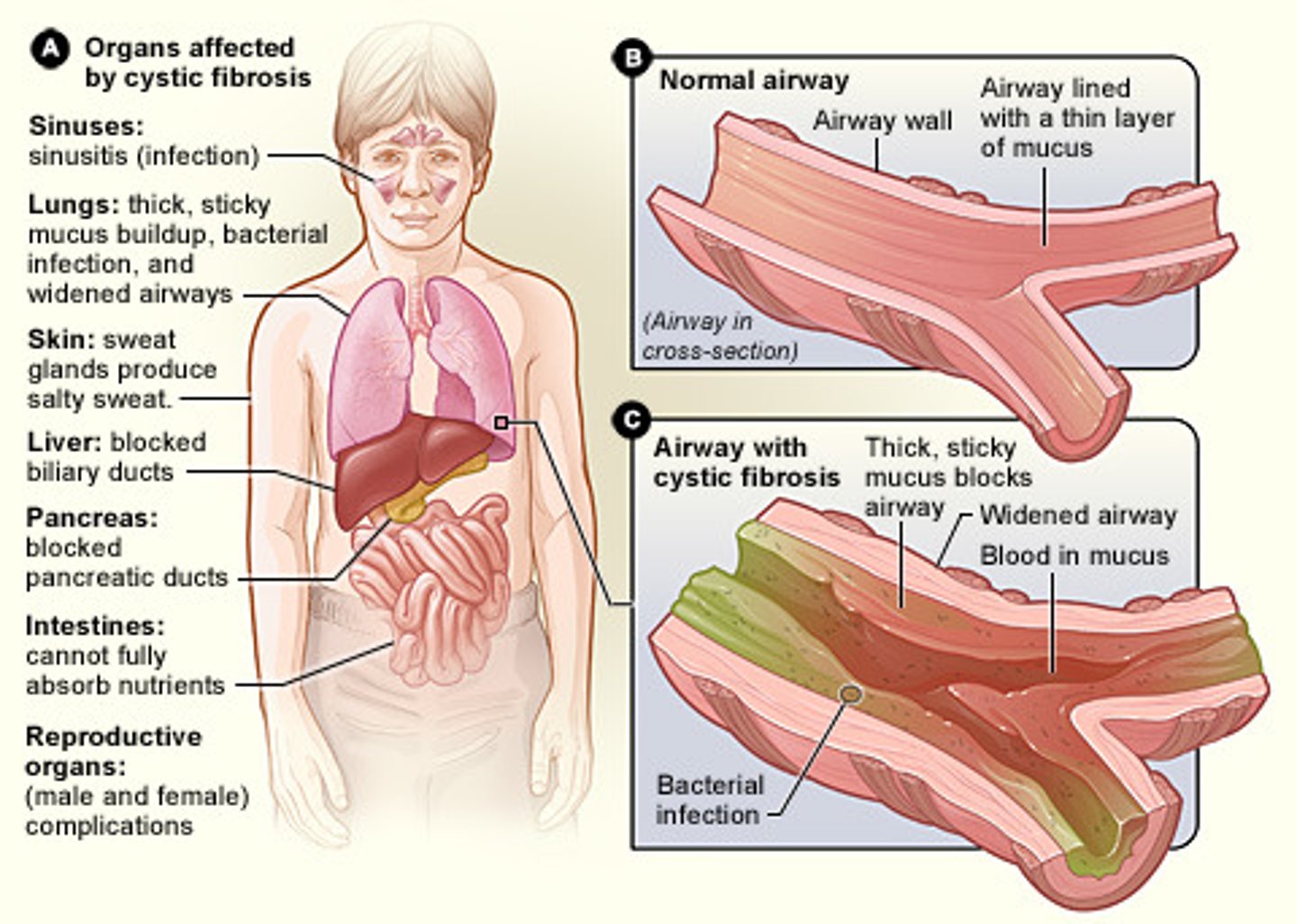
what is cystic fibrosis? (3 questions)
-an inherited/genetic life threatening of the mucous and sweat glands
-primarily affects the lungs and the pancreas but truly any duct that produces some kind of liquid
-affects cells that produce mucous, sweat, saliva, and digestive secretions. the secretions will become thick and sticky!
-a terminal disease! this will kill you!
