APHG Unit 5 — Agricultural and land use patterns\processes
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What is agriculture?
Agriculture is the science, art, and practice of cultivating the soil, growing crops, and raising animals for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain and enhance human life.
What types of crops are grown in tropical climates?
Coffee, sugar, pineapple
What kind of crops are grown in sub tropical regions?
Rice, cotton, tobacco
What types of crops and livestock are common in dry climates?
Cattle, sheep, goats, horses, and camels
What crops are common in Mediterranean climates?
Grapes, olives, and dates
What crops are common in warm-mid latitude climates?
Vegetables, fruits, rice
What type of crops are common in cold, mid latitude climates?
Wheat, barley, livestock, and cows
What reduced barriers in growing food?
Advancements in agricultural technology such as different fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides that increase yield
What is yield?
Amount of agricultural production harvested per unit of land
What are GMOS.
Genetically modified organism are organisms whose genomes have been altered to promote specific traits that allow for increased production in livestock production. This usually occurs by feeding animals foods that are not apart if their diet to fatten them, and injecting them with growth hormones.
What are intensive agricultural practices?
Practices that often require less land, but require more capital and labor, which are traditionally located closer to larger population centers.
What are some examples of intensive agricultural practices?
mixed crop and livestock, plantation agriculture, and market gardening
What is plantation agriculture?
Usually located in periphery countries located in tropical climates, and many crops grown are cash crops which are grown for sale on the market and not for use by the grower.
What is mixed crop and livestock agriculture?
Mixed crop and livestock agriculture is a farming system in which both crops and livestock are raised on the same farm
What is market gardening?
Market gardening is a type of small-scale farming that focuses on the intensive production of vegetables, fruits, and flowers for sale in local markets. Usually occurs in areas that have longer growing seasons, such as the southeastern part of the US
What are extensive agricultural practices?
Practices that tend to use less labor and capital, but require more land for the production of food. Crops in this climate often have a lowe yield and are grown away from population centers.
What are some examples of extensive agricultural practices?
Shifting cultivation, nomadic herding, and ranching
What is shifting cultivation?
Usually in tropical climates located in rainforests, and burns down areas to make room for farming (slash and burn)
What is nomadic herding?
Common in central of southwest Asia/Northern Africa, herders move cattle, sheep, or goats
What is ranching?
In areas where the land is not ideal for farming, less expansive and rather away from population centers
What is a clustered pattern and what is a dispersed pattern?
Settlements are very close to each other and dispersed is when they are very far away from each other.
What is terrace farming?
Common in Southeast and east Asia, method of farming that involves planting crops on graduated terraces on the slope of a mountain of hill. Used in areas with less land available.
What is a long lot survey map?
A narrow parcel of land that traditionally connects to a waterway. Originally popular in Europe and areas that were settled in by the French such as Louisiana and Quebec
What is metes and bounds?
Boundary that is based off landmarks in a geographical area to create the boundary (based in Europe
What is township and range?
Survey method that creates a grid pattern by creating rectangular prism of land (originally used in the US)
What was the first agricultural revolution? (Also known as the Neolithic revolution)
Occurred in the Fertile Crescent (Middle East - between Euphrates and Tigris river). Was a time period in which humans shifted from hunters and gatherers to sedentary agricultural practices.
What were the agricultural hearths?
Fertile Crescent, Sub-Saharan Africa, Central America, East Asia, and Southwest Asia
What was the Colombian exchange?
The transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the old and new world
What were some effects of the Columbian exchange?
Reduced the amount of famine in Europe due to food surplus, but also lead to the spread of many diseases which killed millions of indigenous people
What was the Silk Road?
Network of trade routes that United China and the Mediterranean from roughly around 130 bce to 1450 ce
What were some byproducts of the Silk Road?
Lead to new goods, services, plants, animals, and ideas to be introduced to different geographic areas around the world
What was the second agricultural revolution?
Has its roots in Britain thanks tot eh Industrial Revolution, which lead to a flood of new agricultural inventions (gin, seed dril, seed plow, grain elevator, etc.)
What is cross breeding?
The identical mating of two different breeds of varieties of the same plant or animals to produce offspring with desirable traits. Can result in hybrid seeds which have shorter growing seasons and are more resistant to different climates,
What is another effect of hybrid seeds being invented?
Efficiency uh farming because farmers could now have multiple harvests in year
What are some advancements in chemical usage?
Increased the use of chemical pesticides, fertilizers, and herbicides, as well as increasing yields of crops.
