Principles of Toxicology and Risk Assessment
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Toxicology
Study of harmful effects of chemicals on organisms.
Common toxicants around the home
ibuprofen, gas, rubbing alcohol, bleach, cleaning agents
Risk Assessment
Process to evaluate potential health risks from exposures.
Immediate Effects
Rapid adverse reactions to toxic substances.
Delayed Effects
Adverse reactions occurring after a period of time.
Local Effects
Toxic effects occurring at the exposure site.
Systemic Effects
Toxic effects affecting the entire body or organ systems.
LD50
Dose killing 50% of test animals within a time frame.
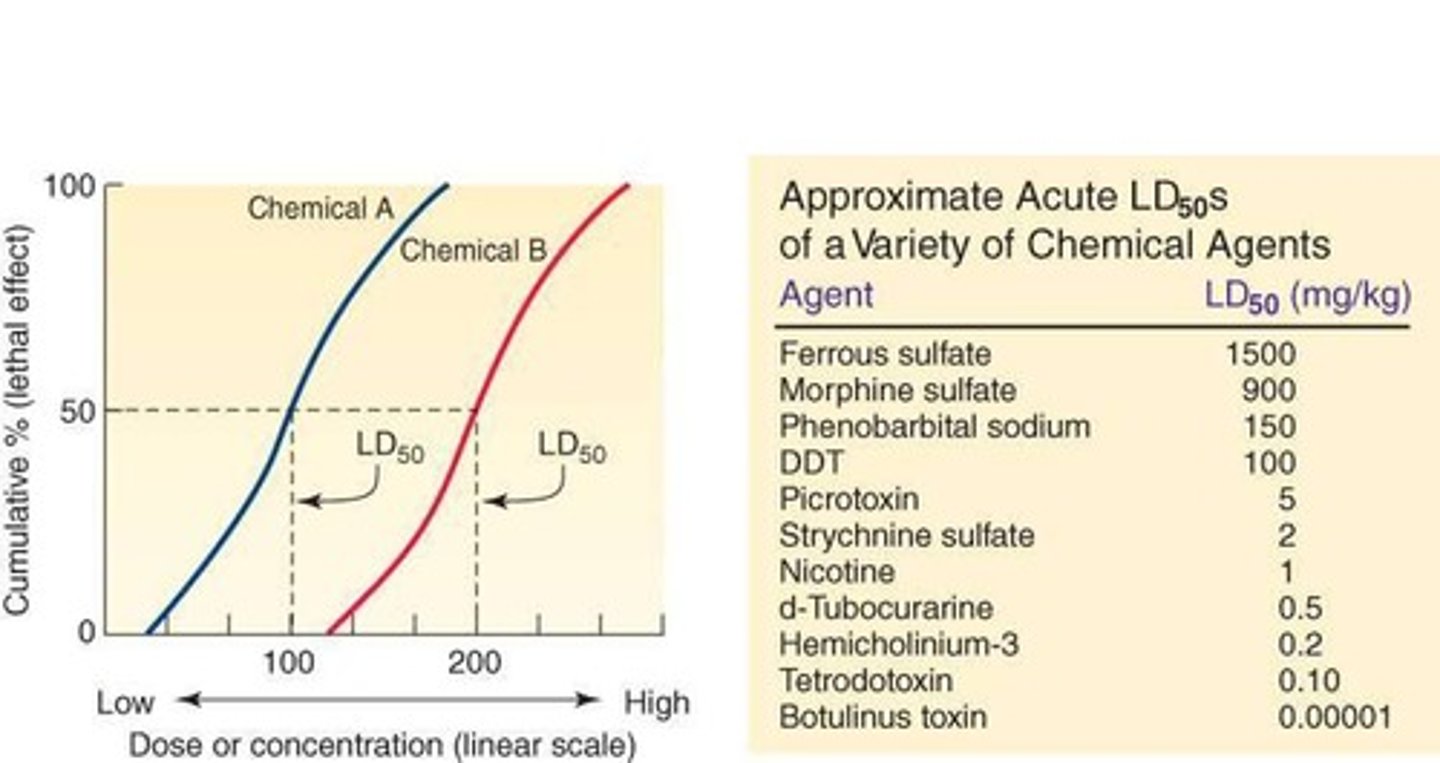
Dose-Response Relationship
Correlation between dose and severity of toxic effects.
How do toxicants work?
bind to enzymes and other important molecules, altering cellular function
Factors Affecting Toxicity
Includes route of entry, dose, and exposure duration
Chemical Routes of Entry
inhalation, ingestion, dermal.
