AP Chemistry Unit 3 Mid-Unit Test
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Nonpolar Molecules IMFs
London Dispersion Forces (LDF), temporary, weak attractions caused by induced diples
Polar Molecules IMFs
Dipole-Dipole Forces + LDF, Permanent dipoles attract each other, stronger than LDF alone
Polar with H bonded to F, O, N IMFs
Hydrogen Bonding + Dipole-Dipole + LDF, Second strongest IMF, hydrogen attached to a F, O, N is attracted to F, O, N of another molecule
Ionic Compounds IMFs
Ion-Ion(solid) or Ion-Dipole(solution), Attraction between full charges (ion-ion) or an ion and a polar molecule (ion-dipole_
Ionic Solid Traits
Ionic bonds, high melting point, brittle, hard
Covalent Network Solid Traits
Covalent bonds, high melting point, hard, nonconducting
Metallic Solid Traits
Metallic bonds, Variable hardness and melting point, conducting
Molecular Solid Traits
Inter molecular forces, low melting point, nonconducting
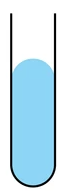
Cohesion
IMFs bind similar molecules to one another
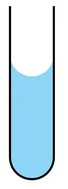
Adhesion
IMFs bind a substance to a separate surface
C° + ___ = K°
273°
1mm Hg(torr) × ____ = 1atm
760
PV=nRT, R = ____
.0821 (most of the time)
What equation to find pressure, volume, moles, or temperature of a gas
PV = nRT
What equation to convert mass to moles
mole = molar mass (g/mol) ÷ mass (g)
What equation to correct for water vapor pressure when a gas is collected over water
Pᵍᵃˢ = Pᵗᵒᵗᵃˡ - Pᴴ₂ᴼ
What equation if there are changes to Pressure, Volume, or Temperature
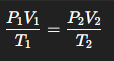
Equation to find density of a gas
P = Pressure
M = Molar mass
R = Constant
T = Temperature
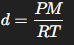
Equation to find gas produced or consumed in a reaction
n = Moles
Coefficient = Number to the left of an element in a formula

Key points of Kinetic Molecular Theory
(1) the particles in a gas are in constant, random motion
(2) the combined volume of the particles is negligible
(3) the particles exert no forces on one another
(4) any collisions between the particles are completely elastic
(5) the average kinetic energy of the particles is proportional to the temperature in kelvins
Effusion
Escape of gas molecules through a hole into an evacuated spaced, volume increases, pressure decreases
Diffusion
Spread of one substance throughout a space or second substance
When making a Maxwell Boltzmann Distribution Curve…
Molar Mass:
Higher molar mass substances have taller, narrower curves, Lighter gases have shorter broader curves.
Temperature:
Higher temperature → Flatter curve, more kinetic energy (Right)