cell membranes
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Name of model proposed by singer and Nicholson 1972
Fluid mosaic model
Explain the name of the accepted plasma membrane structure
Fluid → protein and PL molecules are free to move
Mosaic → protein molecules embedded in the membrane
Explain how the distinction of charged and uncharged parts determine the position a protein will take up in a membrane
Charged particles will associate with hydrophilic heads
Uncharged particles will associate with hydrophobic tails
For lipid soluble molecules mode of transport, component of the membrane through which it passes, factor affecting rate of transport
MoT: diffusion
Comp: PL bilayer
Factor: concentration gradient
For water soluble molecules in high external concentration
MoT: facilitate diffusion
Compon: channel/ carrier proteins
Factor: concentration gradient/ size of molecule/ pH
Water soluble molecules in low external concentration
MoT: active transport
Compon: carrier proteins
Factor: respiratory rate, ATP production/ pH
Explain the pattern of results of temp against colorimeter reading referring to cell membrane structure
Membrane proteins are stable between .. and .. (at low temps)
Appearance of the red pigment means that the tonoplast and cell membrane has been damaged between .. and … (high temp)
Meaning pigment has leaked out of cell/ sap vacuole/ change in membrane permeability/ damaged membrane
Proteins change shape and denature and come out of bilayer
Explain the difference in results if you were investigating the effect of ethanol on the permeability of the membrane
Dissolve phospholipids/ destroys cell membrane structure
So pigment leaks out
Suggest one problem in performing any investigation using blood
Blood clots/ infection
Explain why the time taken for the RBC to burst (haemolysis) occurred quickest when placed in distilled water
in distilled water Water has highest water WP
Water passed down water potential gradient- from high to low water potential
Passes into the cell by osmosis
Explain
Allows results to be comparable
Initial masses would differ
A sample of RBC were placed in a concentration solution of sodium chloride draw a diagram to show the expected appearance of one of the blood cell after 5 minutes
Mark scheme says: crinkled cell, high WP inside cell, water passes out of cell causing shrinkage / distortion
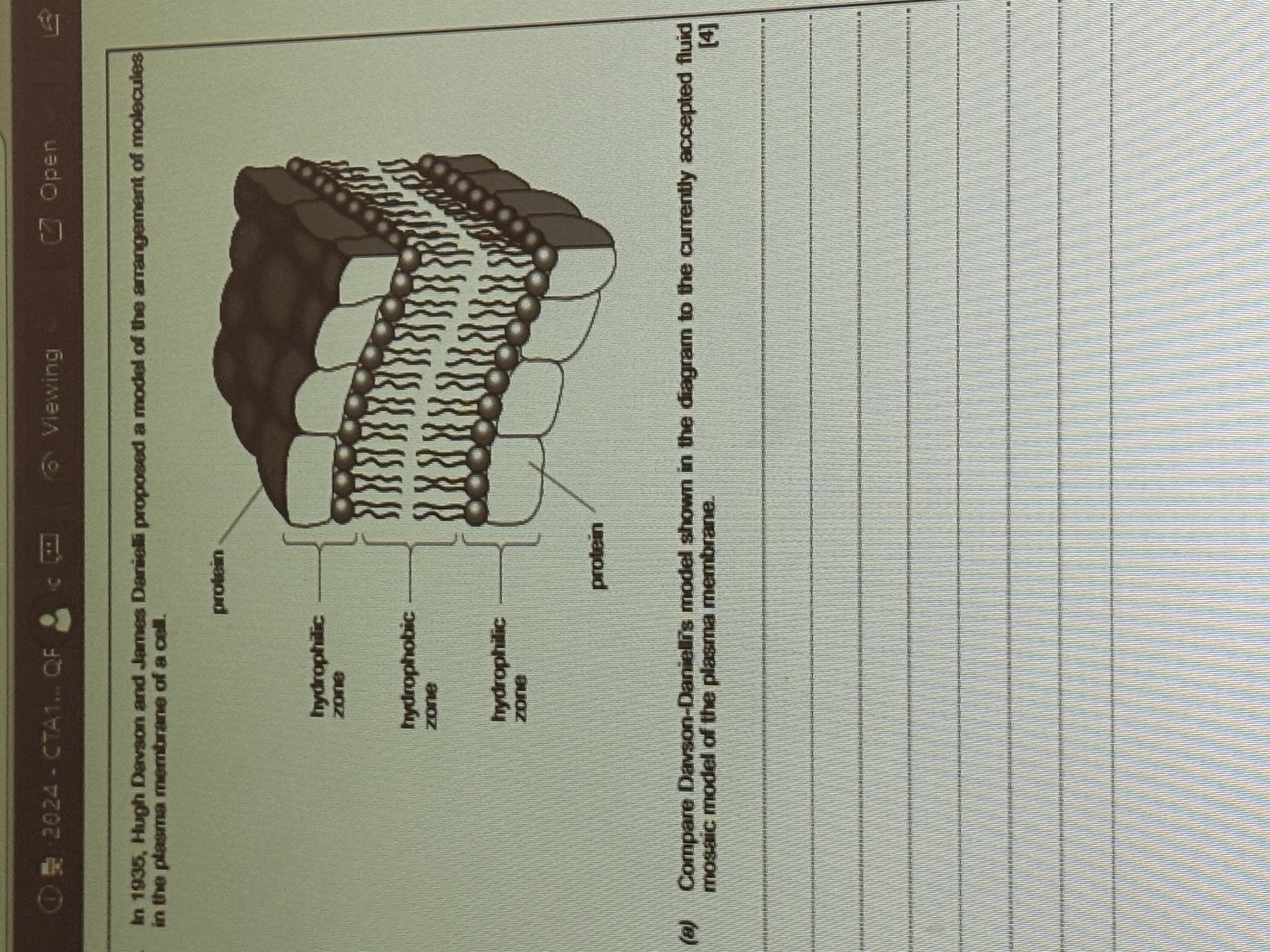
Difference between this model and currently accepted fluid mosaic model
Have PL bilayer, hydrophobic takls and hydrophilic heads , have proteins
However for the F-M model proteins are embedded in the lipid layer, there are instrinsci proteins as well as extrinsic
Also the F-M model there are glycocyx, glycolipids, glycoproteins
An investigation was carried out on the uptake of pottasium ions by root tissue stete with reasons the variables that should be kept constant
Temperature or pH BECAUSE
they change enzyme activity, affect reaction rate
Explain why as the O concentration increases the rate of pottasium ions also increases
Active transport is the main method of transport of pottasium ions
Which is energy dependent, uses energy from ATP and oxygen is required for aerobic respiration for ATP production
Greater O concentration produces greater uptake
State the rate of uptake you would expect of a drop of cyanide solution had been added to each of the four solution
They would all be .. (the starting rate of ion uptake)
cyanide inhibits aerobic respiration which prevents or reduces ATP production when no oxygen is present there is still some uptake by diffusion which is a passive process
Explain why increasing the temp increases the permeability of the cell membrane and result in more .. being realised
PL and protein molecules movement increases as temp increases
Creates gaps between PL molecules
Protein loses tertiary structure as hydrogen bonds weaken/ break
Pores in membrane proteins get larger
More .. can escape more quickly
Methods of transport that transports individual molecules or ions
All methods except endocytosis and exocytosis (bulk) : D, FD, OSM, AT
Don’t understand the last question on the FA on membranes, it is too confusing but mention plasma membrane model: fluid mosaic model
Describe the function of the PL bilayer
Physical barrier, selectively permeable membrane allows diffusion or transport of small non polar molecules
