PSYCH 1000 Final (Dennis Miller)
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Pseudoscience
claims presented as evidence --> not supported by scientific method
Amiable Skepticism
remains open to new ideas, but is wary. Systematically question and evaluate info --> scientific method
scientific theory
explain the facts, BIG idea, replicable
what is the scientific method
observe, predict, test, interpret, communicate, replicate
Parsimonious vs Replicable
Parsimonious: explains a lot using the fewest assumptions. (Simple > complicated.)
Replicable: can repeat the methods and get the same results → Replication = reliability.
Hypothesis
1. Falsifiable
2. Parsimonious (simple explanation)
Specific, informed, and testable prediction
Descriptive Research
observe behavior to describe behavior (over a long period of time)
types of descriptive research
case study, survey, naturalistic observation, qualitative
case study
observe 1 person (or group) over long period of time
Naturalistic observation
observes behavior in real life
Qualitative Research
data from open ended Q's --> get unstructured answers
Survey
info numeric and quantifiable --> limited response options
Correlational research
the study of the naturally occurring relationships among variables
what is a subset?
sample
what are the types of samples
convenience: easily studies
representative: represents a population
random: same chance of being selected
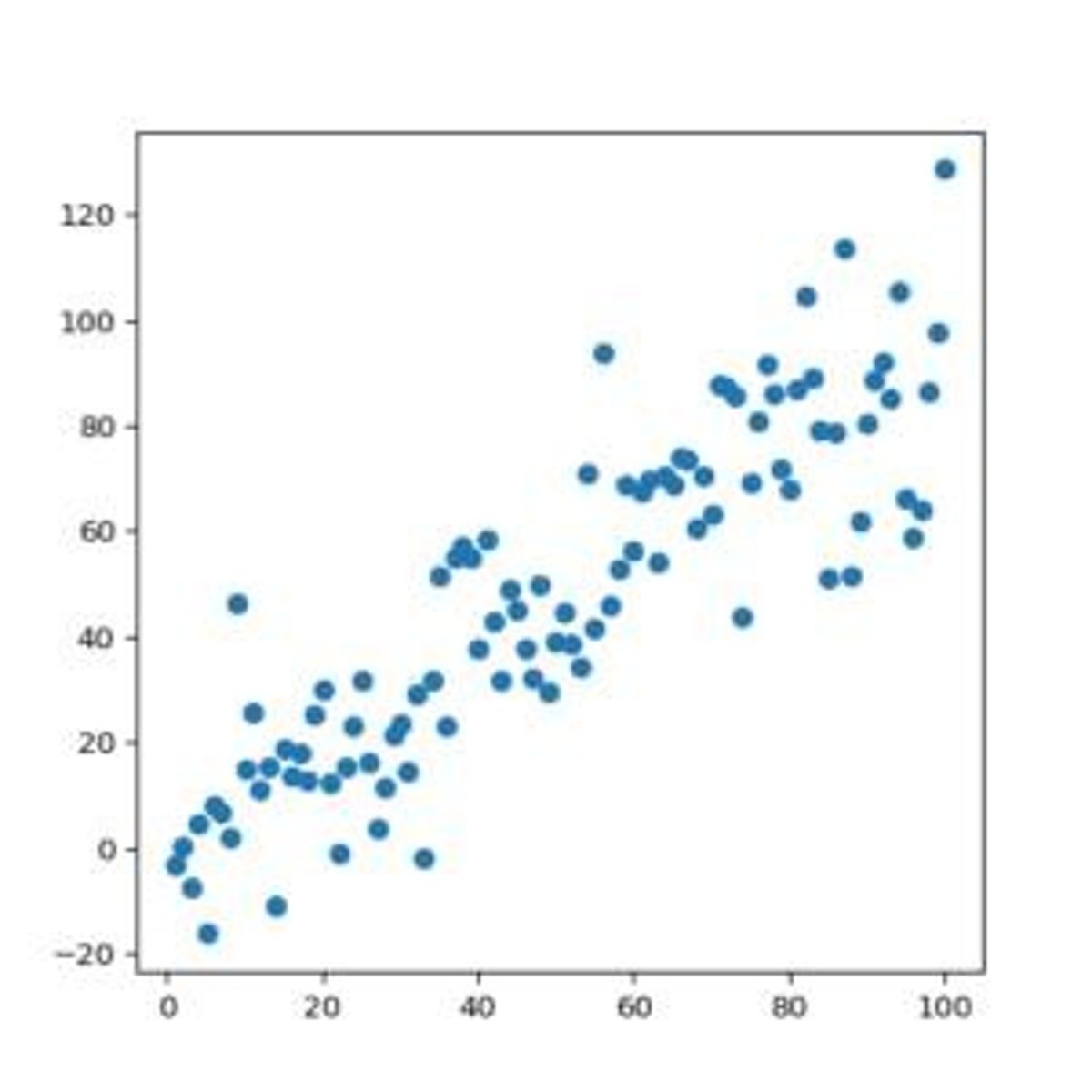
what is a positive correlation
up, up / down, down
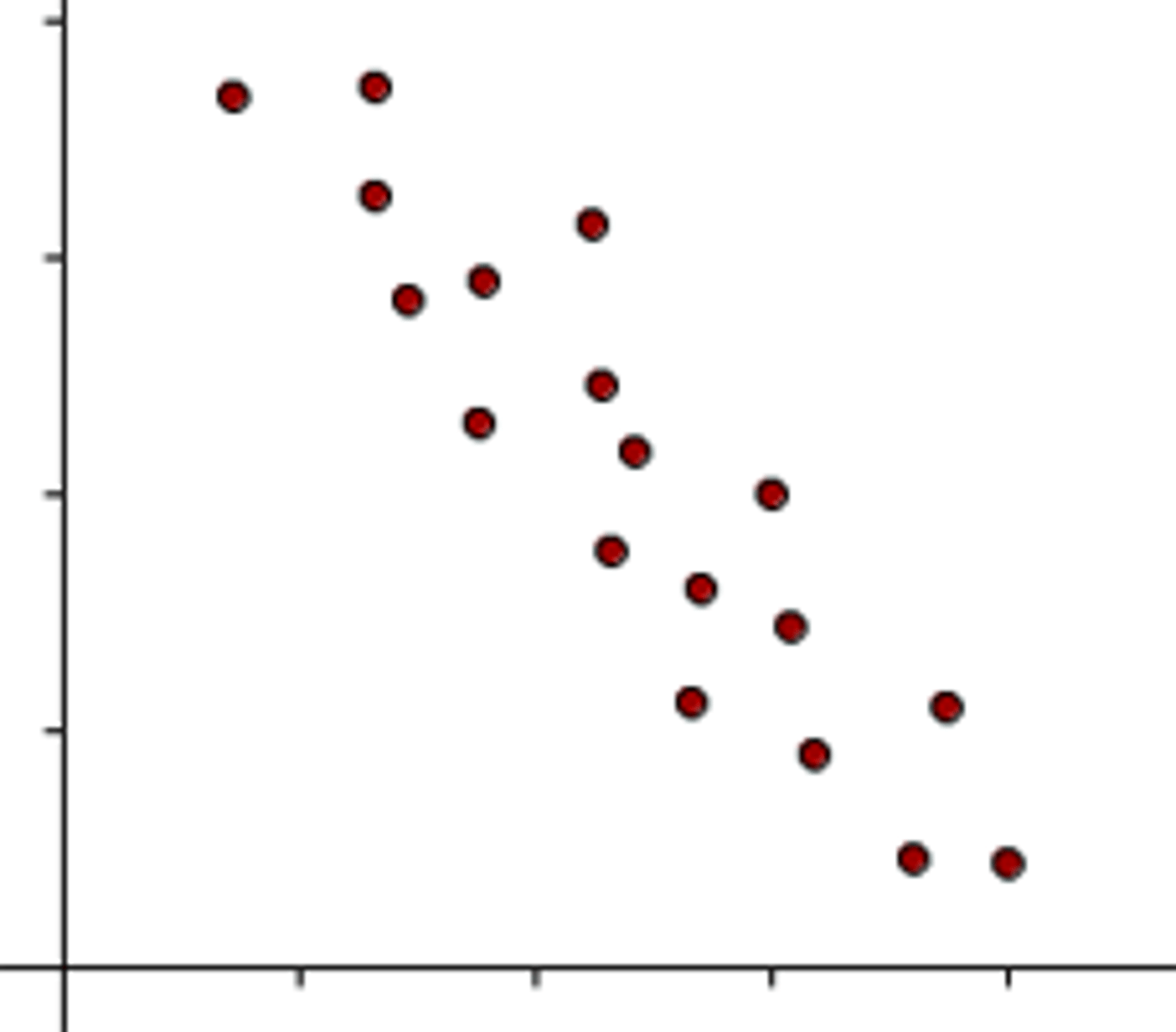
negative correlation
up, down
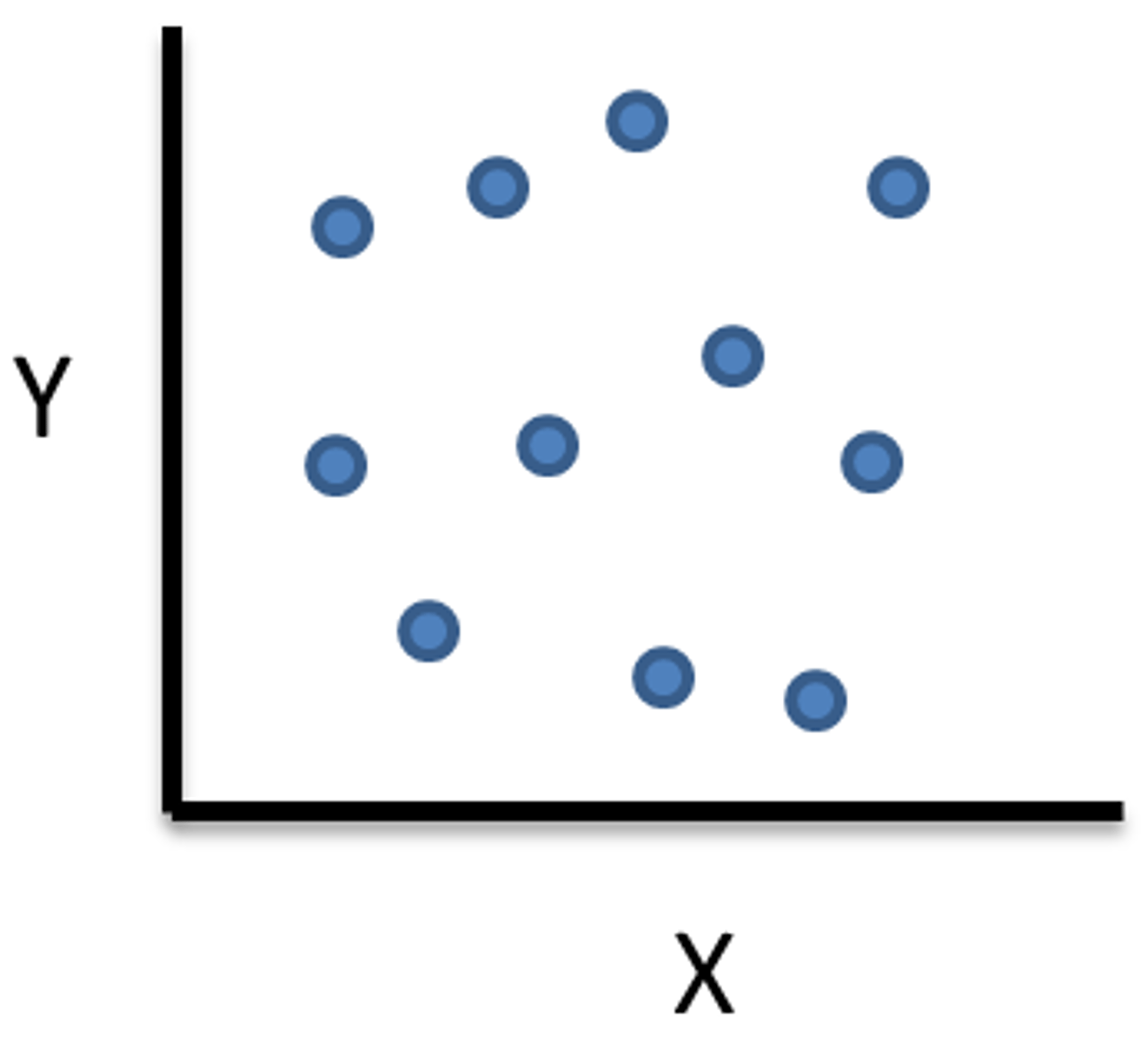
zero/no correlation
no relationship between variables
problems with correlation?
directionality, 3rd variable, and illusory (superstitions)
Experimental Research
this causes this --> tests causal hypothesis by measuring and manipulating variables
true experiment vs quasi-experiment
true: randomly assigned
quasi-experiment: can't use random (sex, gender, location, race)
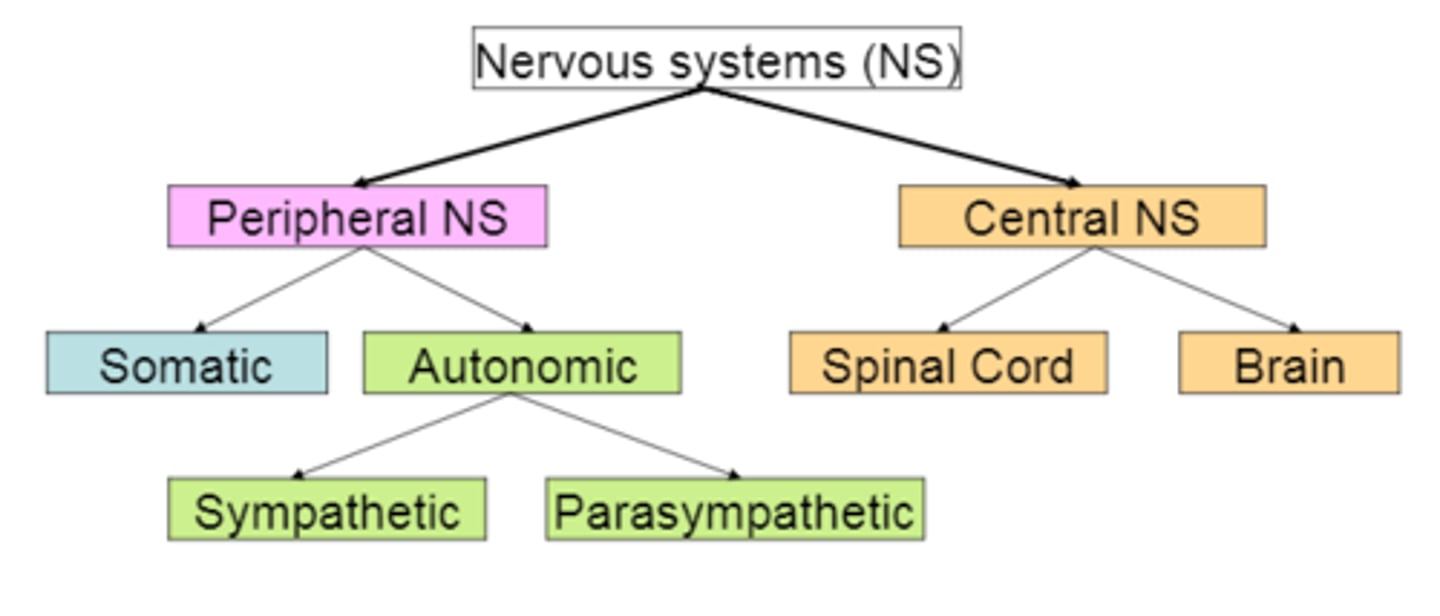
nervous system diagram
somatic = voluntary
