AP Bio- 1.5 Structure and function of proteins
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the primary function of DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase helps synthesize new DNA.
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary.
how do the four levels of protein structure work in general?
- Each level builds on the others.
- Each level is held together by different bonds and interactions formed between amino acids.
what does it mean that proteins have directionality?
they have a N terminus and a C terminus
What defines the N terminus of a protein?
The N terminus is the first amino acid in the chain with a free amine group.
What defines the C terminus of a protein?
The C terminus is the last amino acid in the chain with a free carboxyl group.
do all proteins form into quaternary structures?
no, only some will form into quaternary but all have primary, secondary and tertiary structure
how many amino acids are there in organisms
20
what is the structure of an amino acid?
Each amino acid has the same “peptide backbone” structure made of the
1. Amine Group
2. Carboxyl Group
3. A hydrogen
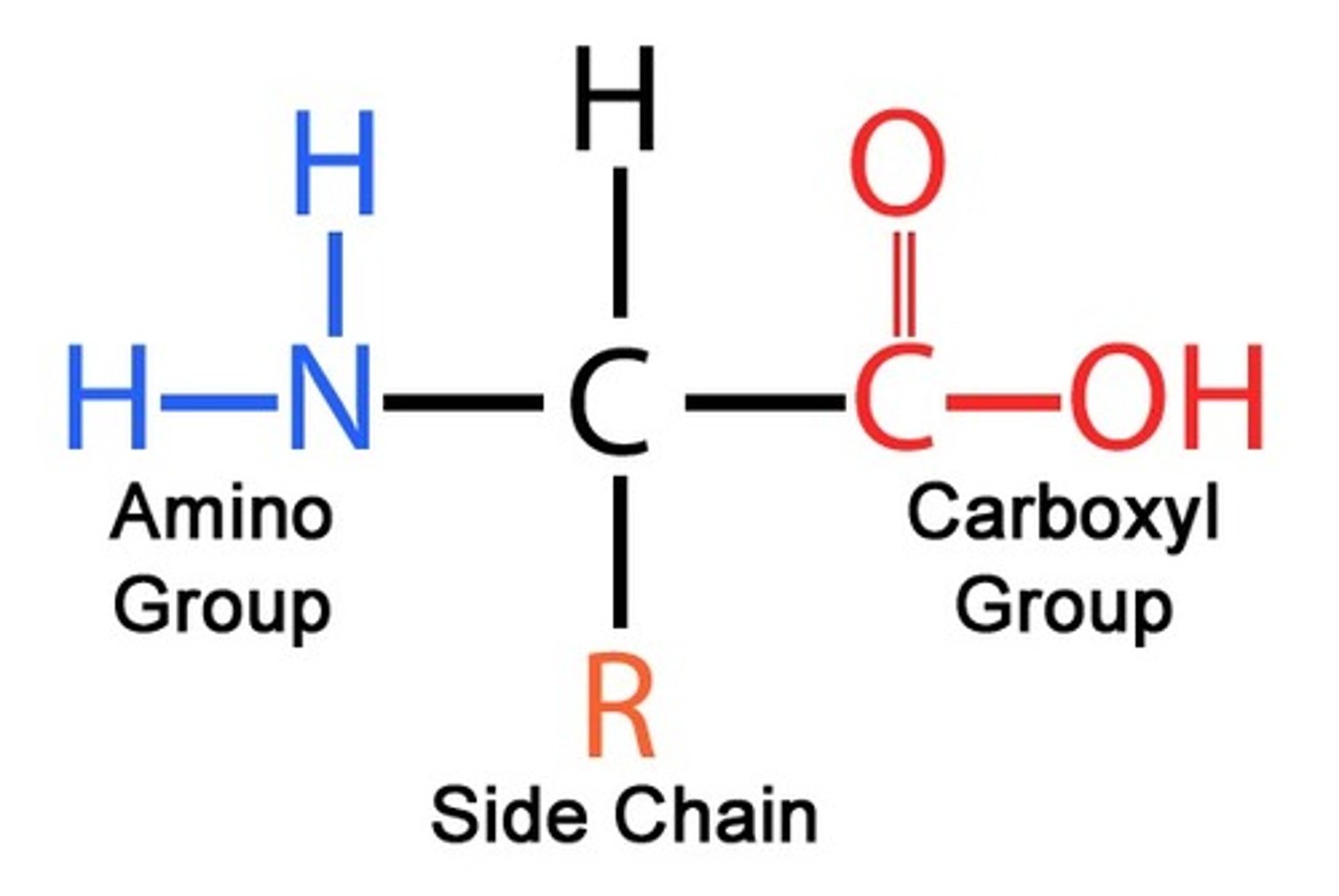
what differentiates each amino acid from one another?