-this is an autosomal recessive mutation that leads to an abnormality in the protein involved in chloride cellular transport

what are manifestations of cystic fibrosis?
-salty skin
-meconium ileus
-steatorrhea (greasy stool)
-delayed growth and development
-cor pulmonal
-chronic cough
-hypoxia (eventually leading to respiratory failure leading to death)
-audible rhonci
what is lung cancer?
-may occur as a primary or secondary tumor
-second most common cancer
-the risk of developing lung cancer is directly related to the amount someone has smoked a day and how many packs per year
what is small cell carcinoma lung cancer?
-almost exclusively in smokers
-extremely fast onset and progression
-deadly
-metastasizes very fast!
-less frequent
what is non-small cell carcinoma lung cancer?
-most common type of malignant lung cancer
-very aggressive
-has several sub-groups
what are the complications of lung cancer?
-airway obstruction
-lung tissue inflammation
-fluid accumulation
-paraneoplastic syndrome
what are the manifestations of lung cancer?
-cough
-hemoptysis
-persistent cough or change in cough
-shortness of breath
-weight loss/anemia
-frequent respiratory infections
-dyspnea
what is pleural effusion?
-excess fluid (blood or pus) in the pleural cavity which can impair breathing
-may also see pleurisy which is inflammation of the pleural membranes
-this can compress the lungs!
-caused by an alteration in ventilation
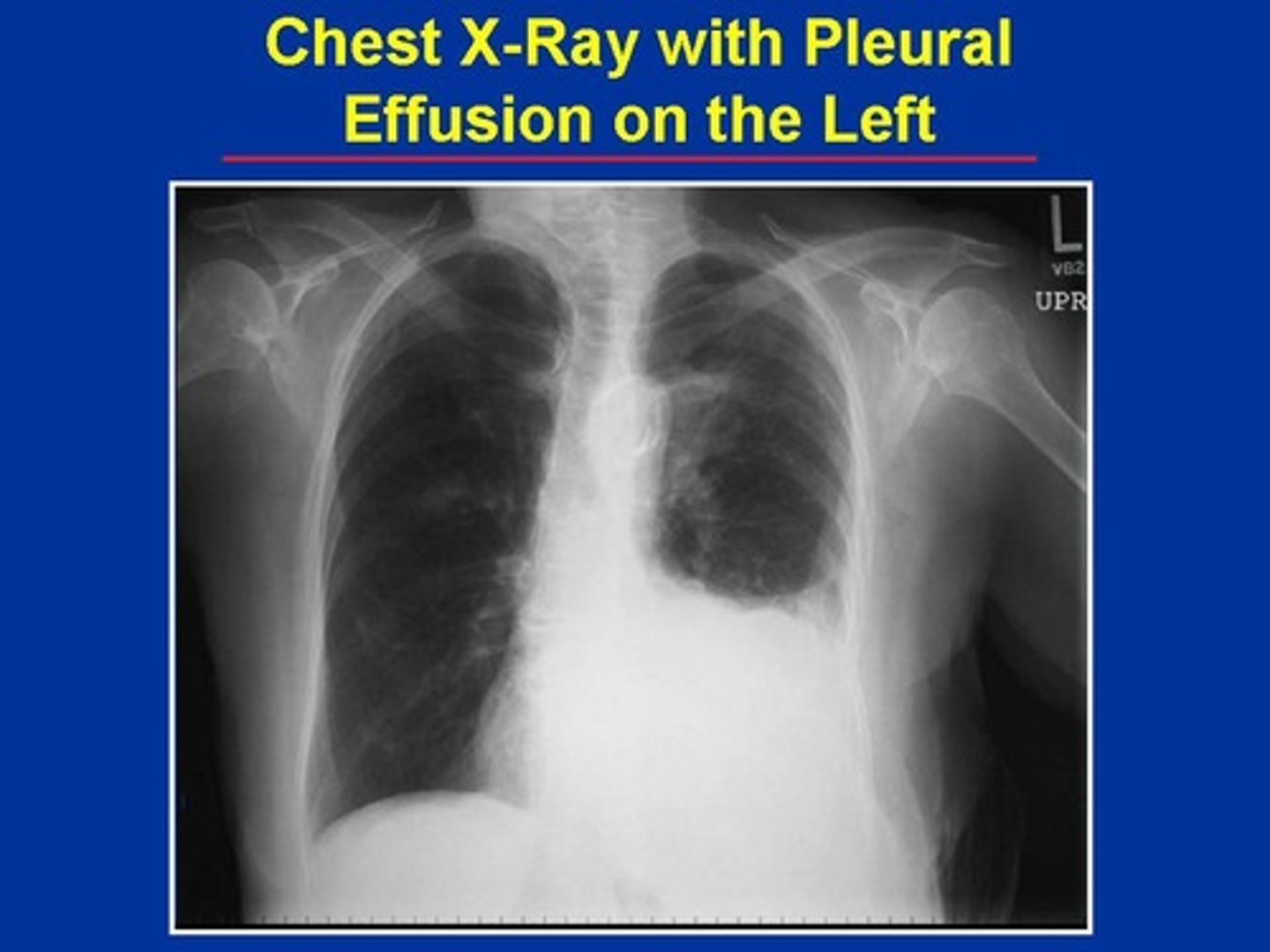
what are the manifestations of pleural effusion?
