Culturing, Counting, and identifying microbes in ecosystems (CH 26)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is axenic?
a pure culture
What is a possible solution for culturing microbes with fastidious growth requirements?
assess growth capabilities of similar microbes
grow in diffusion chambers
What are 2 possible solutions for culturing microbes that rely on signals or cross-feeding from other microbes?
co-cultivate
use diffusion chambers
Are all bacteria culturable? If not, what are some potential reasons why?
no
fastidious growth requirements
dependence on other communities
dormant or in a viable but not culturable state
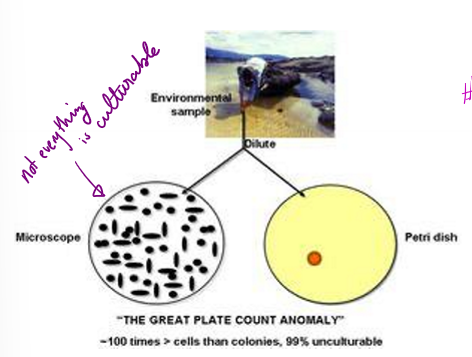
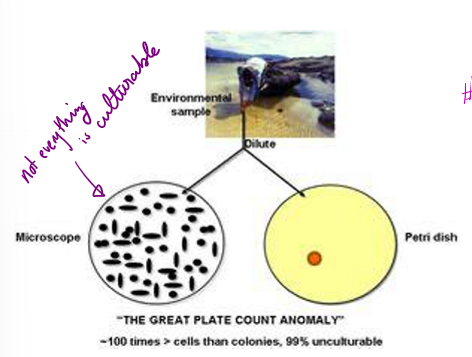
What does the great plate count anomaly refer to?
number in a sample is significantly higher than the number able to be cultured on a plate
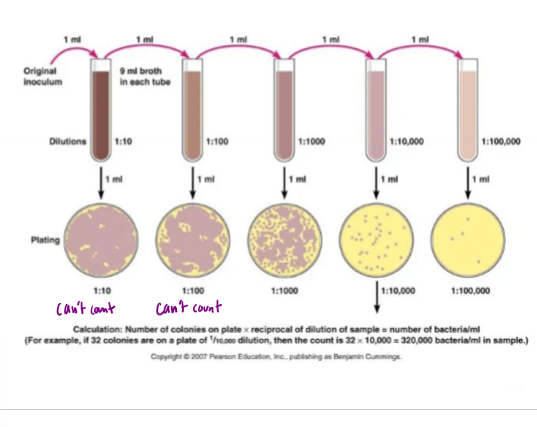
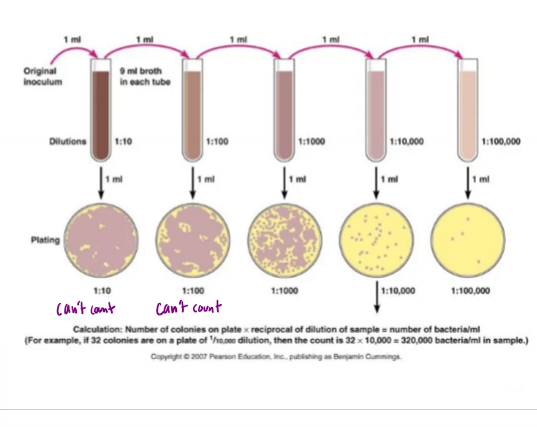
Describe 1:10 serial dilution and what it is useful for
used to estimate microbial population sizes in a sample
best way to get viable count (if bacteria is culturable)
dilute 1ml of sample to 9mL of broth, taking 1mL from each successive sample and diluting in 9mL of broth
streak 3 plates for each broth, and find countable plates with 30-300 colonies
Calculate the number of colonies/mL in sample
ex. if 1/10,000 dilution with 32 colonies, 32×10,000 = 320,000 bacteria/mL in sample
If a 1:10 serial dilution has been performed 3 times and 122 distinct colonies are formed, how many bacteria are present per mL of sample?
10³ = 122 x 10^3 = 122,000 bacteria/mL in sample.
If a 1:10 serial dilution are on a plate of 1/100,000 dilution and 33 distinct colonies are formed, how many bacteria are present per mL of sample?
100,000×33 = 3,300,000 bacteria/mL in sample.