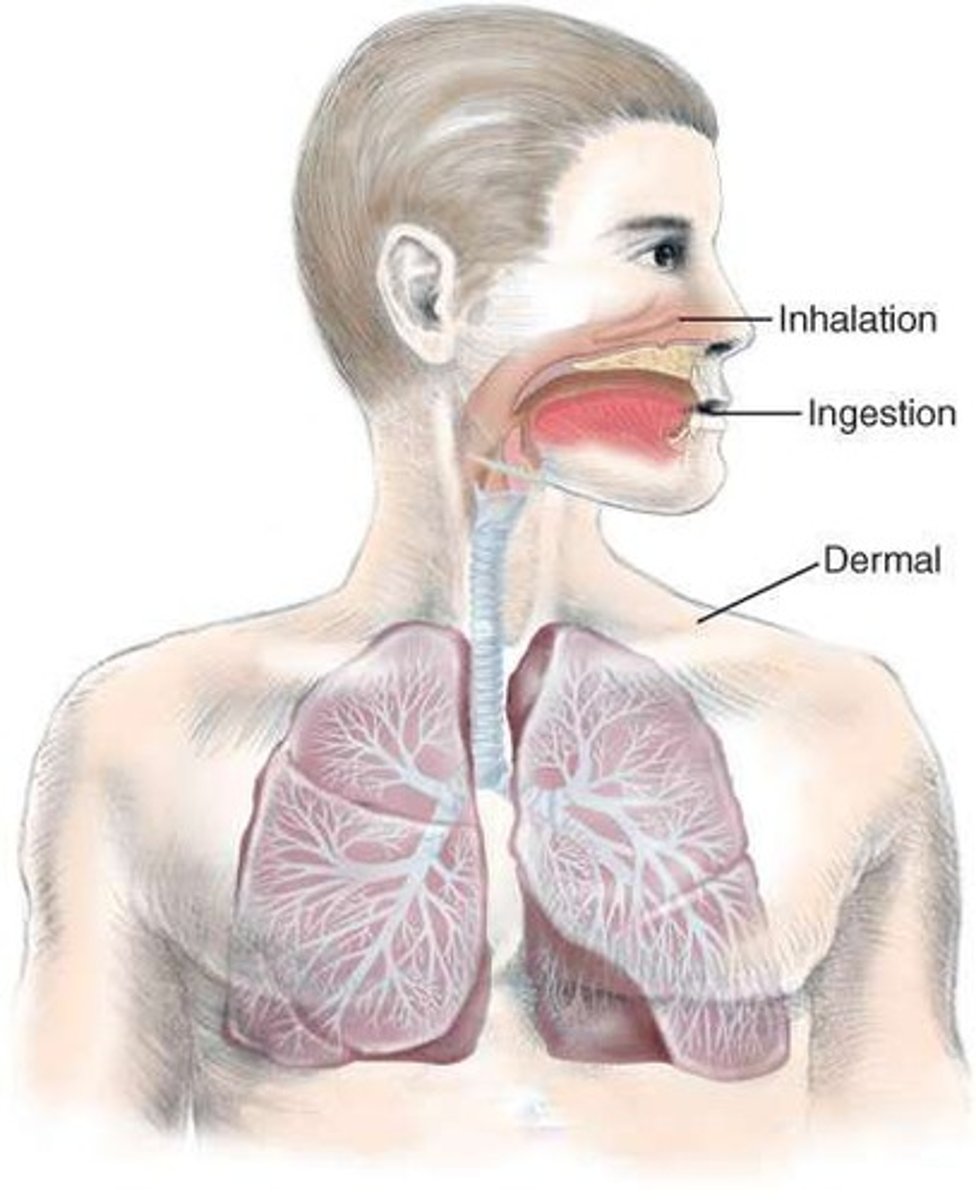
Inhalation
Fastest route for toxicant entry into the body.
Dermal Absorption
Slowest route for toxicant entry into the body.
Reactivity
Chemical property influencing its potential toxicity.
Bioaccumulation
Build-up of toxic substances in tissues or organs.
Food Chain Concentration
Toxicants increase in concentration through food webs.
Who are most susceptible to toxins?
young, sick, and elderly
Chemical Knowledge Gaps
Insufficient data on many chemicals' effects.
Cumulative Toxicity
Effects of multiple exposures over time.
Bioaccumulation
Accumulation of substances in living organisms.
Biological magnification
Increase in substance concentration up the food chain.
