Wounds and hygiene NCLEX
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What’s the integumentary system?
The skin’s LARGEST organ, it is the body’s first line of defense against microorganisms, environmental factors, regulating temperature, and sensing pain and pressure.
Pressure injuries
localized damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue caused by prolonged pressure, friction, and/or shear.
Prolonged pressure leads to
Tissue ischemia and necrosis
Risk factors that cause pressure injuries include
Impaired mobility, frequent moisture exposure, and decreased sensory perception.
RISK FACTORS FOR PRESSURE INJURIES (SORES) EXAMPLES
Sensory perception (neuropathy, paralysis)
Mobility (paraplegia, stroke)
Friction and shear
Moisture exposure (incontinence)
Nutrition
Perfusion (peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus.
When do you preform skin assessments?
FIRST upon admission
then on regular intervals
What scale do you use to assess pressure injuries?
Braden Scale
What’s the score range on the Braden scale for a skin assessment?
6-23
On the Braden scale score range when the number more than ___ indicates that the patient is at risk for a pressure injury?
<18 (more than 18)
What are 5 pressure point areas on the body for pressure injuries?
Head
Shoulder blades
Elbows
Sacrum
Heels
If the patient slides down or is pulled down the skin might
Shear (tear)
For clients with darker skin, assess for pressure injuries by comparing….
