Coordination Compounds
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NCERT-based; corner-to-corner; for low-time high yield revision
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
First chemist to formulate the structures of Coordination Compounds
Alfred Werner
Other name for valency of central atom in Coordination sphere
Primary valence
Other name for Coordination number in Coordination sphere
Secondary valence
Meaning of Coordination Polyhedra
Ions/groups bound by secondary linkages to the metal having characteristic spatial arrangements corresponding to different coordination numbers (C.N.)
Which geometrical shapes are more common in coordination compounds?
Octahedral, Tetrahedral and Square planar
Difference between Double Salt and Complex
Double Salt: Dissociate into simple ions completely
Complex Salt: Don’t dissociate into simple ions completely
Meaning of Coordination Entity
Constitutes a central metal atom or ion bonded to a fixed number of ions or molecules
Meaning of Central atom
The atom/ion to which a fixed number of ions/groups are bound in a definite geometrical arrangement around it
Central atoms/ions in a coordination entity are referred as
Lewis acids
Meaning of Ligands
Ions/molecules bound to the central atom/ion in the coordination entity
Structure of EDTA4-
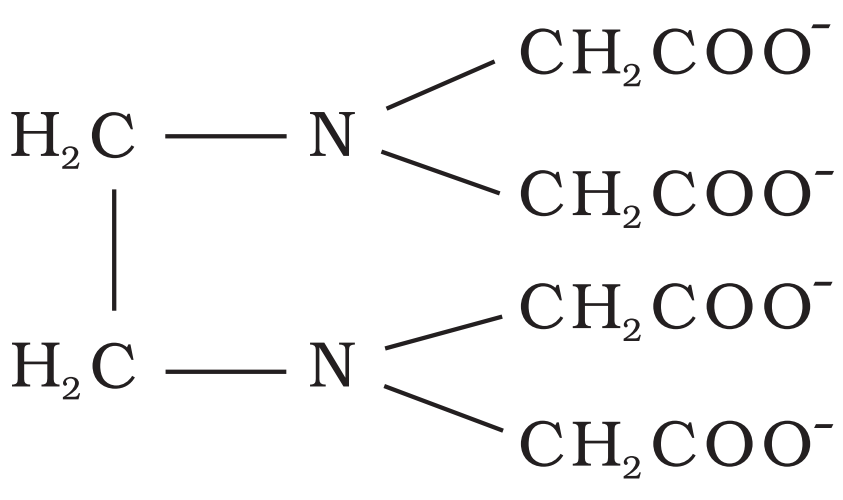
Chelate ligand
When a di- or polydentate ligands uses two/more donor atoms to bind with metal atom simultaneously
Meaning of Denticity
No. of chelating groups
Compare stability of complexes:
Chelated Complex and Unidentated Complex
Chelated Complex > Unidentated Complex
Meaning of Ambidentate Complex
Ligands which possess two different donor atoms and either of the two ligetes in the complex
The number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded is called:
Coordination Number or Secondary Valence
To determine Coordination number, we only count no. of Sigma bonds True/False
True and we don’t count and Pi bonds involved (if any)
In K4[Fe(CN)6],
1) [Fe(CN)6]4- is:
2) K+ is:
3) CN- is:
4) Fe+2 is:
5) 6 in (CN)6 is:
6) +2 in Fe+2 is:
1) Coordination Sphere
2) Counter ion
3) Ligand
4) Central atom
5) Coordination number/Secondary valence
6) Oxidation number of central atom/Primary valence
The spatial arrangement of the ligand atoms which are directly attached to the central atom/ion is _____________ about the central atom.
Coordination Polyhedron
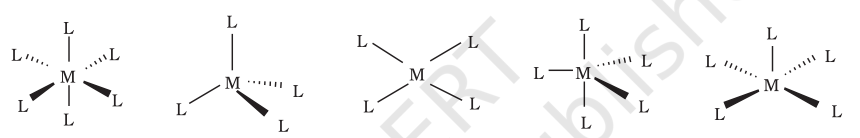
Name these different coordination polyhedra:
Octahedral; Tetrahedral; Square Planar; Trigonal bipyramidal; Square pyramidal
[Co(NH3)6]+3 is __________ complex while [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+3 is is __________ complex. (in terms of kind of donor groups attached)
Homoleptic; Heteroleptic
IUPAC of:
1) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)]
2) K3[Cr(C2O4)3]
3) [CoCl2(en)2]Cl
4) [Co(NH3)5(CO3)]Cl
5) Hg[Co(SCN)4]
1) Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum(II)
2) Potassium trioxalatochromate(III)
3) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) chloride
4) Pentaamminecarbonatocobalt(III) chloride
5) Mercury (I) tetrathiocyanato-S-cobaltate(III)
Formulas of:
1) Tetraammineaquachloridocobalt(III) chloride
2) Potassium tetrahydroxidozincate(II)
3) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate(III)
4) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)
5) Tetracarbonylnickel(0)
1) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl
2) K2[Zn(OH)4]
3) K3[Al(C2O4)3]
4) [Co(en)2Cl2]+
5) [Ni(CO)4]