EDEXCEL A LVL Maths year 2 moments/SRB/Slopes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what does uniform mean
The weight acts at the centre
what does non uniform mean
the weight does not act at the centre
what does it mean when something is on the point of tipping about point A?
all other reactions are now 0
what 3 things does modelling something as a beam mean
only has 1 dimension (length)
its mass is concentrated along a line
It is rigid (can’t bend)
what is the order of calculation for horizontal beams
resolve vertically
take moments
what is the order of calculation for static rigid bodies
resolve vertically
resolve horizontally
take moments (usually around the bottom)
In a static rigid body against a wall, if there is friction between the plane and the wall (where friction is vertical), will we resolve the friction so that we can use the friction in the moments calculation
yes
if you have lots of sin thetas and cos thetas in an equation (when doing a calculation), what should u do to make it easier / simpler
(after cancelling through anything where u can e.g any unkown variable lengths)
divide everything by cos theta
as this will cancel some cos thetas and will turn the sin theta ones into tan thetas
for any “state what would happen to…” question, in SRB for example, what do u need to do before coming up with a hypothesis
do some sort of maths / calculations so that u can prove it to be the case
what does equilibrium mean in mechanics
all forces are balanced
what does it mean when there is acceleration
what equation do we use with acceleration
forces are imbalanced (there is a resultant force)
F = ma
does friction resist motion?
yes
what is the formula for friction
FMAX = mew R
what are the bounds / limits of friction
can be anything from 0 up until (mew*R)
for what 3 cases does friction take its max value?
limiting equilibrium
constant velocity
acceleration
for any sub questions, should you redraw a force diagram if anything changes?
yes
when dealing with forces on a slope (regular) what is the order of calculation?
resolve perpendicular to the plane
resolve parallel to the plane
should u draw big diagrams?
yes
for connected particles / pulleys on slope, what is the order of calculation
use F = ma vertically (on the particle not on slope)
resolve perpendicular to the plane
use F = ma on particle on slope (using the resolved parallel to slope)
then do simultaneous equations
for the first part of a connected particle on slope question, where do u draw tension?
ONLY away from the particle
for the first part(s) of the question DO NOT label tension going to the particles (near the pulley). should only be 2 T’s if on a regular one

label where the tension would be in this part of a question to do with tensions from pulley
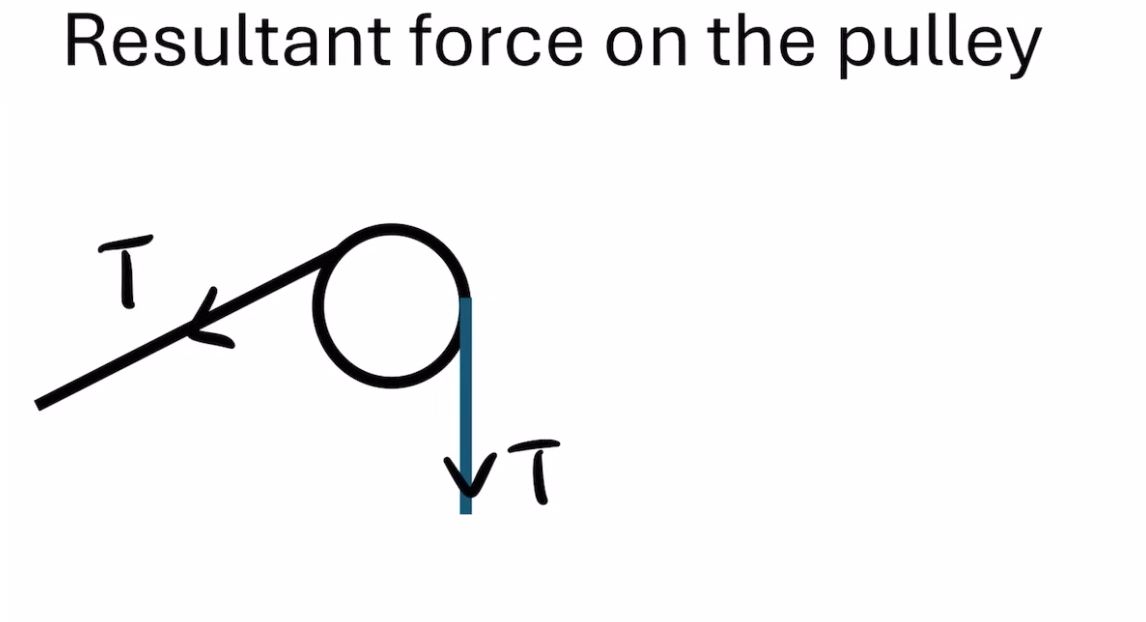
what is the equation used to calculate the resultant force (Tension) exerted on the pulley by a string
2Tcos(90-theta/2)

derive the equation used to calculate the resultant force (Tension) exerted on the pulley by a string