Function of intrinsic or channel/ carrier proteins
Allows FD / AT/ transport of large or polar molecules or ions
Explain why no glycocalyx is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane
No need for recognition/ receptor
Explain why there are more carrier/ channel proteins in inner mitochondrial membrane than cell membrane
More FD/ active transport
Maybe transport of ATP
Evidence that P ions can occur both by AT and Diffusion explain how evidence supports this conclusion
Absorption is highest with oxygen which indicates active transport as this requires ATP
Also occurs in the absence of oxygen which indicates diffusion as this is not dependent on respiration passive process
Explain how the properties of the head and the tail of the chlorophyll molecules results in its position in the PT memrbane
Hydrophobic tail and fatty acid hydrophobic regions of the memrbane
Head is hydrophilx
Suggest an adv of the position of the chlorophyll molecules
Holds chlorophyll head in optimum position for absorption of light
Explain how glucose is reabsorbed from the filtrate into the blood even at very high blood glucose levels
Na+ ions actively transported out of epithelial cell lowering the concentration of Na+ inside
Na+ in filtrate at higher concentrated than inside the cell
Na+ Co transported with glucose into epithelial cell
Glucose concentration in epithelila cell is higher than blood plasma
Glucose moves out of epithelial cell into blood by FD
Circulation maintains plasma concentration below that in epithelial cells maintains concentration gradient
Explain the distribution of Na+ across the membrane
More Na+ outside than inside
Actively transported out of axon by pump
Relatively impermeable to Na+ CJ channels shut
Explain why Na+ ions don’t diffuse across PL bilayer despite concent gradient
Ions are hydrophilic and memrbane has hydrophobic tails
explain in terms of WP why the transmission was lowest between NaCl concentration 0 to 3
water moves in by osmosis, higher WP inside than outside of cell, down a WP graident into the cell, no cell wall to preevent bursting, most .. is released therefore lowest transmission of light
as the concentration of NaCl increases the number of bursted (haemolysed) cells decreases explain why there is a range of concent at which haemolysis occurs
different cells have different water potentials or solute potentials so each cell would require a different external, water potential or solute concentration before haemolysis or bursting
what would happen to the cell after it had been placed in a concentrated solution
cell plasmolysis, vacuole and cytoplasm would decrease in volume, cell membrane pulls away from cell wall
state the pressure potential of the cell after it had been placed in a concentrated solution for 30 mins
0 kPa
explain why temp needs to be controlled in experiment of permeability
would affect KE of the molecules which would allow more pigment to escape , proteins would be denatured
explain the effect of increasing the concent of the NaCl solution on the permeabilty of the membrane
as the concent increases the absorbance decreases , less absorbance means less pigment released, more NaCl reduces pigment released, more NaCl the less permeable the membrane
explain why it is not directly proportional
as the graph is not a straight line it is a curve
explain trend of pigment (absorbance)- pigment is stored within the cell vacuole when the membranes are disrupted the pigment leaks out into surrounding solution
as the temp increases the membrane becomes more fluid as PL gain more KE and more gaps form
proteins then start to denature where there is a large increase in absorption , then at higher temps membrane is fully destroyed so all pigment is released
explain how acid and ethanol affect the membrane there is a lot of red pigment in the solution
pigment leaks/ diffuses out of cells through the CM as acid denatures the proteins changing their shpae and ethanol dissolves the PLs
why has the beetroot in the water increased in size
water entered the cells by osmosis as the beetroot cells had a lower WP than the water
the movement of glucose from the cell to the bloodstream requires cncent gradient explain how this is maintained
blood flows removing glucose that has been absorbed and lowers glucose concent in bloodstream
