PSY100 Final UofT
1/308
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
309 Terms
Lev Vgotsky Cognitive Development (zone of proximal development and scaffolding)
More emphasis on sociocultural factors
Zone of proximal development: Things learner can do with help as opposed to doing on their own or cannot do
Scaffolding: Gradually developing competence in a subject, learners can be helped to move beyond current developmental level
False-belief task (TofM)
Someone places an object down and leaves, the object is moved and the person returns. Where will the person look for the object
If no TofM child will say they’ll look in the new location
If TofM child will say they’ll look in the old location
Theory of Mind
Child can disregard own knowledge and acknowledge a different kind of knowledge (usually by age 5)
Egocentrism
Inability to think that other people’s views of the world exist
Piaget’s Cognitive Development 4 Stages
Sensorimotor stage (0-2 years): acquiring information only through the senses, object permanence
primary circular reactions: infant interactions with own body
Secondary circular reactions: repetition of actions involving external object
Tertiary circular reactions: children adapt tactics to surroundings
Preoperational Stage (2-6 years): Begin to think symbolically, he believed that they lacked understanding law of conservation
Concrete Operational Stage (6-11 years): Develop more logical thinking, but limited to concrete objects
Formal Operational Stage (12+ years): Able to think and reason abstractly, deductive reasoning and problem solving
Jean Piaget Cognitive Development (assimilation, accommodation, equilibration)
During each stage of development, children form schemas (ways of perceiving, organising, and thinking about how the world works)
Assimilation: incorporating new information into existing schema
Accommodation: modifying existing schemas or creating new ones to fit new information
Equilibration: balancing assimilation and accommodation so our cognitive structures match reality
Eric Erikson’s Psychosocial Model
Lifespan theory of development
Trust vs Mistrust (birth to 2 years)
Identity vs Role Confusion (adolescence)
Intimacy vs Isolation (early adulthood)
4 Types of parenting styles

Mary Ainsworth’s “Strange Situation” Test
Secure attachment, insecure-resistant, insecure-avoidant, disorganised attachment
Secure attachment: upset when caregiver leaves, comforted upon return
Insecure-resistant (anxious-ambivalent): clings to caregiver, gets upset, wants and resists comfort
Insecure-avoidant: little distress when caregiver leaves, avoids caregiver upon return
Disorganised attachment: inconsistent, odd behaviours
Harry Harlow Experiment
Cloth mother vs wire milk mother
Monkey preferred cloth mother but went to wire mother for milk
Attachment Theory
Emotional bond with caregivers early in life, it’s adaptive which means it encourages proximity between child and caregiver, oxytocin plays an important role
What are the brain development trends with blooming and pruning
Synapse formation till age two, then pruning, then second period of overproduction in the prefrontal cortex just before adolescence followed by about a decade of pruning
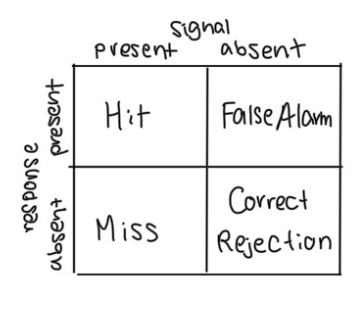
Signal Detection Theory
Common research techniques for determining what infants know (there’s two)
Preferential looking technique: if baby prefers one stimulus it has a preference
Habituation/Orienting reflex: something new is presented to us we orient to it
Windows of plasticity
Sensory, then motor/language, then higher cognition
Reflexes present at birth
Grasping, rooting, sucking
Auditory Transmission Steps
Outer Ear (pinna, tympanic membrane), Middle ear (middle ear bones, oval window), Inner ear (cochlea, basilar membrane (pitch)), auditory nerve, medulla (bottom most part of brain, controls vital processes like heartbeat and blood pressure), midbrain, thalamus, primary auditory cortex
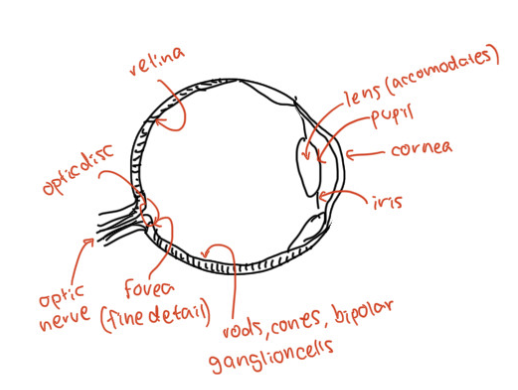
Parts of the Eye
Fusiform Face Area (FFA)
Particularly active when people look at faces
Interpreter
Left-hemisphere process that attempts to make sense out of events (remember left-hemisphere is responsible for language)
Lateralization of Function
Localisation of a function in right or left hemisphere
E.g, language in the left
Motion parallax
Objects that are further away seem to move slower than objects that are closer
Muller Lyer Illusion
