BC Biology 12- cell biology
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Matter
Flashcard
This refers to substances that can exist in various states, such as solid, liquid, and gas. It is made up of atoms and molecules and is fundamental to physical science.
Elements
Substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. They consist of atoms, which are the basic units of matter.
Each has a unique number of protons in its nucleus, defining its properties and position on the periodic table. Elements combine to form compounds and play crucial roles in chemical reactions.
Examples include oxygen, gold, and iron.
Atoms
Subatomic particles such as the proton, electron, and neutron.
Ex. Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N)
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with a positive electrical charge.
They are found in every atomic nucleus of every element
Neutron
An uncharged elementary particle that has a mass nearly equal to that of the proton and is present in all known atomic nuclei except the hydrogen nucleus.
Electron
A stable subatomic particle with a charge of negative electricity, found in all atoms and acting as the primary carrier of electricity in solids.
Molecule
Two or more atoms combined to form a molecule
Ex. water, amino acids
Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds.
A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound.
Ionic bond
Ionic bonds are formed when electrons are transferred between a metal and a non-metal element. As atoms gain or lose electrons, they become charged particles called ions.
generally found in salts
Ex. NaCl
Covalent bond
Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between two non-metal elements
Each atom has an octet of electrons in its valence shell (or 2 electrons in the case of hydrogen)
When the sharing of electrons between two atoms is equal, the covalent bond is said to be a nonpolar covalent bond
Ex. CO2
Polarity
Polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is primarily an electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen atom which is covalently bonded to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group, and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor.
Hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.
Hydro- water
Philic- loving
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be non-polar
They only dissolve in oil-based substances
Hydro-water
Phobic-fearful
Acid
Acids are substances that dissociate in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+)
acidity of a substance depends on how it fully dissolves in water
Strong acid/ Hydrochloric acid (HCI) dissolves almost completely (HCI= H+ + CL-)
Base
Bases are substances that either take up hydrogen ions (H+) or release hydroxide ions (OH-)
Strong base/ Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) dissociates almost completely
pH scale
The pH scale is used to indicate the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution
traditional scale ranges from 0-14
pH of 7 represents a neutral state, hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion concentrations are equal
below 7 is an acid
above 7 is a base
Buffer
A buffer is a chemical or combination of chemicals that keeps pH within a specific range
living organisms maintain pH within a narrow range 7.35 to 7.45
if pH drops, acidosis results
if pH rises, alkalosis occurs
mechanism to maintain pH
Homeostasis
The self-regulating process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to optimal conditions for survival.
regulated by positive and negative feedback loops
disruption in homeostasis often lead to diseases or disorders
Ex. Body temperature and blood pressure
Organic molecule
Essential to human functioning
they must contain carbon
almost always contain hydrogen
also known as biological molecules
the smallest organic molecule is methane (CH4)
Functional groups
Specific combination of bonded atoms that always react in the same way.
Monomer
Basic units or building blocks of organic compounds
Polymer
Monomers that repeat over and over to form larger molecules
aka macromolecules
Dehydration synthesis
The making of a polymer through H2O removal
the building of biological molecules
Hydrolysis
The splitting of a bond using H2O
the breaking down of biological molecules
Carbohydrate
