Chapter 26: Vision and Optical Instruments
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
aberration
failure of rays to converge at one focus because of limitations or defects in a lens or mirror
accommodation
the ability of the eye to adjust its focal length is known as accommodation
adaptive optics
optical technology in which computers adjust the lenses and mirrors in a device to correct for image distortions
angular magnification
a ratio related to the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece and given as 𝑀=−𝑓o𝑓e
astigmatism
the result of an inability of the cornea to properly focus an image onto the retina
color constancy
a part of the visual perception system that allows people to perceive color in a variety of conditions and to see some consistency in the color
compound microscope
a microscope constructed from two convex lenses, the first serving as the ocular lens(close to the eye) and the second serving as the objective lens
eyepiece
the lens or combination of lenses in an optical instrument nearest to the eye of the observer
far point
the object point imaged by the eye onto the retina in an unaccommodated eye
farsightedness
another term for hyperopia, the condition of an eye where incoming rays of light reach the retina before they converge into a focused image
hues
identity of a color as it relates specifically to the spectrum
hyperopia
the condition of an eye where incoming rays of light reach the retina before they converge into a focused image
laser vision correction
a medical procedure used to correct astigmatism and eyesight deficiencies such as myopia and hyperopia
myopia
a visual defect in which distant objects appear blurred because their images are focused in front of the retina rather than being focused on the retina
near point
the point nearest the eye at which an object is accurately focused on the retina at full accommodation
nearsightedness
another term for myopia, a visual defect in which distant objects appear blurred because their images are focused in front of the retina rather than being focused on the retina
numerical aperture
a number or measure that expresses the ability of a lens to resolve fine detail in an object being observed. Derived by mathematical formula NA=𝑛sinα,
where 𝑛 is the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the specimen and 𝛼=𝜃/2
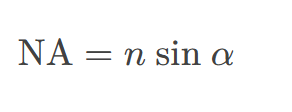
objective lens
the lens nearest to the object being examined
presbyopia
a condition in which the lens of the eye becomes progressively unable to focus on objects close to the viewer
retinex
a theory proposed to explain color and brightness perception and constancies; is a combination of the words retina and cortex, which are the two areas responsible for the processing of visual information
retinex theory of color vision
the ability to perceive color in an ambient-colored environment
rods and cones
two types of photoreceptors in the human retina; rods are responsible for vision at low light levels, while cones are active at higher light levels
simplified theory of color vision
a theory that states that there are three primary colors, which correspond to the three types of cones
Image formation by the eye is adequately described by the thin lens equations:
the mathematical relationships that relate the object distance, image distance, and focal length of a lens
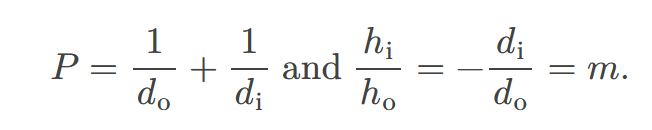
Magnification for a two-element system with an objective and an eyepiece,
is given by the product of the magnification of both lenses.
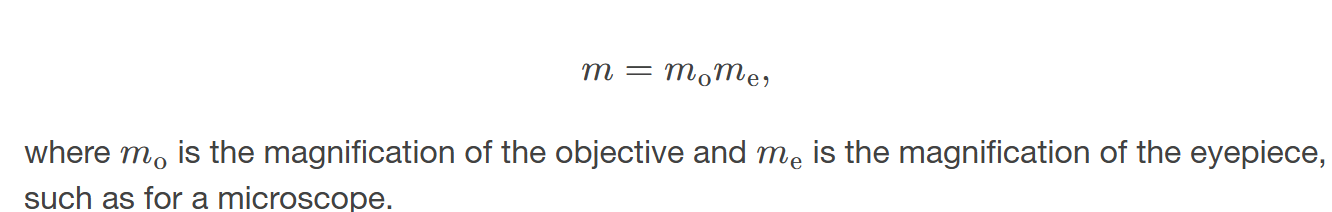
𝑓/#
describes the light gathering ability of a lens.
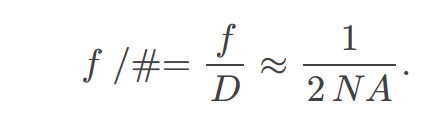
angular magnification M for a telescope
is the ratio of the angle subtended by the image at the eye to the angle subtended by the object at the eye, indicating how much larger an object appears through the telescope compared to viewing it with the naked eye.