only difference between each of the amino acids is the structure and chemical properties of the R Side Chain
What is the amine group in an amino acid?
Either NH2 or NH3
What does amine mean?
Contains nitrogen
What are the properties of amine groups in amino acids?
Capable of hydrogen bonding; amine groups found in the R side chain will usually be positively charged
what is the purpose of the hydrogen in an amino acid?
it is present because carbon must form 4 bonds
what are the chemical properties and bonding abilities of the amino acid side chains (R groups) determined by?
determined by the elemental composition.
what 4 types of side chains (r groups) of AA's ?
hydrophobic, hydrophilic, acidic (hydrophilic), basic (hydrophilic)
what is the polarity of the 4 different types of chains?
non polar - hydrophobic
polar - hydrophilic, acidic and basic
how to determine if AA side chain (R-group) is hydrophobic?
Look for:
1. Long hydrocarbon chains (C and H only)
2. Big hexamer rings
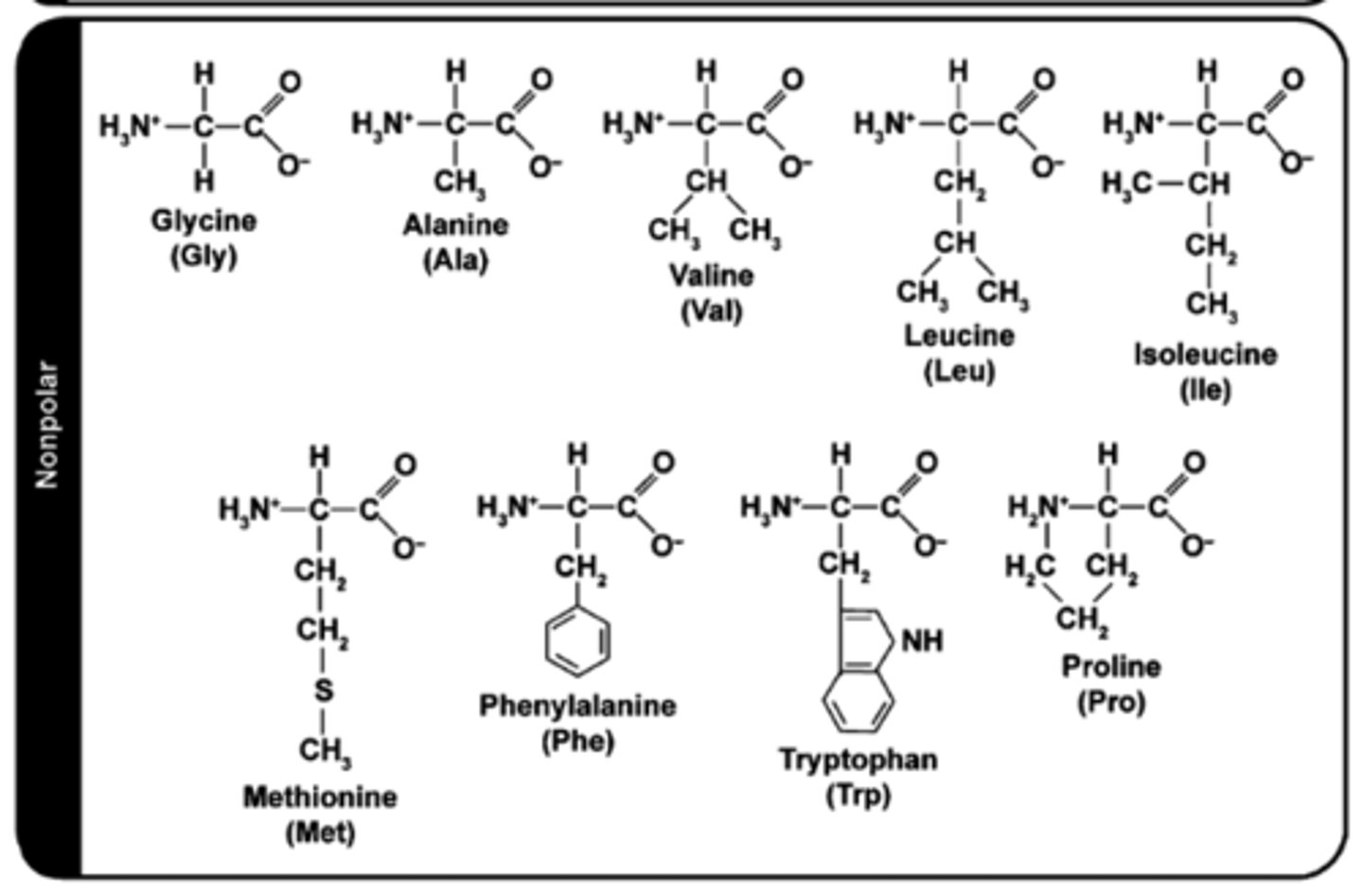
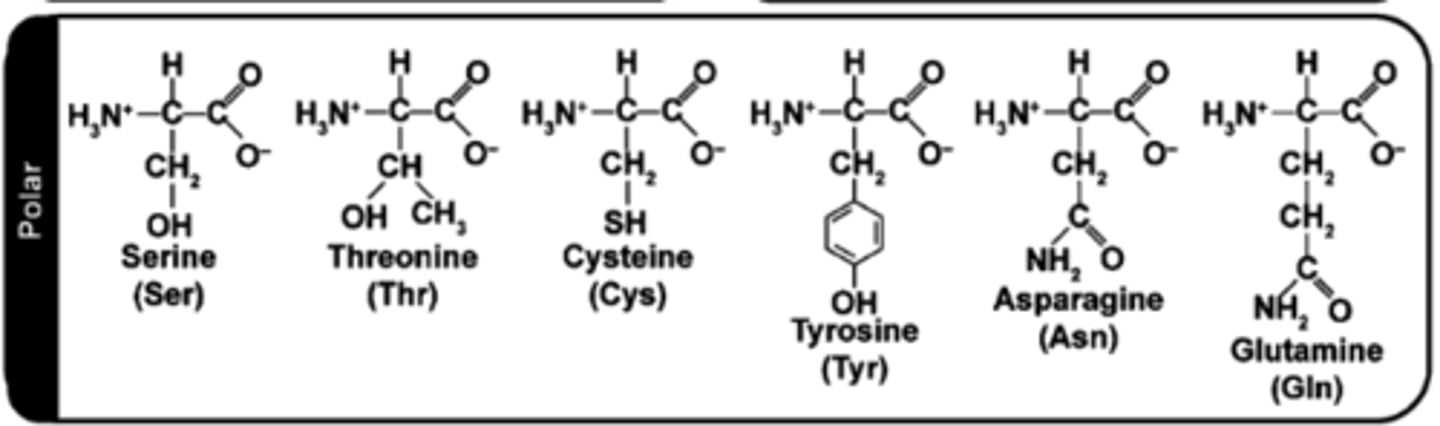
how to determine if AA side chain (R-group) is hydrophilic?
Look for:
Oxygen or nitrogen in the side chain
No charges
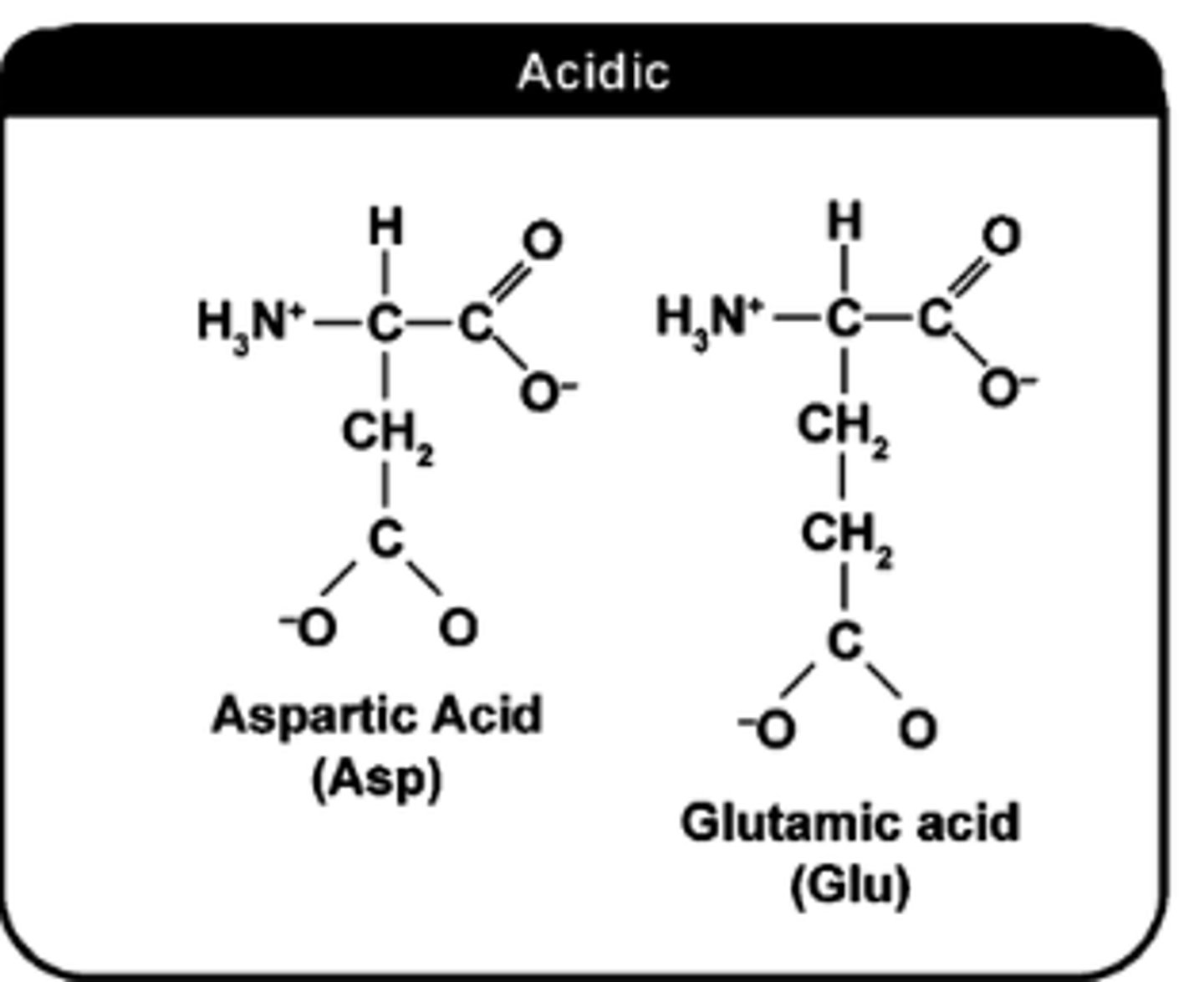
how to determine if AA side chain (R-group) is acidic?