Temperature and blanching (condition where the skin may appear pale or white) of affected area to that of the surrounding skin.
What should you NOT to an area that it affected by a pressure injury?
Reddened or affected areas of the skin should not be massaged, it could cause further tissue injury.
What do you have to DOCUMENT when your patient has a pressure injury?
Wound location
Size
Color
Tissue involvement
Drainage characteristics
Serous drainage
Clear, watery
Serosanguineous drainage
Pink or red-tinged
Sanguineous drainage
Bright red which is a sign of ACTIVE BLEEDING.
Purulent Drainage
Thick, yellow, green indicates INFECTION
What are the signs of infection of a wound?
Purulent
Foul smelling drainage
Edema (swelling)
Fever
Warmth
Excessive/ high amount of drainage.
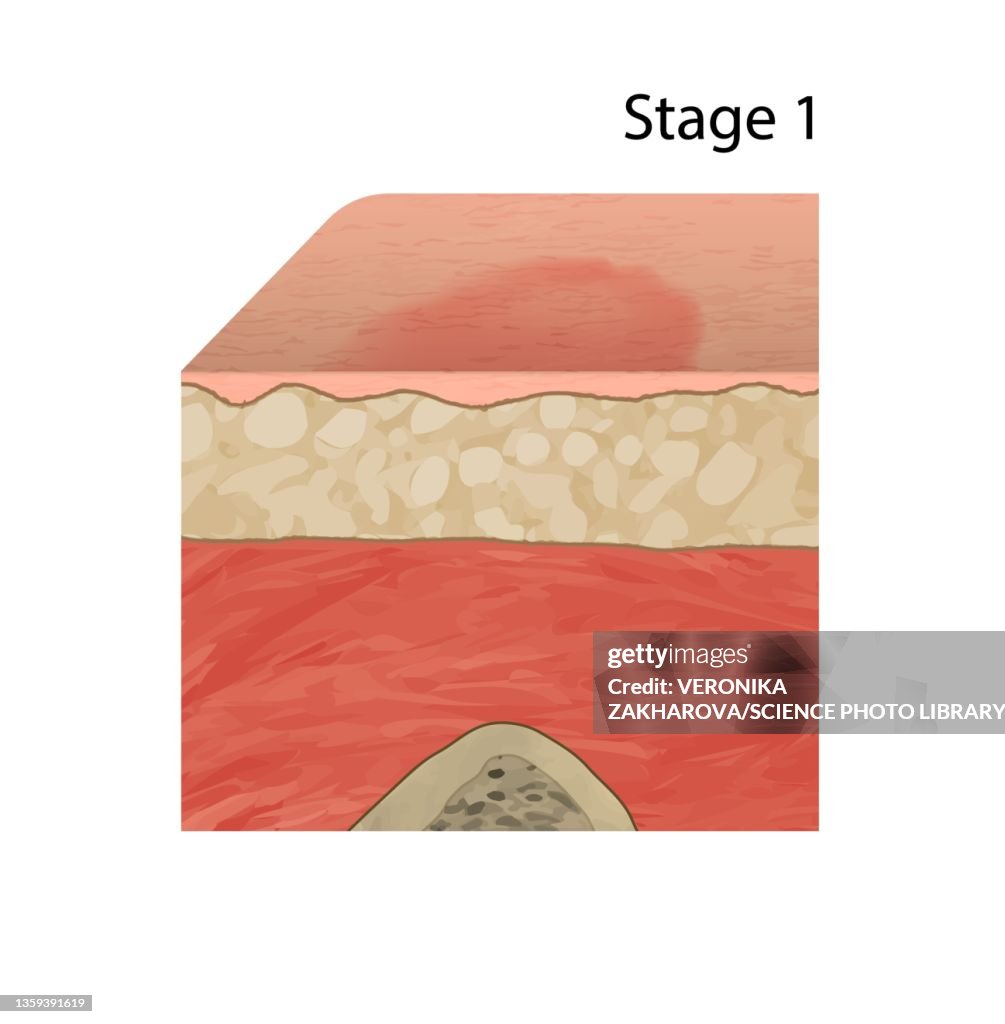
Stage 1
Intact skin with non-blanchable redness
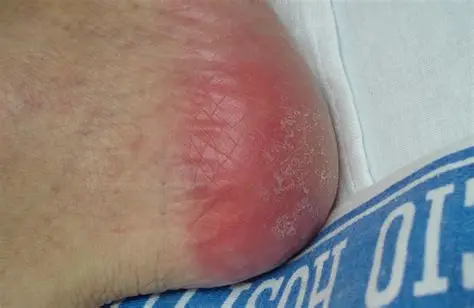
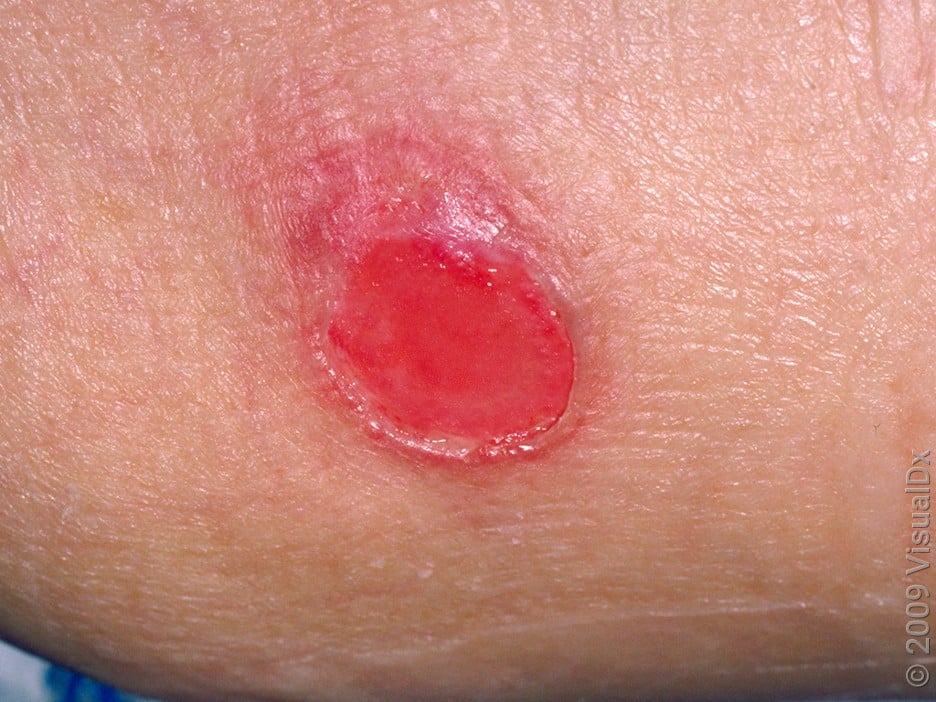
Stage 2
Partial-thickness loss with shallow wound or blister
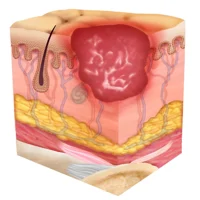
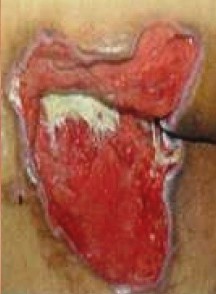
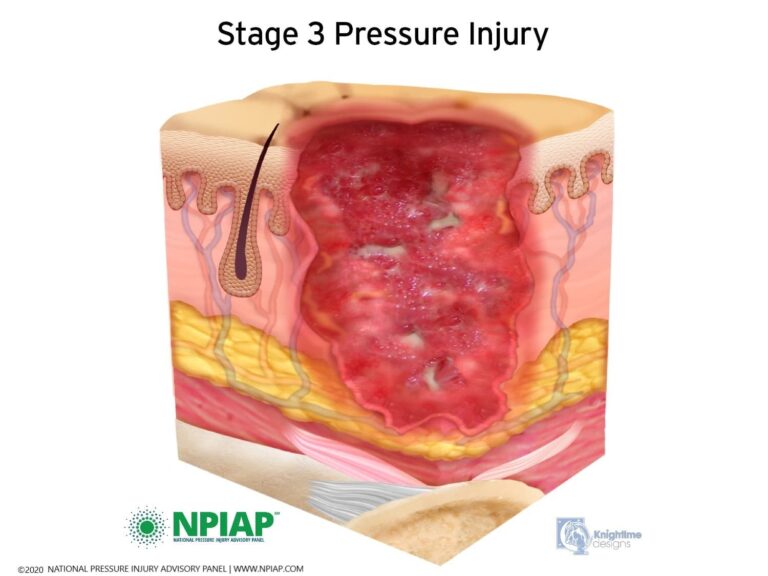
Stage 3
Full-thickness loss with visible subcutaneous tissue
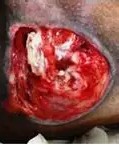
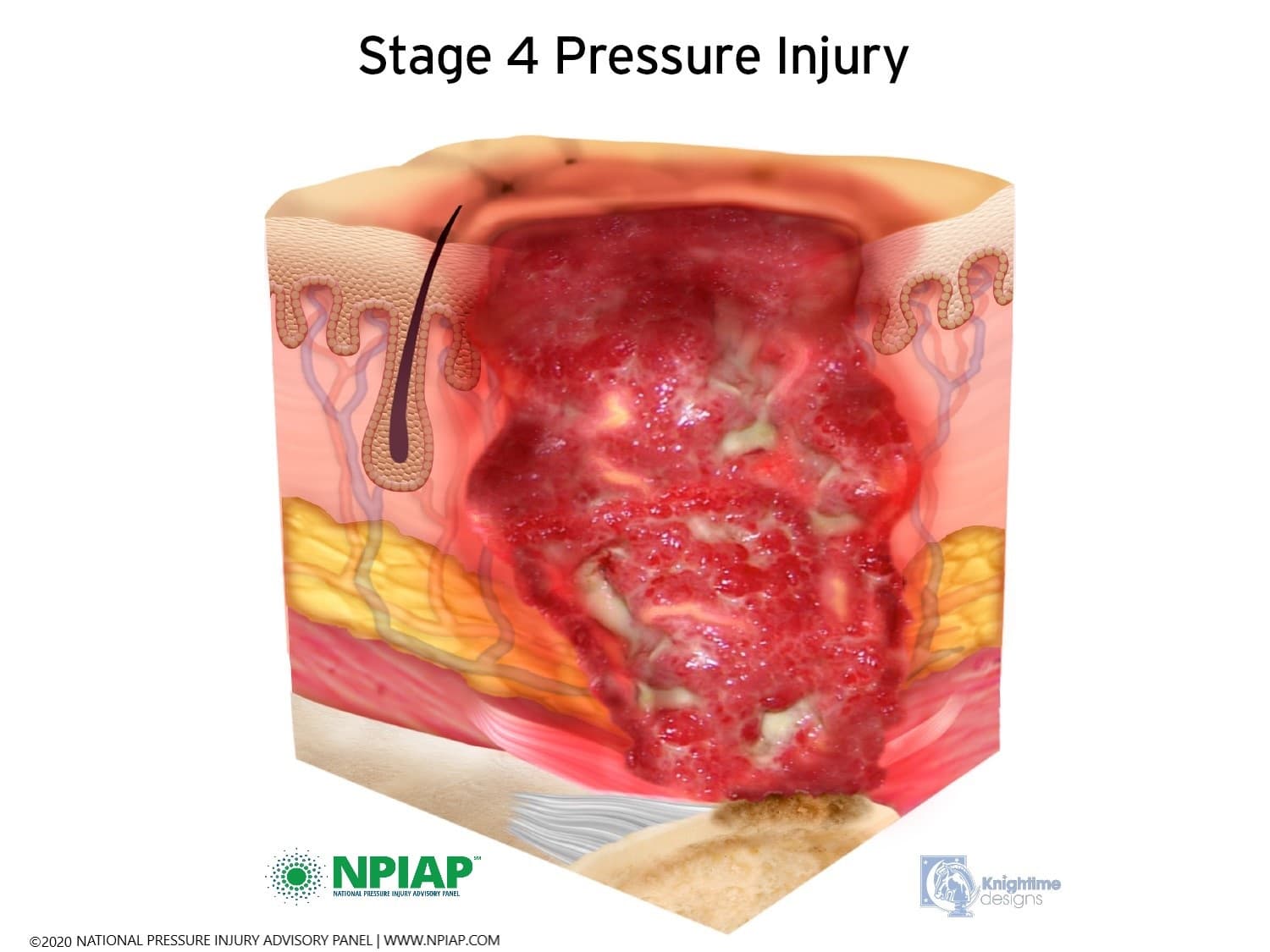
Stage 4
Full-thickness loss with exposed muscle, tendon, or bone

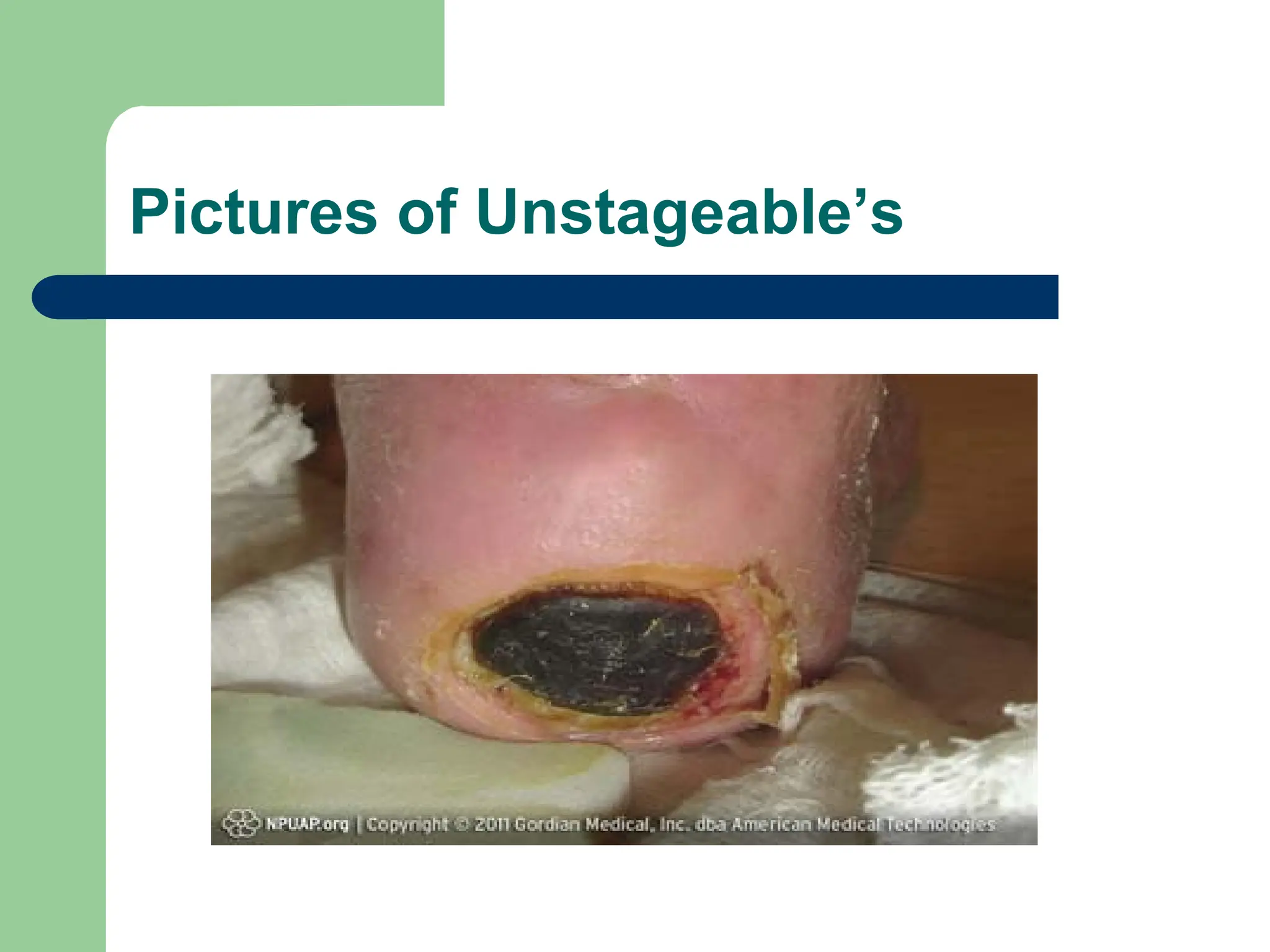
Unstageable
Full-thickness loss; slough and/or eschar obstruct wound visualization.