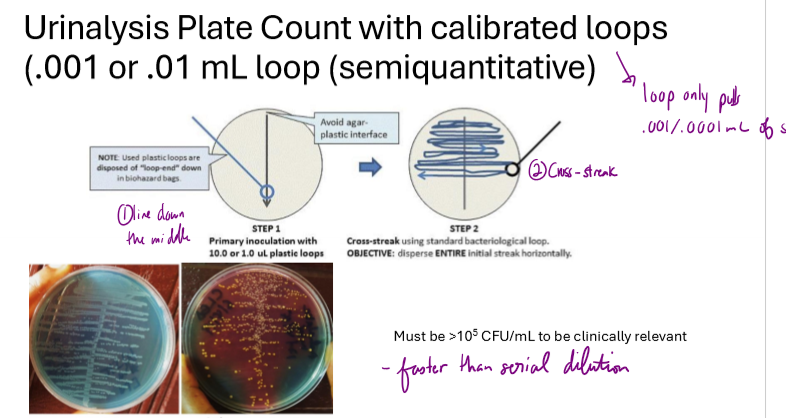
What is a urinalysis plate count?
used to measure bacteria in urine sample
use .001/.0001mL loops
draws a line down the middle of a TSA plate then cross streaks
must have greater than 10^5 microbes/mL to be clinically relevant
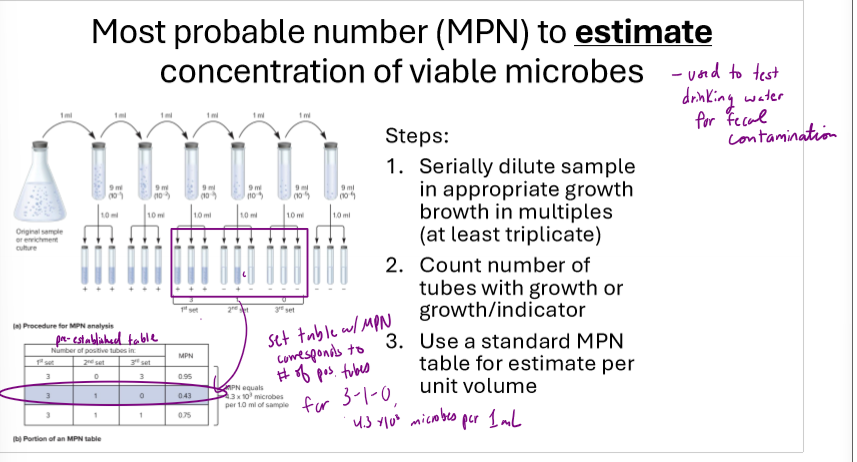
How does a Most probable number (MPN) estimate work?
serially dilute sample in growth broth several times
create 3 1mL tubes from each dilution
count number of tubes with growth
use a standardized MPN table to estimate bacteria/mL
What are coliforms? Include their morphology, fermentation, and significance.
indicator organisms of potential fecal contamination
gram negative bacilli
non spore forming
ferment lactose to acid and gas
present in feces of warm-blooded animals, wide spread in soil
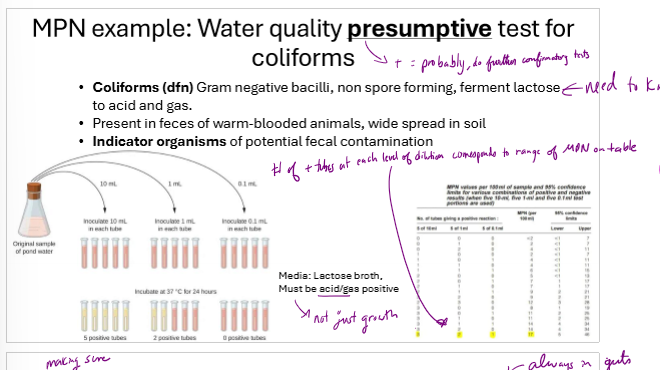
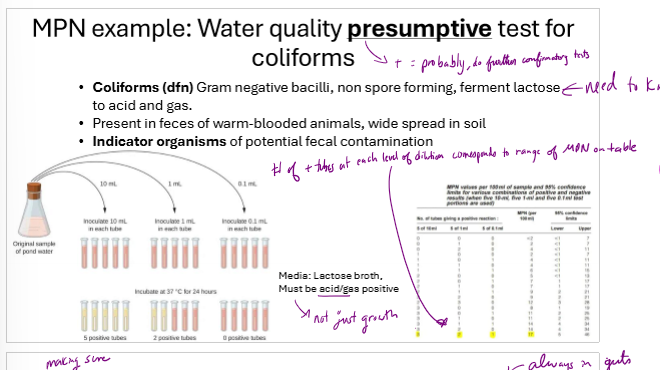
How are coliforms in water often initially counted?