Look For:
Carboxyl Groups
Negative charges
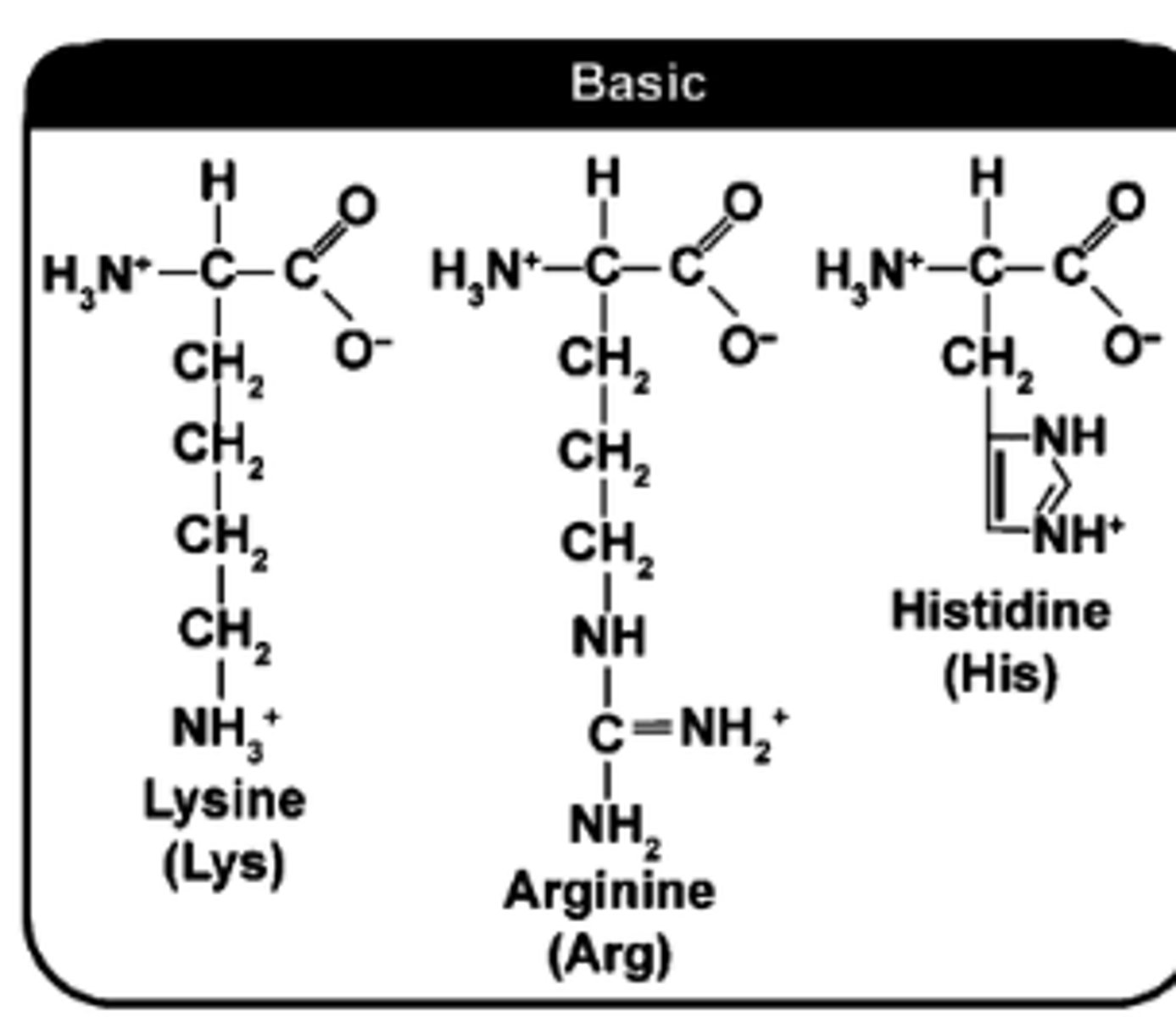
how to determine if AA side chain (R-group) is basic?
Look For:
Amine Groups
Positive Charges
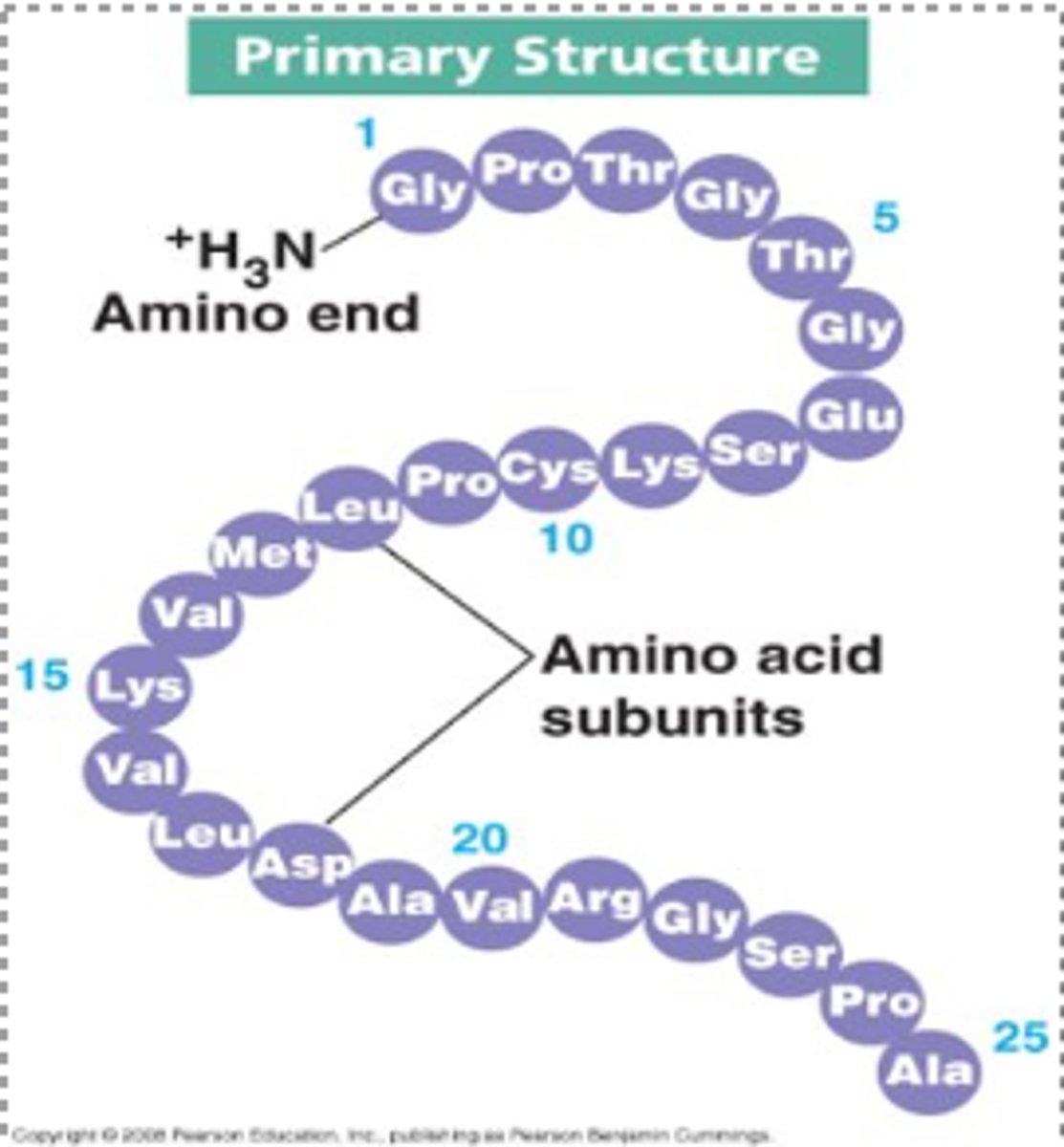
What is the primary protein structure?
The sequence of amino acids formed via protein synthesis.
- this determines how the protein folds at all levels
what would changing the aa sequence cause, and what would that lead to?
Changing the amino acid sequence will usually cause the protein to misfold and stop working
- can lead to disease of death
How is the primary protein structure formed?
By covalently bonding two amino acids together via dehydration synthesis.
