Opiates + Opioids
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms

- air dried milky exudate
- unripe capsule seed
___________ contains 10-10.5% morphine
___________ camphorated opium tincture
___________ opium tincture or deodorized opium tincture
opium
poppy capsule
powdered opium USP
paregoric
laudanum
___________: any natural or synthetic agent derived from, or structurally related to morphine
___________: opium-like or morphine-like, with reference to a drug’s pharmacological activity (includes enkephalin peptides and endorphins, which are not structurally related to morphine)
____________: neuronally located proteins to which opioid agents bind to + elicit a biological response
opiate (structurally related)
opioid (acts like)
opioid receptors
Morphine belongs to a group of medicines called _________ ________ and acts on the CNS at opioid receptors
Bioavailability of oral morphine is only about ______% and has many unwanted side effects
ER caps/tabs should NOT be used for ________ pain
narcotic analgesics
30%
acute
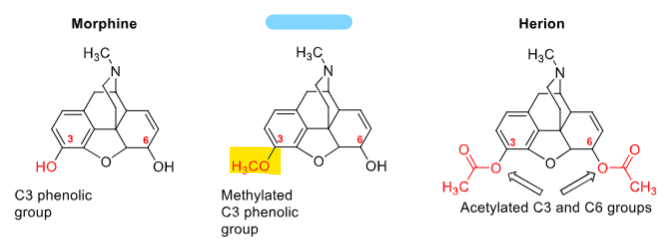
Morphine + Side Effects
Produces several serious limitations as a drug molecule → 5
Methylation of phenolic OH of morphine gives __________ (will decrease analgesic, physical dependence, resp depress, etc)
addictive, resp depression (high doses), emetic (N/V), GI, tolerance
codeine
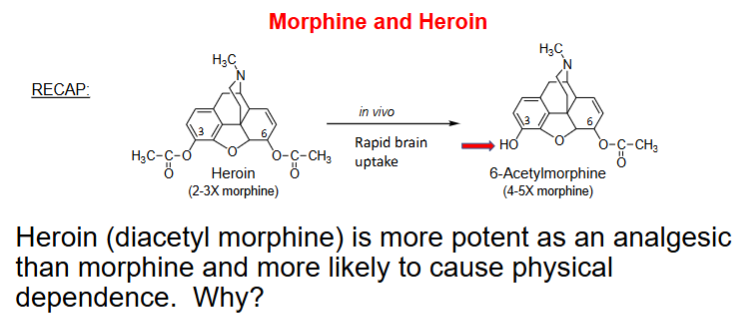
The greater analgesic activity of heroin may result from a combination of more rapid brain uptake due to increased ____________ and a rapid brain _________ of the “less active” to “more active” metabolite
lipophilicity, metabolism
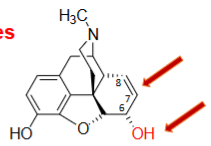
Morphine Derivatives SAR
+analgesic activity
________ C6 OH (OH to =O) and ____________
C6 OH substitution →
__________ of C6 OH group
Conversion of C6 OH to an ________
REQUIRED for analgesic activity
-
-
Oxidation, reduce C7/8 double bond
H, Cl, or F
esterification
ether
C3 OH
tert amine in piperidine ring
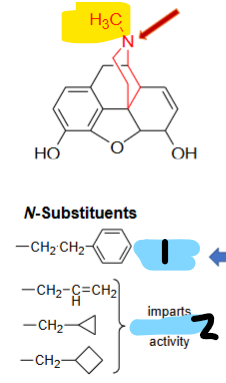
_____ activity
imparts _________ activity
Replacing N-methyl group with a HYDROGEN ______ activity
+
antagonist
-
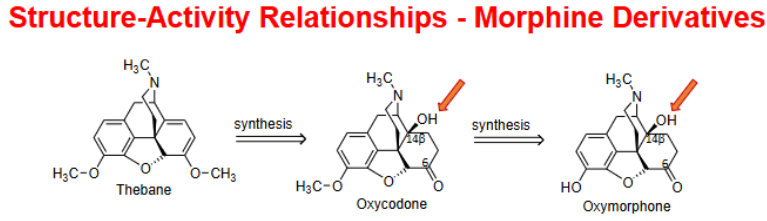
The potent “oxy” analogues:
Oxycodone and Oxymorphone → examples of analogs containing the …
C14 OH + C6 ketone (oxidation)
___________________: increase in analgesia compared to morphine/codeine – examples of 7,8-double bond reduction and C-6 hydroxyl group oxidation → keto group
hydrocodone, hydromorphone
Two well-known analgesic opium alkaloids are present in the seed capsule exudate of the opium poppy. What are they?