the cell mebrnae is adapted to these 3 functions show is mitochond, RER, GB, ribosomes so for active transport of substances from the cell into the blood
mitochondria produces ATP is AR, transporting substances against concent gradient
synthesis of enzymes
ribosomes make proteins, enzymes are proteins
determine the WP of the potato used from experiment results
where it crosses the x axis (% change in mass is 0) this is where the WP of the external solution = the WP of tissue it is the isotonic solution
explain why there was a gain in mass
the external WP is higher than the WP of the cell so water moves in by osmosis gaining mass
explain why there was a decrease in mass
the external WP is lower than the WP of the cell so water moves out by osmosis so decreasing the mass
explain why there was no decrease in mass at any of sucrose concent for sweet potato
sweet potato has a very low WP a very high sugar concent
how to modify this
increase the sucrose concent until a point is reached where water will flow out of the potato
State which temp provide the most reliable results and explain why
The highest temp where all three experiments gave the same absorbance - the cell had ruptured, membrane proteins were denatured and all pigment has leaked out of cells
Describe how intrinsic proteins would transport a molecule against a concentration gradient
By active transport , using energy from ATP
To determine the structure of the plasma membrane membrane proteins from different cells were labelled using different coloured dyes explain the results after fusion using knowledge of the structure and properties of plasma membrane
Fluid mosaic model, , proteins are free to move within the membrane
After fusion there is a new arrangement of proteins
The value of the membrane width
7-8 nm
Vitamin A is lipid soluble explain how it crosses the membrane
Dissolves in the phospholipid bilayer and is transported by diffusion
Glucose is water soluble, explain how it it crosses the membrane
Cannot pass through the phospholipid layer so it uses transport proteins, transported by facilitated diffusion
Explain the leakage of pigment when the beetroot is placed in ethanol
The ethanol dissolves the phospholipid and makes the proteins denature creating gaps in the membrane making membrane more porous
When the experiment was repeated at a higher temp the time taken for ethanol to turn red decreased
Increased temp increases KE of dye or membrane molecules which increases the rate of diffusion of dye across the membrane , dye diffuses across the e membrane more rapidly
Explain lipid solubility and rate of diffusion through the membrane
As lipid solubility increases the rate of diffusion increases because membrane contains a bilayer of phospholipids , lipid soluble substances can diffuse or move through the membrane more easily than water soluble molecule s
Why can small molecules diffuse faster than larger molecules
They have a higher KE
It is easier to pass between phospholipid molecules
Factors affecting the rate of facilitated diffusion
Concentration difference / gradient
Temp
Number of carrier or chem El proteins
Vitamin B is water soluble explain the route taken by it into the cell is determined by the structure of the plasma membrane
polar, cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer which is hydrophobic, uses transport proteins / channel proteins which are hydrophilic
Vitamin K is fat soluble
It is non polar, so it dissolves in the hydrophobic phospholipid bilayer so it can pass directly through the phospholipid
Explain the name fluid mosaic
Fluid- lipid layer is fluid as it can move
Mosaic of protein molecules are they are randomly arranged
Describe the function of channel proteins
Facilitated diffusion of polar hydrophilic molecules
Explain the meaning of active transport
Movement against a concentration gradient that requires energy from ATP
Why is transport across the membrane vital to the cell
Obtain nutrients and obtain oxygen
Remove CO2 and remove toxic substances
Maintain water potential
Explain what is meant by the term lipid bilayer
Double layer of phospholipids
State the hydrophobic parts of the memrbane
Fatty acids
State functions of the membrane proteins
Form hydrophilic pores
Active transport
Facilitated diffusion
Don’t understand 5b PMT questions by topic
Name the process by which oxygen is ansorbed by the roots given the graph is a straight line (oxygen concentration rate of uptake)