-absent lung sounds on the affected side
-tachycardia
-pleural friction rub you will hear on auscultation (when fluid rubs together aka abnormal lung sounds)
-dyspnea
-chest pain
what is ventilation pneumothorax?
-air in the pleural cavity which can cause lung to collapse
what is spontaneous pneumothorax?
where air enters from an opening in the internal airways
1. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax: usually mild
-occurs when a small air blister (bleb) on the top of the lung ruptures
- blebs are caused by a weakness in the lung tissue
-occurs in people with no hx of lung disease. they are usually tall, thin men
2. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax:
-more severe and even life-threatening
-develops in people with preexisting lung disease
-weakened lung tissue ruptures
what is traumatic pneumothorax?
-caused by blunt (i..e rib fracture) or penetrating (i.e. gunshot) trauma
what is tension pneumothorax?
-the most serious type! big emergency!
-can cause the affected lung to collapse!
-due to trapped air in the pleural space or air from a positive-pressure mechanical ventilator
-ultimately can put pressure on the heart and cause it to stop beating!
what are the manifestations of pneumothorax?
-sudden chest pain
-drop in blood pressure (hypotension) and oxygen and rise in the hear rate (tachycardia)
-chest tightness,
-dyspnea and tachypnea
-decreased breath sounds over the affected area
-asymmetrical chest movement
-trachea and mediastinum deviation
anxiety
-pallor
what is a pulmonary embolism?
-usually caused by a thrombus from the lower legs that moves up to the lungs (blood clot is most common)
-can also be caused fat (from bone marrow especially following femur fracture) or air or a foreign body
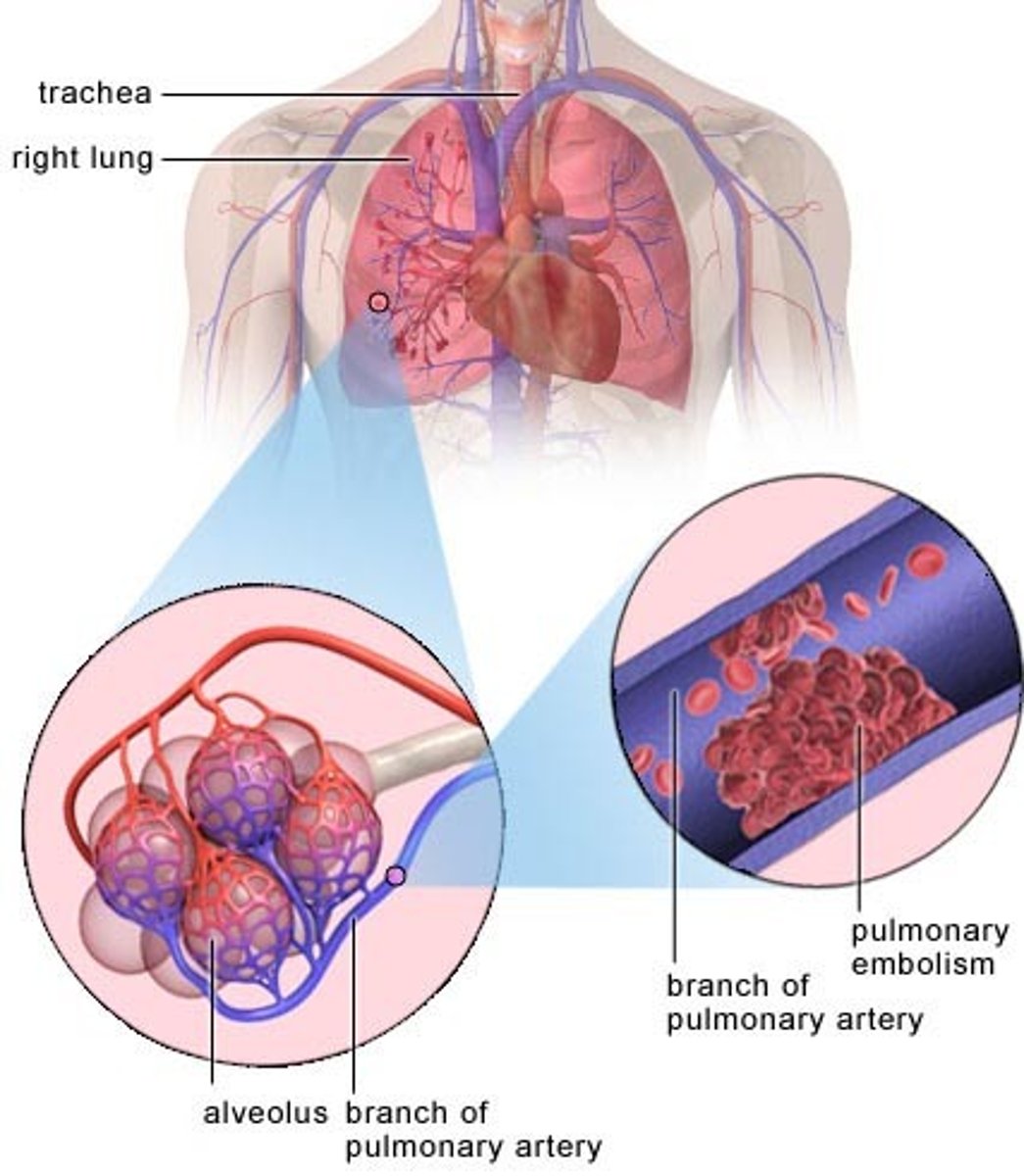
what can a pulmonary embolism result in?
-embolus with infarction (death of lung tissue)