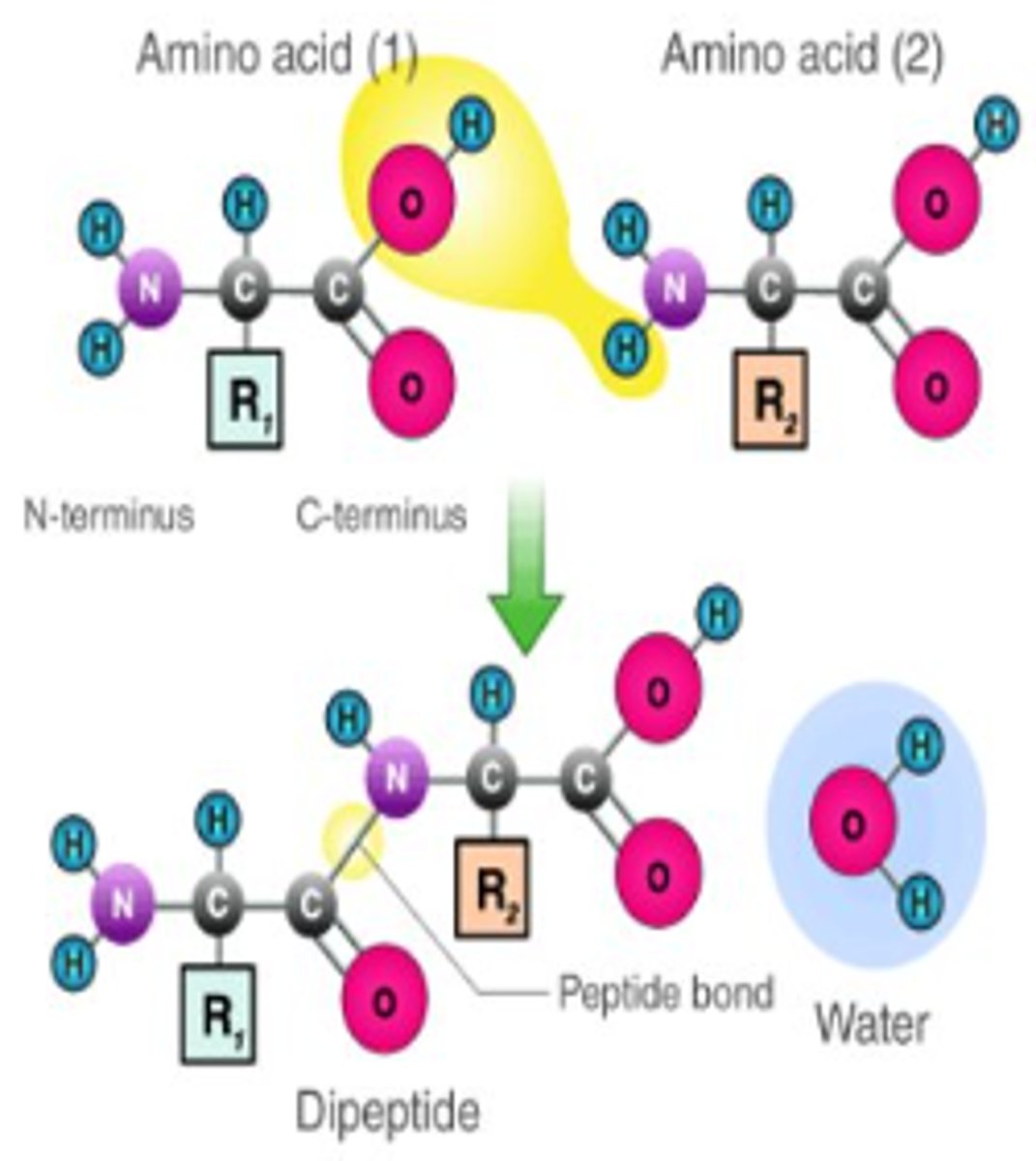
what is dehydration synthesis?
the process of joining two molecules, or compounds, together following the removal of water
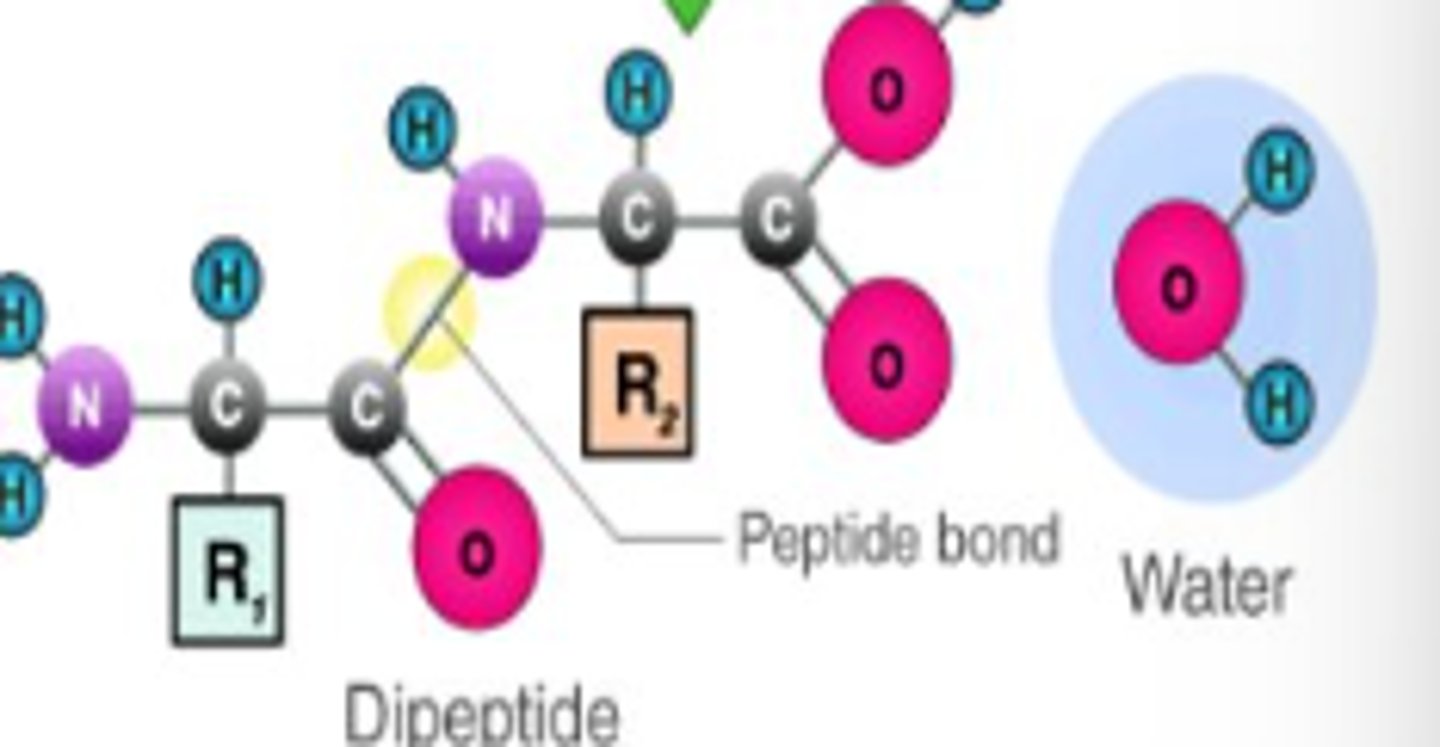
What is a peptide bond?
A covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of the first amino acid and the amine group of the second.
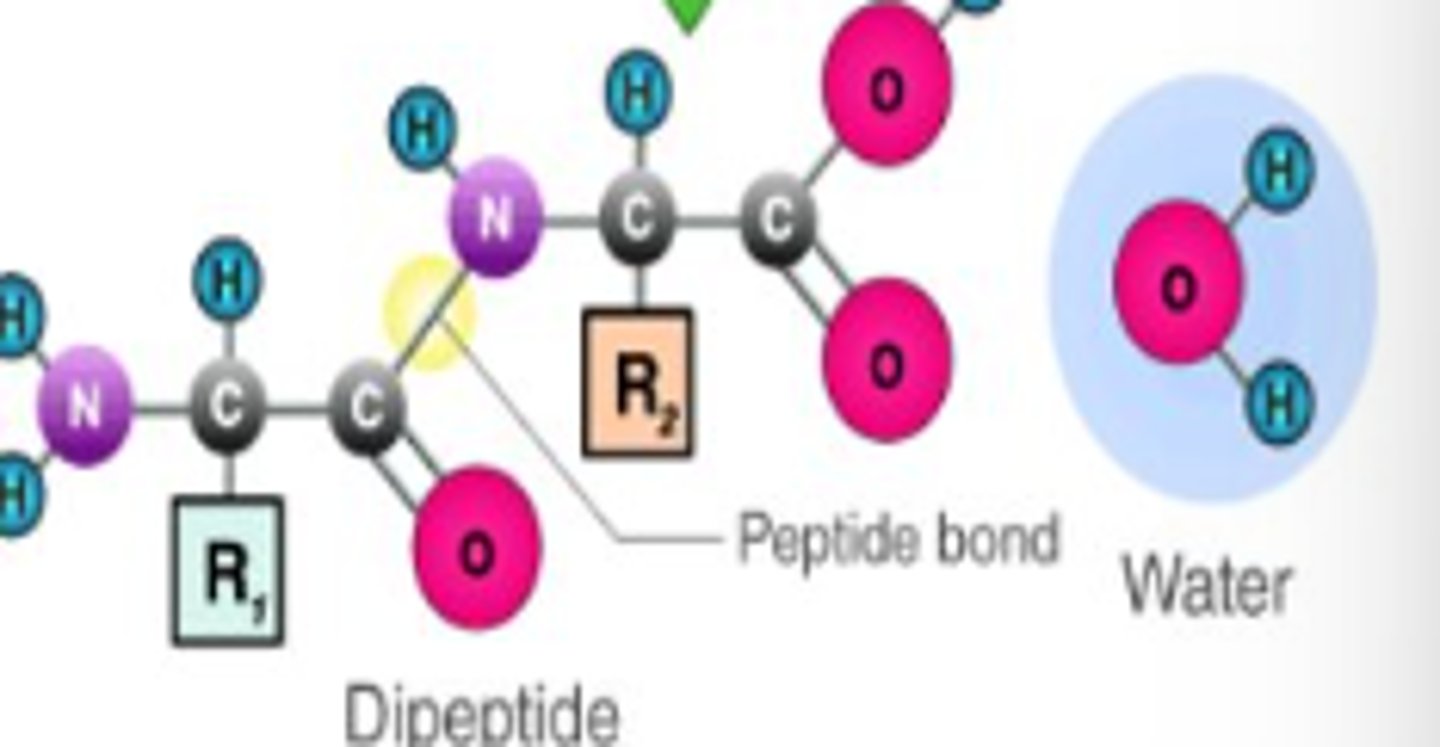
what help is required to form the primary protein structure?
