peds - neurology
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
gross motor and fine motor expectations

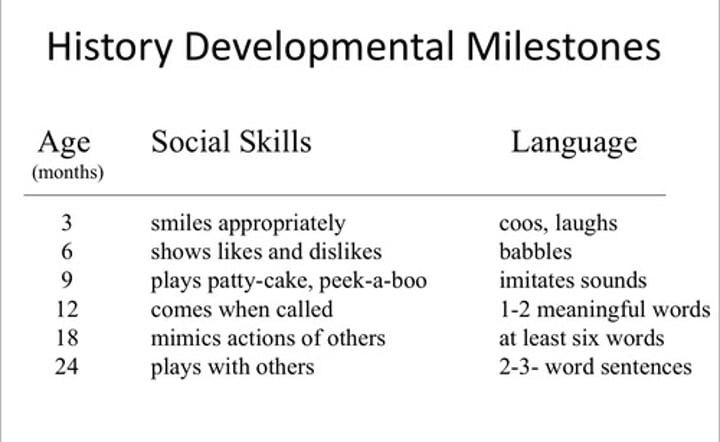
social skills and language expectations
symptoms of neurological issues in children
vomiting
headache
bowel/bladder dysfunctions
failure to meet developmental milestones
important family history to assess in children with suspected neurological issue
epilepsy
migraines
CVA
metabolic or degenerative disorders
anterior fontanelle should close by
12 to 18 months
posterior fontanelle should close by
2 months
craniotabes
softening of the cranial bones
- seen in prematurity
when auscultating during a neurological examination of a child, cranial bruits may be present over
anterior fontanelle
soft cranial bruits may be normal in
children less than 4 years old
children with loud cranial bruits should be suspected of having
AV malformation
increased ICP
severe anemia
horner's syndrome triad
ptosis, miosis, anhydriasis
horner's syndrome
damage to sympathetic trunk resulting in ipsilateral ptosis (sympathetics innervate superior tarsal muscle), anhydriasis of the ipsilateral face (sweating is sympathetic and muscarinic - M3) and ipsilateral miosis (sympathetics innervate radial fibers providing mydriasis)
papilledema
swelling of the optic disc, sign of increased cranial pressure
fundoscopic exam findings of increased cranial pressure
papilledema
constricted arterioles, dilated veins
retinal hemorrhages
macular star
innervations of the EOM
(LR6SO4)3
- lateral rectus = CN6 (abducens)
- superior oblique = CN4 (trochlear)
- all others = CN3 (oculomotor)
examination of the EOMs assesses what cranial nerves
3, 4, 6
clinical presentation of oculomotor paralysis
eye is displaced "down and out" with ptosis and mydriasis
- abduction and elevation
clinical presentation of trochlear paralysis
Up and out
(head slight turned away from lesion, eyeball displace up and out
diplopia when looking down and toward the nose
SO: depression and abduction, intorsion)
clinical presentation of abducens paralysis
medial deviation of the eye
- lateral rectus abducts the eye
nystagmus
involuntary, jerking movements of the eyes
horizontal nystagmus may be due to
labyrinth or vestibular injury
vertical nystagmus may be due to
brain stem injury
mydriasis may be seen in
sympathetic overactivity (hyperthyroidism, anxiety, etc)
miosis may be seen in
morphine poisoning (pinpoint pupils), neurosyphilis
pinpoint pupils
opioid overdose
unequal pupils may be seen in
oculomotor lesions, iritis
irregularly shaped pupils may be seen in
iritis
Argyll Robertson pupil
Neurosyphilis (tabes dorsalis)
- irregularly shaped pupils with absent pupillary light reflex and INTACT accommodation (called light-near dissociation)
light near dissociation occurs in
neurosyphilis
parinaud's syndrome (compression of pretectal nuclei in dorsal midbrain)
diabetes
pupils are fixed and dilated in
brain death
ways to assess trigeminal nerve function
jaw jerk
masster/pterygoid/temporalis strength
corneal blink reflex
corneal blink reflex
CN V feels the pain
CN VII closes the eyelid
facial nerve innervates
the superficial muscles of facial expression
nasolabial folds
anterior 2/3 of tongue to supply taste
taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
facial nerve
isolated loss of CNVII seen in
bell's palsy
paralysis of the lower face on one side only suggests lesion to
contralateral facial nerve in corticobulbar tract (upper motor neuron lesion)
- muscles for the upper face have bilateral representation in the motor cortex
- lesion to an upper motor neuron for the facial nerve on one side would not damage UMN projections from the contralateral side
pt can wrinkle their forehead or furrow their brow, but unable to puff their cheeks or make facial expressions
paralysis of the upper and lower face on on side only suggests lesion of
ipsilateral facial nerve projections from the facial nucleus (LMN lesion)
bell's palsy
LMN CN VII palsy
ramsay hunt syndrome
occurs when VZV site of latency is the facial nerve near the ear
reactivation of latent infection results in herpes zoster of the ear (herpetic pinna) and bell's palsy
ocular complication of bell's palsy/ramsay hunt syndrome
exposure keratopathy (corneal ulcerations from being unable to close the eye fully)
ways to examine CN8
assess hearing function
assess vestibular function
how to assess vestibular function
caloric test
dolls head in comatose patient
caloric test
cold: simulates turning of the head in the opposite direction of the ear in which cold water was injected = ipsilateral slow phase with contralateral fast phase
- cold water in the left ear results in right beating nystagmus
warm: simulates turning of the head in the same direction of the ear in which warm water was injected = contralateral slow phase with ipsilateral fast phase
- warm water in the left ear results in left beating nystagmus
mnemonic: COWS (cold = opposite, warm = same)
hearing loss in children is associated with
prematurity
ototoxic drugs
hyperbilirubinemia
bacterial meningitis
TORCH infections
taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
assessment of CNIX
taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue
gag reflex (provides sensory information to soft palate)
gag reflex assesses the function of
CNIX (in on 9) and CNX (out on 10)
- sensory fibers of CN9 innervate the soft palate and synapse in the nucleus ambiguus to trigger CNX LMN fibers to contract the levator palatini
