psych 120a midterm dis only
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
synapse
where neurons are transferred from one neuron to another
gray matter
cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axonswhi
white amtter
myelinated axons, increases speed of conduction
anterior
front
posterior
back
dorsal/superior
upper/top
ventral/inferior
lower/bottom
lateral
side
medial
middle
how is the brain categorized
in a meaningful way - info can be transferred faster if neurons are closer tgt
sensory homunculus
the more connections you have from something you use more, the larger physically that part of the brain gets
neuroimaging techniques focus
look at the brain structurally
goals of neuroimaging techniques
volume - see which brain regions are larger/smaller
diagnosis - various clinical differentiations
functional associations - which regions are more/less active during a task
brain more active, need more resources, can measure metabolic changes
cognitive subtraction
based on logic can find 2 tasks differing in components to find effect of experimental component
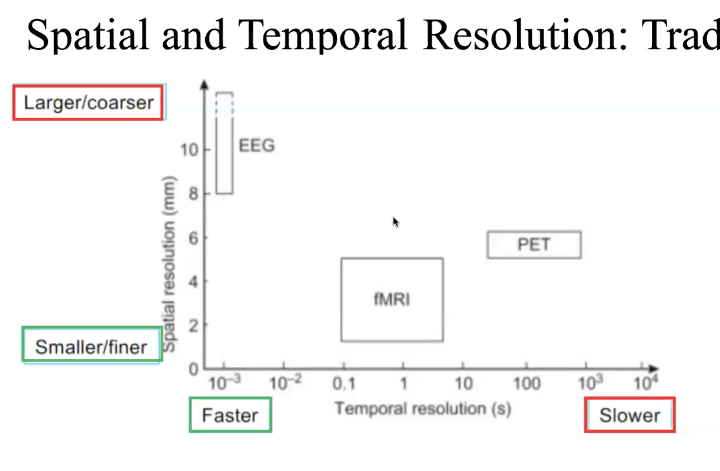
PET
positron emission tomography - visualizes active brain areas via injection of tracer (radioactive substance) into blood, revealing where blood is going, showing active areas that need O
indirect measure of brain activity
PET advantage and disadvantage
adv
relatively good spatial resolution
can aid in diagnosis of disorders
disadv
poor temporal resolution
invasive (uses radioactivity)
expensive
fMRI
functional magnetic resonance imaging - examine where brain is active during task. measures blood flow based on O signal (which perturbs local magnetic field)
indrect
fMRI adv and disadv
adv
spatial resolution - precise localizetion
non invasive
widely available
disadv
so so temporal - better than PET, worse than EEG
expensive
very loud
EEG adv and disadv
electroencephalography?
adv
more direct - only one looking at neural activity directly - neurons firing
good temporal resolution
non invasive
relatively inexpensive
portable formats avail
disadv
poor spatial resolution
skull and brain tissue distort electrical fields
TMS
transcranial magnetic stimulation - coil on top of head, send electrical pulse traveling through skull and into brain to alter brain activity
TMS adv and disadv
adv
safe, non invasive, temporary
experimentally contorlled
test necessity of specific brain regions (causal evidence)
good temporal resolution
disadv
relatively brief effects
greater impact on surface cortical areas
potential spread of activations
not effective on deeper brain regions
resolution tradeoff
gestalt principles
how humans process info - naturally group similar elements, recognize, and simplify complex images when perceiving
template theory
for object recognition. template for everything, match input to mental template. may involve mental transformations.
problem: too many templates
RBC
recognition by components. use geons to reconstruct objects
problem: difficult to extract geons from real images, too many geon candidates, deriving structural reps can be hard, etc.
problem w/ template and RBC
no mechanism for contextual influences
shape constancy
angle viewing the shape
size constancy
adjustment for distance of an object
brightness constancy
correct perception of object regardless of actual luminance conditions
3 properties of visual perception
shape constancy
size constancy
brightness constancy
selective attention
Focus on 1 task while simultaneously ignoring everything else
Dichotic listening task
demonstrates selective attention
Attended channel
shadow, or repeat what they hear
Unattended channel
told to ignore what’s going on, can report physical attributes but usually not semantic
Early selection hypothesis
Only attended input is analyzed and perceived
Unattended info little to no analysis and never perceived
Late selection
All inputs analyzed
Selection occurs after analysis
Only attended info reaches consciousness
3 selective attention models
broadbent’s (early) filter model
attenuator theory (treisman)
late selection model (deustch & deustch)
broadbent’s early filter model
unattended stimulus is fully ignored
meaning of unattended ignored
attenuator theory
treisman
unattended msgs attenuated and attended msgs enhanced
late selection model
deustch and deustch
meaning of an unattended stimulus is processed
which of early or late selection hypothesis true
depends on exact circumstances
spatial attention
mechanism by which person focuses on particular position in space
attention as spotlight
beam of spotlight represents region of space youre prepared for, inside beam processed more efficiently
posner attention study
reaction times faster when appeared on side they told would appear
change blindness
failure to notice that some aspect of a scene has changed over time
occurs while attention is engaged in current task, but spotlighting elsewhere
inattentional blindness
failure to notice existence of an unexpected yet fully visible item
occurs while attn is engaged in some demanding task
endogenous control of attention
you choose what you pay attention to
exogenous control of attention
element of a scene (stimulus of some kind) seizes your attention
top down processing
bottom up processing
modal model
atkinson & shiffrin
Sensory registers as buffers, preventing input from overloading STM
Bidirectional b/t STM and LTM - LTM can affect what we’re processing in STM
iconic memory
associated w/ visual system
no limit to amt of visual info held
rapid decay (<1 sec)
echoic memory
serial position effect
where each word is located in a list affects likelihood of correct recall
primacy effect
more opportunity for rehearsal of words presented first
recency effect
words experienced most recently still present in working memory