Final Exam Review: Key Historical Events and Concepts
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
The Stock Market Crash of 1929
October 1929
*Investors began to panic during late October 1929, creating tremendous losses in the stock market
*On October 24, 1929 (Black Thursday), the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped fifty percent and over 13 million shares of stock were traded
*On 29th, (Black Tuesday), over 16 million shares of stock were traded
*The crash led to the Great Depression
The Great Depression
the economic crisis beginning with the stock market crash in 1929 and continuing through the 1930s
Protectionism
the practice of shielding one or more industries within a country's economy from foreign competition through the use of tariffs or quotas
Adolf Hitler
Austrian-born founder of the German Nazi Party and chancellor of the Third Reich (1933-1945). His fascist philosophy, embodied in Mein Kampf (1925-1927), attracted widespread support, and after 1934 he ruled as an absolute dictator. Hitler's pursuit of aggressive nationalist policies resulted in the invasion of Poland (1939) and the subsequent outbreak of World War II. His regime was infamous for the extermination of millions of people, especially European Jews. He committed suicide when the collapse of the Third Reich was imminent (1945).
Mohandas (Mahatma) Gandhi
Political leader and spiritual leader of the Indian drive for independence from Great Britain after WWI; he stressed non violent but aggressive protesting and civil disobedience.
Japanese Imperialism
The conquering and annexing of neighboring countries by Japan; it was the result of a growing population and limited natural resources in Japan at the time. Japan Compared themselves to Great Britain.
Axis Powers
Alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan during World War II.
Appeasement