morphine, codeine
What common tricyclic aromatic ring system scaffold are morphine-related drugs based on?
phenanthrene
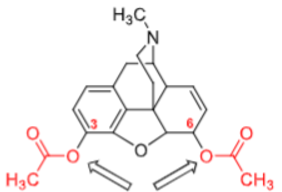
What is the name of this highly addictive synthetic morphine analog?
How is it obtained from morphine?
heroin, acetylation C3 + C6 phenols
What is the side-effect of morphine that is responsible for most patient deaths?
respiratory depression
Codeine is an analgesic when given orally but has NO analgesic activity when given by intracerebral injection. Why?
prodrug → must be activated in liver
What two modifications to the morphine molecule improved analgesic potency and are both present together in the hydromorphone molecule?
C6 oxidation, C7/8 = reduction
What common structural feature do oxycodone and oxymorphone both have that is not present in the structures of hydromorphone and hydrocodone?
C14 OH
__________________: sections of the morphine molecule are cut away in order to determine which parts are essential for analgesic activity, and which parts are superfluous (unnecessary)
molecular trimming
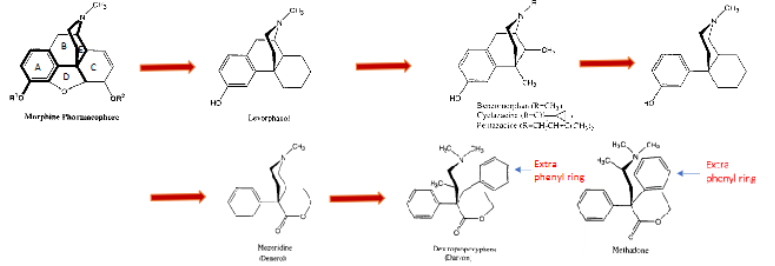
“Molecular Trimming” of the Morphine Molecule
D ring removed → _________ are obtained, ex: levorphanol. levomethorphan → characteristic?
Half of C ring removed → ___________ → analogs = cyclazocine, pentazocine → characteristic?
Cut away B ring → __________ → characteristic?
Open piperidine ring → dextropropoxyphene (________) and ________
morphinans → 3-4x more potent
benzomorphan → mixed agonist/antag
demerol → 10-12% potency
Darvon, methadone
How many fused rings are missing in the Morphinan-based analgesics Levorphanol and Levomethorphan?
How many fused rings are missing in the benzomorphan-related morphine analogs?
1 (D ring)
2 (C and D)
Which severely trimmed morphine analog was not initially designed as a morphine prototype, but still has 1/10th the analgesic potency of morphine?