Additive response
Combined effect equals the sum of individual effects. 2+2=4
Additive response example
acetaminophen and aspirin
Synergistic response
Combined effect exceeds the sum of individual effects. 2+2=6
Synergistic response Example
barbituates and alcohol; tobacco and asbestos
Potentiation
Non-toxic chemical enhances toxicity of another. 0+2=6
Potentiation example
isopropanol and carbon tetrachloride
Antagonistic response
Combined effect reduces the harmful impact of chemicals. 2+4=3
Antagonistic response example
naloxone and opioids
Carcinogens
Substances that can cause cancer after repeated exposure.
Biotransformation
Chemical alteration of substances by body enzymes.
Teratogens
Agents causing structural or functional birth defects.
Organogenesis
Critical period of organ development in embryos.
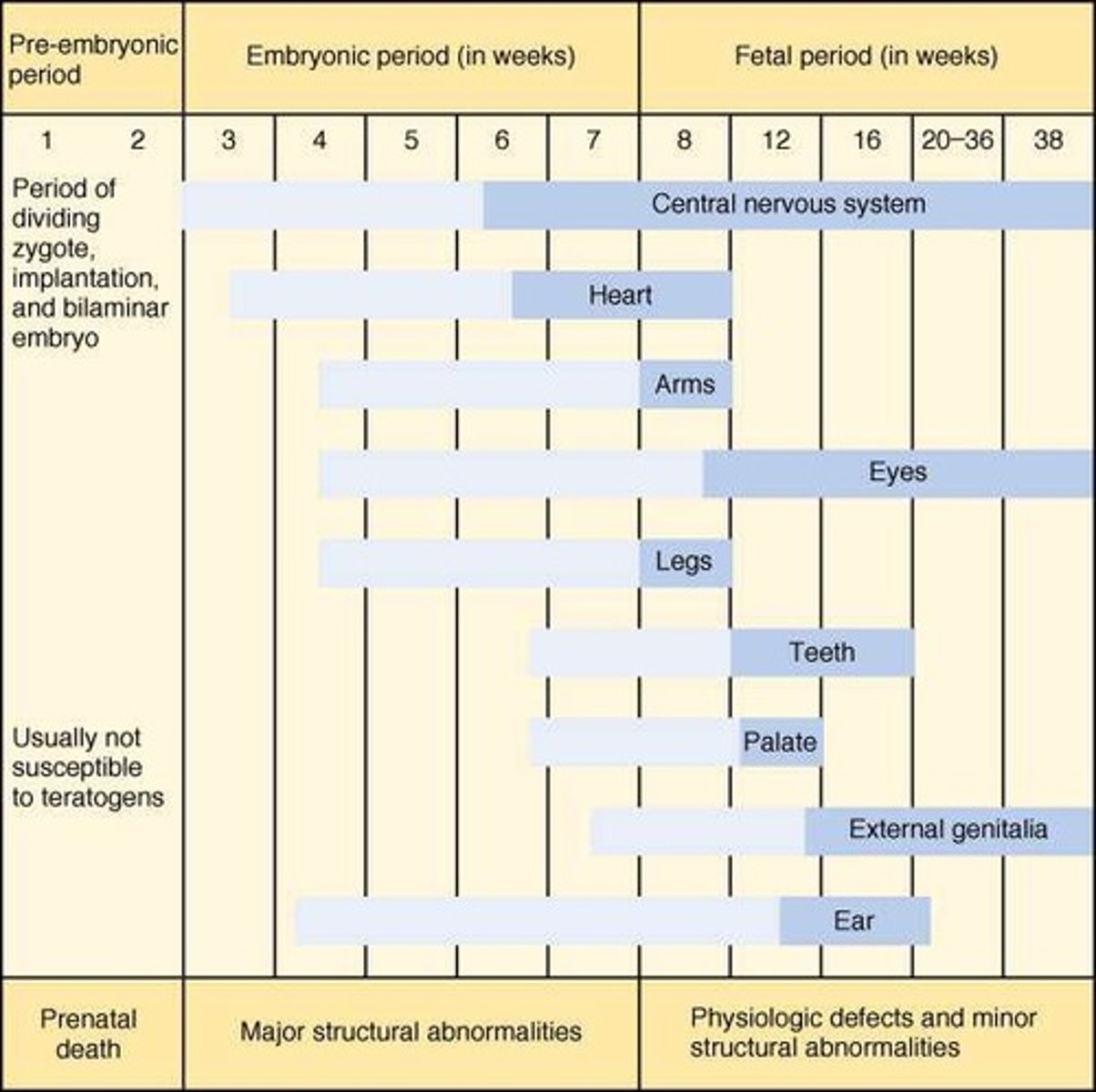
Reproductive Toxicity
Interference with reproductive processes by agents.