Function
quick fuel
short-term energy storage
structural role in woody plants, bacteria, and animals
cell-to-cell recognition
Monosaccharide
consist of monomer subunits called monosaccharides
often called simple sugars
readily dissolve in water
end in -ose
Pentose
5-carbon sugar (C5 H10 O5)
ribose (in RNA)
deoxyribose (in DNA)
Hexose
6-carbon sugar (C6 H12 06)
glucose (blood sugar, vital reactant for cellular respiration)
fructose (found in fruits and honey)
galactose (found in milk)
Disaccharide
are made by dehydration synthesis
2 monosaccharides bonded together
glucose + glucose = maltose (“malt sugar”)
glucose + fructose = sucrose (common table sugar)
glucose+ galactose= lactose (found in milk)
Polysaccharide
is a carb that contains a large number of monosaccharide
linked together by dehydration synthesis
often called complex carbs
polysaccharides are the form in which living things store excess sugar
Starch (storage form of glucose in plants) is unbranched or slightly branced
Cellulose/dietary fibre (used as a structural material in the cell walls of plants) is linear
Glycogen (storage form of glucose in animals) is highly branched
Lipids
Function
contains more energy than carbs
long-term energy storage
main component of cell membranes
many types of hormones
insulates against heat loss
forms a protective cushion around major organs
waxes prevent water loss and minimizes contaminants
Fats
saturated fatty acid
animal in origin (lard)
solid at room temperature
Oils
unsaturated fatty acid
plant in origin (olive oil)
liquid at room temperature
Glycerol
one of the 2 subunits of lipids
“backbone”
3-carbon compound with 3 -OH groups
Triglyceride
common lipid
also referred to as a neutral fat
has 3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule
is formed by dehydration synthesis
Saturated fatty acid
no double bonds between the carbons
contain as many hydrogens as they can hold
Ex. fat (lard)
Unsaturated fatty acid
does have double bonds in the carbon chain which reduces the number of hydrogen atoms
Ex. oil (olive oil)
Phospholipid
important lipid
tend to form a bilayer
are essential the structure and function of cell membranes
phospholipids are basically triglycerides except that in place of the 3rd fatty acid, there is a polar phosphate group
The polar phosphate group is the hydrophilic head
The 2 fatty acids become the non-polar hydrophobic tails
Steroid
classified as lipids
distinctly different structure
composed of 4 fused carbon rings
each type differs by the types of functional groups attached to the carbonskeleton
Cholestrol (provides structural stability)
Testosterone and Estrogen (reproductive system hormones)
Protein
Functions
Metabolism
Support (keratin and collagen give strength to ligaments, tendons, and skin)
Transport (channel and carrier proteins allow substances to travel through the cell membrane)
Defense (antibodies prevent antigens from destroying cells and disrupting homeostasis)
Regulation (insulin regulates how much glucose is in the blood)
Motion (actin and myosin allow parts of the cell to move)
Amino acid
amino acid monomers construct protein polymers
composed of a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen, amine group (-NH2), carboxyl group (-COOH), R
Amine group
(-NH2)
The amine group is a functional group that is composed of a nitrogen atom that is forming a total of three bonds: One bond with the parent organic chain. Two different bonds with either a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group R.
Carboxylic acid group
(-COOH)
Carboxyl groups are a combination of two functional groups attached to a single carbon atom, namely, hydroxyl (single-bonded OH) and carbonyl (double bonded O) groups.
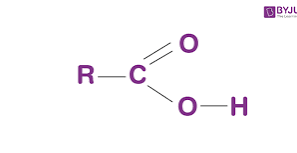
R-group
R (variable)
R has 20 variations that can be polar, non-polar or ionized
Enzymes
act as biological catalysts which speed up chemical reactions in cells
Hormones
Hormones are chemical substances that act like messenger molecules in the body.
After being made in one part of the body, they travel to other parts of the body where they help control how cells and organs do their work
Ex. growth hormone, insulin, melatonin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (Hb) is the protein contained in red blood cells that is responsible for delivery of oxygen to the tissues.