What are herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers?
Pesticides - used for destroying insects and invasive species, Herbcides - target invasive plants and destroys unwanted vegetation, Fertilizer - used to increase plant growth
Describe the rise in mechanized farming?
Lead to increased food production, less global hunger, new economic growth, and cheaper food and production costs
What was a negative byproduct of the rise in mechanized farming?
Lead to decreased amount of jobs for women who worked in traditional agriculture
What was the enclosure movement?
Movement in England which took publicly owned land used for agriculture and privatized it (countered the tragedy of the commons which was the abuse of shared resources by the general public)
What was the green revolution?
Characterized by the development of high yield seeds, increased chemical usage, and mechanical farming. Food production goes up and price goes down which leads to food surplus and reduced hunger
Who was at the forefront of the green revolution?
Dr Normal Borlaug - who developed disease resistant, high yield wheat. Helped increase food production globally and is credited of being the pioneer behind the green revolution
What are some negative consequences of the green revolution?
It increased soil degradation, water contamination, and monoculture farming — which is the peat ice of growing one type of crop on a large scale or over a wide area
What is a consequence of monoculture?
Lead to more efficiency and profit, but can lead to soil depletion and reduced biodiversity
What were the consequences of the green revolution?
Industrial and commercial farms grew and family owned farmers declined
What is agribusiness?
Large scale industrialized and coroporate controlled food production system, includes farming, processing, distribution, and marketing of agricultural products.
What is a global consequence of agribusiness?
Many periphery and semi periphery countries become dependent on core countries and multinational corporations because large Argo business often controlled the distribution of high yield seeds and chemical fertilizers
What is commercial agriculture?
Producing food for profit, more prominent in MDCS as ldcs lack funds to run businesses due to lack of advanced machinery
what is monoculture?
The practice of cultivating a single crop at a given time (periodic- crop may be switched)
What are economies of scale?
As a company grows, it is able to reduce the average cost to produce its product (as companies get larger, they have access to more capitol, which allows them to scale up productions
What is the von thunen model?
Model that was first proposed in 1826 by johan henrich von thunen
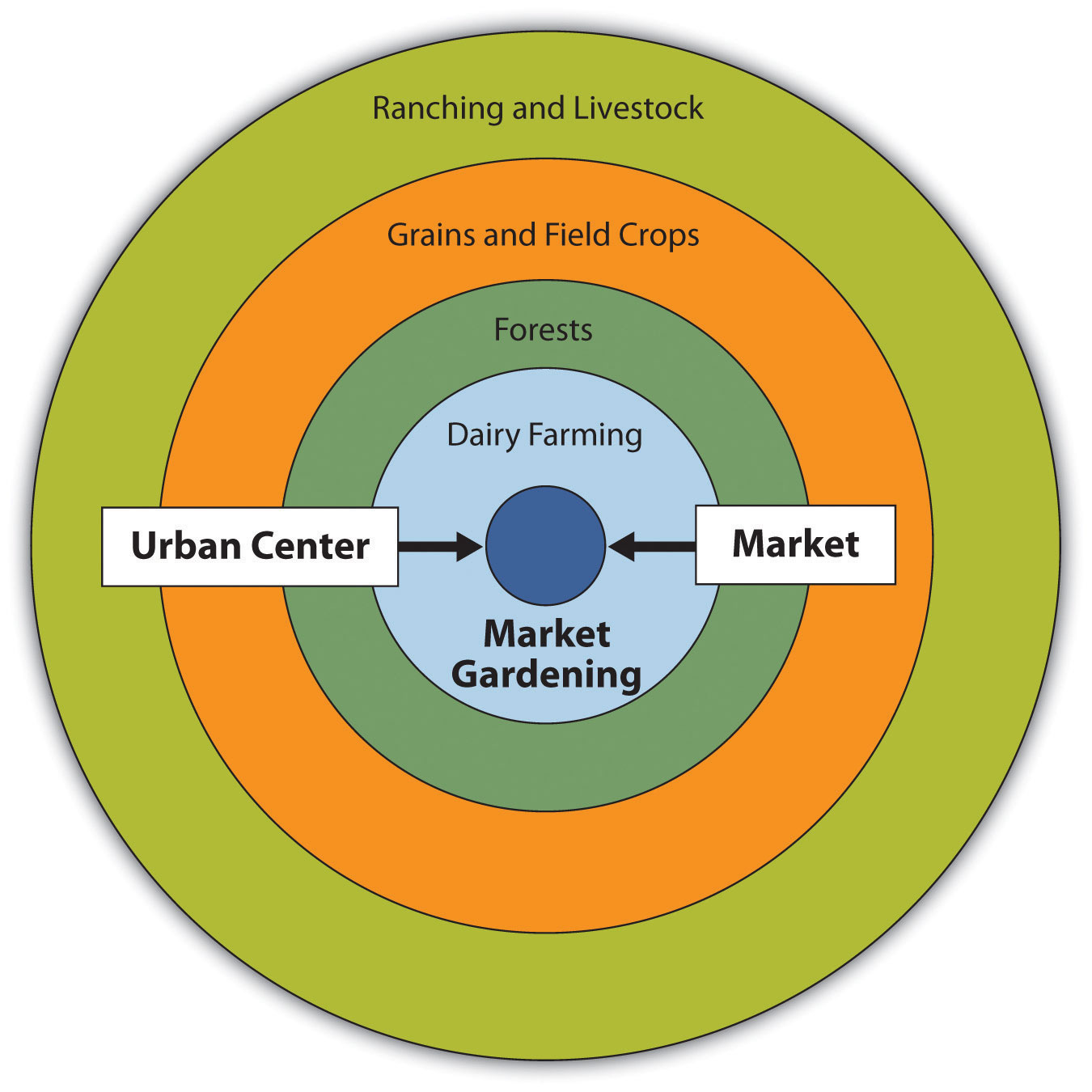
What are the assumptions of the von thunen model?
Land is flat, there is a single market, and all land has equal access to the market
What is bid rent theory?
Bid rent theory explains how land users compete for land near a central market. It posits that land value decreases as distance from the market increases, leading to different bids for land based on the user's ability to pay. It is the driving force behind the Von Thunen model
Why is livestock so far away from the market?
Farmers can help offset transportation costs with the savings they get from cheaper land ranching
How has globalization effected the economy?
It has allowed companies to create large commodity chains and global supply chains, as well as helping producers achieve economies of scale. Has also changed diets, traditions, and cultural landscape.