Environmental hormones
Herbicides, Dioxins, Nonylphenols, Phthalates
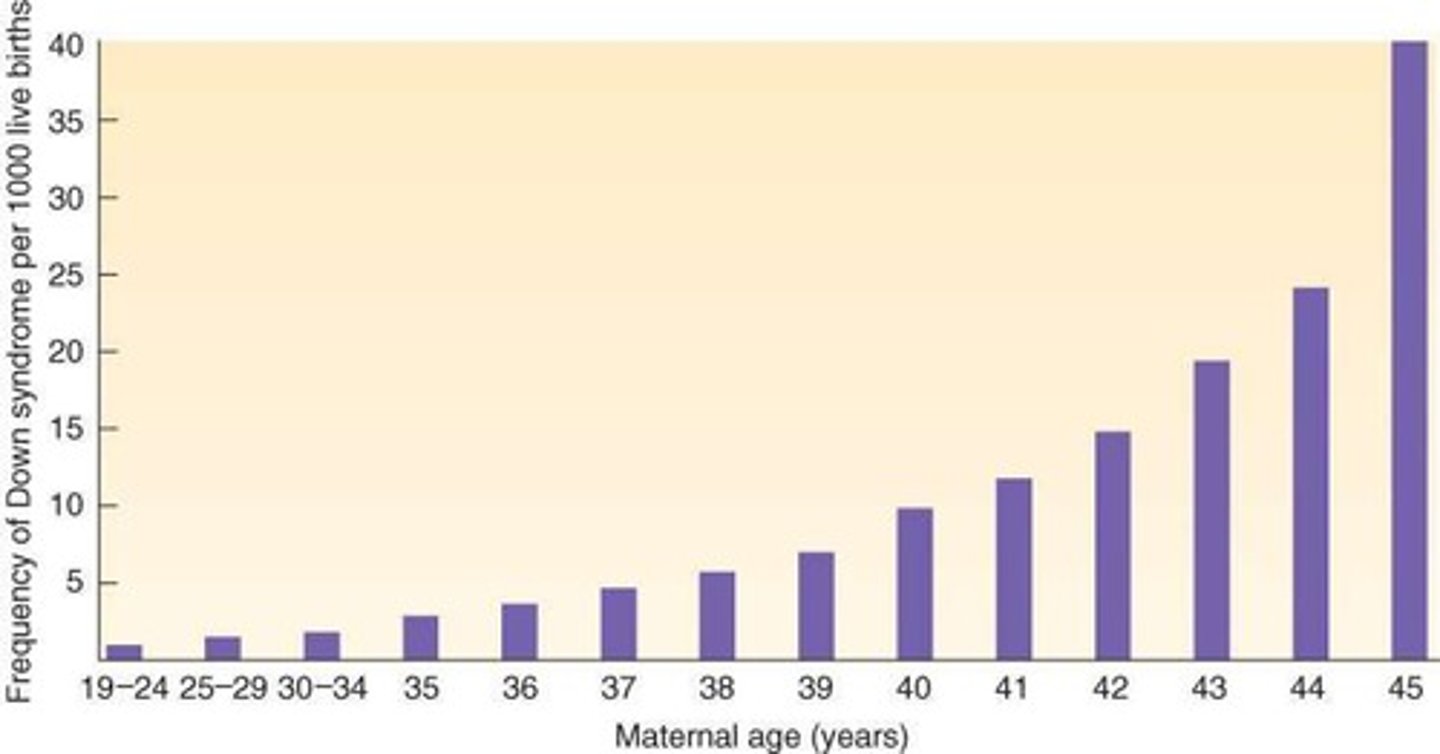
Incidence of Down Syndrome
Linked to maternal age and chromosome abnormalities.
Asbestos
Mineral fiber linked to respiratory diseases including pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, and mesothelioma
Chemical agents
Substances that can cause harmful biological effects.
Physical agents
Environmental factors causing biological harm.
Biological agents
Living organisms that can cause health issues.
ELF Magnetic Fields
Extremely low-frequency fields from electricity flow.
Cancer Incidence
Rate of new cancer cases in a population.
Toxic Substances Control Act
U.S. law to manage harmful chemicals. seeks to prevent the introduction of chemicals that will be harmful and eliminate those already in use that pose an unacceptable risk
End-of-Pipe Controls
Pollution control measures applied after pollution occurs.
Pollution Prevention
Strategies to eliminate hazardous waste production.
Market Incentives
Economic strategies to encourage safer chemical use.