Requires the help of enzymatic RNA in ribosomes.
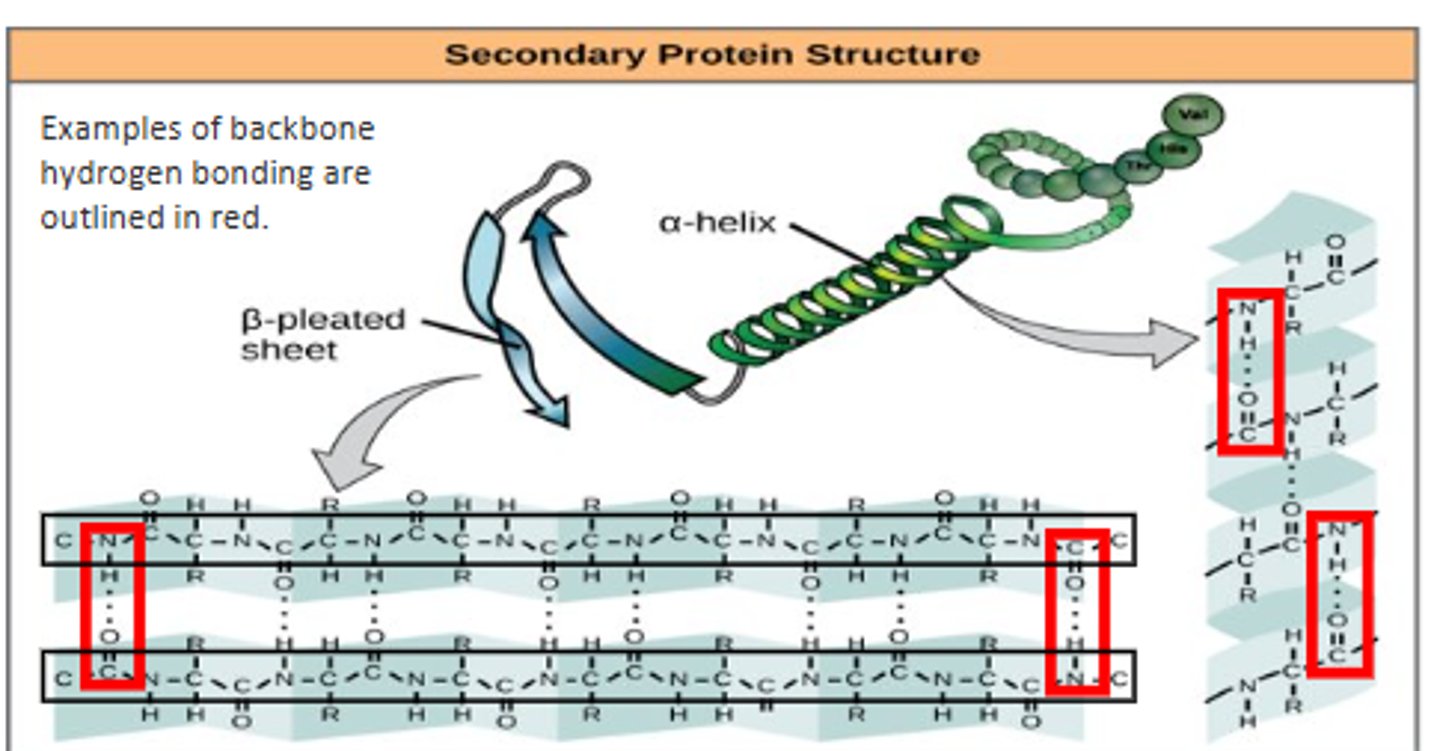
What are the two different secondary protein structures?
Alpha helices and beta pleated sheets.
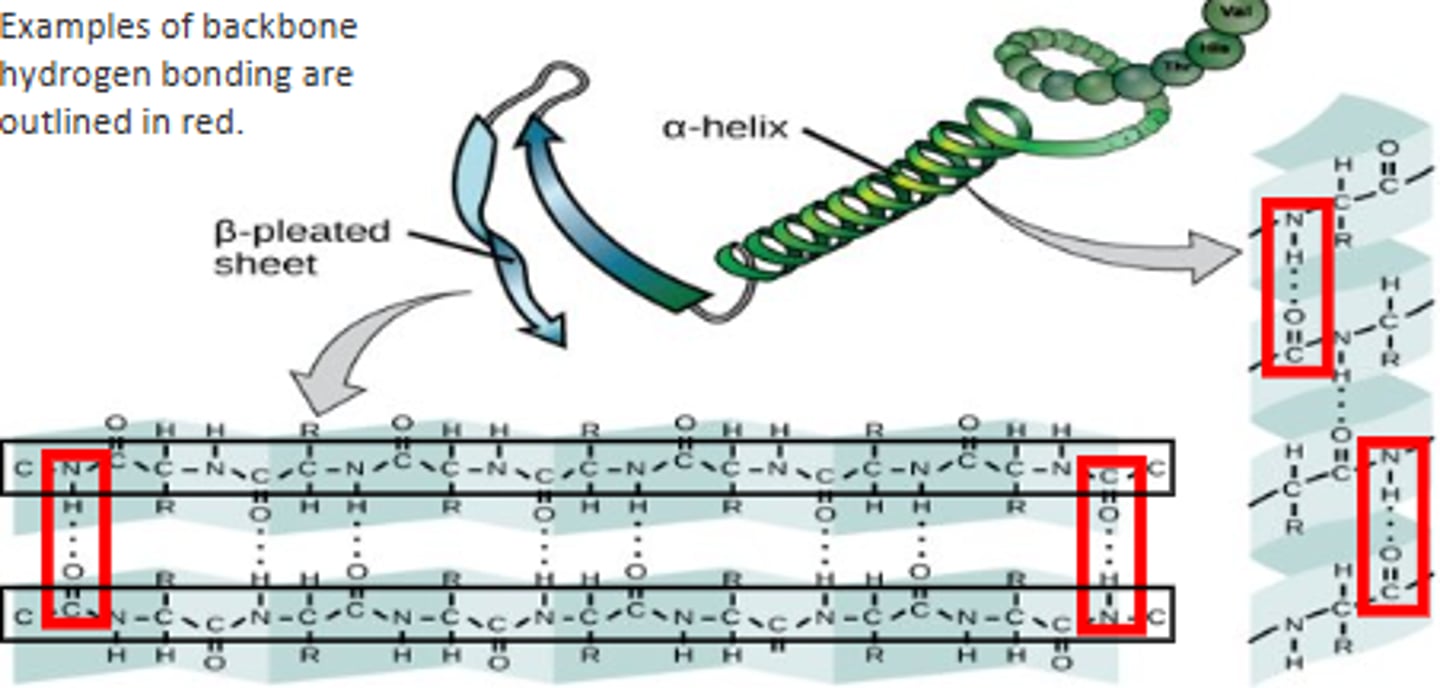
What holds together the secondary structure of proteins?