Lines might look different in length when in reality they’re the same length
Monocular depth cues
Occlusion, relative size, familiar size, linear perspective, texture gradient, and position relative to horizon
Binocular depth cues (Retinal Disparity)
For depth perception, caused by distance between the eyes and comparing disparity between two retinal images
6 Gestalt Principles
Figure Ground
Illusory contours: we perceive contours even when the don’t exist
Objects close together are grouped together (proximity)
Points that form smooth lines when connected belong together (continuity)
Seeing a complete unbroken image even when there’s gaps (closure)
We group figures together that resemble each other (similarity)
Agnosia
Inability to recognise and name objects, but can still use them
Ventral vs Doral stream
Ventral: perception of information about objects (“what”)
Dorsal: perception of spatial location and other information needed for action (“why”)
What happens when certain motion sensitive neurons are fatigued
Motion after-effects (waterfall illusion)
Opponent-process theory
Focus on ganglion cells, three opposing pairs (if one Color pair is stimulated, other is inhibited)
Red/Green, Yellow/Blue, White/Black
Trichromatic theory
Color perception determined by ratio of activity of 3 types of cones
3 types of cones
S cones (short wavelengths blue)
M cones (medium wavelengths green)
L cones (long wavelengths red)
Visual transmission steps
rods and cones -> bipolar, a machine, horizontal cells -> ganglion cells/optic nerve -> thalamus -> primary visual cortex
Cones
Color perception
Rods
Black and white perception
Photoreceptors
Convert photons to electrical signal (transduction)
Nociceptors
Responsible for sensing pain
Sensory homunculus
Representation of how much cortical space is devoted to each sense
Gate control theory of pain
For pain to be experienced pain must be activated the neural “gate” in the spinal chord must be open
Two different types of fibres in pain reception
Myelinated (“A delta”) fibres: sharp immediate pain
Non-myelinated (“C”) fibres: dull steady pain
primary somatosensory cortex
Connected parts of the body tend to be represented beside each other (somatotropin organisation)
More sensitive regions have more cortical areas devoted to them
Contralateral organisation
Left hemisphere processes right sensations and vice versa
Somatosensory cortex
Processes pain (in the parietal lobe), touch, pressure, temperature, position, movement and vibration
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to mechanical distortion or pressure, most sensitive in the cochlea for sound transduction
Vestibular system
In the inner ear, responsible for body position and movement
Where are olfactory receptors located
Olfactory epithelium (mucosa), thin layer of tissues embedded with smell receptors which transmit information to olfactory bulb and then the olfactory cortex
Where are taste receptors located?
Taste buds
Signal-detection (2 step process)
Intensity of stimulus
Individual observer’s criteria for deciding whether stimulus occurred
Psychophysics
Studying relationship between stimuli (physics) and perception of stimuli (psyche/mind)
Bottom-up processing
Incoming signals construct perceptions
Top-down processing
Knowledge from prior experience used to perceive stimulus
Sensory adaptation
Reduced response to unchanging stimulus
Difference threshold
Noticeable difference between two stimuli (minimum amount of change required for a person to detect a difference 50% of the time)
Absolute threshold
Minimum intensity of stimulus that must occur before you experience sensation
Synesthesia
Stimulation of one pathway = simultaneous stimulation of another pathway
Transduction
Translation from stimulus to neural signal
Perception
Involves processing and interpreting sensory signals resulting in internal representation of stimuli and conscious experience of it
Sensation
Detection of external stimuli, responses to those stimuli, and transmission of responses to the brain
Prefrontal cortex
Attention, regulation, memory processing, response inhibition
Orbitofrontal cortex
Emotion, antisocial personality disorder, receives info for senses (except touch)
Nucleus accumbens
Important for brain’s reward system, motivation, emotion, addiction, memory, learning, release dopamine
Neurogenesis
Creation of new neurons (hippocampus and olfactory bulb), contributes to plasticity
Glia