-embolus without infarction (does not cause permanent lung injury)
-massive occlusion (occludes a major part of the pulmonary circulation)
*can vary in severity based on size and location
what is atelectasis?
-collapse of the alveoli in the lung
prevents normal exchange of O2 and co2
-hypoventilation occurs
-caused by too much surfactant (watery and soapy substance that prevents the alveoli from collapsing) deficiencies
what are the manifestations of atelectasis?
-restlessness
-diminished breath sounds
-dyspnea
-tachypnea
-asymmetrical lung sounds
-shallow breathing
-coughing
-wheezing
what is acute respiratory failure (ARF)?
-life threatening inability of the lungs to maintain adequate oxygenation
-the result of many respiratory conditions
-can lead to heart failure and death
what body systems are affected by covid?
-thrombi (thrombus aka blood clot)
-the heart
-acute coronary syndromes
what is viral pneumonia?
-caused by a virus
-usually mild
-can lead to secondary bacterial pneumonia
-a nonproductive cough with a low grade fever
what is bacterial pneumonia?
-more common than viral pneumonia
-more often due to the bacteria causing pneumonia
-a productive cough with a higher fever than viral pneumonia
what is aspiration pneumonia?
-occurs when aspirated fluids enter the lungs
what causes aspiration pneumonia?
-impaired gag reflex
-improper lower esophageal sphincter closure
-inappropriate gastric tube placement
what is lobar pneumonia?
-confined to a single lobe
-all based on the affected lobe
what is bronchopneumonia?
-most frequent type
-a patchy pneumonia across several lobes
what is interstitial (atypical) pneumonia?
-occurs in the area between the alveoli
-routinely caused by viruses or by uncommon bacteria
-more rare
what is nosocomial pneumonia?
-hospital acquired pneumonia
-develops more than 48 hours post hospital admission
what is CAP?
