pulmonary pt 3
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
inspiratory reserve Volume (IRV)
Additional amount of air (above tidal volume) that can be inhaled after a normal inspiration
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
the additional amount of air (above tidal volume) that can be expired from the lungs after a normal expiration
Residual volume
the amount of air that remains in the lungs after fully exhaling
tidal volume
the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inhalation and exhalation when extra effort is not applied
total lung capacity
maximum amount of air that can fill the lungs (TLC = Vt + ERV + IRV + RV
Inspiratory capacity
the volume of air that can be inspired following a normal, quiet expiration (IC = Vt + IRV)
Functional residual capacity
volume of air present in the lungs at the end of passive expiration
Vital capacity
the greatest volume of air that can be expelled from the lungs after taking the deepest possible breath
0.5 L (or 500 ml)
What is a typical tidal volume for a young adult male?
6 L (or 6000 ml)
What is a typical total lung capacity for a young adult male?
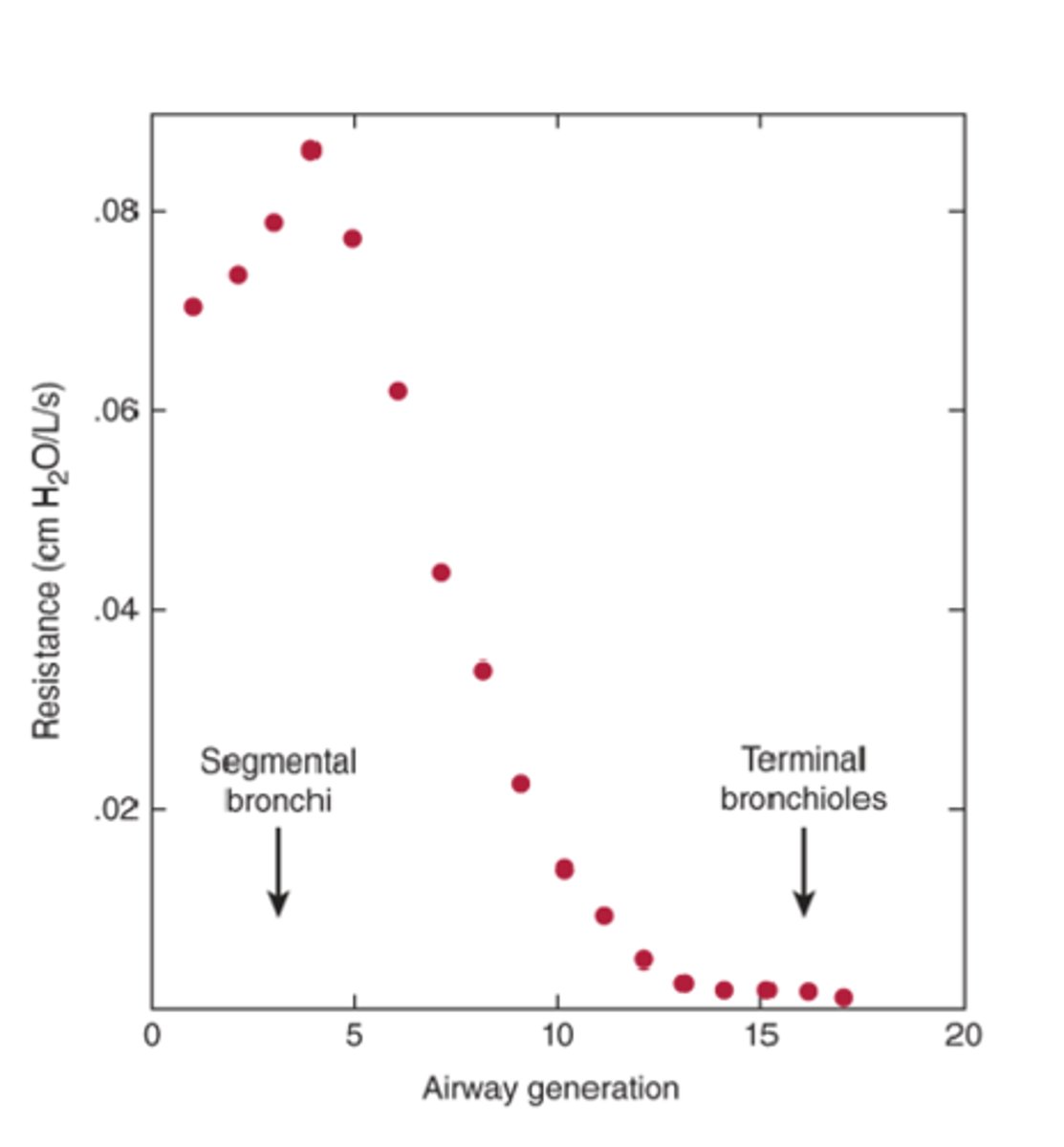
highest
this graph shows that resistance is the _______________ at the 4th generation
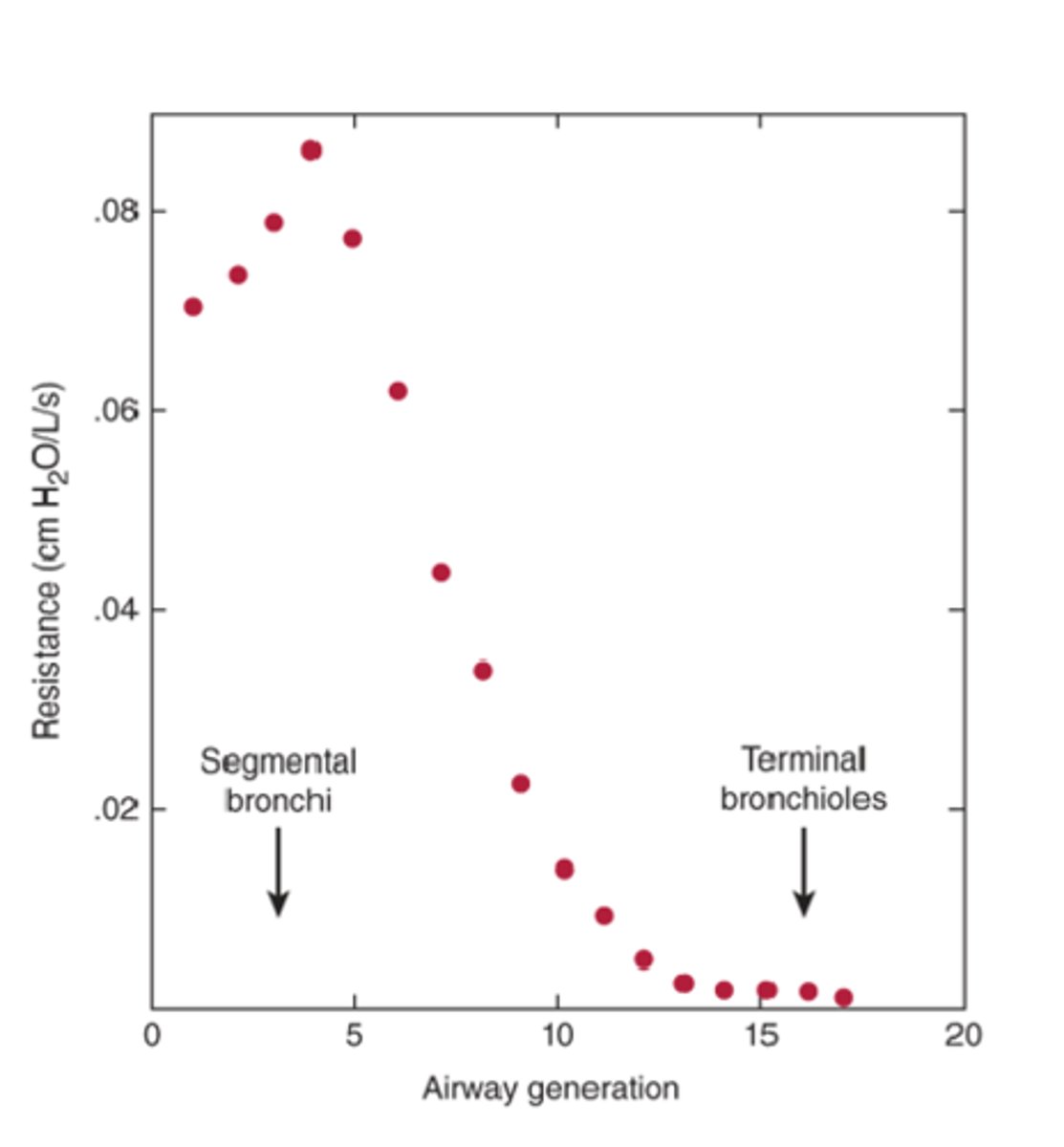
decreases
This graph shows that after the 4th generation, resistance ________________ as the branching of the generations continues