sympathetic = arousing aka fight or flight
parasympathetic = calm (ex: digestion)
The Neural Doctrine
NS is not random --> behavior from neural communication
behavior comes from communication, change behavior
glial cells
provide structure, support and protection, regulate chemicals, AID communication, repair damage
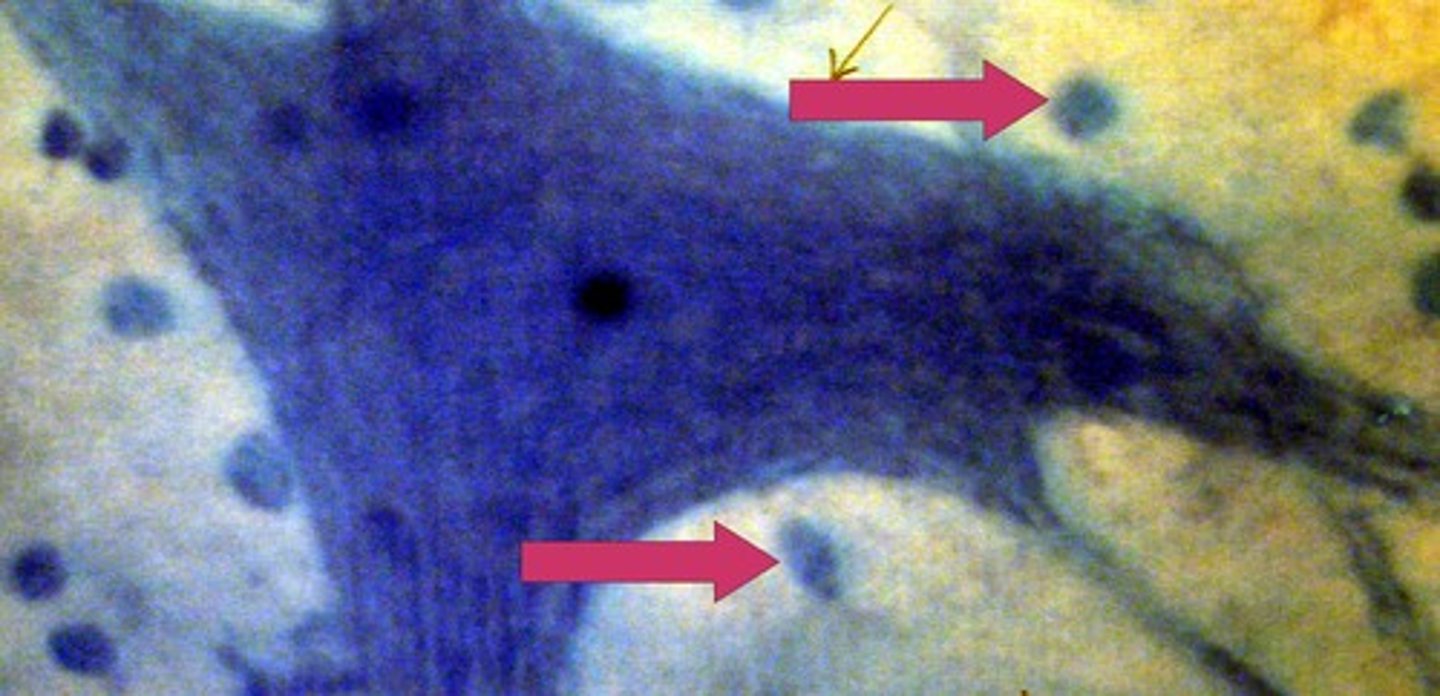
neurons
specialized to receive integrate and transmit info
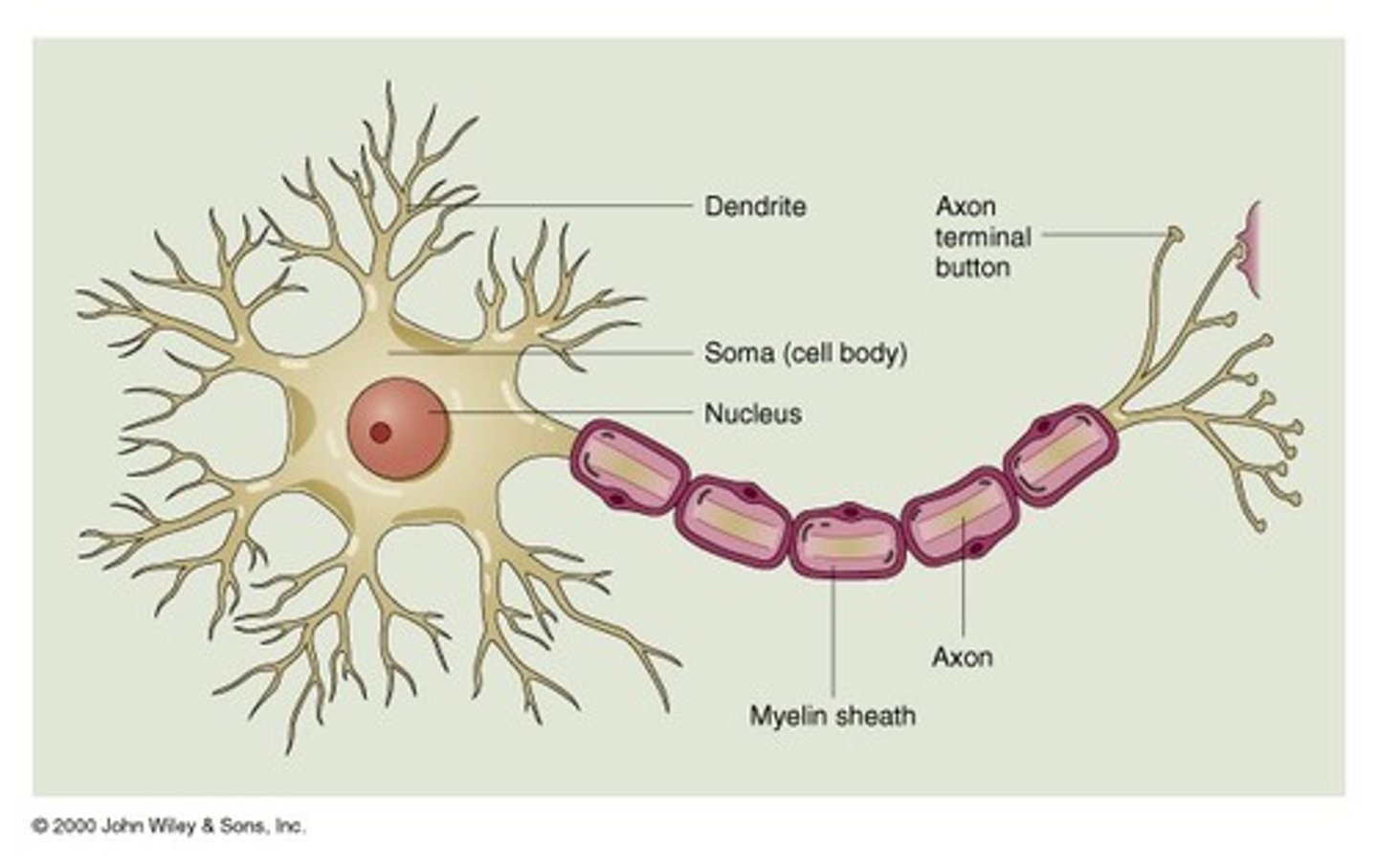
how do neurons communicate?
Electrochemically
chemical: BETWEEN neurons (neurotransmitters)
electical: WITHIN neuron (mem polarization and action potential)
(-70 mV resting mem potential, depolarized -> closer to zero, hyperpolarized -> further from zero)
what is the frontal lobe in charge of
personality, decision-making, high cognition
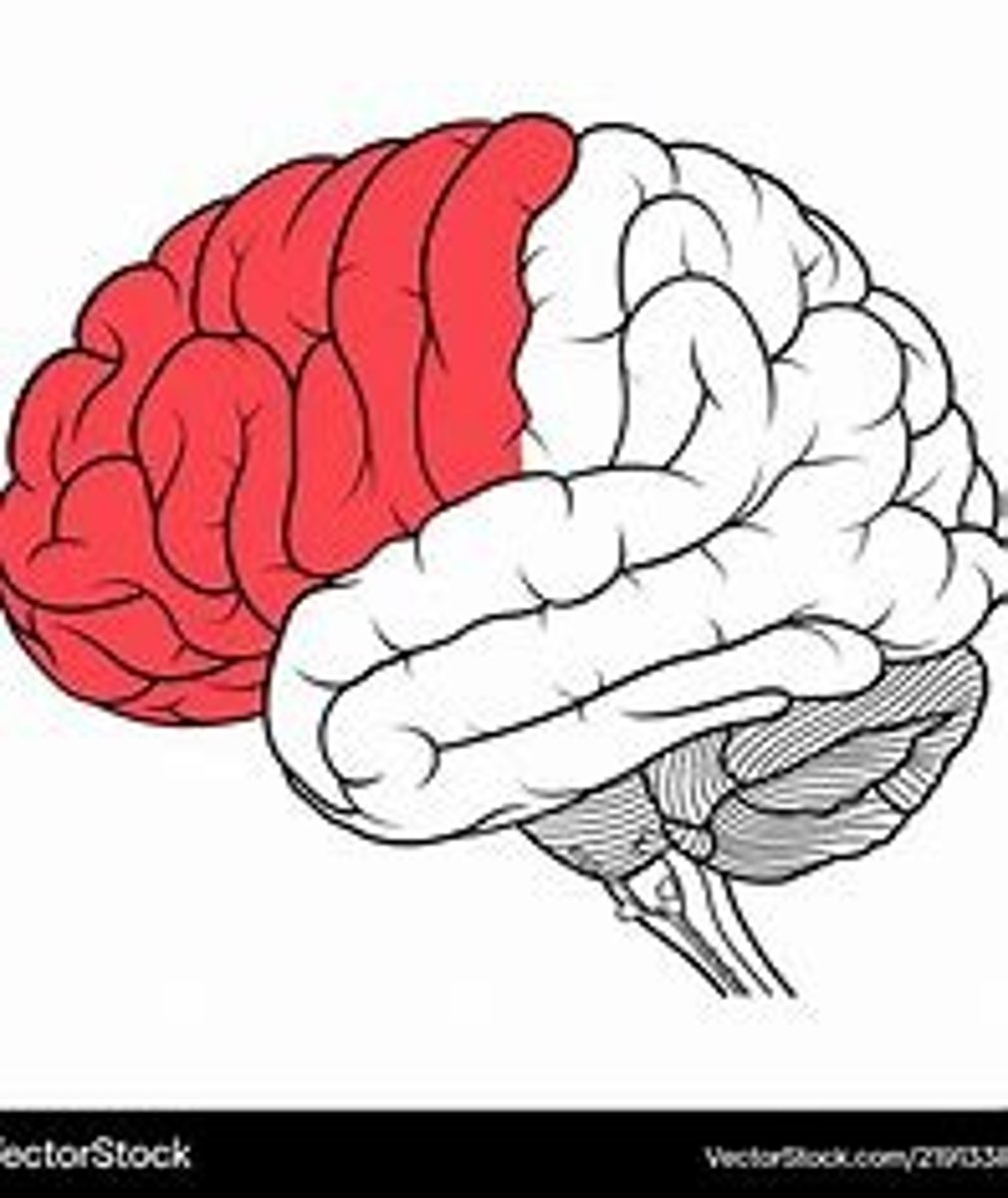
what is the parietal lobe in charge of
perception of touch
what is the temporal lobe in charge of
hearing, memory
what is the occipital lobe in charge of
sight
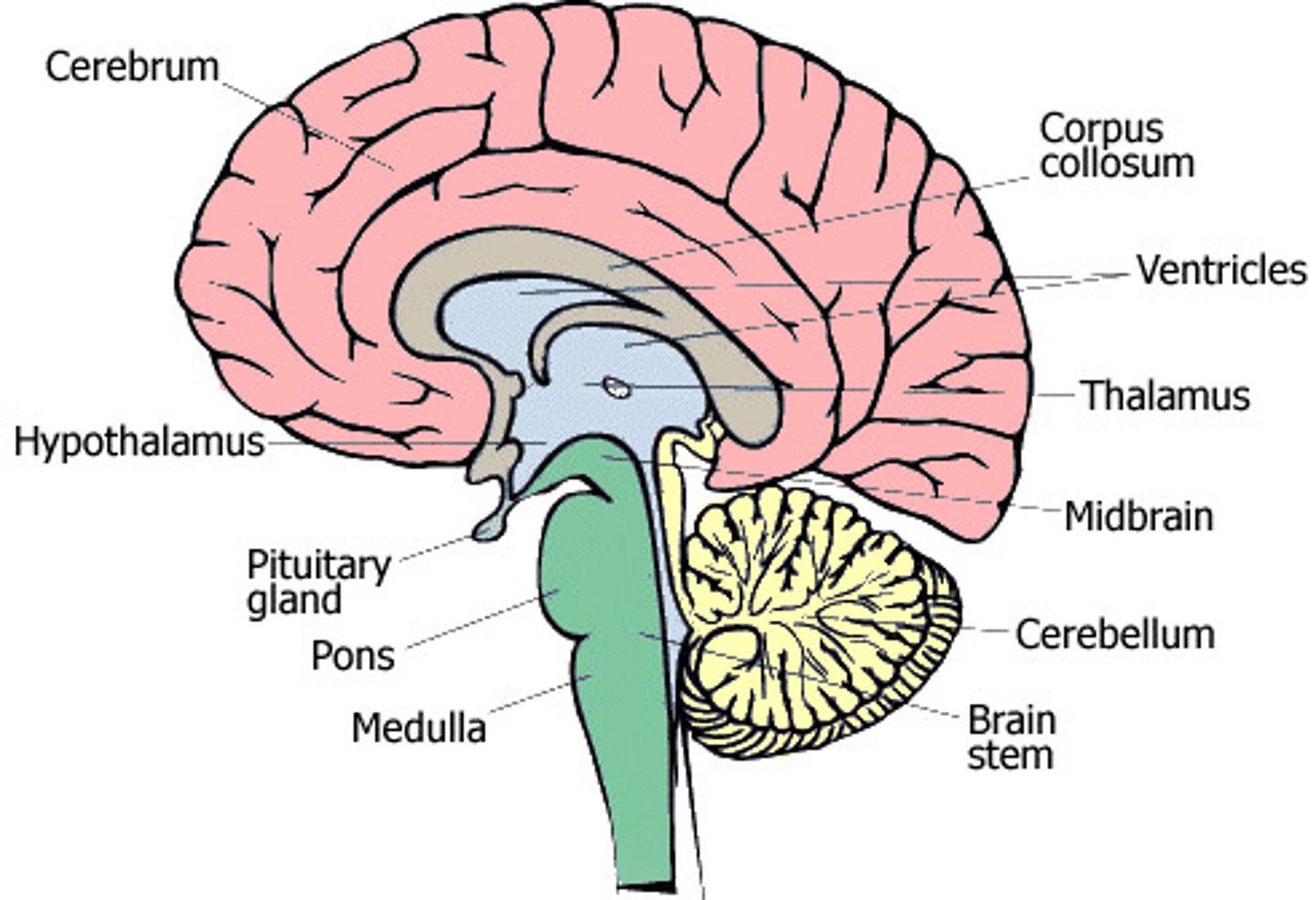
what is the cerebellum in charge of