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
Polypeptide
Many amino acids linked together
Peptide bond
Amino acids are linked by dehydration reactions that link the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amine group of another
the covalent bond that forms is a peptide bond
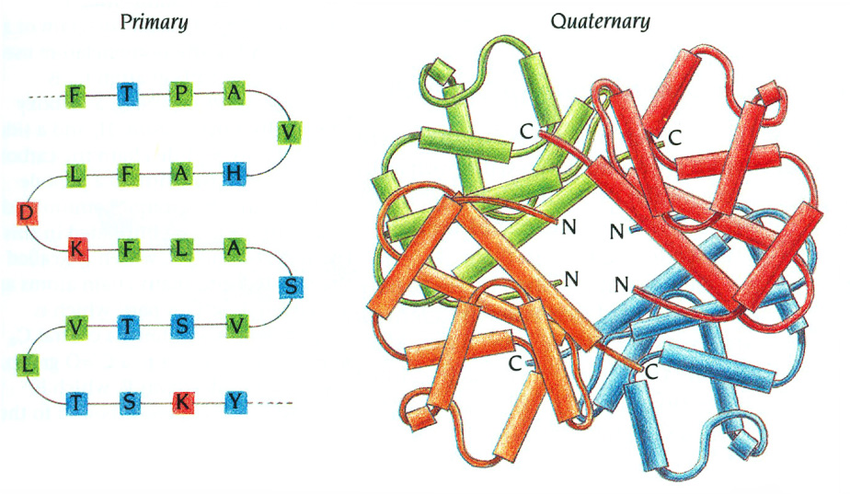
Primary structure
The linear sequence of amino acids, coded for in the genes of DNA, held together by peptide bonds

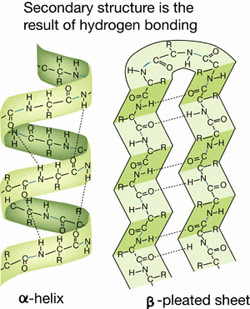
Secondary structure
Alpha helix or beta pleated sheet, caused by hydrogen bonding between amino acids
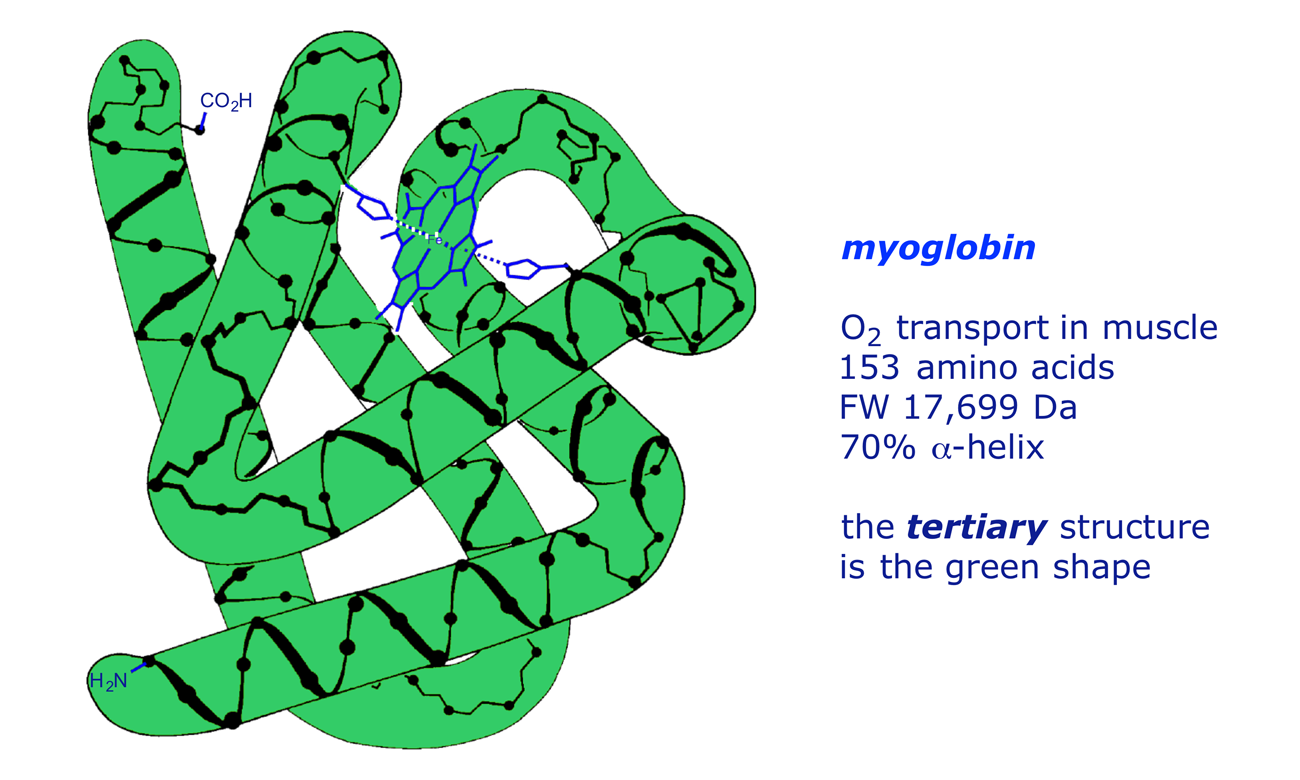
Tertiary structure
Interaction of amino acid side chains with water along with hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and covalent bonds between the R groups leads to the final 3D structure of proteins.