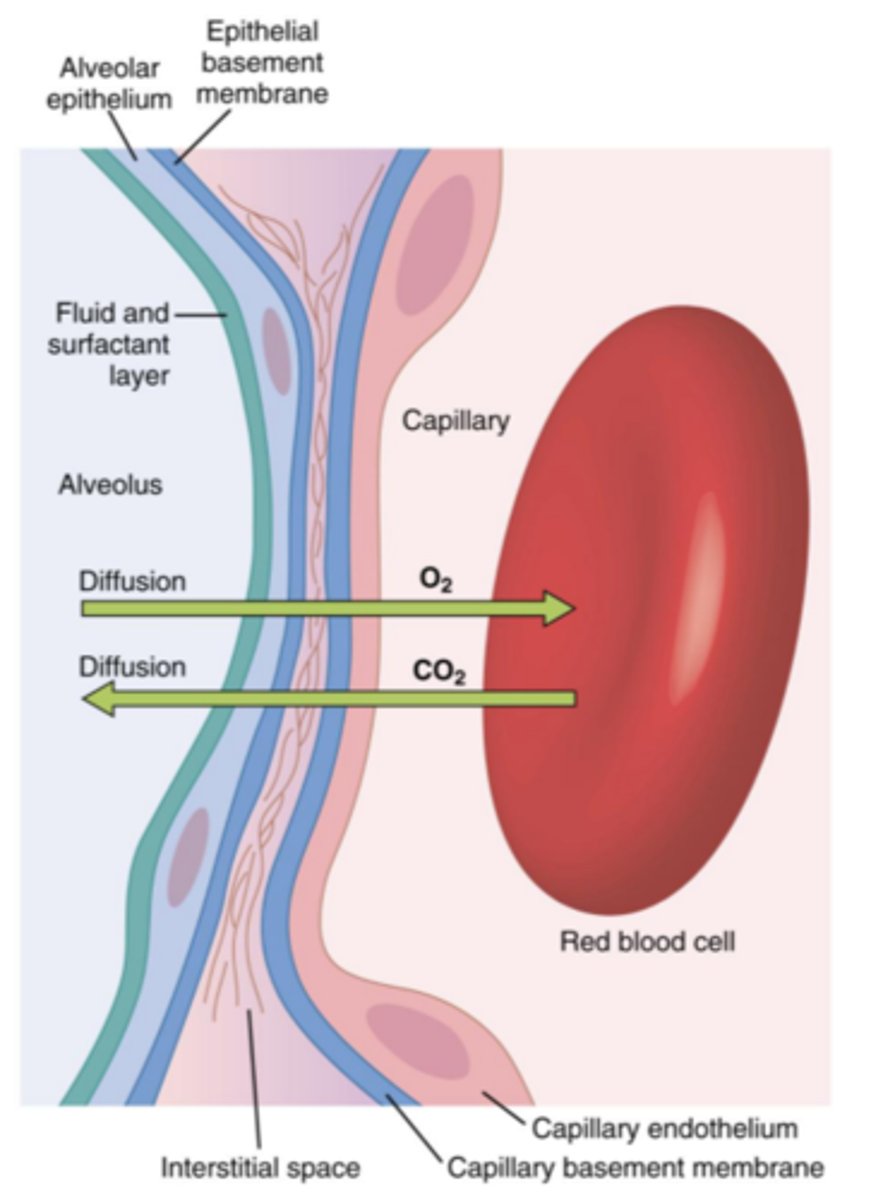
Alveoli
Smallest functional unit of the respiratory system, where gas exchange occurs
respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli
The respiratory zone includes...
External respiration
The exchange of gases in the lungs
internal respiration
The exchange of gases in body tissues.
Physical, alveolar
Both types of respiration (internal and external) are influenced by:
• _____________ properties of gases
• Composition of ______________ gas
Flow down gradient
Gases (e.g., O2, CO2) move by diffusion along their partial pressure gradients until equilibrium is reached
What core concept is this?