Hydrogen bonding between the carboxyl and amine groups on the peptide backbone.
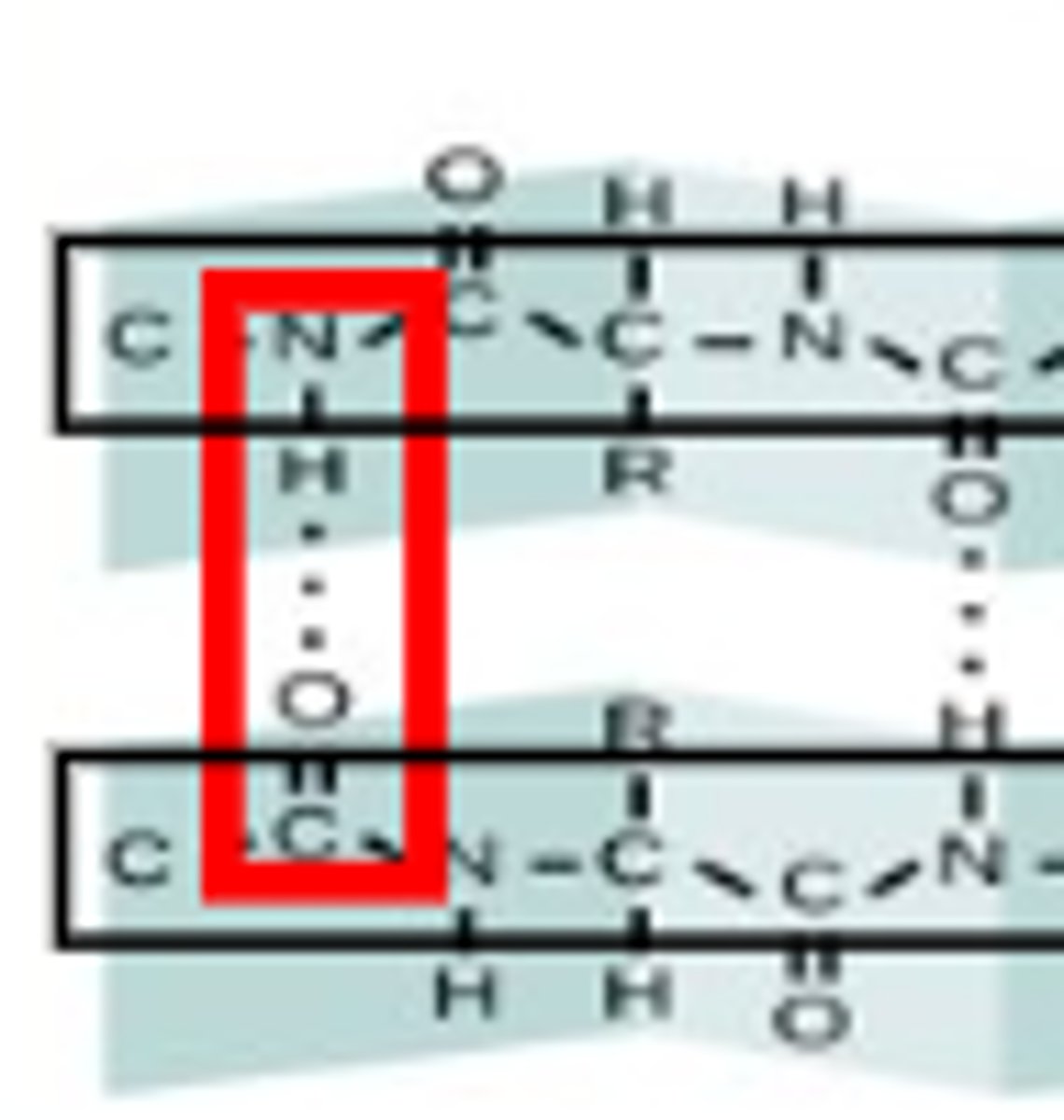
when does the secondary structure occur?
- occurs as the protein begins to fold
- no R groups involved
- protein is not active yet
What occurs during the tertiary structure of a protein?
The protein finishes folding, it now has a three-dimensional shape and is usually functional at this point.
