Pedia 2 Module 3B: Alterations in Nutrition, GI, Metabolism, and Endocrine
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Colic
paroxysmal abdominal pain or cramping manifested by loud crying and drawing the legs up to the abdomen
infants that cry more than 3 hours a day, more than 3 days a week, for more than 3 weeks
Regurgitation
return of undigested food from the stomach, usually accompanied by burping
Spitting up
dribbling of unswallowed formula from the infant’s mouth immediately after a feeding
Trigger of colic
this disease can happen due to
mothers who smoke
allergy to formula milk
growing digestive system and muscles spasm
emotional stress or tension
Relieving Colic
treatment for this disease are the following:
stimulate, change infant position, massage
warm bottle at baby’s belly and warm bath
swaddle and pacifier
avoid caffeine, small feedings, burping
change nipple, change cow’s milk to soy formula
homeopathic drops for colic
Poisoning
when a person is exposed to a substance that can damage their health or put their life in danger
signs and symptoms of poisoning
patients appear to have the following:
vomiting/ stomach pains, fever
drowsiness, burns, difficulty in breathing
sleepiness and confusion
Management of poisoning
to relieve the symptoms of the disease:
take away the substance
rinse when skin contact
flush inner corner of eye
stimulate fresh air
start CPR if without RR
cleft lip and palate
are birth defects that occur when a baby’s lip or mouth do not form properly
causes of cleft lip and palate
predisposing factor
genetics
maternal hypoxia
seasonal causes
maternal diet and vitamin intake
anticonvulsant drugs
lack of folic acid
Unilateral incomplete cleft lip