body movement, balance, coordination, fine motor skills, some cognitive abilities
what are the pons in charge of
internal functions (vomit, respiration, HR, BP)
what is the medulla in charge of
label internal brain anatomy
Parkinson's Disease
dec of dopamine --> tremors, studdering, impaired walking
ways to measure the brain
EEG (brain waves, cap with electrons)
PET (radiation)
fMRI (pic of inside and function)
Split Brain
surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (from corpus callosum)
how do we experience flavor
taste (gustation), small (olfaction), Hepatic Senses (temp, pressure, and pain)
the chemical senses for taste
small and taste -->
1. physical stimulus
2. sensation
3. transduction
5 taste receptors
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
steps on how to taste
neural info from taste bud --> to hindbrain --> thalamus (sensory info) --> cerebral cortex (gustatory) or hypothalamus (reason for overeating) or amygdala (stress --> foods we hate)
gustatory effect
recognize foods
garcia effect
taste aversion
What brain regions contribute to foods that taste good (and makes us sick)?
amygdala
Why do we sniff when we try to smell something?
Odorants: molec. come into our system (forcing them to top of nasal passage → interact with olfactory receptors)
Use combinational coding → how we detect smells!
What's responsible for the person that I am? Is it biology or is it the environment?
<-------------------------------------->
0 1.0
(nurture) (heredity nature)
Heritability: value attributed in a particular trait that can be attributed to genetic vs. environmental
Multiplier affect: small initial advantage in some behavior (possibly genetic) alters the environment and magnifies the advantage (ex: sports)
Where does the nervous system come from and how does it change across the lifespan?
Proliferation (2-3wks after conception) - stem cells can become anything
Migration (4-5wks after) - stem cells move to needed, Differentiation (8 wks after) - change into certain/needed cells
Myelination (slows down with age)
Synaptogenesis (entire lifespan) - connection between neurons