Demerol/meperidine
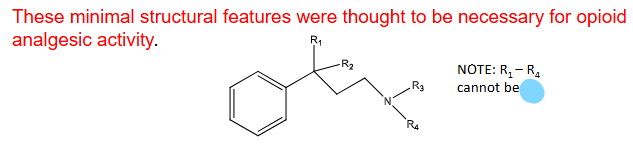
SAR considerations for opioid analgesics
An __________ ring bound to a _________ carbon
A __________ _________
The ^ is separated from the quat carbon by ____ carbon atoms
Four substituents, R1-R4, CANNOT BE _____
aromatic, quaternary
tert nitrogen
2
H
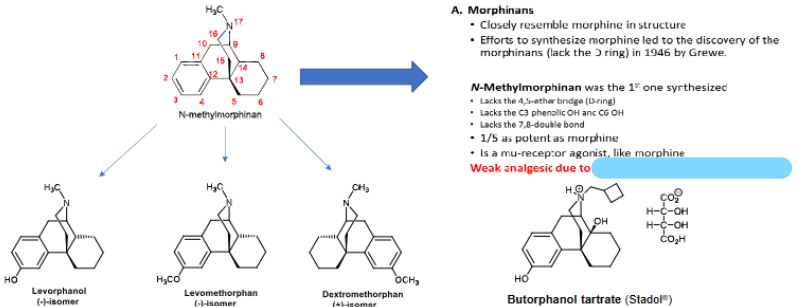
MORPHINANS
Levorphanol interacts w ___________________ receptors → _____x more potent
Levomethorphan causes dysphoria, psychotomimetic effects + hallucinations → ______x more potent
Dextromethorphan used as an ___________ → _________ at HIGH DOSES
N-methylmorphinan was the 1st one synthesized → weak analgesic due to ___________________
Butorphanol tartrate → ____________, 5x more potent → ClnCON:
^ Why does butorphanol act as a partial agonist at opioid receptors?
NMDA Gly + GABA, 6-8x
5x
antitussive, hallucinogen
absence of C3 OH
partial agonist, do not use in CHF/MI
bulky N substituent
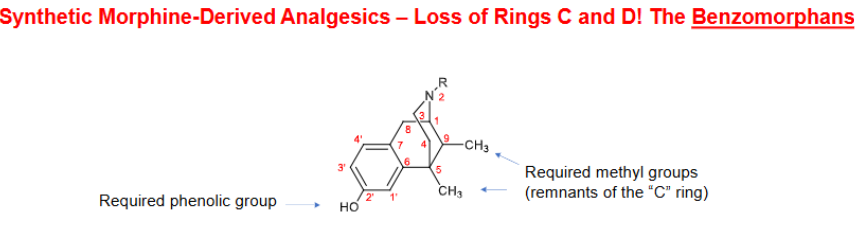
BENZOMORPHANS (D ring + ½ C ring removed)
First series to show any significant separation of analgesic activity from ________ __________
*MOST ACTIVE BENZOMORPHANS possess ___________________
dependence liability
C2 OH, C5 + C9 dimethyl
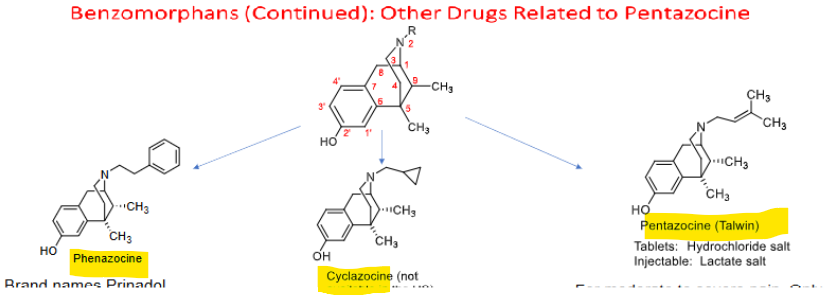
Benzomorphans (cont)
Phenazocine (Prinadol) →
Cyclazocine →
Pentazocine (Talwin) tab + injectable →
no longer marketed in US
not available in US, 1st drug effective in heroin addiction tx
mod-severe pain (1/6 to 1/3 potency of morphine)
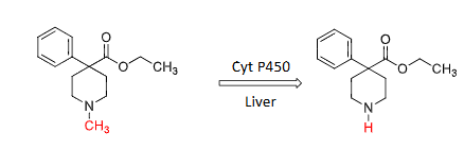
Meperidine (Demerol)
______x as potent as morphine
Synthesized in an effort to find an ________________
____________ may occur when used with a MAOI
Meperidine (N-CH3) → __________ (N-H) TOXIC metabolite limits the use of meperidine to short-term treatment!