Supporting cells, provide structural matrix, clean up debris, form myelin sheath, holds neurons in place, reflexes, body functions (e.g, heart rate), blood-brain barrier
Executive Functions
Set of mental skills that help people manage information, make decisions and plan ahead
Include working memory, cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, self-awareness, emotional regulation, motivational regulation
cingulate cortex
Part of the limbic system, processes pain, empathy, impulse control, motivation and decision making
HPA axis
Hormone system that helps the body manage stress and maintain homeostasis
Example of plasticity and rats
Enriched rats had more synapses and neural connections
Impoverished rats had less
Is the nervous or endocrine system slower
Endocrine
Coordinated system process in the endocrine system
Hypothalamus secretary’s releasing factor which causes pituitary gland to release a hormone specific to that factor. Hormone travels through bloodstream to target sites
What neurons does the somatic system use primarily
Motor neurons (efferent)
Sometimes use sensory neurons
Peripheral Nervous System
Transmits info to the CNS and responds to messages from CNS to perform certain behaviours or make bodily adjustments
somatic and autonomic
Cerebral cortex lobes
Occipital (primary visual cortex)
Parietal (primary sensory cortex)
Temporal (primary auditory cortex)
Frontal (primary motor cortex)
Corpus Callosum
Connects hemispheres and allows info to flow between
Cerebral cortex
Outer layer of brain, each hemisphere has four lobes
Limbic System
Hippocampus: formation and storage of long-term memory and amygdala: processing fear, essential to our ability to associate things with emotional responses
Basal Ganglia
Motor control
Diencephalon: thalamus and hypothalamus
Hypothalamus: regulatory structure -> nervous system to endocrine (4 Fs)
Thalamus: relay station, sensory information except smell
Cerebellum
Coordinated movement and balance
Reticular formation
Alertness, sleep
Brainstem
Controls functions of the autonomic nervous system including breathing digestion, heartbeat, etc.
Neuroplasticity
Brain is plastic
Agonist vs antagonist
Agonist: bind to receptors and mimics neurotransmitter, or increasing release of neurotransmitters, blocking re-uptake of neurotransmitters
Antagonist: inhibiting action of neurotransmitter by blocking release, destroying neurotransmitters, mimicking neurotransmitter and blocking binding
Epineprine & norepinephrine
Stress response, fight or flight
Acetycholine
Movement; memory, cognition, sleep
Dopamine
Reward and motivation, voluntary movement
Serotonin
Mood, impulsiveness, hunger, sleep
GABA
Primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Glutamate
Primary excitatory neurotransmitter (GO)
Presynaptic membrane vs postsynaptic membrane
Presynaptic: membrane of the neuron that is sending the signal
Postsynaptic: membrane of the neuron that is receiving the signal
All-or-None Principle
A neuron fires with the same magnitude each time, frequency can vary
Excitatory vs Inhibitory signals
Excitatory: increase likelihood of neuron firing
Inhibitory: decrease likelihood of neuron firing
Action potential process
Positive in the nodes of ravenier, negative at the myelin sheaths

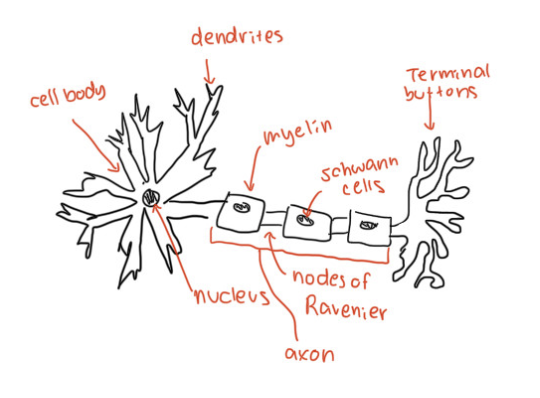
Parts of a Neuron
Neuron Types
Sensory (afferent): to the brain
Motor (efferent): exit the brain
Interneurons (between afferent and efferent)
PNS and its components
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System (conscious)
Autonomic Nervous System (unconscious)
Sympathetic Nervous System: system on alert
Parasympathetic Nervous System: relax systems
CNS and its components
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal chord
Heredity vs Heritability
Heredity: Genetic transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring
Heritability: estimate of the genetic proportion of the variation in some specific traits (within a population)
Estimate of heritability: % of variation that is explained by genetic differences
Epigenetics
Changes in gene expression due to non-genetic influences
Francis Galton
Eugenics guy
Reproducibility vs Replicability
Reproducibility: study can be duplicated in method and/or analysis
Replicability: study about phenomenon produces similar results from previous study of same phenomenon
close/exact: trying to recreate original study
Conceptual: test same underlying hypothesis or theory, may use different methods