What are the different baby personalities we're born with?
Born with different temperaments: easy, difficult, slow to warm up
How is a child connected to their caregivers? What's their attachment style? How do we assess attachment style?
Secure and Insecure
insecure avoidant - little distress to parent leaving and ignores parent when returned
insecure resistant - very upset with parent leaving cannot be comforted on reunion, insecure
disorganized/disoriented- odd conflicted behaviors)
How do babies, toddlers, kids (and us) think about the way the world works?
Sensorimotor (birth- 2yrs), Preoperational (2-7), Concrete Operations (7-12), Formal Operations (12+)
Sensorimotor Stage
Recognize their own free will
Dev object permanence
impossible/possible events
Sense of self (kid in front of mirror)
Preoperational stage
Begin to use language to represent objects
Less egocentric and begin to understand another's perspective
Distinguish appearance from reality
Sense of conservation
Concrete Operations Stage
Think logically
Classifies and organizes objects on many dimensions
Formal Operations Stage
Think logically about abstract propositions
Test hypothesis about world
Concerned with future and ideology
What are the Stages of Crisis
Trust and Mistrust
Autonomy (I can do it) vs. Shame & Doubt
Initiate vs. Guilt → CHORES!!
Industry vs. Inferiority → OTHER kids
Identity vs. Role Confusion
Intimacy vs. Isolation
What does it mean to be conscious?
An awareness of one's surrounding and of what is in one's mind at a given moment; includes aspects of being awake and aware
How does our brain contribute to consciousness?
Hypothalamus → SCN (bio clock)
When we sleep → regulated by body's circadian rhythm
Zeitgebers "resets" bio clock (ex: sunlight)
Pineal gland also resets clock → melatonin
What controls when we're tired and when we're aroused?
Arousal is regulated by the activity of neurons
From hindbrain through the forebrain
Hypocretin/Orexin: high arousal
Adenosine: low arousal
How do we study the brain in arousal and sleep? How does it change through the day/night?