0.1x
atropine substitute
serotonin syndrome
normeperidine
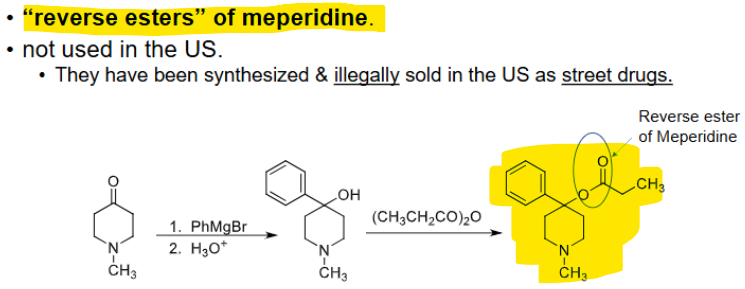
___________ → “reverse esters” of meperidine → ILLEGAL!
prodines
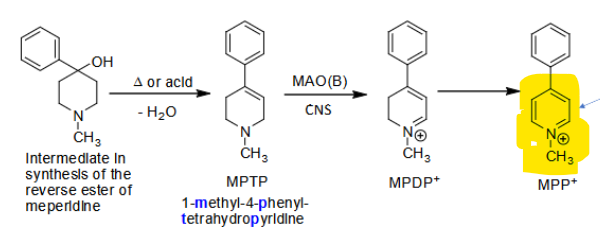
Possibly by-products of PRODINE SYNTHESIS
_________ in the brain causes oxidation of MPTP → MPDP+ → MPP+
MPP+ toxic metabolite → inhibits ________ uptake + destroys neurons in substantia nigra → causes ______________________
MAO(B)
DOPA, irreversible Parkinson effects
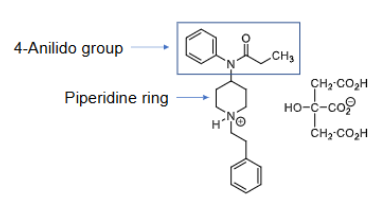
What extremely potent pain modulating molecules belong to the 4-anilidopiperidine class of analgesics?
Broke the pharmacophore rules of opiates!
fentanyls (-fentanils)
Which drugs are 100-200 times more potent than morphine, is used in anesthesia and affords rapid onset and rapid post-operative recovery?
A. sufentanil
B. alfentanil
C. carfentanil
D. remifentanil
E. fentanyl (Sublimaze)
D + E
(sufentanil - 1000x morphine → labor and delivery
alfentanil - 25x morphine
carfentanil - 10,000x morphine → horse tranquilizer)
What Fentanyl-like drug is 10,000 times more potent than morphine, is used as a large animal tranquilizer?
A. sufentanil
B. alfentanil
C. carfentanil
D. remifentanil
c
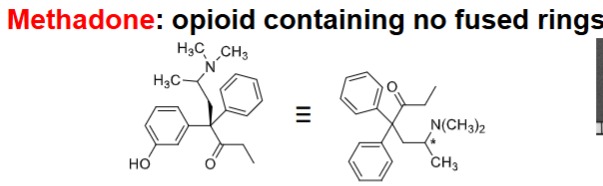
METHADONE (NO fused rings)
Racemate → ___ isomer MOST potent
MOA:
_______ acting than morphine
^ due to active metabolites → name them (3)
Blocks _____ effects of subsequent doses of opiates + blocks ______________ of addicts
R
u-agonist
longer
a-methadol, LAAM, N-demethylation products (1°, 2° active)
euphoric, drug-seeking behavior
T or F:
The secondary amine metabolites have shorter half-lives than methadone.