Unilateral complete cleft lip

bilateral complete cleft lip

unilateral complete lip and palate
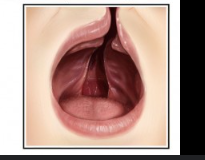
bilateral complete lip and cleft palate
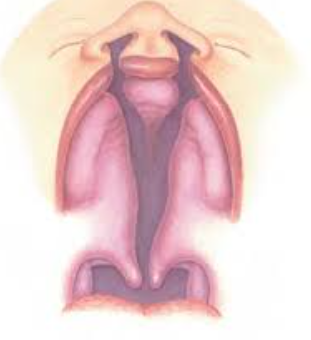
complete cleft palate
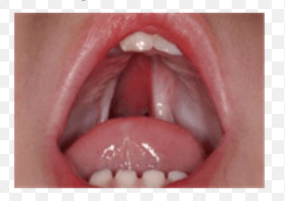
incomplete cleft palate
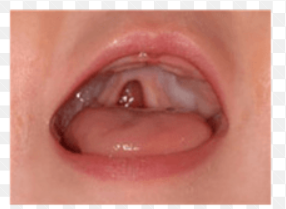
diagnostic procedure for cleft lip and palate
ultrasonography
as early as 14 - 16 weeks of gestation
cheiloplasty
surgical correction of cleft lip
2-3 months after birth
Palatoplasty
surgical correction of cleft palate
6 - 12 months
Preoperative care Cleft lip
before surgery follow
elbow restraints
feeding infant in the manner to be postoperatively
medication
feed the child using ESSR
Enlarge the nipple with head elevated
Stimulate the sucking reflex
Swallow thoroughly
Rest as much as possible
Post operative care cleft lip
follow the procedure after operation
avoid prone position
side lying on the opposite side of the operative site
apply elbow restraint
NPO x 4h
clear liquids and soft diet (no spoon)
clean suture line
monitor bleeding
Imperforate anus
a birth defect where the anus has no normal opening or is blocked
the condition develops in utero during the 5th to 7th weeks of pregnancy
low lesion imperforate anus
the colon remains close to the skin
high lesion imperforate anus
the colon is the higher up in the pelvis
persistent cloaca
the rectum, vagina, and urinary tract are joined into a single large opening
causes of imperforate anus
sacrococcygeal teratoma
VACTERL anomalies
Vertebral defects
Anal atresia
Cardiac anomalies
Tracheal fistula
Esophageal atresia
Rena Abnormalities
Limb Abnormalities
signs and symptoms of imperforate anus
patients may appear to have the following:
anal opening near to vagina
missing or misplaced opening
stool passes out of the genetalia or base of the genetalia
no 1st stool within 24-48 hours
swollen belly area
Diagnostic procedures for imperforate anus
to diagnose the condition, the following are the procedures
physical exam
absence of anal opening
flat perineum
no midline intergluteal groove
ultasonography
radiography
echocardiogram
CT scan
pelvic and esophageal MRI
fluoroscopy
IV pyelogram and cystourethrogram
surgical treatment for Imperforate anus
following are the surgical treatment for the disease
colostomy
anoplasty with pull through operation
anal dilatation
Intussusception
invagination of one portion of the intestine - either the small intestine or colon slides into another part of the intestine
causes of intussusception
predisposing factors can be:
occurrence is between ages 5- 9 months
rotaavirus
anatomical factors
socioeconomic status
improper vaccination
currant jelly stool
sausage-shaped mass RLQ (dance sign)
dehydration
lethargy and crying spells
Diagnostic procedures to intussusception
procedures done to diagnose the disease
barium enema
abdominal radiograph
rectal examination
ultrasound
Therapeutic management to intussusception
procedures to manage the disease
hydrostatic reduction
non surgical treatment
reduction of affected part
laparoscopy
manual reduction
segmental resection with anastomosis
medications
complications of intussusception
can happen when the disease is not treated
perforation
wound infection
internal hernias
sepsis
intestinal hemorrhage
necrosis and bowel perforation
recurrence
Hirschsprung’s disease
congenital ganglionic megacolon
clinical manifestation of Hirschsprung disease
disease can be observed by
failure to pass meconium
abdominal distention
green and brown vomitus
chronic constipation - “ribbon like, foul smelling stools”
fecal impaction
watery diarrhea
jaundice
poor feeding and failure to thrive
diagnostic procedure for Hirschsprung disease
this procedure can help diagnose the disease
abdominal x-ray
anal manometry
barium enema
rectal biopsy
rectal exam
palpate loops of bowel in the swollen belly
treatment of Hirschsprung disease
the following are needed to manage the disease
serial rectal irrigation
colostomy
resectioning
complication of Hirschsprung disease
the following can happen if the disease is disregarded
enterocolitis
perforation ad rupture of intestine
short bowel syndrome
Failure to thrive
growth failure, feeding disorder, poor feeding, faltering weight
Endogenous failure to thrive (Organic)
failure to thrive cause by inborn error of metabolism
Exogeneous failure to thrive (Non Organic)
failure to thrive cause by caregiver’s actions
Clinical manifestation of FTT
can be manifested by
poor hair texture and amount, nails, hygiene, and rashes
protruding abdomen
irritability and excessive crying
easily fatigability
avoid eye contact
lethargy
constipation, inappropriate weight gain
slowed growth and delayed motor development
Diagnostic procedures for FTT
disease can be diagnose by the following
screening test
radiologic studies
laboratory exams
treatment for FTT
to treat the disease
provide sufficient calories
correct vitamins and minerals
identify complications
Diabetes mellitus
a chronic disorder of metabolism characterized by a partial or complete deficiency or insulin because the body does not produce enough insulin
fasting blood sugar is 126 mg/dL or higher
Type 1 DM
can develop any time during childhood, even during infancy, but usually begins between ages 6 - 13 years
insulin-dependent DM
Type 2 DM
occurs mainly in adolescent but is becoming increasingly common among overweight or obese children
non-insulin-dependent DM
clinical manifestation of DM
symptoms of the disease are:
polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria, pruritis, paresthesia
weight loss
irritability
fatigue
blurred vision
headache
enuresis or nocturia, flushed skin
short attention span
poor wound healing
frequent infection
diagnostic procedure of DM
to identify the disease the following procedures can be done
8-hour fasting blood glucose level (more than 126 mg/dL)
random blood glucose (200 mg/dL or higher)
oral glucose tolerance test (140 - 200 mg/dL impaired glucose tolerance)
postprandial blood glucose
Insulin therapy
a hormone released by the pancreas
the goal is to maintain near-normal blood glucose values while avoiding too frequent episodes of hypoglycemia
rapid acting insulin
used as a bolus dosage
starts to lower blood glucose levels 10 - 15 mins after injection
peak actions in 30 - 90 minutes last as as long as 5 hours
Lispro - human insulin used in injection replacing the insulin produced by the body
short acting insulin
work 30 min - 1 hr after injection
peaks after 2-3 hrs but remians active 4-6 hrs
clear insulin
regular, humulin - R; semilente. crystalline zinc, actrapid
intermediate acting insulin
cloudy insulin
works 2-4 hours after injection, peaks after 6-12 hours
NPH, Lente, Humilin - N, Monotard
long acting insulin
cloudy insulin
slow onset of action 6-8 hrs relatively small peak effect 12-16 hrs
last for 20-30 hrs
usually given around bedtime
Ultralente insulin, PZI
therapeutic management of DM
recommended management for the disease
insulin therapy
diet
exercise
Obesity
is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated
more than 20% over their ideal weight
BMI of 30 and above
causes of obesity
this disease can be caused by the following:
sedentary lifestyle
imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure
slow metabolism
psychiatric illness
insufficient sleep
endocrine disruptors
genetics
used of medications
hormones
Diagnostic procedure for obesity
the following diagnostic test can help assess the disease
waist-hip ratio
waist circumference
body mass index
underwater weighing
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
skin calipers
waist circumference
estimate the amount of a person’s abdominal fat
body mass index
classifies obesity according to height and weight
underwater weighing
calculate lean body mass and body fat
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
used to measure bone density
determine percentage of body fat and where and how much fat is located in the body
skin calipers
used to calculate the percentage of body fat
management for obesity
to manage the disease here are the following procedures
physical activity and exercise
anti-obesity drugs
surgery
gastric balloon
bariatric surgery
Anorexia Nervosa
intense fear of becoming obese
an eating disorder characterized by:
immoderate food restriction
inappropriate eating habits
obsession with having a thin figure
an irrational fear of weight gain
a distorted body self-perception
Restricting type Anorexia
individuals does not utilize binge eating nor displays purging behaviors as their main strategy for weight loss. instead, the individual uses restricting food intake, fasting, diet pills, and/or exercise as a means for losing weight
Binge-eating Anorexia
individuals utilizes binge eating or displays purging behavior as a means for losing weight (eating a lot of food and then trying to get rid of the calories by forcing themselves to vomit, using laxatives, or exercising excessively, or some combination of these).
Bulimia Nervosa
is a binge eating combined with inappropriate ways of stopping eating such as self-induced vomiting, abuse of laxatives and diuretics, or excessive exercise
it can occur in a normal body weight person
Binge Eating Disorder
similar to anorexia and bulimia because a person binges regularly on food. but, unlike the other eating disorders, does not try to compensate by purging the food
causes of Anorexia Nervosa
predisposing factors of the diseases are
cultural pressures
family environment
psychological issues
food rituals