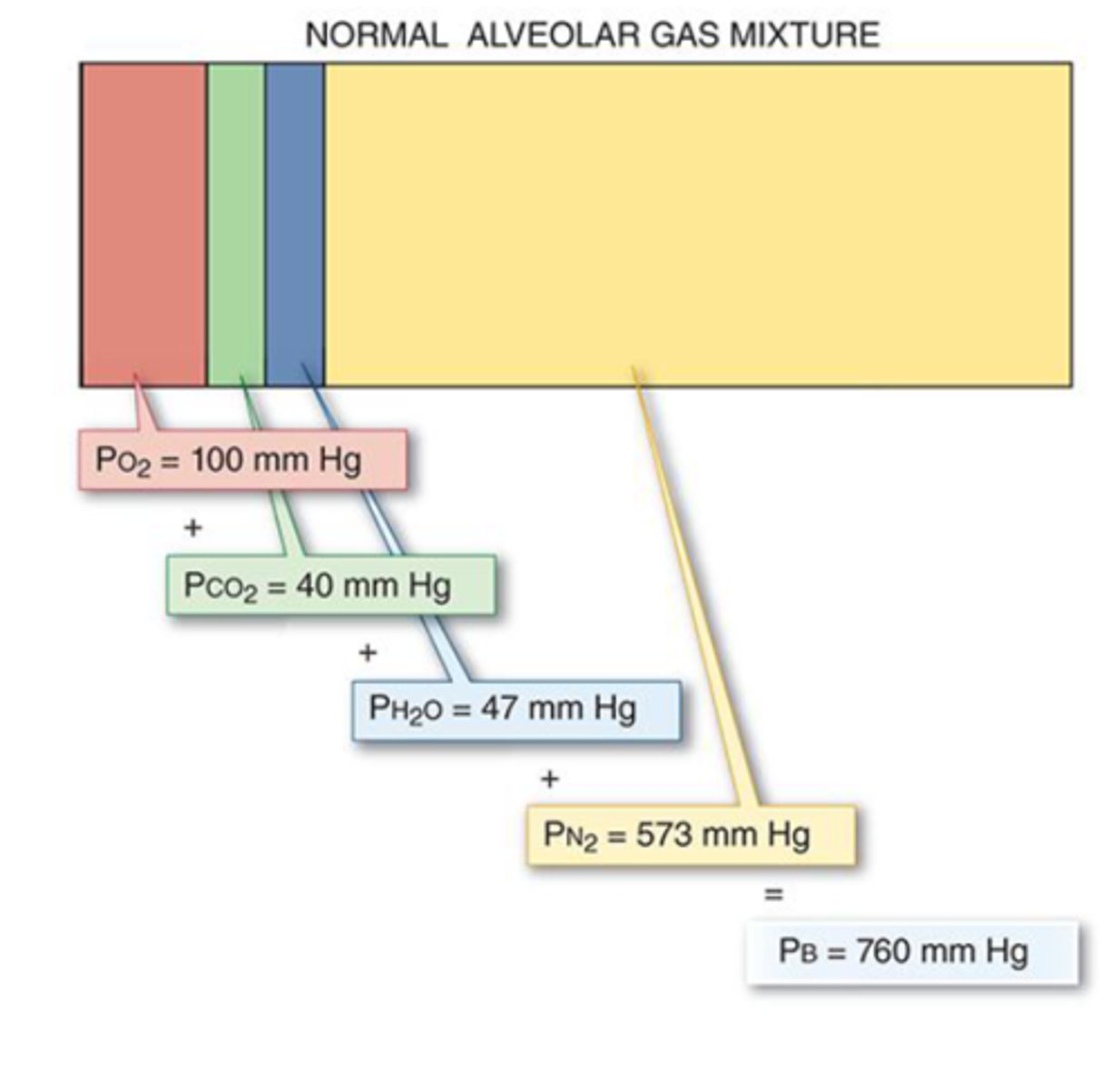
Dalton's Law
each gas in a mixture of gases exerts a partial pressure that is proportional to its concentration.
- the sum of partial pressures = total pressure
Dalton's Law
What is this image illustrating?