F (longer)
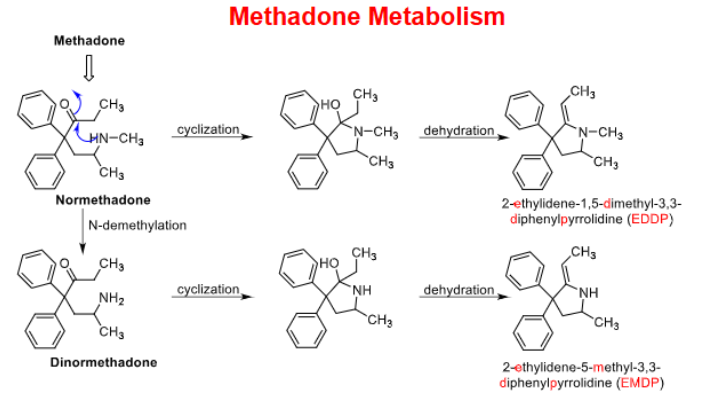
______ and ______ are plasma biomarkers used to identify drug abuse OR for compliance w drug abuse therapy
EDDP, EMDP
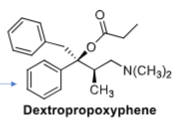
Dextropropoxyphene is a structural variant of methadone (+________ group) that was a widely used analgesic both in the US + Europe UNTIL it was found to have life-threatening _________ effects → MOA: ________ u-agonist → Potency = __________ of morphine
phenyl, cardiotoxicity, weaker, 1/12

Tramadol (Ultram)
Prodrug →
For tx of ___________ pain
Exhibits ______ affinity for u, k, and delta receptors
remove CH3 to activate
mod-severe
equal
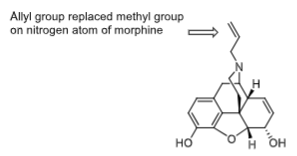
_________ was the first clinically useful opioid receptor ANTAGONIST that has partial agonist effects due to its bulky N substituent
Nalorphine
The severely trimmed down morphine analog methadone can be used for severe pain; what other indication can Methadone be used for?
addiction
What is the primary metabolite(s) of methadone? Does it have analgesic activity?
a-methadol, LAM, yes
What is unique about the analgesic activity of Tramadol when given orally?
Must undergo ________ for good analgesic activity
metabolism (P1 oxidative demethylation)

How is the morphine antagonist NALOXONE different from Nalorphine?
Both are pure ____________
Antagonist selectivity:
Structural differences:
antagonists
Naloxone: u > k > delta, Nalorphine: u = k > delta
C14 OH, reduce C7/8 =, C6 ketone
What is the drug of choice for reversing opioid-induced respiratory depression?
Naloxone (Narcan)
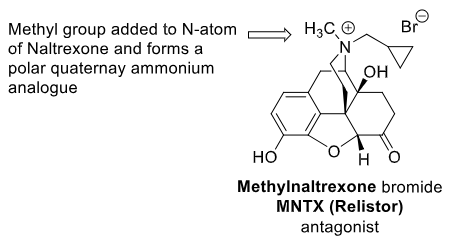
Methylnaltrexone Bromide (Relistor)
_________ acting opioid receptor antagonist (NON-CNS ACTING)
Targets the __________ (cannot pass GI memb or BBB)
Uses: 2
peripherally
GI tract
OIC (opioid induced constipation), chronic non-cancer pain
Buprenorphine (Buprenex)
MOA:
______x potency morphine
Use:
Tx for opioid dependence in combination w naloxone = ____________
Exhibits _____ receptor dissociation kinetics
partial u-agonist
20-50x
mod-severe pain
Suboxone
slow
Suboxone for Opioid Dependence
(Buprenorphine + Naloxone combination drug)
Buprenorphine → u-agonist + k-antagonist → limitations?