Diffusion as rate is proportional to concentration
Explain why as nitrate ion concentration increases the rate of uptake increases
Increasing ion concentration increases the chance that molecules will collide with carrier protein
When does the rate of ion uptake decrease to 0 during active transport
In the presence of respiratory inhibitor cyanide
Describe endocytosis
The cell membrane engulfs to form a vesicle around the substance
two circle structures on the diagram are involved in the digestion of molecules that have been engulfed name the organelle where these structures are formed
The structures are lysosomes, organelle is Golgi body
Explain why water cannot easily pass through the PL bilayer
Water is a polar molecules and the fatty acids of the PL hi alter are hydrophobic regions
Explain which region is non polar
The region that is adjacent to the fatty acids
Explain why the WP of the cell can be assumed to equal to the solute potential of the solution that causes 50% plasmolysis
Because the cell is at IP which means the presssure potential is 0 as the cell memerbane has pulled away from the cell wall
Use the results in the table to estimate a value for the WP of the cell
Roughly when 50% of the cells are plasmolysed
Outline how the data could be used to determine a more accurate estimate of the cell water potential
Plot solute potential on X axis and % plasmolysed on y axis
Read down from 50% plasmolysed to dilute potential this is also the WP
State how the procedure could be modified to improve reliability
Observe more pieces of onion tissue from each solution , count more cells in each piece of tissue and calculate the mean
State how it could be modified to improve accuracy
Narrower range around 50% plasmolysed between 0.4-0.6
Explain why a cell was plasmolysed after placed in a solute with a SP of -1800 kPa
External water potential was lower than the cell WP so water moves out of the cell by osmosis
When dissolved in water NaCl dissociates to form Na+ and Cl- ions, suggest how interaction between Na+ ions and the phospholipid affects fluidity of membrane
Efeu as AS level paper 1 2023
Describe how oxygens and sodium ions cross the membrane
Oxygeb crosses the membrane by simple diffusion, passes through the PL bilateral
Sodium ions pass through intrinsic/ channel/ carrier proteins by FD, AT
Carp have high % compostipn of ions in the blood plasma, lower than % composition of ions in the habitat suggest what is importing for the survival of the carp
The % ion composition of fresh water/ habitat is greater than that of blood plasma, fresh water is hypotonic to the blood, WP of fresh water is higher than the WP of the carp’s blood, the carp takes in water by osmosis
Therefore
It is important for the carp to produce large volumes of dilute urine, as this prevents bursting of cells, maintaining ion composition, reducing loss of ions
Suggest why cells that maintain ion composition of the blood plasma are important for flounder fish
% ion composition of sea water is greater than that of blood plasma, sea water is hypertonic, WP in the fish is highe than in sea water
Ions will move into the blood plasma by FD down a concent gradient
Therefore ions must be actively transported out of the blood plasma into the surrounding sea water
Sea water has a high % composition of ions , low WP whilst fresh water has a low % composition of ions and a high WP explain which cell has been taken from the sea water
The cell containing more mitochondria to provide ATP for respiration/ for active transport
more highly folded to give larger S.A.
% composition of ions in the blood plasma is higher than in fresh water explain how acidification of this water cause death
The % ion concentration of the blood plasma is higher than the surrounding water, ions will move out of the blood plasma by facilitated diffusion down a CG, acidification will denature enzymes involved in ATP production, change the shape of carrier/ chemo protein in cells
Therefore fewer ions are actively transported into the fish , fewer ions can diffuse out
Explain why as the temp increases the absorbance of the cell increases
As the temp increases the PLs gain more KE, more gaps form
Above 40°C the proteins in the membrane start to denature
Above 70°C the membrane fully destroyed so all the pigment is released