A policy of making concessions to an aggressor in the hopes of avoiding war. Associated with Neville Chamberlain's policy of making concessions to Adolf Hitler.
Great Purge
The widespread arrests and executions of over a million people by Josef Stalin between 1936 and 1938. Stalin was attempting to eliminate all opposition to his rule of the Soviet Union.
Chinese Communist Revolution
A political revolution in China led by Mao Zedong. After several years of fighting the Kuomintang, the communists won control of the country in 1949.
Winston Churchill
A noted British statesman who led Britain throughout most of World War II and along with Roosevelt planned many allied campaigns. He predicted an iron curtain that would separate Communist Europe from the rest of the West.
Mussolini, Stalin, and Hitler
Totalitarian dictators of the 1930s
Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by Hitler to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled.
Nuremberg Laws
1935 laws defining the status of Jews and withdrawing citizenship from persons of non-German blood.
Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
led to Victory in Japan.
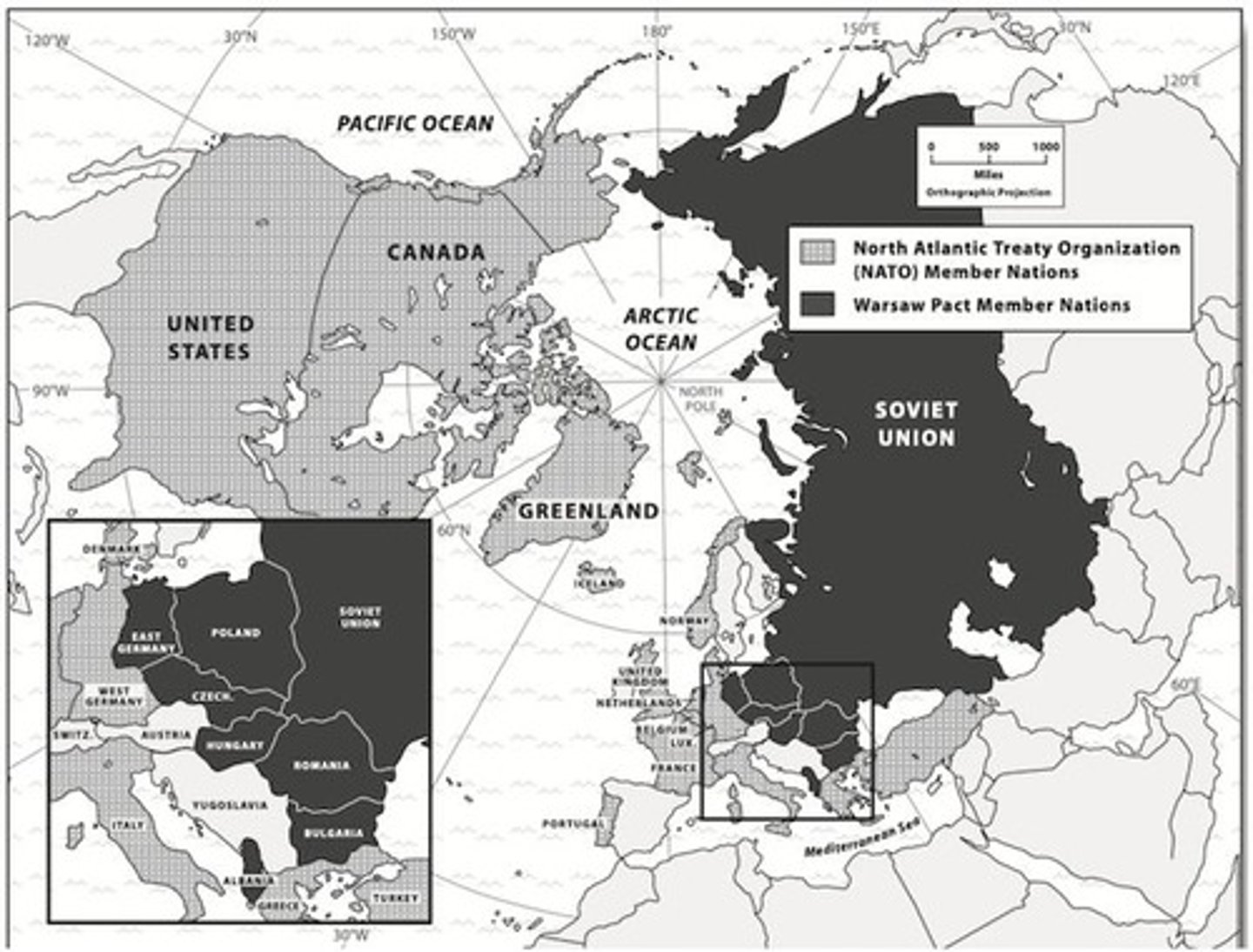
Warsaw Pact
An alliance between the Soviet Union and other Eastern European nations. This was in response to the NATO
Korean War and Vietnam War
The U.S. became involved in both conflicts to stop the spread of communism.
Perestroika
A policy initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev that involved restructuring of the social and economic status quo in communist Russia towards a market based economy and society
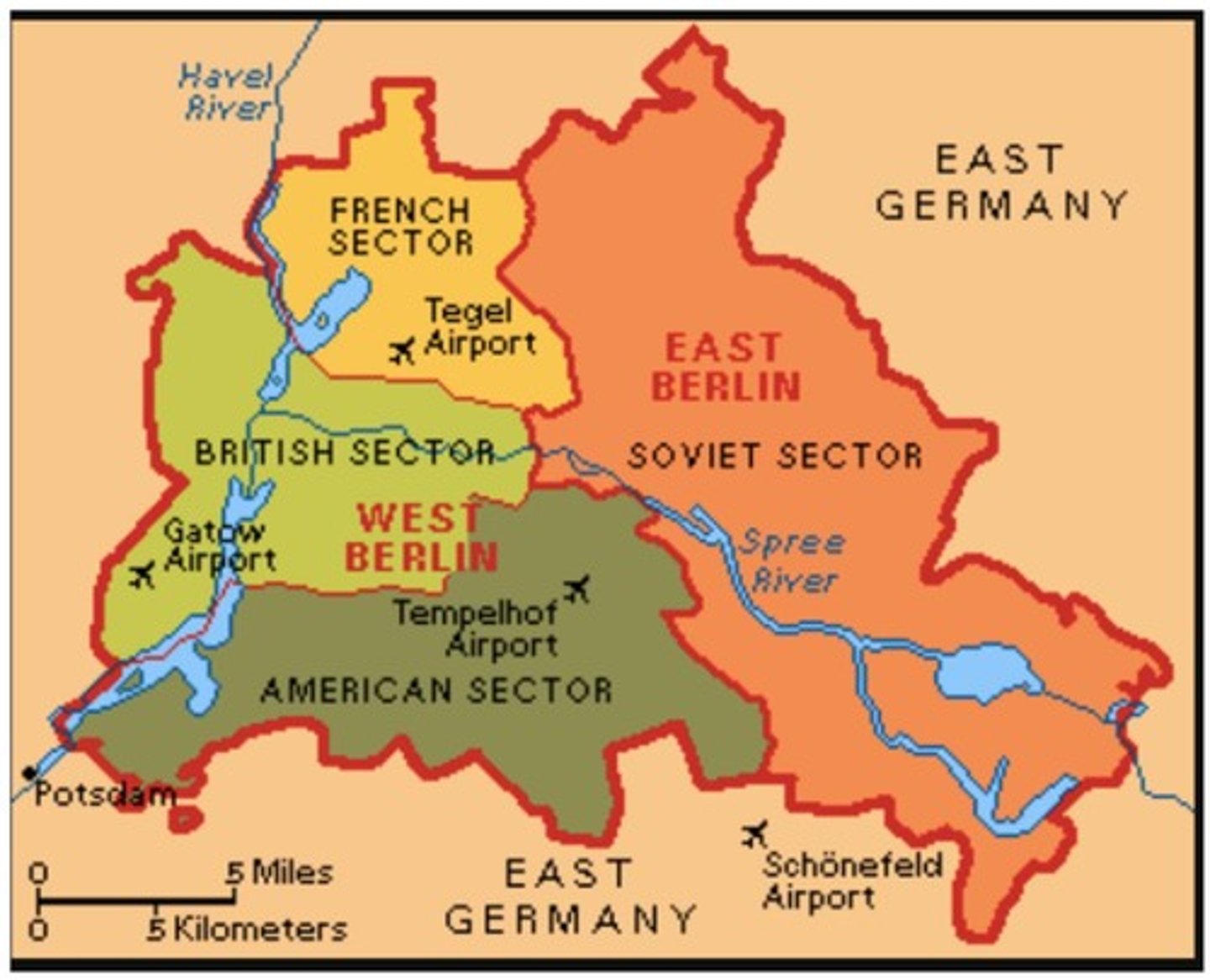
Berlin Airlift
airlift in 1948 that supplied food and fuel to citizens of west Berlin when the Russians closed off land access to Berlin
Cuban Missile Crisis
The 1962 confrontation bewteen US and the Soviet Union over Soviet missiles in Cuba.