Naloxone → pure ________
Suboxone → produces _________ symptoms when INJECTED → reduce parenteral misuse, tx of opioid addiction
u-agonist limited by ceiling effect at higher doses
u-antagonist
withdrawal
Why is the design of Methylnaltrexone Bromide, a quaternary ammonium bromide salt, appropriate considering its therapeutic use?
salt = polar = cannot pass memb = stuck in GI
What features did the Beckett and Casey model of the mu-receptor describe for the binding of morphine?
_______________, such as meperidine and methadone, took on similar shape to that of morphine when binding to the u-receptor
Proposed that newer u-agonists (eg. the ____________) that did NOT resemble morphine did not fit this model
non-rigid opioids
fentanyls
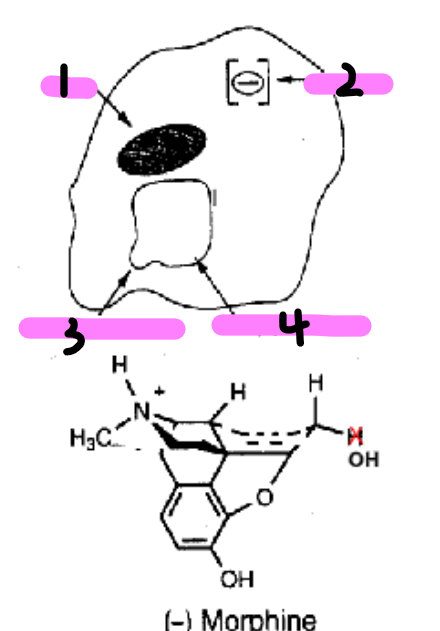
Original model of the u-opioid receptor proposed (Beckett + Casey)
name the parts
cavity
anionic site
H bond acceptor site
flat lipophilic surface
Why did Portoghese formulate his Bimodal Model of the mu-receptor?
→ Reason: If all opioids bind to the receptor in the same conformation + same surface area, then they SHOULD contribute the SAME _____________________
Thus, his bimodel receptor binding model proposed that different opioid series (RIGID OR NON-RIGID) bind to different surface areas of the SAME receptor protein
analgesic effect
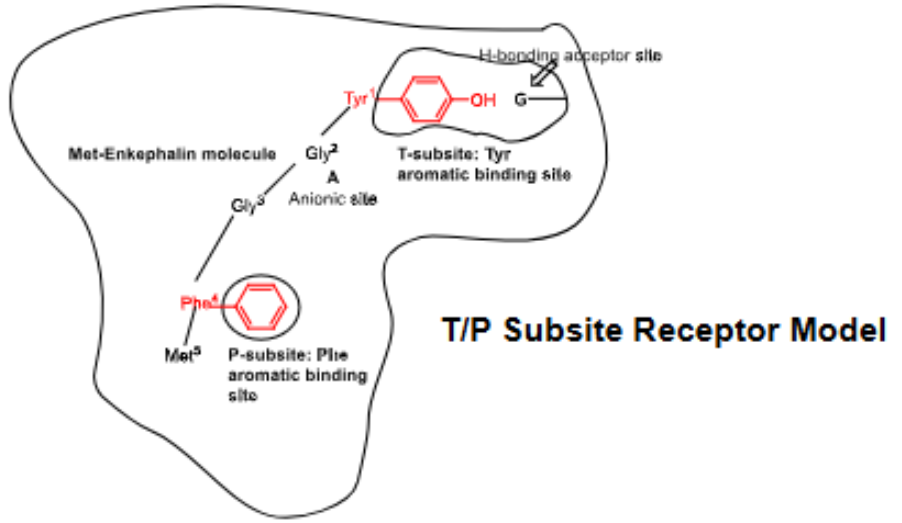
T/P Subsite Receptor Model
accommodates binding of both morphine analogs + natural enkephalin peptides
P-subsite represents → _______ of enkephalin
T-subsite → binds _____ of enkephalin
Thus …
phenylalanine
tyrosine
rigid opioids → T-subsite, non-rigid opioids → P-subsite
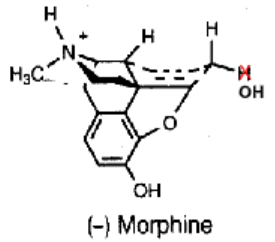
Which subsite would you expect morphine to interact with in the T/P subsite model?