Innovation Promotion
Encouraging new solutions to reduce pollution.
Integrated Pollution Control
Regulating multiple pollution sources simultaneously.
Risk Identification
First step in risk assessment to recognize hazards.
Probability Determination
Second step assessing likelihood of risk occurrence.
Severity Assessment
Evaluating potential impacts of identified risks.
Risk Acceptability
Determined by perceptions and societal values.
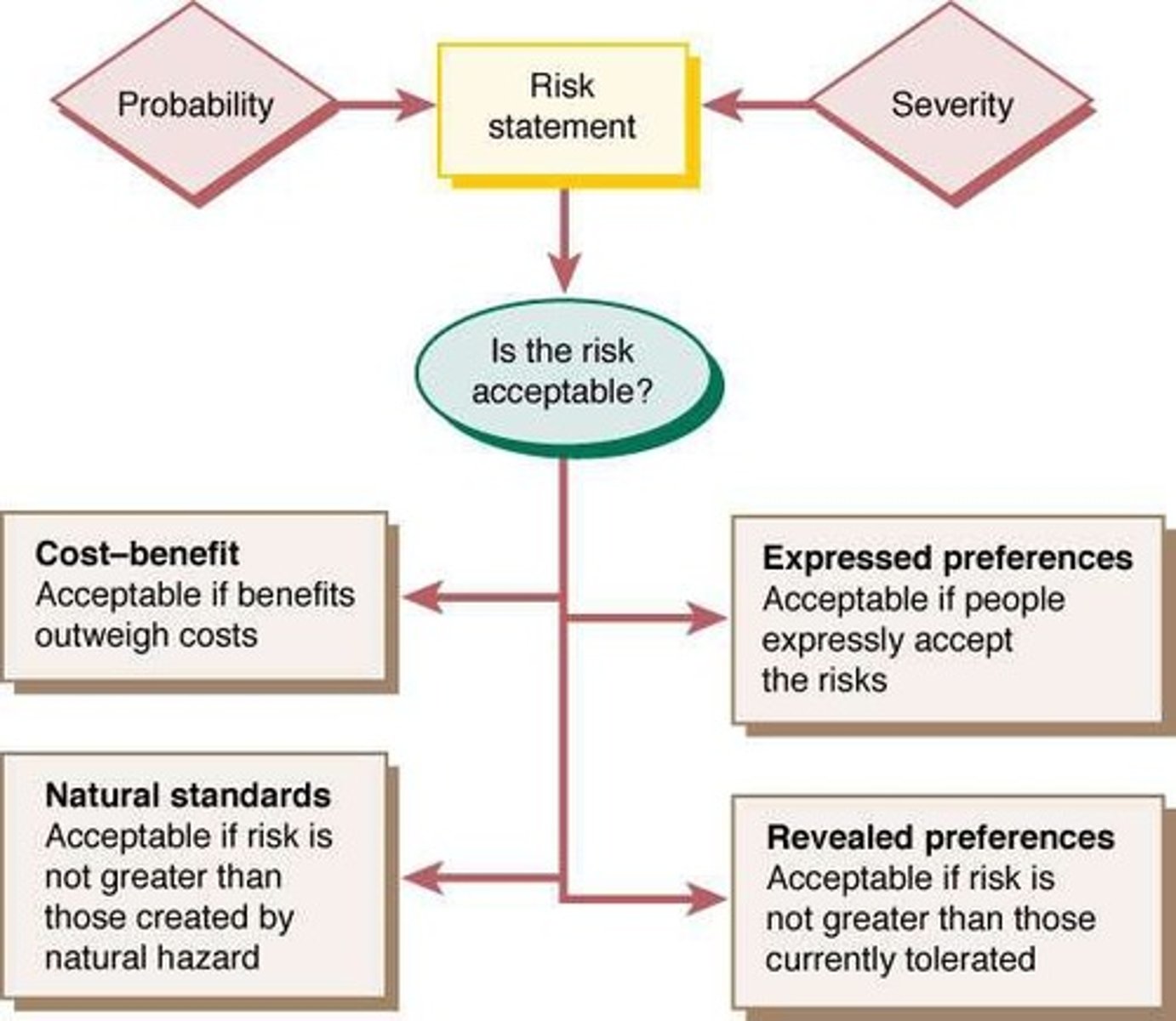
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Weighing costs against benefits to assess risk.
Sustainable Development
Minimizing costs while maximizing benefits for society.
Values in Decision Making
Personal beliefs influencing risk perception and choices.
Long-Range View
Perspective considering global sustainability over time.