Chapter 1 Human Genetics
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Genetics
the study of traits and conditions encoded in DNA
DNA
Stores genetic information
Heredity
the transmission of traits and biological info between generations
Genetic Genealogy
how people are related
Genes
units of heredity, passed from one generation to
the next.
Genome
complete set of genetic information
Exome
part of genome that encodes proteins
Genomics
compares and analyzes the functions of genomes.
Bioethics
addresses issues and controversies that arise in applying medical technology and using genetic information
Components of DNA
phosphate, sugar, base
Bases of DNA
A,T,C,G
DNA Replication
a new double helix is formed from the old one
using free DNA bases.
DNA Transcription
copies the DNA information into RNA through the process called Gene Expression
DNA Translation
uses the information in RNA to assemble amino acids into proteins.
Mutation
change in gene
Alleles
variants of genes
Heritable mutation
in sperm and eggs
Chromosome
contains DNA and Protein
Stem Cells
divide to yield other stem cells and cells that
differentiate.
Somatic cell
any cell in the body, 2 genome copies ( diploid)
Autosome
22 pairs
Karyotypes
display the chromosome pairs from largest to smallest
Traits
Any observable characteristic
Mendelian Trait
trait mostly controlled by one gene
Complex trait
trait influenced by many genes and the environment
Genotype
underlying DNA instructions (alleles present)
Phenotypes
visible trait, biochemical change, or effect on health
Dominant
exerting an effect in a single copy
Recessive
requiring two copies for expression
Pedigrees
Family tree diagram showing who has a traits
Gene Pool
collection of alleles
DNA profiling
comparing DNA sequences to identify people or relationships
Differentiation
process by which cells become specialised
Biobanks
Place where many people’s samples and genetic data are stored for research.
Biogenomics
Study and comparison of whole genomes.
Precision medicine
Tailoring treatment to a person’s genes
Pharmacogenetics
Using genes to predict how someone will respond to a drug
Genetic modification
Changing genes in ways that don’t happen naturally.
Recombinant DNA
DNA made by combining genes from different species
Genome editing
can replace, remove, or add specific genes into the cells of any organism.
Exome sequencing
determines the order of the DNA bases
Metagenomics
involves sequencing all of the DNA in a habitat
Germ cell
reproductive, 1 genome copy( haploid)
Ribosomes
build proteins
Nucleus
holds DNA (genetic materi
Nuclear pores
allows movement of bio chemicals
Nuclear lima
provides support and holds nuclear pores in place
Nucleolus
produces ribosomes
Lysosomes
act as the cells waste disposal systems
Rough ER
synthesises proteins (have ribosomes on the surface)
Smooth ER
synthesises lipids
Golgi apparatus
packages and labels proteins and sugars
Endoscopes
vesicles derived from the plasma membrane that transport materials to lysosomes.
Peroxisomes
breakdown fatty acids and toxic substances
Vesicles
sacs used for transport
Biological membrane
transport of nutrients and waste, cell integrity
Signal transduction
detects signals from outside the cell and transmit them inwards
Cellular adhesion
Plasma membrane helps cells attach to other cells
Apoptosis
Cell death
Interphase
Chromosomes are uncondensed
Mitosis Cytokinesis
microfilament band contracts, seperating 2 cells
Single Gene Disease
caused by mutations in a single gene (monogenic)
True Breeding
offspring have the same trait as parent
Hybrids
plants that inherit a different gene variant (allele) from each parent.
Monohybrid
follows one trait
Dominant
the observed trait
Recessive
the masked trait
Homozygous
carry same alleles TT or tt
Heterozygous
carry different alleles Tt
Wild Type
Most common phenotype
Mutant phenotype
Variant of a gene’s expression that arises when the gene undergoes mutation
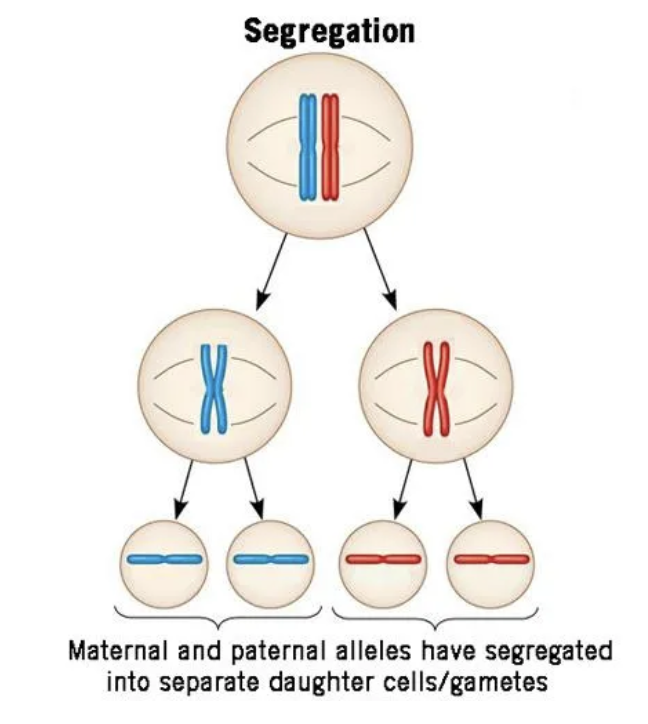
Law of segregation
allele pairs separate during the formation of gametes
OCA2
Help control melanin production in the iris
HERC2
controls expression of the OCA2 gene
Autosomal inheritance
can be dominant or recessive
Autosomal Dominant
equal frequencies and traits appear in every generations
Autosomal Recessive
equal frequencies and can skip generations
Recessive traits
loss of functions and proteins are missing
Dominant traits
arise from gain of function
dihybrid
heterozygous (RrYy)
Probability
likelihood that an event will occur
Lethal Alleles
genotype causes death before reproduction
Multiple Alleles
two alleles for each autosomal gene
Compound heterozygote
An individual with two different mutant recessive alleles for same gene
Codominance
both alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote
Epistasis
one gene masks or affects another’s phenotypes
Penetrance
All-or-none expression of a single gene
Expressivity
Severity or extent
Pleiotropy
where one gene controls several functions
Genetic Heterogeneity
Different genes can produce identical phenotypes
Phenocopy
Trait that appears inherited but is caused by the environment
mtDNA
Contains small circular DNA
Heteroplasmy
condition where the mtDNA sequence is not the same in all copies of the genome
Linkage
Genes that are close on the same chromosome