Most enzymes display this level of structure and can be denatured by high temperature or changes in pH
Quaternary structure
Occurs when two or more folded polypeptides interact to perform a biological function
Denaturation
process modifying the molecular structure of a protein.
Denaturation involves the breaking of many of the weak linkages, or bonds (e.g., hydrogen bonds), within a protein molecule that are responsible for the highly ordered structure of the protein in its natural (native) state.
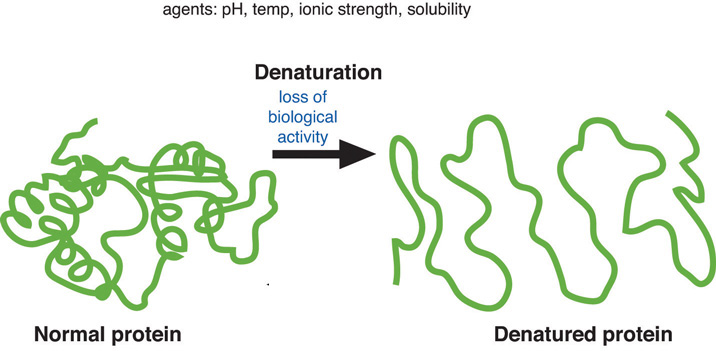
Nucleic acids
Function
Each cell has a storehouse of information that specifies how a cell should behave, respond to the environment, and divide to make new cells
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses. A major function of nucleic acids involves the storage and expression of genomic information.
Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, encodes the information cells need to make proteins.
Nucleotide
nucleotide monomers make up nucleic acids
they are composed of three types of molecules; pentose sugar (either deoxyribose is DNA or ribose in RNA), phosphate group (phosphoric acid), nitrogenous base
Nitrogenous base
DNA- adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine
RNA- adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine
Phosphate
A form of phosphoric acid, which contains phosphorus
Pentose sugar
DNA- deoxyribose
RNA- ribose
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
stores information about how to replicate itself
specifies the order in which amino acids are to be joined to make a protein
Double helix
two strands of DNA twist around each other to form a double helix
Sugar-phosphate backbone
The sugar-phosphate backbone is a chain of alternating phosphate groups and deoxyribose sugars that holds together a series of different nucleotides
nucleotides are joined into a DNA or RNA polymer by a series of dehydration reactions, this results in a linear polymer called a strand
Complementary base sharing
Complementary base pairing in DNA refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases:
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G)
Adenine (A)
double ring structure with nitrogen atoms
it is a purine nucleotide base
Thymine (T)
Also known as 5-methyluracil, thymine pairs with adenine (A) in DNA
pyrimidine nucleobase
Cytosine (C)
Cytosine has a heterocyclic aromatic ring, an amine group at position 4, and a keto group at position 2
pairs with guanine
Guanine (G)
guanine is paired with cytosine
formula C5H5N5O