- palate should elevate bilaterally, uvula should elevate on midline
palate deviation suggests
lesion to contralateral circuit (CNX innervates levator palatini)
CNX lesion could present with
palate deviation, vocal cord paralysis (recurrent laryngeal nerves are branches of vagus nerve)
how to assess CNXI function
SCM and trapezius
CNXI innervates
SCM and trapezius
how to assess CNXII function
tongue protrusion
- deviation suggests lesion on contralateral side (tongue deviates toward intact innervation)
gower's sign
when asked to get up from sitting on floor, child will move hands on legs as though crawling up to the thighs and then assume a standing position
gower's sign suggests
pelvic girdle/lumbar/proximal LE muscle weakness which may be due to DMD
clasp knife rigidity
in response to sudden passive stretch of a muscle, the antagonists will fire and contract to resist the stretch until stretch reaches a certain point at which the antagonist will no longer contract and the muscle will be suddenly stretch to full length, like opening or closing a clasp knife
abnormal response seen in UMN lesions
cogwheel rigidity
muscle tension that intermittently halts movement as an examiner attempts to manipulate a limb
seen in lesions of the basal ganglia (parkinson's)
scarf sign
exam for gestational maturity, resistance to attempt to bring one elbow farther than the midline of the chest
assesses the passive tone of the shoulder girdle flexors in a newborn
- in preterm infants, elbow may be able to cross midline before resistance is met
- in term infants with normal tone, the elbow should not be able to cross midline
opisthotonus
tightness in the entire body with the head back and an arched neck
- seen in tetanus, meningitis, hyperbilirubinemia
frog leg posture in infant
indicates hypotonia of the hip girdle muscles
Truncal ataxia, dysarthria. Where is the lesion?
cerebellar vermis (spinocerebellar system)
cerebellar signs
ataxia
- gait
- truncal
disdiadochokinesia
dysarthria
nystagmus
romberg's
romberg's sign
SENSORY ataxia
falling to one side while standing with eyes closed
- cerebellar sign
chorea
sudden, rapid, jerky, purposeless movement involving limbs, trunk, or face
seen in huntington's (most common hereditary cause) and post-stroke in caudate/putamen strokes
spastic gait
a stiff, foot-dragging walk caused by one-sided, long-term, muscle contraction; seen with cerebral palsy
also called scissor gait or tin solider gait
gait seen in hemiparesis
circumduction gait/waddling gait
where is LP performed
L4/L5
protein content of CSF in neonate
up 120 mg/dL
normal protein content of CSF
10-40mg/dL
normal glucose of CSF
60% of serum glucose
CSF characteristics of bacterial meningitis
- very high WBC
- Low to very low glucose
- Very high protein
- High opening pressure
normal RBC content of CSF
NONE (in an ideal draw)
in neonates, in addition to LP sampling, CSF may be drawn from
ventricles via the anterior fontanelle
- usually in treatment of hydrocephalus
normal lymphocyte content of CSF
0 to 5 lymphocytes per mm^3
NORMAL lymphocyte count in CSF in neonates may be as high as
15 lymphocytes per mm^3
myelography use
analyze spinal cord in suspected SC lesion
definition of seizure
paroxysmal, involuntary disturbance of brain function involving altered consciousness and motor activity
epilepsy
recurrent seizures unrelated to fever or brain insult
types of seizures
partial and generalized
types of partial seizures
simple and complex
which type of seizure is consciousness maintained
simple partial ONLY
partial seizures
focal, involve one lobe or one part of a lobe
simple partial seizure
Focal seizure in which consciousness is NOT impaired
- may be motor, sensory, autonomic
complex partial seizure
Focal seizure (at onset) in which consciousness IS impaired, either at onset or following a simple partial seizure
- MAY spread to become generalized (partial seizure with secondary generalization)
generalized seizures
diffuse/bilateral involvement with impaired consciousness
types of generalized seizures
absence, myoclonic, tonic-clonic, tonic, clonic, atonic, infantile spasms
absence seizures
May be seen in children who are accused of inattention in class and confused with ADHD
- child "turns off"
- generalized seizure involving loss of consciousness
up to 40% of childhood seizures are what type
partial
EEG of complex partial seizures
abnormal even in interictal phase
signs of complex partial seizure
preictal aura seen in 30% of patients
automatism seen in 50-70% of patients (lip smacking, chewing, rubbing, pulling, jerking, etc)
EEG in simple partial seizures
spikes and or waves
complex partial seizures often involve
temporal lobe
children with complex partial seizures should suspect of lesion to
temporal lobe
absence seizures in children may be mistaken for
ADHD (teacher may think child is unable to pay attention and dozes off)
unique findings of absence seizures
NO aura and NO postictal phase
- almost like child just reboots randomly
absence seizures are unusual in children under
5 years old
in a child with history of absence seizures, these seizures may be induced with
hyperventillation
EEG of absence seizures
3 Hz spike and wave (3 per second) - important
generalized tonic clonic seizure
preictal aura, tonic-clonic activity, postictal phase
tonic seizure
Muscle stiffness, rigidity, usually bilateral extension = arching of back
clonic seizure
repetitive jerking movements