China's Great Leap Forward
Was a disastrous economic and social campaign undertaken by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1958 to 1962, aimed at rapidly transforming China from an agrarian society into a socialist industrial power.
Containment Policy
Established by the Truman administration in 1947 to contain Soviet influence to what it was at the end of World War II.
Chinese Civil War
War between communist Mao Zedong and nationalist Chaing-Kai Shek. The communists took over and forced the nationalists to retreat to Taiwan
Partition of British India
To create separate nations for Hindus and Muslims due to religious tensions.
Apartheid
A social policy or racial segregation involving political and economic and legal discrimination against non-whites.
Decolonization and political unrest in Africa
The sudden withdrawal of colonial rule left power struggles, leading to ethnic conflict and violence, such as the Rwandan Genocide.
Domino Theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control.
Communism
A theory or system of social organization based on the holding of all property in common, actual ownership being ascribed to the community as a whole or to the state.
Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Cause
A major root of the conflict is that Israel has been increasing their territory into Palestinian land.
Ethnic Cleansing
Process in which more powerful ethnic group forcibly removes a less powerful one in order to create an ethnically homogeneous region
Asian Tigers
Collective name for South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Singapore-nations that became economic powers in the 1970s and 1980s.
Gorbachev's Policies
Mikhail Gorbachev's policies that were meant to open up and restructure the Soviet Union were known as Perestroika and Glasnost.
NATO
North Atlantic Treaty Organization; an alliance made to defend one another if they were attacked by any other country; US, England, France, Canada, Western European countries
Totalitarianism
A political system in which the state holds total authority over the society and seeks to control all aspects of public and private life.
World War II Causes
1) 1930's- Italy, Germany, and Japan aggressively sought to build new empires
2) League of Nations was weak
3) Western Countries were recovering from the great Depression and didn't want any more war
4) Acts of aggression occurred and were allowed to go unchecked
Berlin Airlift
airlift in 1948 that supplied food and fuel to citizens of west Berlin when the Russians closed off land access to Berlin
Impact of the Berlin Crisis on international relations
It heightened tensions between the Soviet Union and the West, leading to the formation of NATO.
Genocide
the deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially those of a particular ethnic group or nation.
Define Cuban Missile Crisis
A 13-day confrontation in October 1962 between the United States and the Soviet Union over Soviet ballistic missiles deployed in Cuba.
Space Race
A competition of space exploration between the United States and Soviet Union.
Arms Race
Cold war competition between the U.S. and Soviet Union to build up their respective armed forces and weapons
Bay of Pigs
In April 1961, a group of Cuban exiles organized and supported by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency landed on the southern coast of Cuba in an effort to overthrow Fidel Castro. When the invasion ended in disaster, President Kennedy took full responsibility for the failure.
Greatest Loss of Life in WWII
Soviet Union
Nuremberg Laws
1935 laws defining the status of Jews and withdrawing citizenship from persons of non-German blood.
League of Nations (1919)
A world organization of national governments proposed by President Woodrow Wilson and established by the Treaty of Versailles in 1919. It worked to facilitate peaceful international cooperation. Despite emotional appeals by Wilson, isolationists' objections to the League created the major obstacle to American signing of the Treaty of Versailles.
Africa and Asia Independence
Effect of WWII on European countries led to a lack of resources to rule other countries
Partition of India
This led to the movement of millions of people in South Asia after India got its independence from Britain.
Israel Pakistan Conflict
Conflict over land leading to war
Middle East Peace Failure
The inability to achieve lasting peace between Israel and Palestine, marked by several conflicts, negotiations, and territorial disputes since the mid-20th century.
Glasnost
the policy of openness and transparency in Soviet government initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev in the 1980s.
Allied Powers
The coalition of nations, including the United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union, that fought against the Axis Powers during World War II.