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Diverse type of nucleic acid with multiple roles in protein synthesis
made up of adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine
Uracil (U)
uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds
weak acid
it is very resistant to oxidation and so it allows the RNA to exist outside of the nucleus freely without any hassle. This DNA can’t do.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
It is a special high-energy nucleotide that acts as the universal energy currency of the cells
it has three phosphate groups
the bonds of the last 2 phosphate groups are unstable and easily broken
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
In cells, hydrolysis of the terminal phosphate produces the molecule ADP as well as a lot of energy
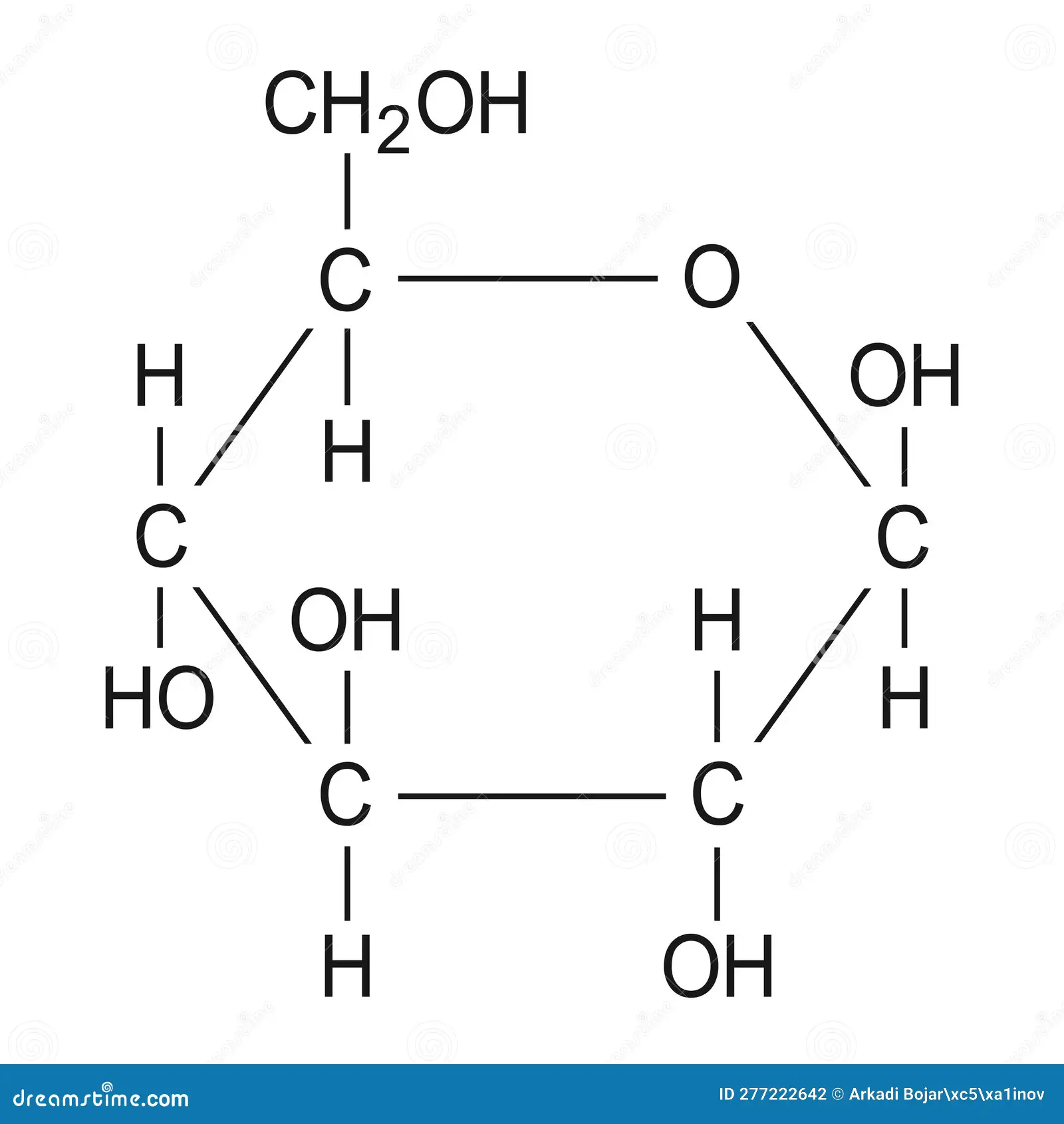
Monosaccharide (Glucose)