Do this question
a) mew = 0.25
b) = particle will slide down the plane

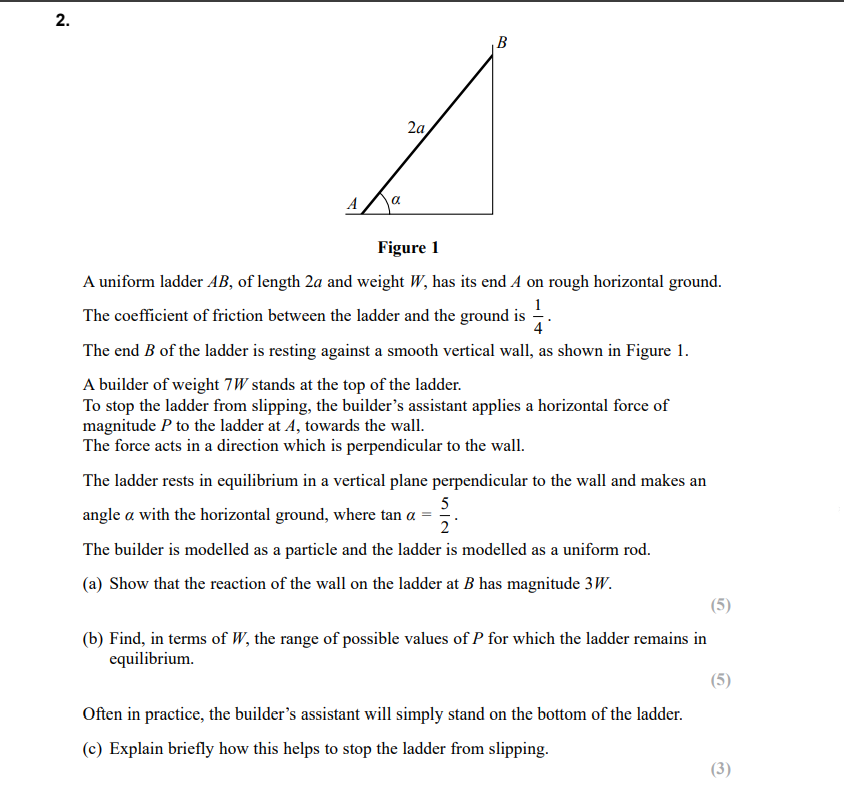
do this question
look at image for answers