How has participation in the global food trade impacted countries?
Countries no longer need to produce all of their own food or wait for growing seasons, since they can purchase food from other countries with favorable climates for the crops they are seeking to buy
How are Ukraine and Russia an example of interdependence in the global food supply chain?
Ukraine and Russia are significant suppliers of wheat and other grains, which are essential for global food security. Their production and export activities directly affect food prices and availability worldwide, highlighting how conflicts or shifts in either country can lead to food supply disruptions in other nations.
How are Ukraine and Russia an example of interdependence in the global food supply chain?
Ukraine and Russia are significant suppliers of wheat and other grains, which are essential for global food security. Their production and export activities directly affect food prices and availability worldwide, highlighting how conflicts or shifts in either country can lead to food supply disruptions in other nations.
How has advancements in agriculture unevenly impacted countries?
More developed countries have access to more agricultural resources and often control the distribution of high yield seeds and farming equipment, as well as having access to more robust transportation networks which makes it easier for them to sell and export their products
How do periphery countries have a cycle of food export and insecurity?
Periphery countries have growing populations and need food —> farmers need to increase yield and output —> loca markets are nor profitable and farmers turn to foreign markets —> farmers earn more money which helps them buy new equipment —> allows farmers to increase output and yield —> less food is produced for local populations due to exports
What is commodity dependence?
When a country has more than 60% of its exports made up of just commodities, many countries in the periphery & semi periphery have economies that are commodity dependent.
What is a commodity?
A commodity is a basic good used in commerce that is interchangeable with other goods of the same type, often a raw material or primary agricultural product such as oil, gold, or wheat
What are government subsidies?
A financial incentive or payment that is given by a government to support a specific industry, company, or individual (goal is to promote production of certain products or practices)
What describes the relationship between core and periphery countries in the global food supply chain?
Periphery and semi periphery countries have their natural resources, cheaper labor costs, and looser regulations exploited by core countries
What did the expansion of commercial agriculture cause?
Health concerns over pollution, sustainability, and treatment of animals, but also lead to increased food production, which helped global food insecurity
What is desertification?
The process by which arable land loses its fertility and becomes a dessert.
What are pastoral nomads?
Herders that migrate with their livestock: can cause desertificationz by overgrazing
What is soil salinization?
When excessive amounts of salt build up in soil, which makes it difficult for plants and crops to grow
What is soil erosion?
The wearing away and displacement of the upper layer of soil due to human activities, water, wind, and other natural factors
What are wetlands?