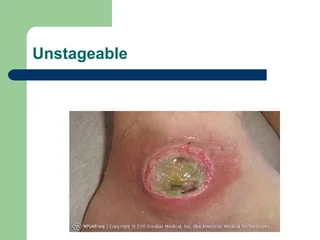
Unstageable “Slough”
Stringy yellow or white tissue.
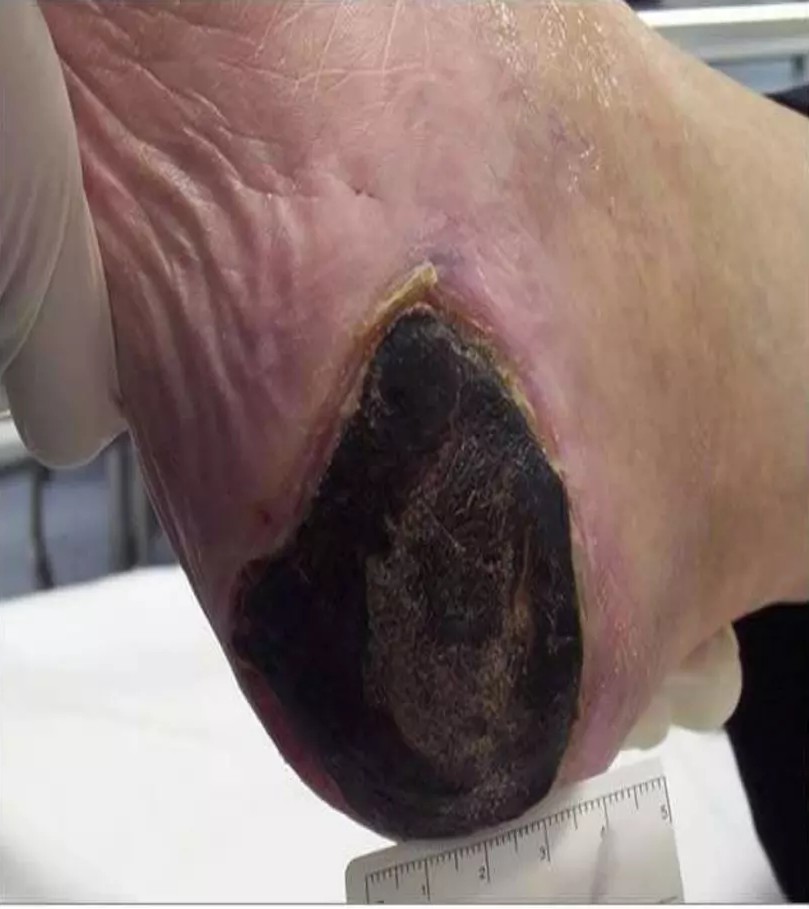
Unstageable “Eschar”
Black, brown, or tan necrotic tissue.
What should the nurse do when an unstageable pressure injury has “slough” or “eschar”
Slough and eschar must be removed (debrided) to visualize and stage the wound bed.
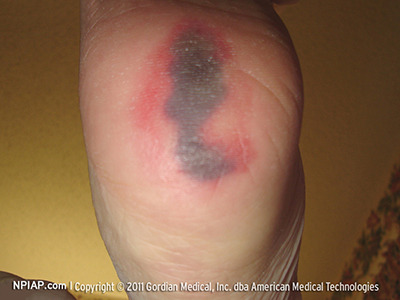
Deep tissue pressure injury
Non-blanchable, dark discoloration (red or purple) that feels spongy or boggy
Nursing Intervention #1 for pressure injury
Repositioning and offloading pressure
Nursing intervention #2 for pressure injuries
Protecting skin
Nursing intervention #3 for pressure injuries
Promoting nutrition and hydration
Every ___hours a patient should be turned
Every 2 hours
Lateral tilt the bed ___ degrees to lower risk of pressure injuries risk on bony prominences.
30 degrees
Head of bead (HOB) should be elevated to ___
30
What can you use to aleviate the body for pressure injuries
pillows, wedges, heel protectors, mattress overlay
DO NOT USE ___when seated
donut cushions because it decreases perfusion to the affected area
What are lifting devices that can be used to “boost” the patient
draw sheet, mechanical sheet
When a wound is healing what does it need?