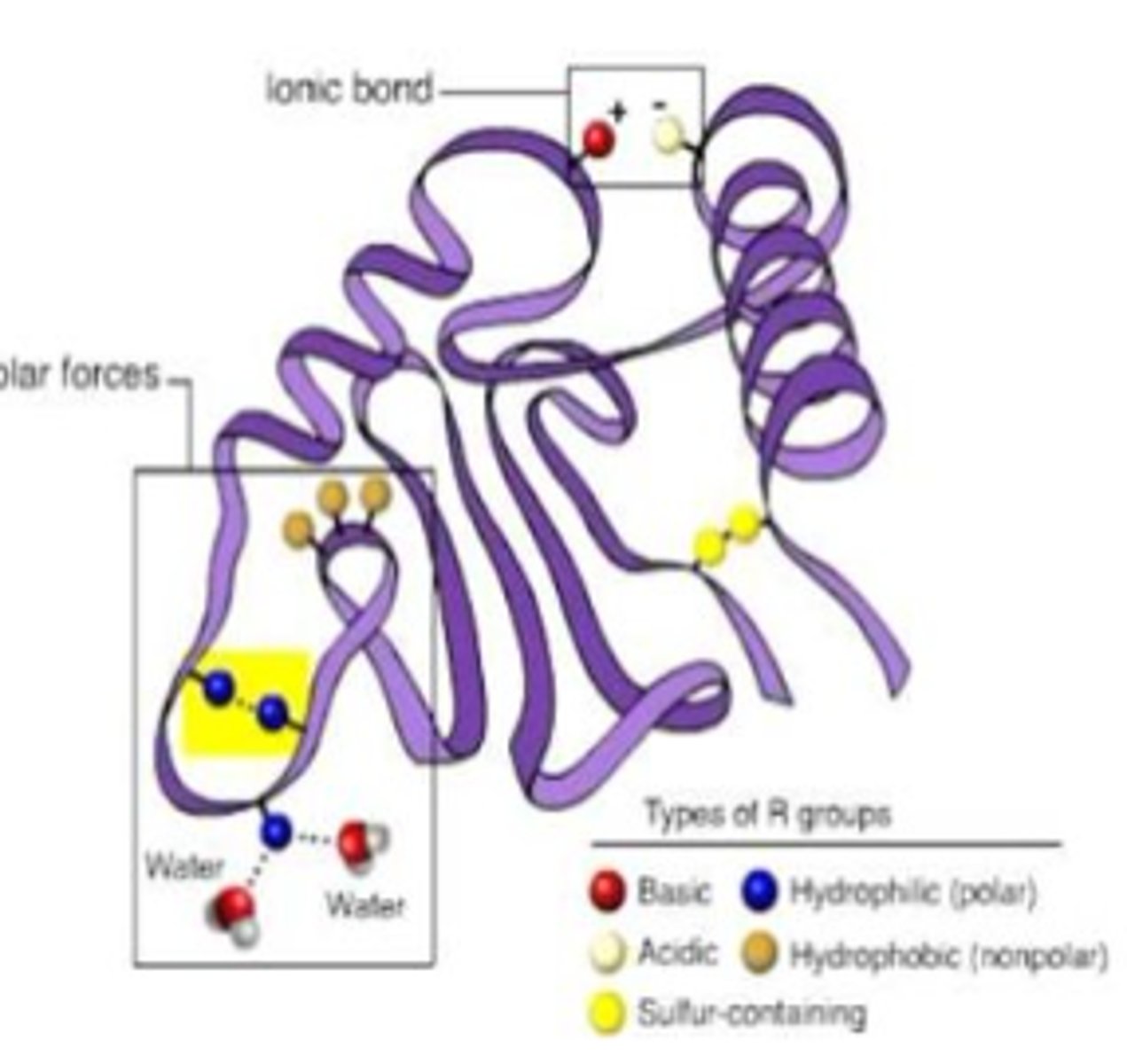
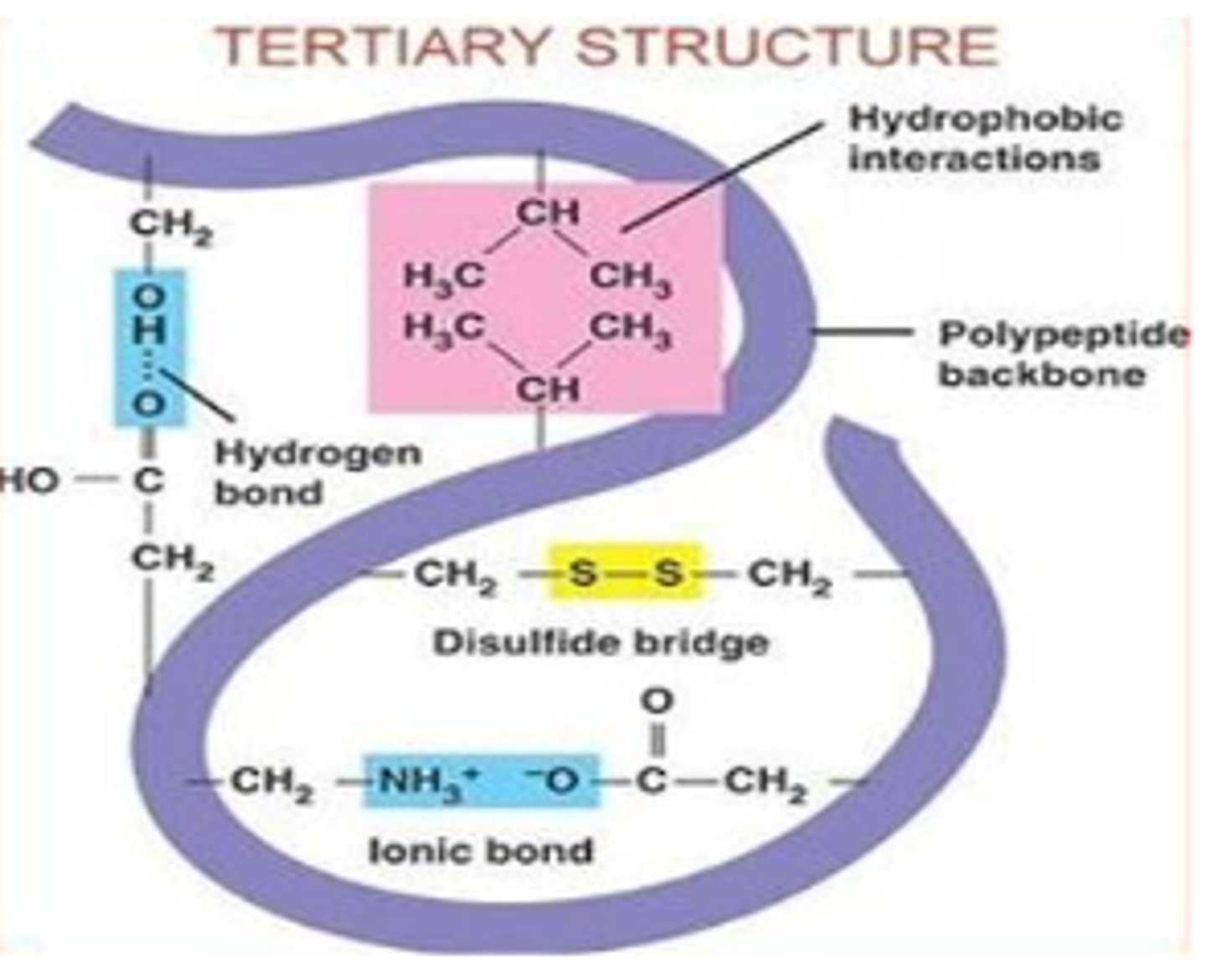
how is tertiary structure controlled?
Tertiary structure is controlled by interactions between the R side chains on the amino acids.
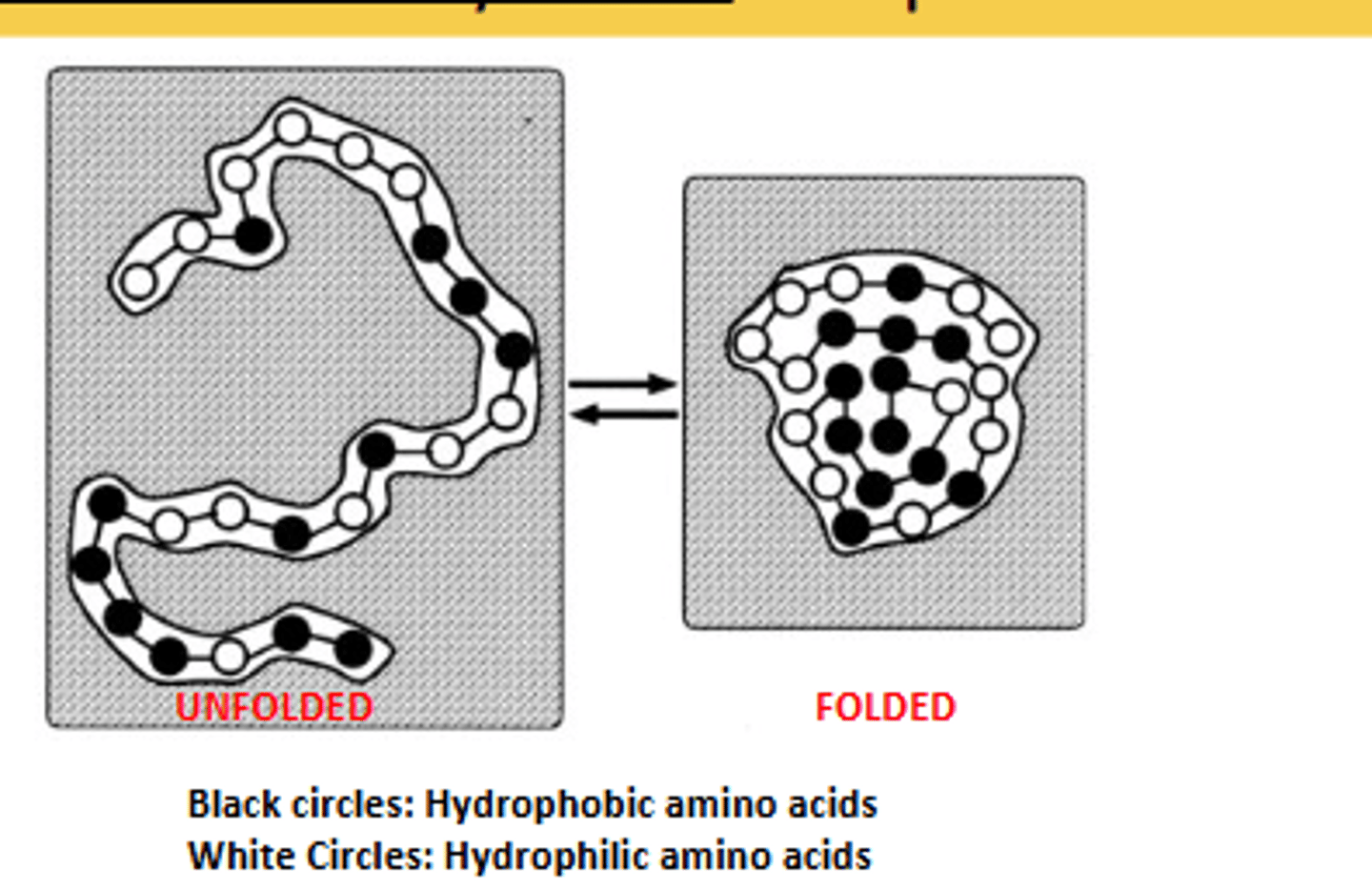
What is the major driving force behind the formation of tertiary structure?
Hydrophobic collapse.