Electroencephalogram (EEG) → measures brain's electrical activity, Looks and amplitude and freq
- Awake: low amp, high freq
- Asleep: high amp, low freq
Rem vs. Non-REM
-REM: Rapid Eye Movement; darting movements of the eyes under closed eyelids
-Non-REM: The first stages of sleep that are distinct from both wakefulness and REM sleep
Narcolepsy
"seesaw" doesn't work properly
insomnia? How can I manage it
difficulty falling asleep, sleep doesn't feel refreshing
DO: Exercise (not too close to bedtime)
DONT: use alcohol before bed, overdo caffeine, do other things in bed, use/overuse sleep meds
What do we recall when we're given a list of things to remember?
Primary effect: easier to remember beginning
Recency effect: easier to remember end
main types of memory that we have and how do we move information among these types?
-Sensory store (super tiny) - unattended info is lost
-short term memory (small) - unrehearsed info is lost
-Long term memory (infinite space) - some info may be lost
What are some of the types of forgetting we can overcome?
Absentmindedness- lapses of attention lead to forgetting
Blocking- temporary inaccessibility of info in long-term storage
Interference- new mems impair old mems (retroactive) and old mems impair new mems (proactive)
Misattribution- False Memory- memories that individuals believe and recall as true → when it never occurred
Crypomnesia - mistakenly believe that an idea id a product of your own creation → you encountered it previously and then forget
Transience- dec accessibility of info from long-term storage over time
Amnesia- inability to remember events for a period of time often due to damage to CNS (struggles with explicit memory)
retrograde vs. anterograde
forget period leading up to the event vs. can not make new memories
Hebbian learning:
when 2 joining cells fire simultaneously, connection between them strengthens "neurons that fire together wire together"
Long Term Potential (LTP)
enhanced activity → results from strengthening of synaptic connections
types of learning
non-associative, associative, watching others
types of nonassociative
Habituation- a dec in response after lengthy or repeated exposure to a stimulus
Sensitization- an inc in response after lengthy or repeated exposure to a stimulus
Where do we see classical conditioning in our own life?
Forward Conditioning: (strongest learning) - CS shortly precedes the onset of the US
Simultaneous Conditioning: CS and US occur at the same time
Backward Conditioning: (weakest) - US precedes CS
What factors increase/decrease the chance that we'll develop the conditioned response?
Operant (instrumental) conditioning: actions consequences determine how likely an action is to be performed in the future
- Satisfying effect → more likely to occur
- Discomforting effect → less likely to occur
How do we learn by the consequence of our behavior?
Operant Conditioning: process of changing behavior by manipulating the consequences of that behavior
Behavioral Modification
use of operant conditioning techniques to change behavior
Reinforcement
inc probability of behavior
Punishment
dec probability of behavior
What are ways we can increase our motivation
Classical Conditioning → What cues can you create?
Behavior → result of shaping → reinforcement of successful steps to a final behavior
Reinforcer: any stimulus → inc of behavior
Locus of control: degree to which people believe they have control over the outcome of events in their lives
Motivation
factors of differing strength that energize, direct, and sustain behavior
what factors increase (or decrease) motivation
Autonomy: felling one as choice and willingly endorsing one's behavior
Competence: experience of mastery and being effective in one's activity (I can do it)
Relatedness: need to feel connected and belongingness with others
Drive
perceived states of tension that occur when our bodies are deficit in some need
Incentive
any external object or event that motivates behavior
Incentive-Salience
external objects/goals (not internal) entice towards certain actions (can dev from a drive)
Intrinsic Motivation
DESIRE to perform b/c of the pleasure of activity rather than an external goal → I WANT to (ex: love sport, like cleaning, find subject interesting)
Extrinsic Motivation
external reason the activity is directed told (ex: rewards, avoid complaints, good grades)
What factors contribute to starting (and stopping) a meal
Cephalic phase (head factors), gastric phase, substrate phase (intestinal factors)
How do CCK and leptin contribute to starting/stopping a meal?
Low leptin = no E
Low CCK → brain tell you to eat
James-Lange Theory of Emotions
people become aware of their emotions after they notice their physiological reactions to some external event.
Bear → Body response → fear
Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotions
Suggests that the physical and psychological experience of emotion happen at the same time and that one does not cause the other
bear→ brain process → body response AND → emotion (fear)
Schachter and Singer (2 Factor) Theory of Emotions
Event and environment are interpreted to determine emotion
Bear→ body response → emotion label → fear
Health Psych
application of psychological principles to promote health and well-being
Well-being
positive state in which we feel our best
Psychosomatic Theory
the idea that emotional factors can lead to the occurrence or worsening of illness
Personality
characteristic thoughts, emotional responses and behavior that are relatively stable in an individual over time and across circumstances
Persona
the mask or appearance one presents to the world
Self-Reference effect
tendency to better remember info when it has been encoded in reference to the self
Working Self Concept
the immediate experience of the self in the here and now
Temperament
biologically based techniques to feel or act in certain ways
Humanistic Approach (to personality)
ways of studying personality where people seek to fulfill their potential through greater self understanding
What is a fully-functional personality, according to Carl Rodgers?
open to experience (both pos and neg emotions are accepted)
Existential living: living in the moment
Trust feelings: decisions are right
Creativity: risk taking, adjust and seek experiences
Personality types
classification of individuals into different groups (like boxes)