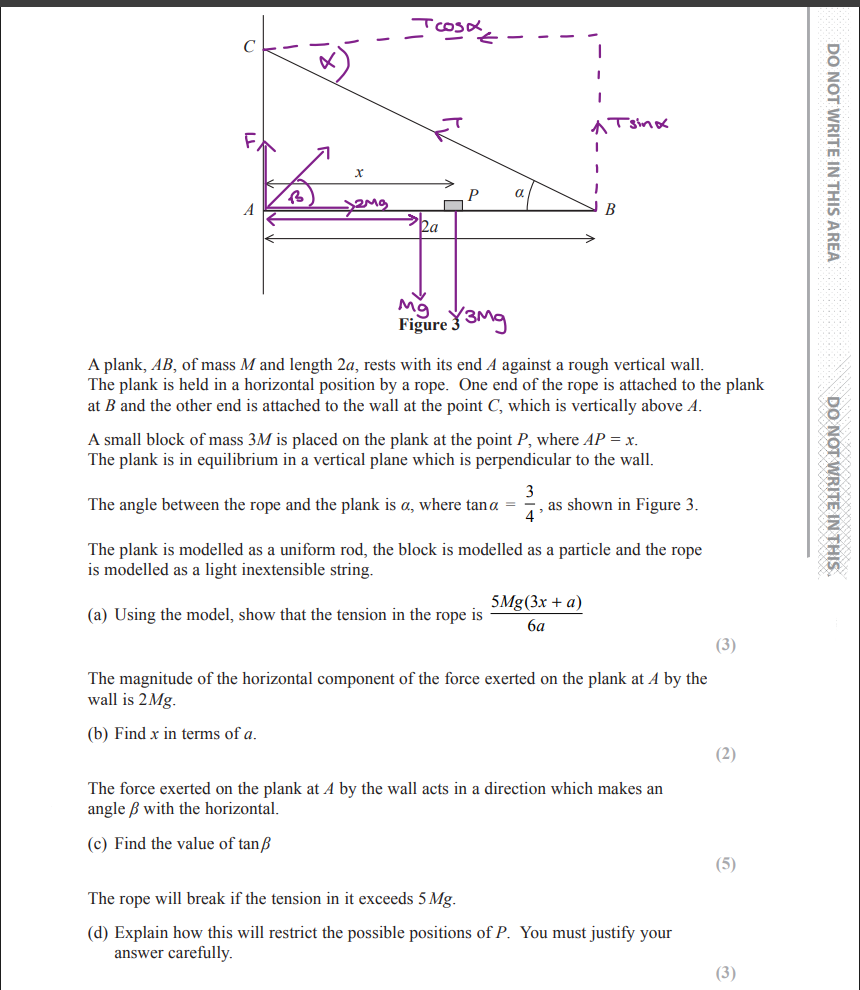
do this question
all done in image
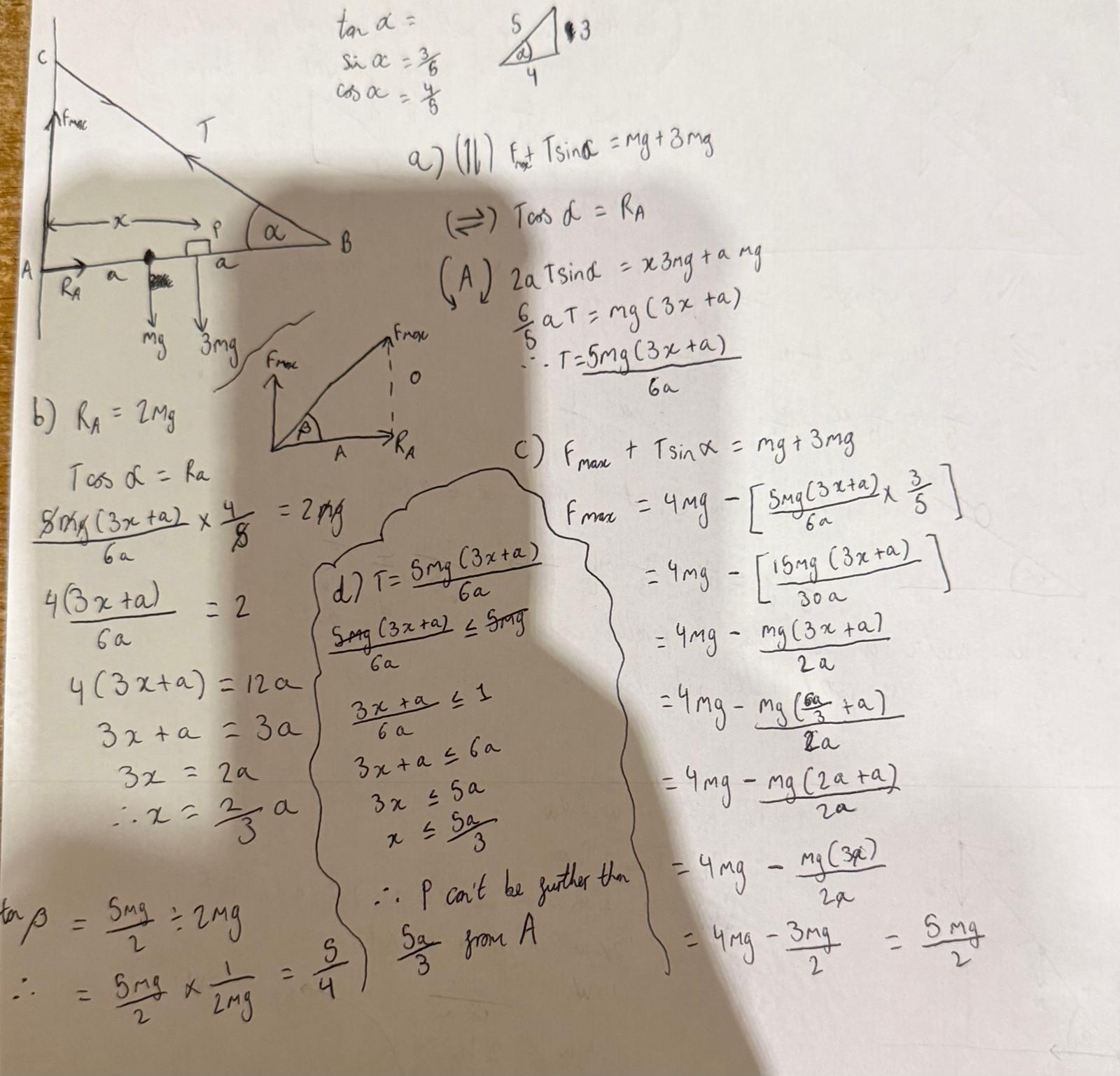
explain why the perp reaction on a plane from something it rests on (e.g a drum) is actually perpendicular
it is perpendicular because the drum/object is smooth
In what direction is the resultant force acting on a slope at point A (the bottom)
the same direction as the slope e.g the force at angle theta
For any question that asks how the normal reaction would change, what do u have to think abt
how it affects the perpendicularly resolved forces
how it affects the horizontally resolved forces
how it affects the moments