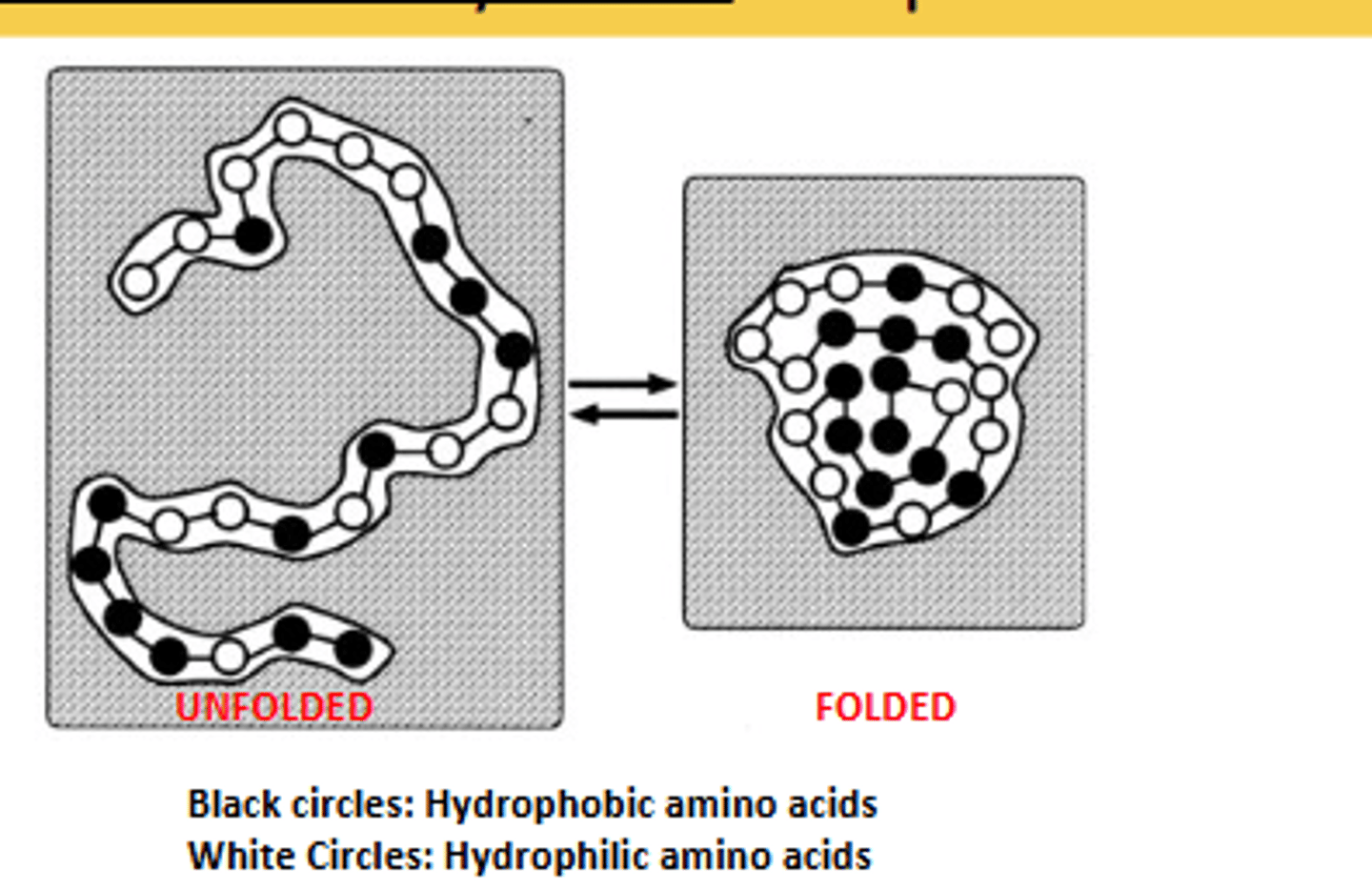
describe hydrophobic collapse
Occurs as the hydrophobic amino acids collapse away from the water and into the interior of the tertiary structure of the protein.
What bonds/interactions occur between side chains (R-groups) during tertiary structure
1. Hydrogen bonds between side chains with electronegative atoms (O and N)
2. Charge attraction between acidic (-) and basic (+) charges
3. disulfide bridges (only when there are at least 2 cysteine aa's)
how does temp. and pH effect H-bonds and charge attractions?
H-bonds and charge attractions are sensitive to changes in pH and temperature and will be broken if the protein is outside of the normal pH or temperature range
What are disulfide bridges?
very strong covalent bonds between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids.
- strengthen structure and NOT sensitive to changes in pH or temp
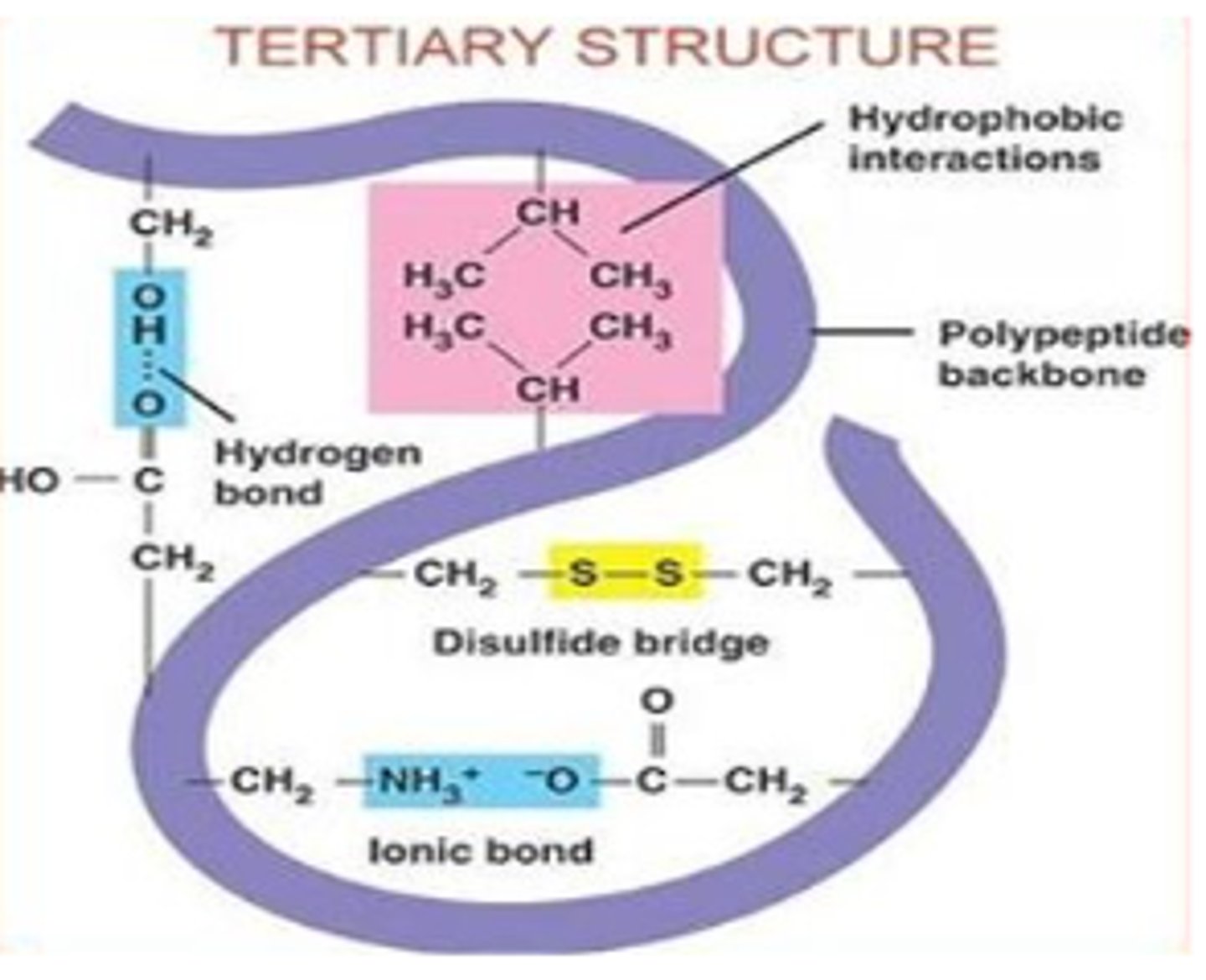
what kinds of proteins are disulfide bridges usually found in?
Usually found in proteins exposed to harsh conditions like High temperature
or Extreme pH
What is quaternary structure in proteins?
The assembly of multiple proteins into a protein complex.
What interactions hold quaternary structures together?
Interactions between variable side chains and hydrogen bonding between peptide backbones.
What is the role of R side chains in tertiary structure?
They control interactions that determine the final folding of the protein.
What are the common features of all amino acids?
They have the same peptide backbone structure consisting of an amine group, carboxyl group, and a hydrogen.
How does the elemental composition of R groups affect amino acids?
It determines their chemical properties and bonding abilities.
What happens to proteins when they are outside their normal pH or temperature range?
Hydrogen bonds and charge attractions can break, leading to loss of function.