-community acquired pneumonia
-acquired outside the hospital or healthcare setting
what is ventilator associated pneumonia?
-occurs in patients that have been on mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours
what are the manifestations of tuberculosis?
- productive cough
- hemoptysis (coughing up blood/bloody secretions)
- night sweats
- fever
- chills
- fatigue
- unexplained weight loss
- anorexia
what are the different stages in an asthma attack?
stage one: peaks within 15 to 30 minutes. usually signaled by coughing and inflammatory response
stage two: peaks within hour 6 of symptom onset. a result of airway edema and mucous production causing air to trap (think narrow airways!)
what is status asthmaticus?
-an often-fatal, prolonged asthma attack unresponsive to usual treatment
-can quickly lead to respiratory alkalosis
and respiratory failure
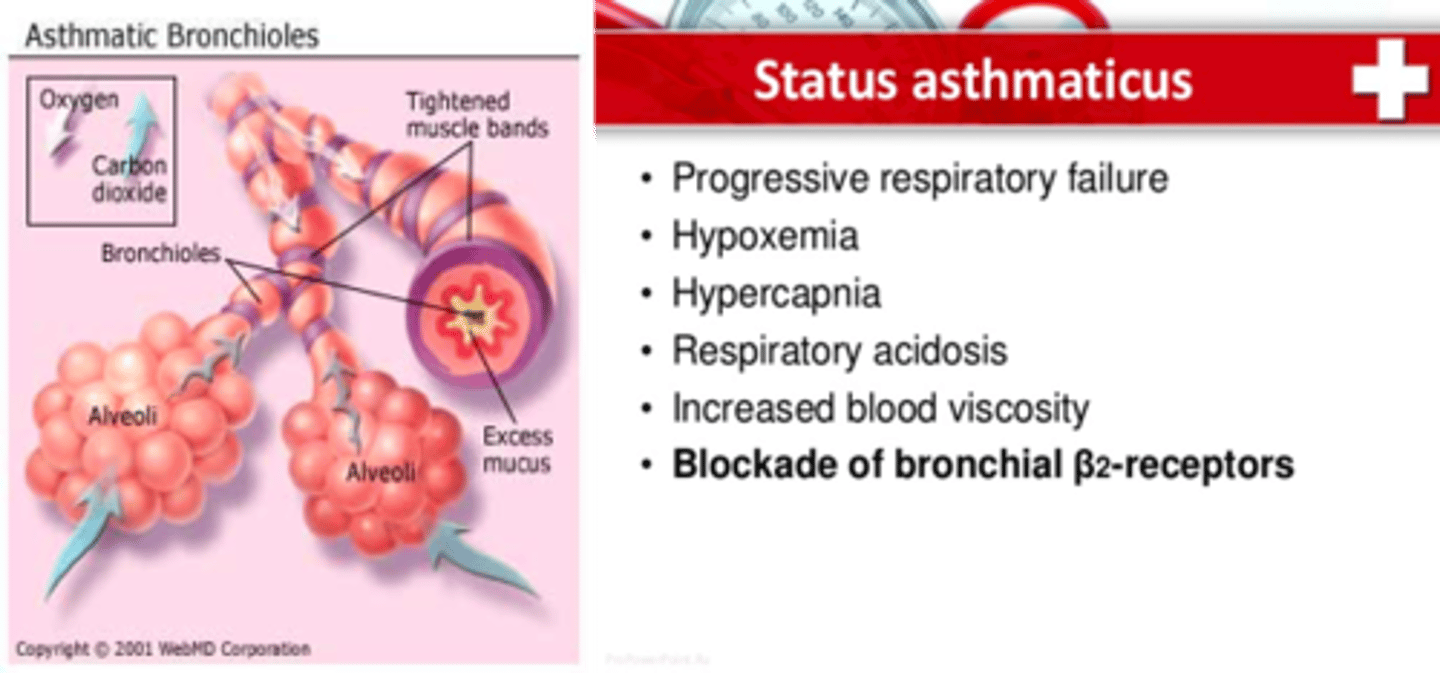
what are the symptoms of status asthmaticus?
-rapid breathing
-extreme wheezing
-shortness of breath
-chest tightness
-chronic cough
-racing heartbeat