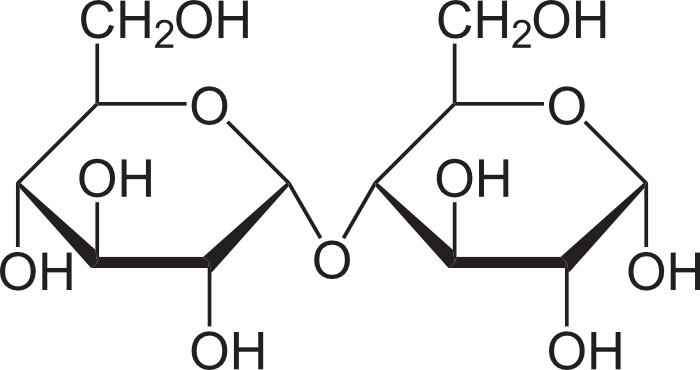
Disaccharide (maltose)
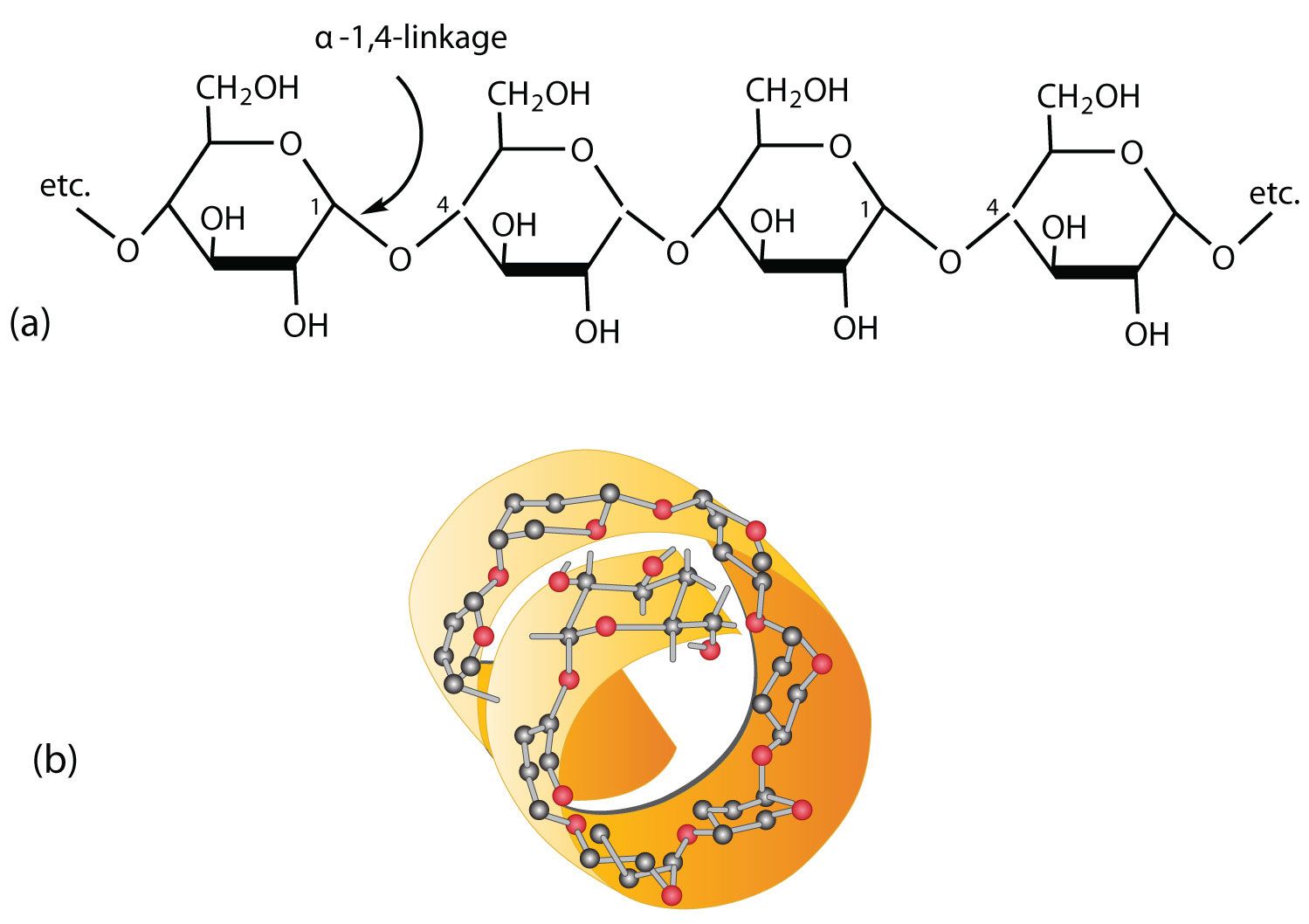
Polysaccharide (starch)
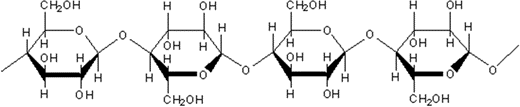
Polysaccharide (cellulose)
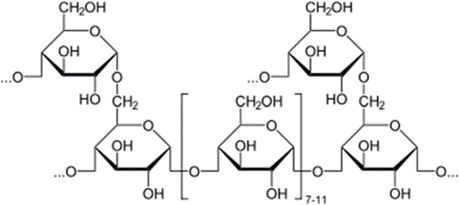
Polysaccharide (Glycogen)
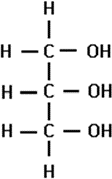
Glycerol
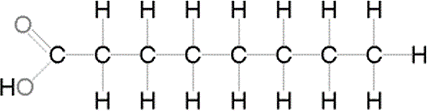
Saturated fatty acid
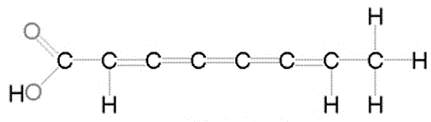
Unsaturated fatty acid
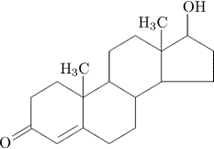
Steriod
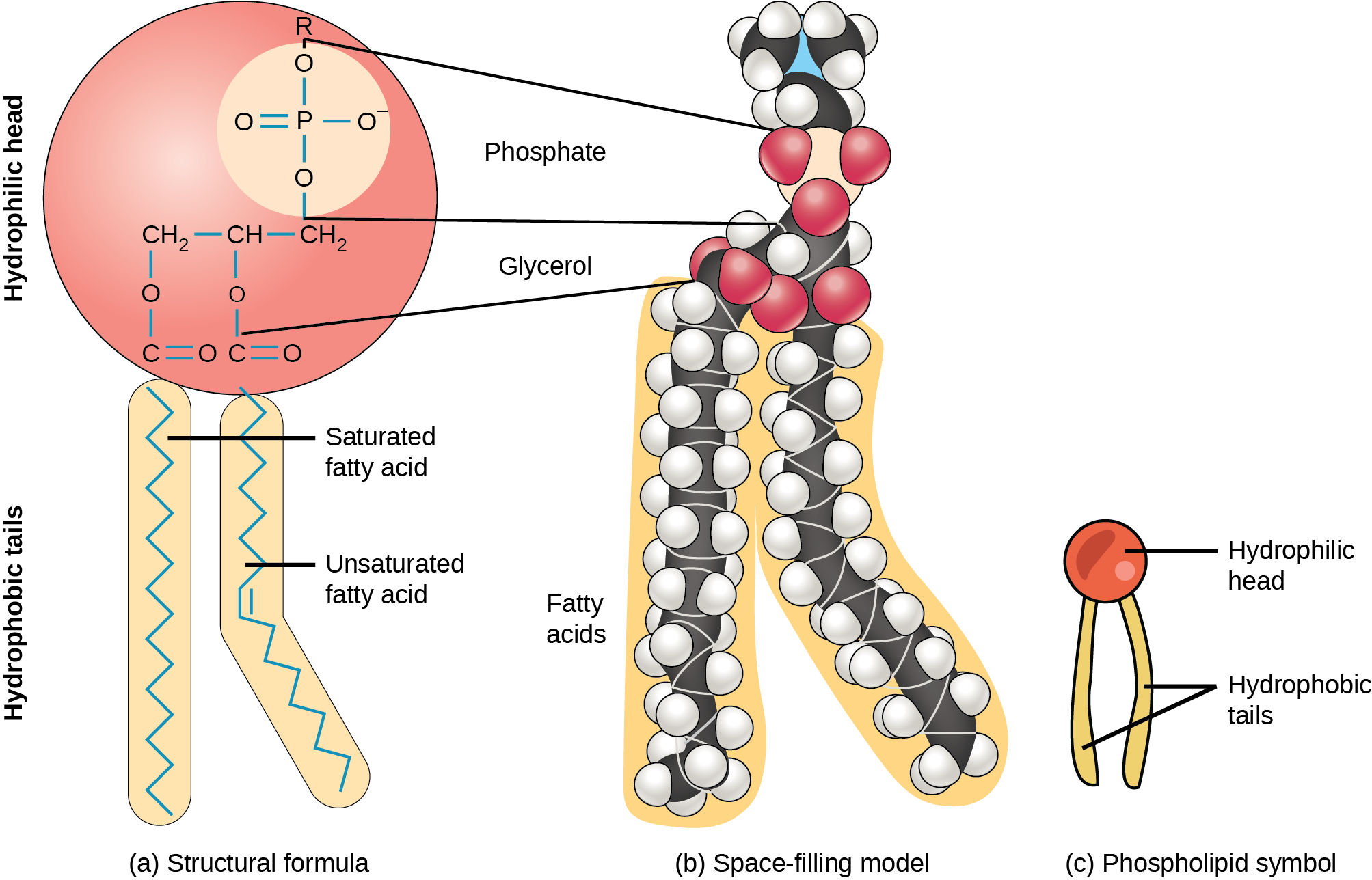
Phospholipid
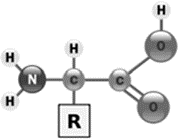
Amino acid
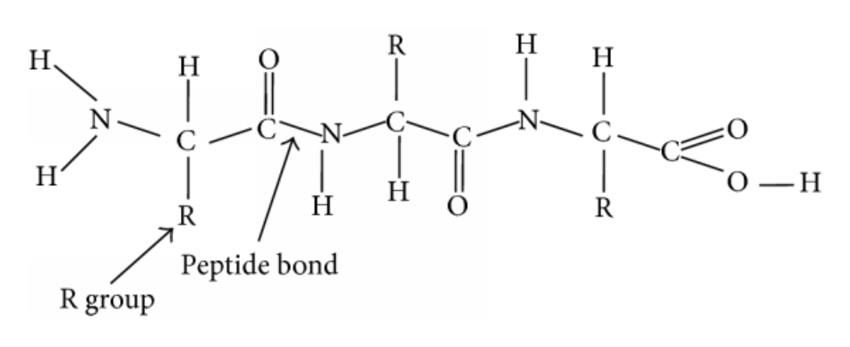
Polypeptide (protein)
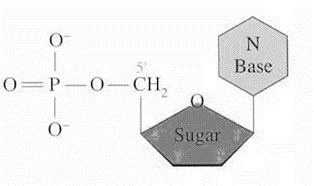
Nucleotide
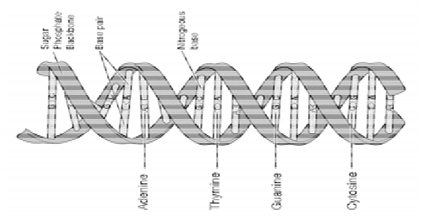
DNA
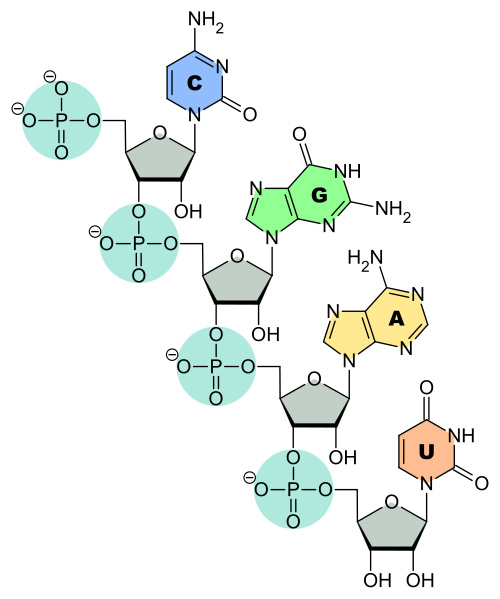
RNA
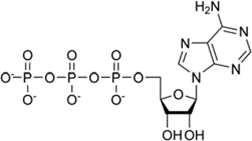
ATP