Sports Med Knee Injuries
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
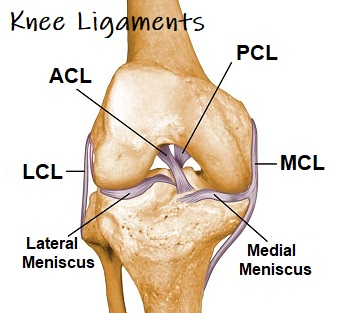
Ligaments of the knee:
ACL (Anterior Cruciate)
PCL (Posterior Cruciate)
LCL (Lateral Collateral)
MCL (Medial Collateral)
ACL sprain mechanism:
Plant and cut
Excessive hyperextension
ACL Sprain signs and symptoms:
Pop or snap
Rapid swelling intra articular
loss of function
instability
PCL sprain mechanism:
Direct blow to anterior tibia
Excsessive hyper flexion
athlete falls and a bent knee bears full weight
PCL Sprain signs and symptoms:
Pop or snap
Minimal swelling
MCL sprain mechanism:
Direct to blow to the outside of the knee
MCL sprain signs and symptoms:
1st degree
2nd degree
3rd degree
LCL sprain mechanism:
Direct blow to the medial side of the knee
LCL sprain signs and symptoms:
1st degree
2nd degree
3rd degree
What injury is more common: MCL sprain or LCL sprain?
MCL
Patellar Tendonitis (jumpers knee) mechanism:
Over use/continual jumping
Chronic
Patellar Tendonitis signs and symptoms:
Quad weakness
point tender
minimal swelling
pain
What is chondromalacia?
Patellar tracking problems
Patella grates across femur casuing the cartilage behind the patella to scrape and wear away
Chondromalacia treatment:
Strengthen Vastus Medialis (controls patella)
correct form
Patella Dislocation Mechanism:
Knee is flexed and forced to turn around
Patella Dislocation signs and symptoms:
Deformity
Pain
Patella Dislocation treatment:
crutches, refer, reduce if trained
What is Osgood-Schlatter’s disorder
microscopic tearing away of soft tissue at tibial tuberosity during pubety, adolescents
Osgood-Schlatter mechanism
repetitive stress
Osgood-Schlatter signs and symptoms
Knee discomfort
swelling tendons
pain during activity
Meniscus function
absorption and stability
Meniscus tear mechanism
Twisting motion of the knee
Can happen with hyper extension or hyper flexion
Unhappy triad:
Injury to ACL, meniscus, and MCL