T
(remember tyrosine structure → aromatic ring + OH
phenylalanine → just aromatic ring)
Opioid Receptors
Mu (u) receptor → Principal pain-modulating site in CNS, ______________ → 2 subtypes
Kappa (k) receptor → mediates ___________ with DECREASED addiction liability + respiratory depression → appears to be coupled to ______ receptor → implicated in ____________ side effects of opiates
Delta (δ) receptor → usually stimulated by the _________ → may have a role in … (4)
morphine selective, m1 = analgesic, m2 = resp depress
sedating analgesia, sigma, psychotomimetic + dysphoric
enkephalins, GI motility + mood + behavior + cardiovasc regulation
Does Fentanyl bind to the same site on the mu-receptor as Morphine or at a different site?
diff
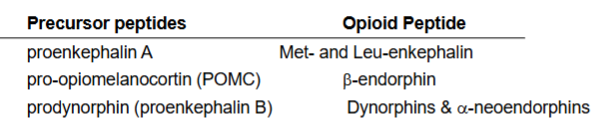
Endogenous Opioid peptides
what kind of molecules are the enkephalins?
what are the other analgesic peptides?
Enkephalins are _____________ (NOT derived from hydrolysis of endorphins)
Where are endorphins found?
___________ promotes GH and PRL release
Endorphins + enkephalins may be ________________ → Gi/G0 type GPCRs → 3 effects
peptides
endorphins, dynorphins, neoendorphins
widespread in CNS
hypothalamus, pituitary gland
b-endorphin
inhibitory → analgesia, inhib DOPA, inhib ACh
What are the three distinct families of endogenous opioid peptides?
endorphins, enkephalins, dynorphins
Enkephalinases: 6 types, FUNCTION =
hydrolyze + inactivate enkephalins
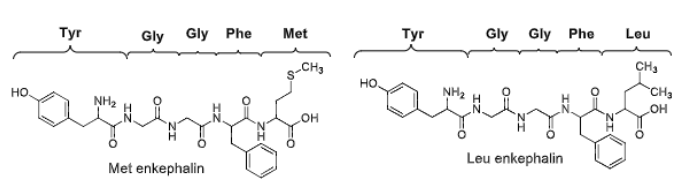
Opioid peptide SAR
All endogenous opioid peptides have ___________________________
The _______ is essential for activity
^ may be alkylated →
Bulky groups (eg. addition of N-methyl to Phe) does what?
Leu or Met enkephalin as first 5 AA residues
Tyr1
methyl - agonist, allyl - antag
+resistance (against peptidases)
Endorphins and opioid receptors in the ____________ of the spinal cord, ________, and _________ (PAG) areas are associated with the transmission of pain signals
dorsal horn, thalamus, periaqueductal gray
OPOID RECEPTORS:
Name 3 types + the preferred endogenous ligands
mu → endorphins, enkephalins, truncated forms of dynorphin
kappa → dynorphins/neoendorphine
delta → enkephalins (ONLY SLIGHTLY)
Compared to Morphine, how potent of an analgesic is Met enkephalin?
(more or less?)
less ~1/33
What kind of receptors + ligand type are opioid receptors? (u, k, δ)
What happens when an opiodi agonist binds to m-receptor? Activation of _________
GPCR → Gi,G0 (inhibitory)
protein kinase A