using MPN, dilute multiple times and inoculate several tubes from each dilution. infer concentration using standardized MPN table using number of positive tubes
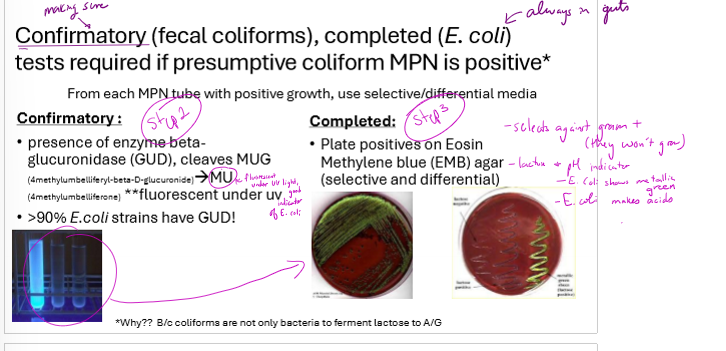
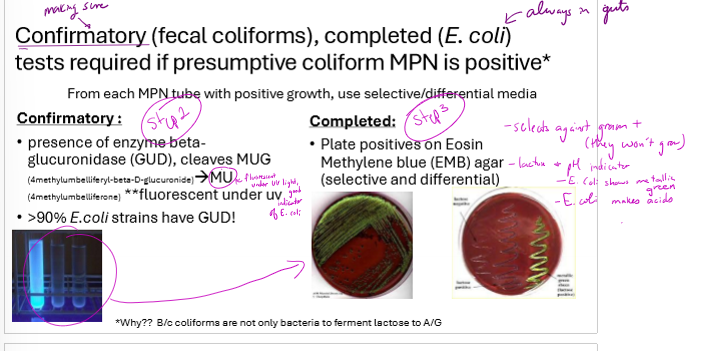
What are the steps for confirming coliforms in water? Include the counting method and decisiveness of each test
presumptibe test: MPN on samples, dilute multiple times, inoculate multiple tubes from each dilution and refer to standardized MPN table for bacteria/mL based on number of positive tubes
confirmatory test: 90% of E. coli strains have GUD. from each MPN tube with positive growth, test for presence of GUD cleaving MUG to MU. will be fluorescent.
complete test: plate positives from confirmatory test on EMB agar. selects against gram positive bacteria and E. coli will appear metallic green. confirms fecal contamination
What are other ways to tell viable cells other than culturing?
staining
FAME analysis
MALDI-ToF
sequencing
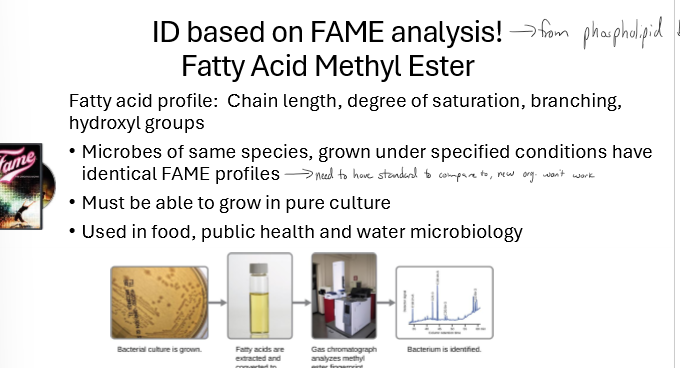
What is FAME analysis and what are some limitations?
fatty acid methyl ester
used to classify organisms
fatty acids from cell membranes extracted and looked at for chain length, degree of saturation, branching, and hydroxyl groups
microbes of the same species grown under specific conditions have identical FAME profiles
limitations: must be able to grow in pure culture
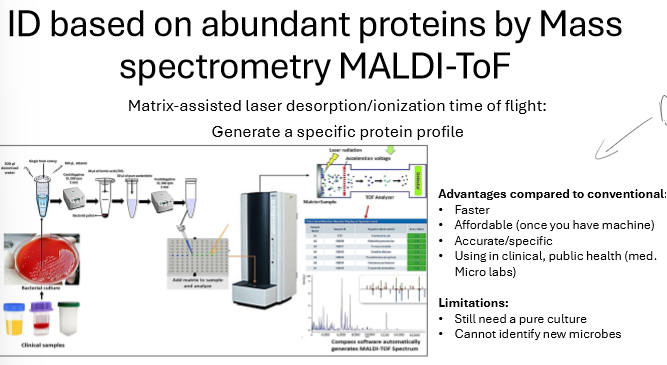
What is mass spectrometry MALDI-ToF? What are the advantages and limitations?
matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight
generates a specific protein profile to ID microbe
advantage: fast, affordable, accurate, good in clinical settings
limitations: need pure culture, can’t identify new microbes
How can organisms be ID’d based on molecular techniques?
signature sequences: sequence using PCR; can ID nonculturable organisms
Whole genome sequencing: determine nucleotide identity to determine species
What are the methods of microbial community analysis?
FISH - fluorescently tag microbes
Metagenomics - comprehensive population diversity from DNA sequencing