Area of land saturated with water, often consisting of marshes, swamps, or bogs. Act as a filter system for water runoff, such as rainwater from irrigation methods. Can cause polluted water to enter local bodies of water
What is irrigation?
Irrigation is the artificial application of water to soil or land to assist in the growing of crops and to maintain landscapes. It is used to provide moisture to plants when there is insufficient rainfall.
What is a negative side effect of mono cropping?
Reduces biodiversity in a ecosystem
What is a food desert?
A food desert is a geographic area where access to affordable, healthy food options is limited or nonexistent, particularly in urban environments where fresh fruits and vegetables are hard to obtain
What is a food desert?
A food desert is a geographic area where access to affordable, healthy food options is limited or nonexistent, particularly in urban environments where fresh fruits and vegetables are hard to obtain
What can cause the formation of a food desert?
Food deserts can form due to factors such as lack of access to affordable, healthy food options, urban planning that limits grocery store accessibility, lack of access to personal vehicles, economic constraints that affect food pricing, and social issues like poverty or low community investment
What is urban sprawl?
Urban sprawl is the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into the surrounding rural land, characterized by low-density development, increased reliance on automobiles, and often leading to the loss of agricultural land and natural habitats
What is suburbanization?
Suburbanization is the process by which people move from urban areas to residential areas on the outskirts of a city, typically leading to the growth of suburbs
What is a negative byproduct of suburbanization and urban sprawl
Reduces amount of land available for agriculture
What is community supported agriculture?
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) is a farming model where consumers buy shares of a farm's harvest in advance, providing farmers with upfront capital and allowing consumers to receive fresh produce directly from the farm throughout the growing season (monthly or weekly).
What are food miles?
The distance food is transported from the producer to the consumer. More food miles means more pollution, food miles are responsible for about 6% of the worlds greenhouse gas emissions
What is urban farming?
Small scale farms located in suburban or urban areas that cultivate different agricultural products; typically located in backyards, balconies, or community gardens
Where are farms most likely to operate?
Areas that offer more agricultural subsidies, cheaper land costs, and pro-farm policies. Subsidized crops have more production.
What is the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)?
NAFTA is a trade agreement between the United States, Canada, and Mexico that was implemented in 1994. It aimed to eliminate trade barriers and promote free trade among the three countries, facilitating increased economic cooperation and commerce.
What are some effects of the NAFTA agreement?
Made it easier to trade between countries and removed tariffs, but put many Mexican farmers our of work — which lead to increased emigration out of Mexico
What is organic farming?
Organic farming is an agricultural method that emphasizes the use of natural processes and inputs, avoiding synthetic chemicals and fertilizers, and promoting biodiversity and ecological balance
What are fair trade policies?
Fair trade policies and practices aim to create equitable trading conditions for producers in developing countries by ensuring fair wages, decent working conditions, and sustainable livelihoods.
What are fair trade practices?
They promote environmentally friendly practices and encourage direct trade relationships between consumers and producers. Allow for producers of goods to gain profit rather than large corporations
What are value added crops?
Value added crops are agricultural products that have been processed or transformed to increase their market value. This can include products like jams, salsas, and gourmet food items that require additional labor and processing beyond the raw agricultural product.
What is the informal economy?
The informal economy encompasses economic activities that are not regulated, monitored, or taxed by the government. This includes unregistered businesses, casual labor, and trades that operate outside of the formal economic framework.
What is the Gender Inequality Index (GII)?
The Gender Inequality Index (GII) is a measure that reflects gender disparities on a scale of 0 to 1, in three key dimensions: reproductive health, empowerment, and labor market participation. It takes into account factors such as maternal mortality, adolescent birth rates, female and male populations with secondary education, and the labor force participation rates of women and men. MDC’s usually have a lower GII
What is agricultural density?
Agricultural density is the ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land in a given area. It helps to measure the intensity of agricultural practices and land use efficiency
What is the tertiary sector?
The tertiary sector of the economy involves the provision of services to consumers and businesses, including services in healthcare, education, retail, hospitality, finance, and entertainment. It focuses on the production and delivery of services rather than goods.
What is the secondary sector?
The secondary sector of the economy involves the processing and manufacturing of goods, transforming raw materials from the primary sector into finished products. It includes industries such as construction, automotive, and textiles.
What is the primary sector?
The primary sector of the economy involves the extraction and harvesting of natural resources. This includes activities such as agriculture, forestry, fishing, and mining, focusing on the production of raw materials.