A moist environment, removing any excess drainage.
Wound dressing depends on
Wound characteristics
(for draining, wounds, moist dressings for dry wounds)
Before beginning a wound dressing or wound change you first
Premedicate with oral analgesics 30-45 minutes prior,
Before beginning a wound dressing or wound change you second
Don appropriate PPE; wear gown, mask, and goggles when there is a risk of splash (wound irrigation).
When wound dressing or wound change you third
Remove old dressing by pulling tape toward the center of the wound.
When wound dressing or wound change you fourth
Don clean gloves, cleanse wound with sterile saline, and clean from center to edges (least to most contaminated)
Do not use povidone-iodine or hydrogen peroxide (cytotoxic).
Perform wound irrigation as needed using sterile technique.
Gently flush wound from top to bottom until fluid runs clear.
After wound care you report
Signs of infection (e.g., foul odor, purulent drainage) and anticipate:
Wound culture: Irrigate or clean wound before
Collecting culture directly from the wound base.
Antibiotics as prescribed
Maintain wound drains to remove drainage from surgical wounds
Transparent film (dressing)
Protects wound and allows
visualization
Moist (dressing)
Maintains moisture for
autolytic debridement
Hydrocolloid, hydrogel
Absorbent (dressing)
Absorbs excessive drainage
Foam, gauze, alginate
Antimicrobial (dressing)
Accelerate healing
Contains silver
sulfadiazine, chlorhexidine
Dry, superficial
wounds (stage 1
pressure injuries), what type of dressing do you use?
Transparent film
Minimal drainage or
dry wounds (necrotic, granulating
wounds) what type of dressing do you use?
Moist
Deep wounds with
heavy drainage, what type of dressing do you use?
Absorbent
Infected wounds and burns, what type of dressing do you use?
Antimicrobial
Wound drains: Jackson-Pratt and Hemovac
Compress drain reservoir before sealing to maintain suction.
Record output and notify HCP for changes in drainage characteristics or amount.
To clean skin (or around affected area) you should always use ___ soap and ___ water
mild soap and warm water NOT HOT
Clients with incontinence make sure they have
absorbent pads and barrier creams to keep skin dry. AWLAYS immediately change soiled linens.
Apply ___ to prevent skin from cracking
Moisturizer
Gently flush wounds from ___ to ___ until fluids run ___
Top
Bottom
Clear
Wash body from ___ to ___
Head
Toes
you should always pat the skin dry but especially between the fold (what are examples of these folds)
under breasts and axillae
Do NOT apply lotion where?
in between toes, increases risk of infection
perineal care for women
Separate labia and clean front to back to prevent UTIs.
perineal care for men
Clean in a circular motion from urethra to glans (from center outward).
Uncircumcised: Retract, clean, and return
foreskin to prevent constriction.
What should you take IMPORTANT consideration when trimming nails?
Specialized foot care should be preformed on a patient with Diabetes Mellitus or peripheral vascular disease, due to foot injury or infection. These clients are prone to infection and wounds are difficult to heal which can lead to complications.
Trim nails straight across to prevent ingrown nails.
YOU NEED HCP ORDER BEFORE CUTTING OR TRIMMING NAILS.
For oral care what should the head of the bed be raised by?
Semi-Flowlers to prevent aspiration.
Patients with high bleeding risks (taking anti-coagulants) use
soft bristle toothbrush
Clients on ventilators, how to you provide oral care?
Provide oral care with chlorhexidine to decrease risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia.
clients going through radiation and chemotherapy treatment (oral care)
Provide frequent oral care and monitor for signs of mucositis (inflammation of the mouth, redness, mouth pain)
Clients with dentures
Clean daily and store in water in a labeled container to prevent accidental disposal.
Oral precaution for children
Do not let children take milk or juice to bed, as it can increase risk for dental caries.
Post-mortem Care
Provide emotional support to the client’s family and allow them time to view the body.
Respect religious and cultural preferences and ask
family if they wish to participate in postmortem care.
Report death to the appropriate organ donation
agency or staff, if applicable.
What position should the patient be in during postmortem care
Position patient in supine with head on a pillow to prevent skin discoloration.
Postmortem cleaning
Remove medical equipment per agency policy.
Gently clean the body, close eyes, brush hair,
Insert dentures (if applicable), and cover with a sheet.
What should the deceased patient have before transportation
Apply identification tags before transporting the body.